Research on the evaluation of land resources carrying capacity in Jinzhou area, Liaoning Province
-
摘要:
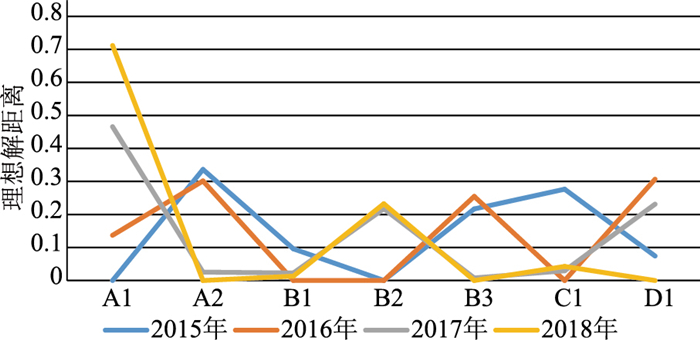
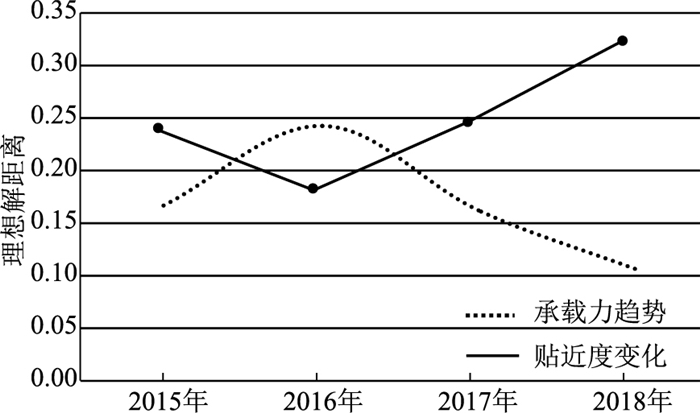
以土地资源综合承载状态最佳为目标层, 以土地资源底线、绿色生活、土地资源安全、土地资源绿色生产为准则层, 建立土地资源承载力评价指标体系, 并从欧氏距离、主客观赋权、优势及短板评价模块三方面建立TOPSIS土地资源承载力评价及优势短板定量分析模型。以此模型开展了锦州地区土地资源承载力评价研究。评价结果显示: 2015—2018年, 锦州地区土地资源承载力先升后降, 2016年达到最高, 2018年最低; 2015年城乡建设用地规模、2016年新增国土空间生态修复规模、2017年和2018年耕地保有量为影响当年土地承载力的主要指标。该成果为研究土地资源承载力演化趋势, 定量分析影响土地资源承载力的指标提供支撑。
-
关键词:
- 土地资源承载力 /
- 改进TOPSIS模型 /
- 短板指标 /
- 承载力提升
Abstract:Taking the best comprehensive carrying state of land resources as the target layer, and taking the bottom line of land resources, green life, land resource security, and green production of land resources as the criterion layers, establish an evaluation index system for the carrying capacity of land resources in Jinzhou.The objective weighting, advantages and shortcoming evaluation modules establish a quantitative analysis model for TOPSIS land resource carrying capacity evaluation and advantages shortcomings.Based on this model, the evaluation research of land resource carrying capacity in Jinzhou area was carriedout.The evaluation results show that from 2015 to 2018, the land resource carrying capacity of Jinzhou area increased first and then decreased, reached the highest in 2016 and the lowest in 2018.The scale of urban and rural construction land in 2015, the scale of ecological restoration of new land and space in 2016, and the amount of cultivated land in 2018 are the main indicator that affected the land carrying capacity of that year. The results provide support for studying the evolution trend of land resource carrying capacity and quantitatively analyzing the indicators that affect land resource carrying capacity.
-

-
表 1 锦州市土地资源承载力评价指标值
Table 1. Evaluation index value of land resource carrying capacity in Jinzhou
目标层 准则层 指标序号 指标层 评价方案 2015年 2016年 2017年 2018年 土地资源承载综合状态最佳 土地资源底线 A1 耕地保有量/km2 5060.29 5058.15 5054.98 5051.67 A2 城乡建设用地面积/km2 915.54 917.74 921.2 923.42 结构效率 B1 人均应急避难场所面积/m2 0.73 0.77 0.75 0.75 B2 人均城镇建设用地/m2 213.61 213.49 217.68 219.18 B3 人均农村居民点用地/m2 366.13 368.9 378.9 381.99 绿色生产 C1 每万元GDP地耗/m2 93.86 123.33 113.47 107.76 生态保护 D1 新增国土空间生态修复面积/km2 3.4386 1.2567 0.2185 7.4261 表 2 规范决策矩阵
Table 2. Standardized decision matrix
方案 正向指标 正向指标 正向指标 负向指标 负向指标 负向指标 正向指标 耕地保有量/km2 城乡建设用地面积/km2 人均应急避难场所面积/m2 人均城镇建设用地/m2 人均农村居民点用地/m2 每万元GDP地耗/m2 新增国土空间生态修复面积/km2 2015年 1 0 0 0.9789 1 1 0.4468 2016年 0.7517 0.2792 1 1 0.8253 0 0.1440 2017年 0.3840 0.7183 0.5 0.2636 0.1948 0.3346 0 2018年 0 1 0.5 0 0 0.5283 1 表 3 锦州市土地资源承载力评价指标权重
Table 3. Evaluation index weights of land resource carrying capacity in Jinzhou
目标层 准则层 指标序号 指标层 熵值法权重 AHP权重 组合权重 土地资源承载综合状态最佳 土地资源底线 A1 耕地保有量/km2 0.124 0.422 0.273 A2 城乡建设用地面积/km2 0.138 0.141 0.1395 结构效率 B1 人均应急避难场所面积/m2 0.121 0.028 0.0745 B2 人均城镇建设用地/m2 0.144 0.168 0.156 B3 人均农村居民点用地/m2 0.156 0.068 0.112 绿色生产 C1 每万元GDP地耗/m2 0.135 0.118 0.1265 生态保护 D1 新增国土空间生态修复面积/km2 0.182 0.055 0.1185 表 4 土地资源承载力区域构成
Table 4. Description of regional composition of land resource carrying capacity
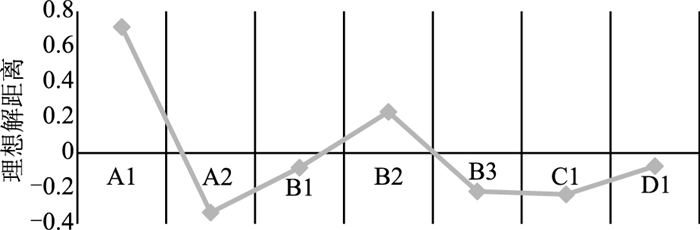
方案 距离半径 区域面积 A1指标扇区面积 A2指标扇区面积 B1指标扇区面积 B2指标扇区面积 B3指标扇区面积 C1指标扇区面积 D1指标扇区面积 2015年 0.240551 0.181788 0 0.061136 0.017437 0.000034 0.039408 0.050273 0.013501 2016年 0.183136 0.105365 0.014435 0.031763 0 0 0.026842 0 0.032325 2017年 0.246413 0.190755 0.088846 0.004851 0.004359 0.041460 0.001495 0.005628 0.044115 2018年 0.323603 0.328984 0.234140 0 0.004359 0.076454 0 0.014031 0 表 5 优势及短板指标贡献值分析
Table 5. Analysis of the contribution value of advantages and shortcoming indicators
指标代码 评价方案 2015年 2016年 2017年 2018年 A1 0 0.1370 0.4658 0.7117 A2 0.3363 0.3015 0.0254 0 B1 0.0959 0 0.0229 0.0133 B2 0.0002 0 0.2173 0.2324 B3 0.2168 0.2547 0.0078 0 C1 0.2765 0 0.0295 0.0426 D1 0.0743 0.3068 0.2313 0 -
[1] 代磊, 王志杰, 张万胜. 贵阳市1998-2018年土地资源承载力分析与预测[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(1): 108-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB202101019.htm
[2] Peng T, Deng H W. Comprehensive evaluation for sustainable development based on relative resource carrying capacity-a case study of Guiyang, Southwest China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(5/6): 1-14.
[3] 苏子龙, 袁国华, 周伟. 基于改进三维生态足迹模型的安徽省土地生态承载力评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(3): 256-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY202003037.htm
[4] 陈璐璐, 敖琦, 陈曦. 基于GIS的哈尔滨市土地资源承载力评价[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2020, 43(S1): 169-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBCH2020S1052.htm
[5] 彭亮, 董斌, 方磊, 等. 基于均方差-TOPSIS模型的土地资源综合承载力评价——以安徽省六安市为例[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(11): 259-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSNY202011050.htm
[6] 于广华, 孙才志. 环渤海沿海地区土地承载力时空分异特征[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(14): 4860-4870. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201514032.htm
[7] 孙钰, 李新刚. 基于空间回归分析的城市土地综合承载力研究——以环渤海地区城市群为例[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2013, 32(5): 128-132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2363.2013.05.024
[8] 刘婷, 王寒梅, 史玉金, 等. 特大型城市地下空间资源承载能力评价方法探索——以上海市为例[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(10): 1609-1616. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.10.002 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20211002&flag=1
[9] 杨瑾, 左坤, 崔斌, 等. 西安市土地资源承载力时空变化研究[J]. 西北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(1): 121-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSF201901021.htm
[10] Li X N, Cundy A B, Chen W P, et al. Dynamic capacity modelling of soil environment carrying capacity, and developing a soil quality early warning framework for development land in China[M]. Elsevier, 2020: 257.
[11] 封志明, 杨艳昭, 闫慧敏, 等. 百年来的资源环境承载力研究: 从理论到实践[J]. 资源科学, 2017, 39(3): 379-395.
[12] Hui Y H, Jiang X H, et al. On system dynami c simulation model of land resourcesbearing capacity in duality model[J]. Geography Research, 2001, 20(2): 191-198.
[13] 赵春丽. 系统动力学方法在区域水资源承载力中的应用研究[D]. 西安建筑科技大学硕士学位论文, 2006.
[14] Liu L, Zhou J Z, An X L, et al. Using fuzzy theory andinformation entropy for land quality assessment in Three GorgesRegion, China[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2010, 37(3): 2517-2521. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2009.08.004
[15] 郑明贵, 吴萍, 尤碧莹. 中国铁矿资源经济安全评价与预警[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(5): 836-845. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20220509&flag=1
[16] 张晓娟, 周启刚. 基于熵权TOPSIS和灰色模型的土地承载力评价与预测——以三峡库区为例[J]. 资源开发与市场, 2017, 33(6): 666-671. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8141.2017.06.005
[17] 徐文斌, 郭灿文, 王晶, 等. 基于熵权TOPSIS模型的海岛地区资源环境承载力研究——以舟山普陀区、定海区为例[J]. 海洋通报, 2018, 37(1): 9-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HUTB201801003.htm
[18] 雷勋平, 邱广华. 基于熵权TOPSIS模型的区域资源环境承载力评价实证研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(1): 314-323. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201601040.htm
-



 下载:
下载: