Analogue modeling of development of rollover anticline and crestal collapse faults of Huimin sag in Bohai Bay basin
-
摘要:
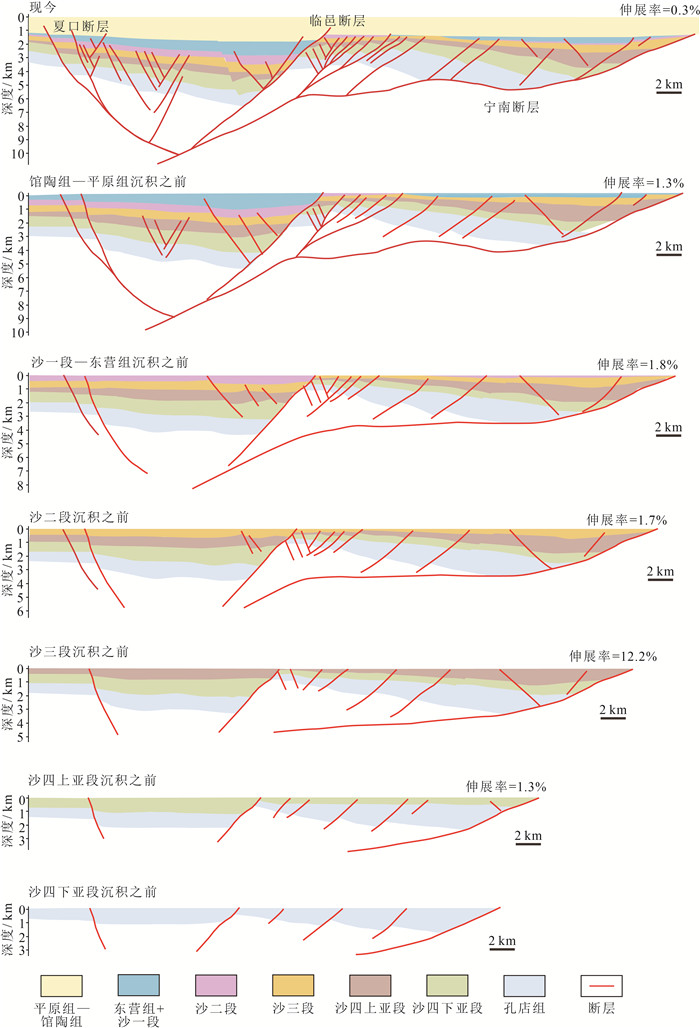
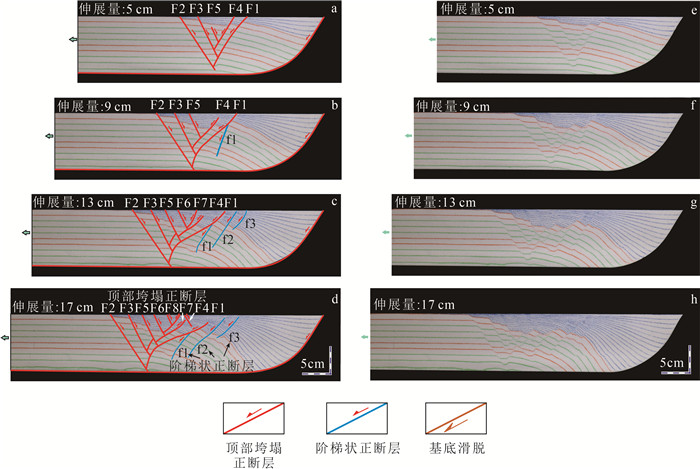
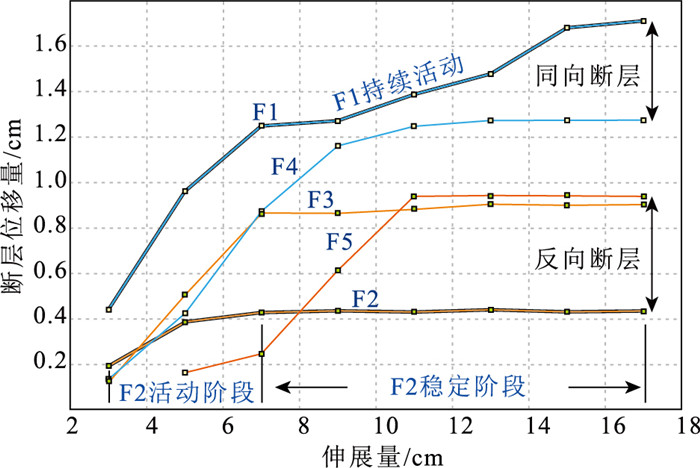
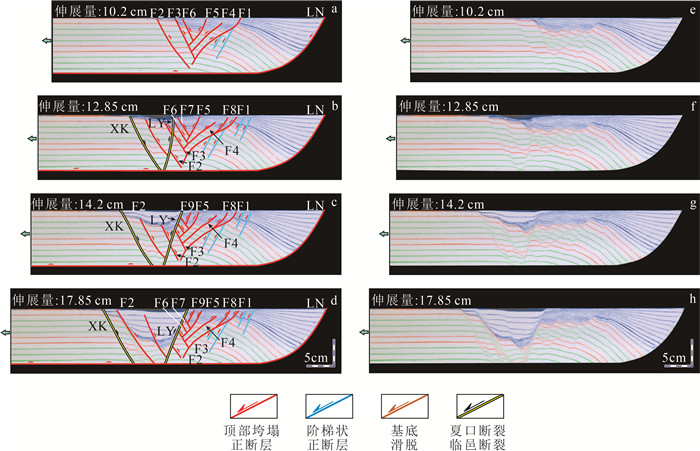
伸展盆地中发育的复杂断裂体系的结构样式、形成过程及成因机制一直是含油气盆地分析中的难点。利用构造物理模拟方法,研究了渤海湾盆地惠民凹陷典型剖面中滚动背斜与顶部垮塌断层的发育过程与形成机制。通过设计2组对照实验(E1和E2),分别研究了惠民凹陷中拆离断层和内部洼陷断裂对上盘褶皱和断裂结构影响和控制机制。其中,E1为预设断层模型,主要模拟弯曲的宁南拆离断层;E2实验采用双底板相对伸展模型和预设正断层模型相结合的方案,主要考虑了伸展盆地中后期次级洼陷的活动。构造物理模拟E1实验再现了渤海湾盆地惠民凹陷滚动背斜与顶部垮塌断层的形成过程,表明宁南断层实际控制了上盘一级褶皱的形态和次级断裂体系的发育。顶部垮塌断层体系由顺向和反向正断层构成,总体为不对称的结构特征,新发育的共轭断层具有同期的活动性,随后呈现侧向迁移的规律。断层位移量演化统计表明,实验存在同时活动、呈共轭关系的2组破裂面,与伸展楔体预测的2组库伦破裂一致,反映其处于或接近临界楔体状态。另一组实验显示,临邑和夏口断层的发育切割了早期形成的顶部垮塌断层,临南洼陷开始形成并不断加宽,最终形成的样式与现今构造剖面一致。本次研究对其他类似的伸展断层相关褶皱中的滚动背斜及其相关垮塌断裂发育机制具有一定的启示意义。
Abstract:The structure, formation and mechanisms of complex fault systems developed in extensional basins remain a challenging issue in the analysis of hydrocarbon-bearing basins.We used sandbox analogy modeling method to investigate the development and formation mechanism of rollover and crestal collapse faults above typical extensional listric faults in the Huimin depression of the Bohai Bay basin.By designing two sets of controlled experiments(E1 and E2), the influence and control mechanisms of the development of detachment and internal depressional faults in the Huimin Sag were investigated.Analogy experiments E1 reproduce the formation process of rollover and crestal collapse faults in the Huimin Sag, indicating that the Ningnan fault actually controls the morphology of the hanging wall and the development of the secondary fault system.The crestal collapse fault system is asymmetric and is composed of antithetic- and synthetic faults, the newly developed conjugate faults are contemporaneously active, and the fault activity shows a pattern of lateral migration.The statistics of fault displacement indicate that two sets of rupture surfaces are simultaneously active and in conjugate relationship.This is consistent with the Coulomb-Mohr failure criterion within the extensional wedge, indicating that the wedge is at or near the critical state.In another set of E2 experiment, the development of the Linyi and Xiakou faults offset the crestal collapse faults formed earlier, and the Linnan depression began to form and widen, eventually forming in a structural pattern consistent with the present-day structural profile.This study reveals the development mechanism of rollover and its associated crestal collapse fault in typical extensional fault-related folds, which has important implications for extensional fault system analysis.
-
Key words:
- extensional fault-related folding /
- rollover /
- crestal-collapse faults /
- analogue modeling /
- Huimin Sag
-

-
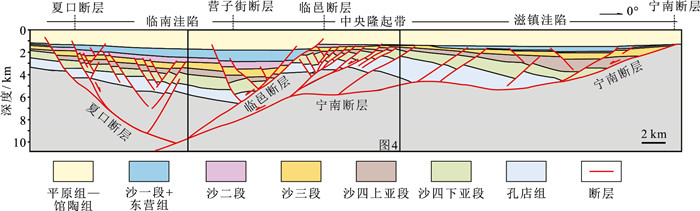
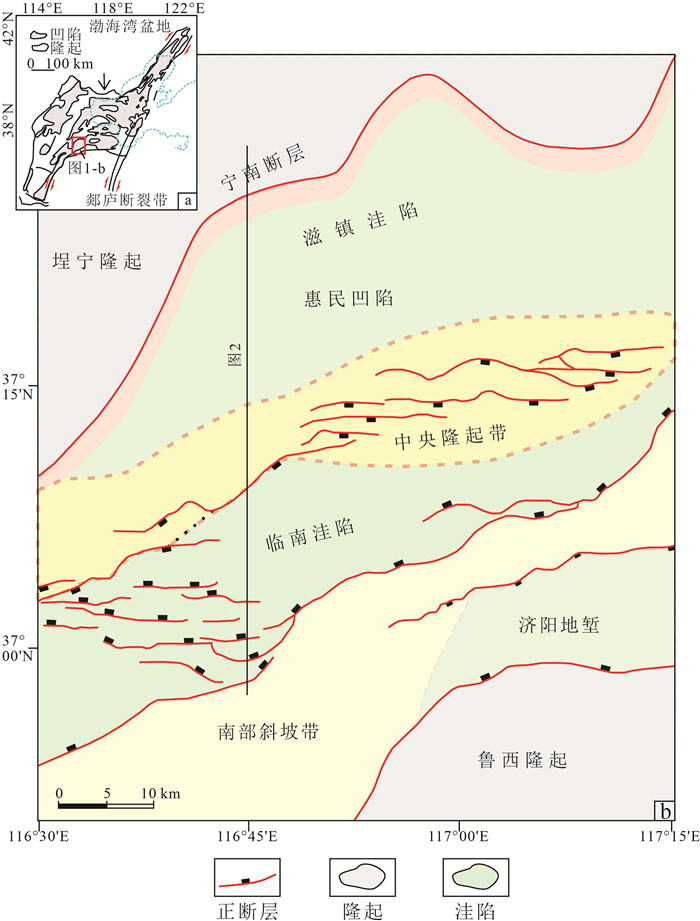
图 2 惠民凹陷典型构造剖面(据封东晓,2015修改)
Figure 2.
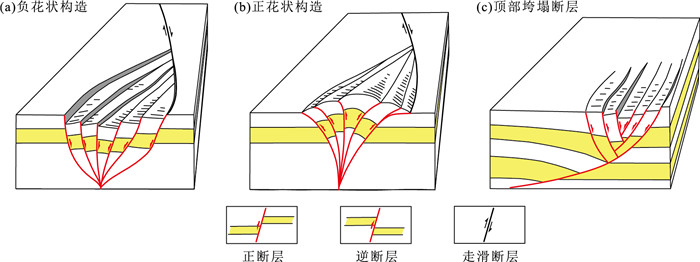
图 10 花状构造与顶部垮塌断层的构造模式图(a、b据Fossen, 2016修改)
Figure 10.
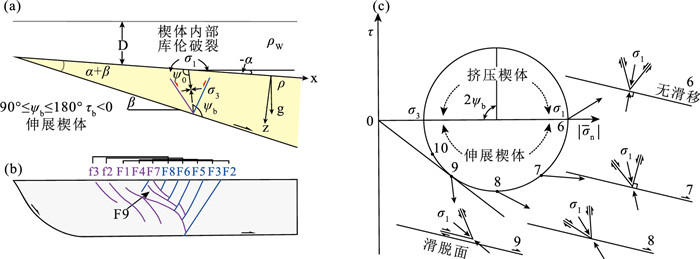
图 11 伸展构造楔体的库伦破裂模型(据Xiao et al, 1991修改)
Figure 11.
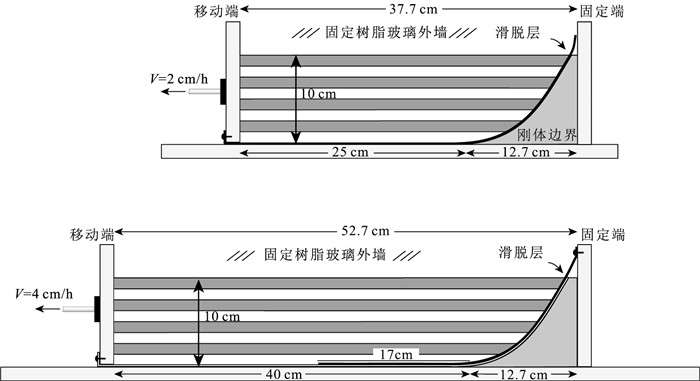
表 1 实验材料与相似系数
Table 1. Experimental materials and similarity coefficient
物理量 地质原型(n) 实验模型(m) 相似比例(m/n) 上地壳岩石密度(ρs) 2400 kg/m3 1400 kg/m3 0.6 内聚力(Cs) 10~ 20 MPa* 50~ 100 Pa** 6×10-6 长度(l) 1 km 1 cm 10-5 重力加速度(g) 9.81 m/s2 9.81 m/s2 1 注:*数据据Handin, 1966; **数据据Krantz, 1991 -
[1] Adam J, Urai J L, Wieneke B, et al. Shear localisation and strain distribution during tectonic faulting—new insights from granular-flow experiments and high-resolution optical image correlation techniques[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2005, 27: 283-301. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2004.08.008
[2] Dahlen F A. Noncohesive critical Coulomb wedges: An exact solution[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1984, 89(B12): 10125-10133. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB12p10125
[3] Del Ventisette C, Bonini M, Agostini A, et al. Using different grain-size granular mixtures(quartz and K-feldspar sand)in analogue extensional models[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2019, 129: 103888. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2019.103888
[4] Dewey J F, Holdsworth R E, Strachan R A. Transpression and transtension zones[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1998, 135(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1998.135.01.01
[5] Ellis P G, McClay K R. Listric extensional fault systems-results of analogue model experiments[J]. Basin Research, 1988, 1(1): 55-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.1988.tb00005.x
[6] Fossen H. Structural Geology[M]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2016.
[7] Groshong R. Unique determination of normal fault shape from hanging-wall bed geometry in detached half grabens[J]. Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae, 1990, 83(3): 455-471.
[8] Hamblin W K. Origin of "reverse drag" on the downthrown side of normal faults[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1965, 76(10): 1145-1164. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[1145:OORDOT]2.0.CO;2
[9] Harding T P. Identification of wrench faults using subsurface structural data: criteria and pitfalls[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(10): 1590-1609.
[10] Khalil S M, McClay K R. Extensional fault-related folding, northwestern Red Sea, Egypt[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2002, 24(4): 743-762. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(01)00118-3
[11] Krantz R W. Measurements of friction coefficients and cohesion for faulting and fault reactivation in laboratory models using sand and sand mixtures[J]. Tectonophysics, 1991, 188: 203-207. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(91)90323-K
[12] McClay K R. Extensional fault systems in sedimentary basins: a review of analogue model studies[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1990, 7(3): 206-233. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(90)90001-W
[13] McClay K R, Scott A D. Experimental models of hangingwall deformation in ramp-flat listric extensional fault systems[J]. Tectonophysics, 1991, 188(1/2): 85-96.
[14] Nunns A G. Structural restoration of seismic and geologic sections in extensional regimes[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1991, 75(2): 278-297.
[15] Shaw J H, Hook S C, Sitohang E P. Extensional fault-bend folding and synrift deposition: An example from the Central Sumatra Basin, Indonesia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1997, 81(3): 367-379.
[16] Shaw J H, Connors C D, Suppe J. Seismic interpretation of contractional fault-related folds[M]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 2005.
[17] Sylvester A G. Strike-slip faults[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1988, 100(11): 1666-1703. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1988)100<1666:SSF>2.3.CO;2
[18] Sun C, Jia D, Yin H, et al. Sandbox modeling of evolving thrust wedges with different preexisting topographic relief: Implications for the Longmen Shan thrust belt, eastern Tibet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2016, 121: 4591-4614. doi: 10.1002/2016JB013013
[19] Suppe J. Geometry and kinematics of fault-bend folding[J]. American Journal of Science, 1983, 283(7): 684-721.
[20] Wang D, Wu Z P, Yang L L, et al. Growth and linkage of the Xiakou fault in the Linnan Sag, Jiyang Depression, Eastern China: Formation mechanism and sedimentation response[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 116: 104319.
[21] Xiao H B, Suppe J. Origin of rollover[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1992, 76(4): 509-529.
[22] Xiao H B, Dahlen F A, Suppe J. Mechanics of extensional wedges[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1991, 96(B6): 10301-10318.
[23] Zhu Y B, Liu S F, Zhang B, et al. Reconstruction of the Cenozoic deformation of the Bohai Bay Basin, North China[J]. Basin Research, 2020, 33: 364-381.
[24] 封东晓. 张扭构造的几何学, 运动学特征及其石油地质意义[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2015.
[25] 何登发, Suppe J, 贾承造. 断层相关褶皱理论与应用研究新进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(4): 353-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200504005.htm
[26] 贾东, 陈竹新, 张惬, 等. 东营凹陷伸展断弯褶皱的构造几何学分析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2005, 29(3): 295-302. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200503002.htm
[27] 贾东, 李一泉, 王毛毛, 等. 断层相关褶皱的三维构造几何学分析: 以川西三维地震工区为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(3): 732-740. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201103013.htm
[28] 李德生. 渤海湾含油气盆地的地质和构造特征[J]. 石油学报, 1980, 1(1): 6-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB198001002.htm
[29] 陆克政, 漆家福, 戴俊生, 等. 渤海湾新生代含油气盆地构造模式[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997.
[30] 马立成, 施炜, 李建华, 等. 庐山岩浆核杂岩隆起-快速伸展变形特征和时代[J]. 地质通报, 2023, 42(4): 589-599. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20230408&flag=1
[31] 漆家福, 肖焕钦, 张卫刚. 东营凹陷主干边界断层(带)构造几何学、运动学特征及成因解释[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(3): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200303002.htm
[32] 沈礼, 贾东, 尹宏伟, 等. 基于粒子成像测速(PIV)技术的褶皱冲断构造物理模拟[J]. 地质论评, 2012, 58: 73-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201203009.htm
[33] 苏金宝, 朱文斌, 贾东, 等. 伸展断层相关褶皱的几何学分析及其在车镇凹陷中的应用[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(10): 563-1573. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201110004.htm
[34] 王义天, 李继亮. 走滑断层作用的相关构造[J]. 地质科技情报, 1999, 18(3): 30-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ199903006.htm
[35] 杨克基, 漆家福, 余一欣, 等. 渤海湾地区断层相关褶皱及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2016, 51(3): 625-636. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ201603027.htm
-



 下载:
下载: