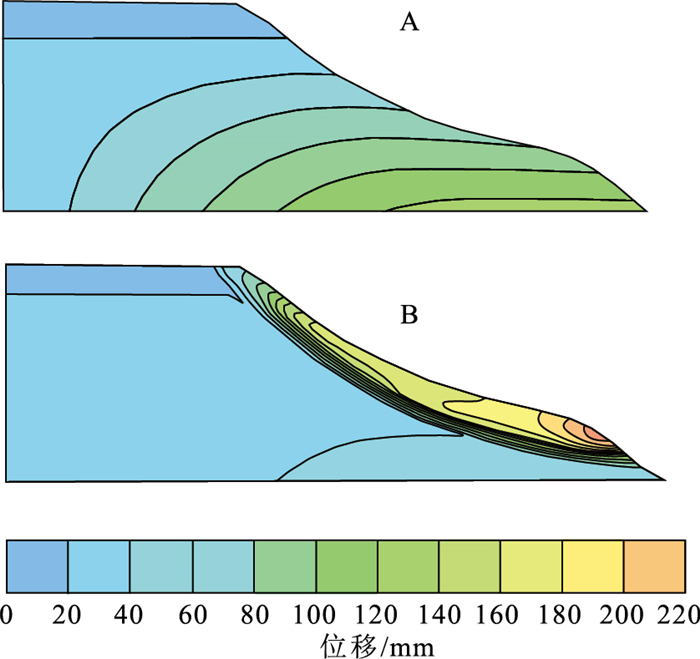
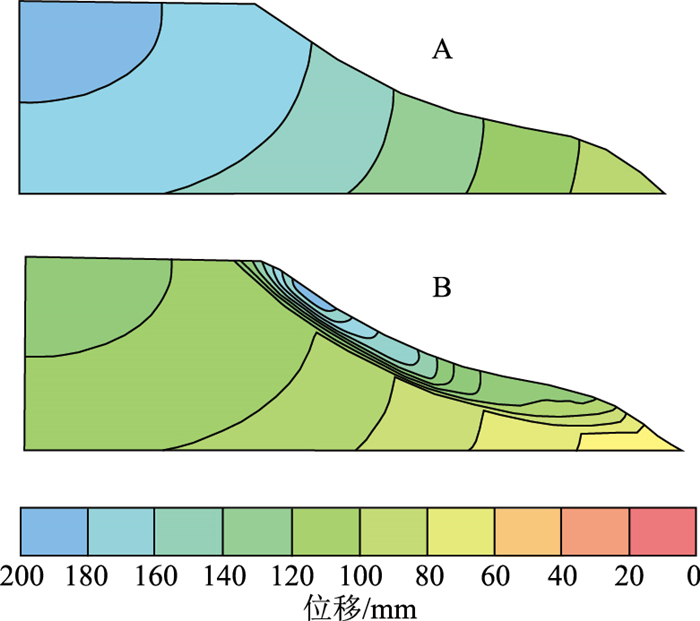
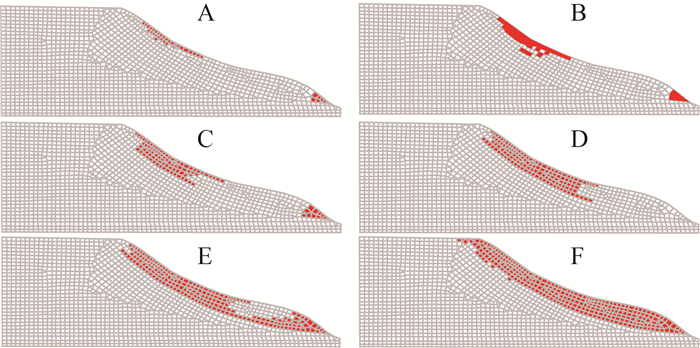
Instability mechanism and stability trend of loess slope during seasonal Freeze-thaw process
-
摘要:
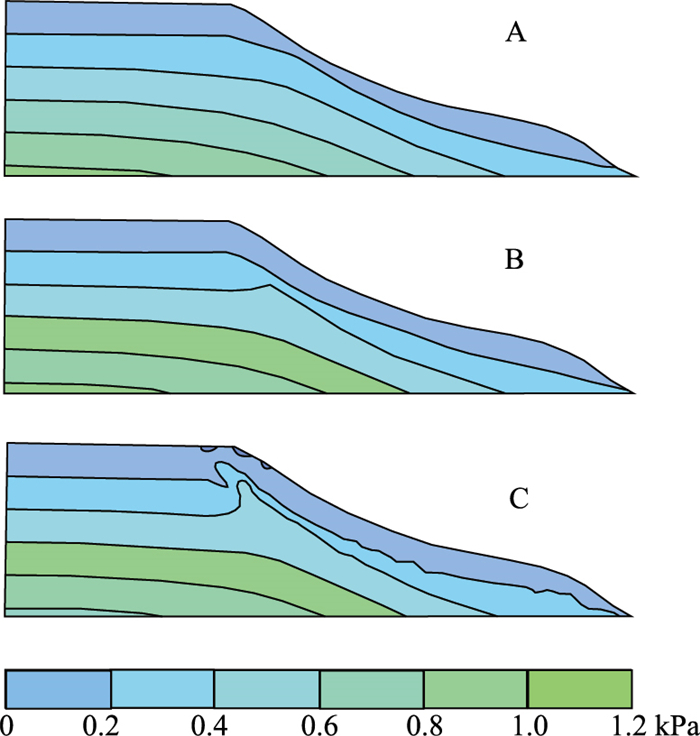
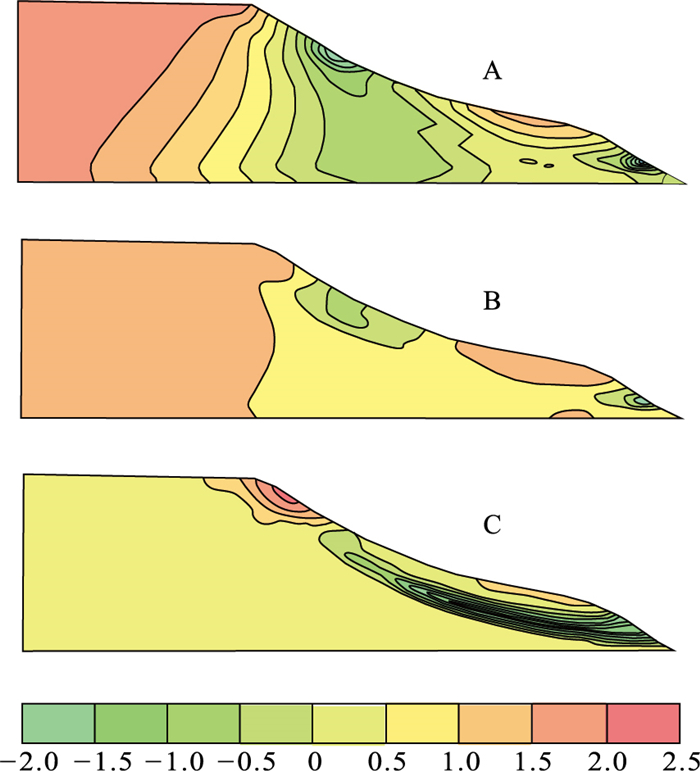
季节性冻融型滑坡是黄土地质灾害的主要类型之一。季节性冻融过程中地下水响应极其敏感, 地下水分布和变化对黄土斜坡体内岩土体的应力状态、力学性状及斜坡稳定性均有较大的影响, 冻结期滞水与融解期疏水引发的斜坡范围内地下水位变化是黄土斜坡稳定性变化及失稳破坏的主要诱发因素之一。在季节性冻融过程斜坡地下水变化全过程分析基础上, 采用基于极限平衡理论的条分法和基于弹塑性理论的有限元数值法, 对黄土斜坡稳定性与斜坡应力应变场的响应进行分析计算, 探讨季节性冻融条件下黄土斜失稳破坏机制及稳定性变化趋势, 认为黄土斜坡在冻融过程中的稳定性状态与冻结融解日期呈现明显滞后效应, 其失稳状态将持续至融解中期, 为季节性冻融型滑坡预警防治提供科学依据。
Abstract:Seasonal freeze-thaw landslides are one of the main types of loess disasters.The groundwater response is extremely sensitive during seasonal freezing and thawing.The distribution and changes of groundwater level have a greater impact on the stress state, mechanical properties and slope stability of the rock and soil in the loess slope.Slope caused by stagnant water during freezing and draining during thawing.The change of groundwater level within the scope is one of the main inducing factors for the stability change and instability of the loess slope.Based on the whole process of slope groundwater change during seasonal freezing and thawing, this paper adopts the slice method based on limit equilibrium theory and the finite element numerical method based on elastoplastic theory to analyze and calculate the slope stability and slope stress and strain field response.Under seasonal freezing and thawing conditions, the failure mechanism and stability change trend of the slope of loess slopes.Provide scientific basis for early warning and prevention of seasonal freeze-thaw landslides.
-
Key words:
- seasonal freezing and thawing /
- loess slope /
- stability /
- numerical simulation
-

-
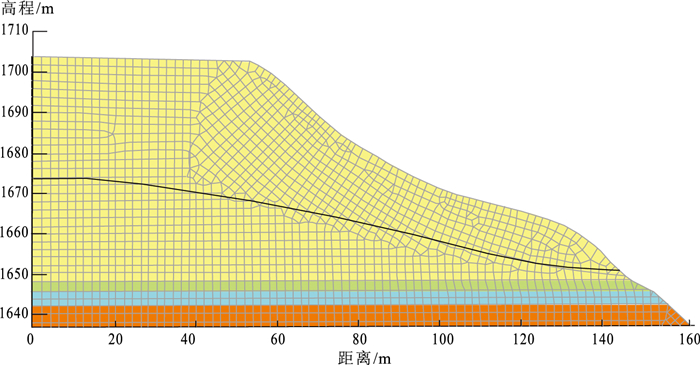
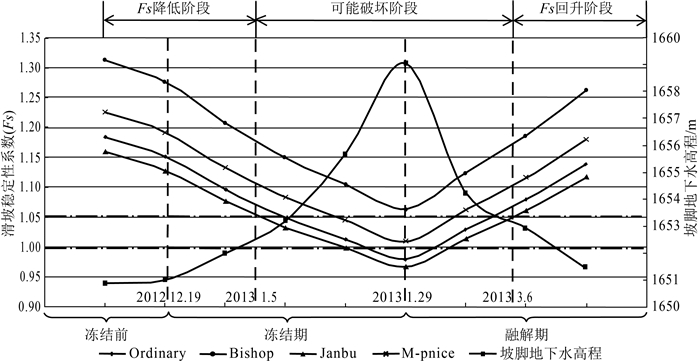
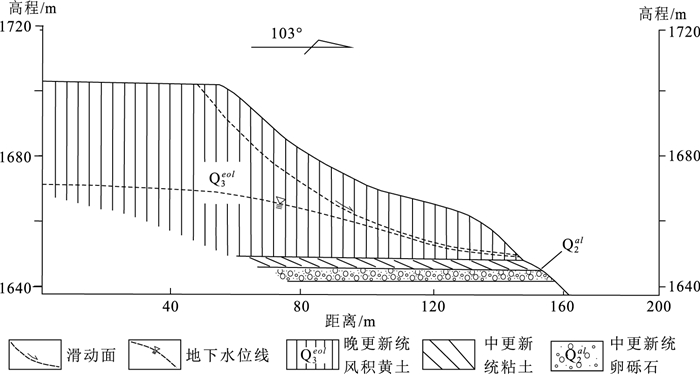
表 1 稳定计算期数与时间、坡脚地下水水位
Table 1. Corresponding table of stability calculation period and time and groundwater level at slope toe
状态 时间 坡脚地下水水位/m 冻结前 2012.10.2 1650.87 2012.12.17 1650.99 冻结 2012.12.29 1651.98 2013.1.9 1653.18 2013.1.19 1655.68 2013.1.29 1659.05 融解 2013.2.10 1654.22 2013.3.10 1652.92 2013.4.10 1651.42 表 2 计算模型岩土体参数取值
Table 2. Parameter values of calculation model for rock and soil mass
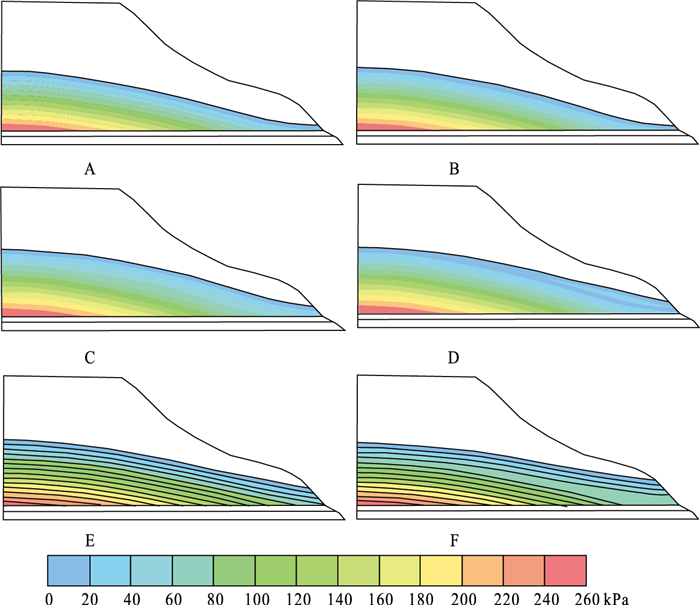
土体类型 弹性模量/kPa 有效粘聚力C'/kPa 有效内摩擦角Ф'/° 密度/(kN·m-3) 泊松比 天然黄土 4×103 16.3 25.1 13.9 0.39 饱和黄土 2.8×103 12.7 14.4 18.1 0.41 粉质粘土 9×103 45.2 26.5 16.5 0.31 砂卵石 3.5×104 1.6 31.8 22.4 0.26 砂泥岩 2.9×106 216 36.7 24.8 0.20 表 3 斜坡稳定性计算结果
Table 3. Calculation resultsof slope stability
序号 时间日期 稳定性系数Fs 水位H/m Ordinary Bishop Janbu M-P 1 2012.10.2 1.184 1.313 1.160 1.226 1650.87 2 2012.12.17 1.152 1.277 1.128 1.192 1650.99 3 2012.12.29 1.096 1.208 1.077 1.133 1651.98 4 2013.1.9 1.049 1.148 1.033 1.083 1653.18 5 2013.1.19 1.013 1.105 0.999 1.045 1655.68 6 2013.1.29 0.980 1.064 0.967 1.009 1659.05 7 2013.2.10 1.029 1.125 1.014 1.062 1654.22 8 2013.3.10 1.079 1.186 1.061 1.115 1652.92 9 2013.4.10 1.139 1.262 1.117 1.180 1651.42 -
[1] 刘传正. 中国地质灾害成因分析[J]. 地质评论, 2020, 66(5): 1334-1348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202005022.htm
[2] 孙建中. 黄土学(上篇)[M]. 香港: 香港考古学会, 2005.
[3] 孙建中. 黄土学(下篇)[M]. 西安: 西安地图出版社, 2015.
[4] 雷祥义. 黄土高原地质灾害与人类活动[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2001.
[5] 张茂省, 朱立峰, 胡伟, 等. 灌溉引起的地质环境变化与黄土地质灾害——以甘肃黑方台灌区为例[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.
[6] 李广, 张明礼, 叶伟林, 等. 甘肃黑方台坡面冻融特征及冻结滞水效应分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(6): 117-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202106017.htm
[7] Zhang M S, Liu J. Controlling factors of loess landslides in western China[J]. Environmental Earth Science, 2010, 59: 1671-1680. doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0149-7
[8] 吴玮江, 宿星, 冯乐涛, 等. 甘肃黑方台滑坡类型与活动特征研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 2019, 41(6): 1483-1495. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT201906022.htm
[9] 朱赛楠, 殷跃平, 王文沛, 等. 新疆伊犁河谷黄土滑坡冻融失稳机理研究[J]. 地球学报, 2019, 40(2): 339-349. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201902010.htm
[10] 叶万军, 杨更社, 彭建兵, 等. 冻融循环导致洛川黄土边坡剥落病害产生机制的实验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(1): 199-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.01.023
[11] 吴玮江. 季节性冻融作用于斜坡整体变形破坏[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1996(4): 59-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH604.009.htm
[12] 吴玮江. 季节性冻结滞水促滑效应——滑坡发育的一种因素[J]. 冰川冻土, 1997, 19(4): 359-365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT704.011.htm
[13] 叶伟林, 康丽娟, 安亚鹏, 等. 甘肃永靖焦家村上庄2·28滑坡特点及成因分析[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版). 2021, 57(3): 369-375, 381. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK202103012.htm
[14] 王念秦, 罗东海. 黄土斜(边)坡表层冻结效应及其稳定响应[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010, 18(5): 760-765. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201005029.htm
[15] 朱立峰. 黑方台滑坡群控制因素与外动力条件分析[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(3): 217-22 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201903022.htm
[16] 程鹏, 杨海军, 张亚卿, 等. 黄土地区季节性冻融触发滑坡的机理分析[J]. 中外公路, 2017, 37(1): 6-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWGL201701002.htm
[17] 黄文强. 冻融循环作用下黄土边坡的浅层滑动探讨[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(4): 1558-1565 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS202204033.htm
[18] 张茂省, 程秀娟, 董英, 等. 冻结滞水效应及其促滑机理——以甘肃黑方台地区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(6): 24-32. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130605&flag=1
[19] 董晓宏, 张爱军, 等. 反复冻融下黄土抗剪强度劣化的实验研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 2010, 32(4): 767-772. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT201004017.htm
[20] 李守定, 乔华, 马世伟, 等. 基于温度-降雨双参数的新疆地质灾害预警模型[J]. 水利水电技术, 2021, 52(11): 207-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJWJ202111020.htm
[21] 曾磊, 赵贵章, 胡炜, 等. 冻融条件下浅层黄土中温度与水分的空间变化相关性[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(11): 2123-2131. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20151119&flag=1
[22] 曾磊, 赵贵章. 季节性冻融过程黄土斜坡地下水响应[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(7): 1300-1307. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20220716&flag=1
-



 下载:
下载: