Disaster characteristics and stability evaluation of the Hanjin Beishan landslide group in Linxia Basin, Gansu Province
-
摘要:
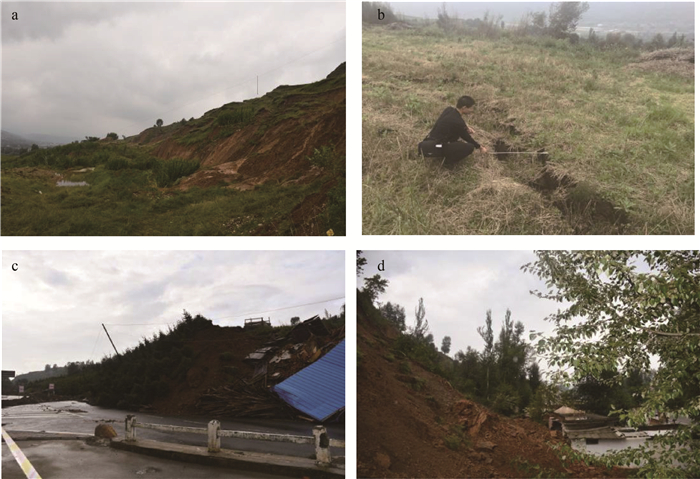
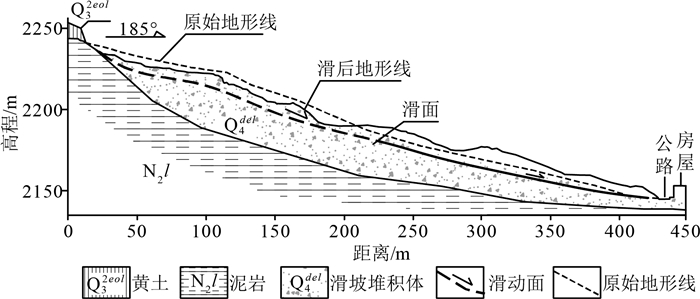
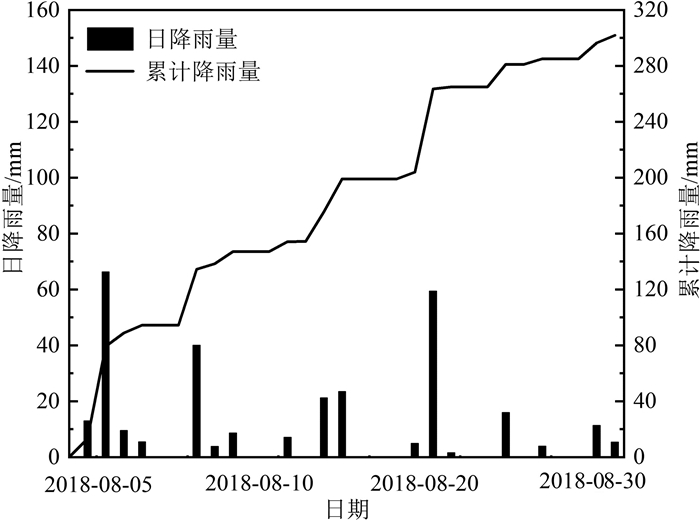
2018年8月24日,甘肃省临夏县韩集镇北山出现明显裂缝、局部下滑并形成滑坡群,紧邻坡脚和坡体上的房屋、基础设施遭到破坏。滑坡群在降雨、地震等影响下存在继续滑动的可能,对集镇和省道交通安全具有潜在威胁,因此开展滑坡群稳定性评价十分迫切。采用野外调查、极限平衡分析和有限元数值模拟方法,对北山滑坡群的各次级滑坡稳定性进行了系统评价,认为连续降雨或强降雨是造成北山出现大面积变形和形成多个次级滑坡的主要诱发因素,滑坡区地形、坡体结构和不合理的人类工程活动为滑坡的形成创造了条件。应用GeoStudio软件对滑坡群不同块体进行定量稳定性评价,结果表明:在自重工况下,滑坡群稳定性较好;在降雨工况下,除H10滑坡外,其余次级滑坡均可能进一步失稳破坏;若区内受到超越其地震基本烈度的地震作用,滑坡群稳定系数将迅速降低,各次级滑坡均可能出现快速失稳现象。根据滑坡群不同次级滑坡的变形特点和成灾模式,建议有针对性地采取坡脚挡土墙、削坡减载、锚杆框架、截排水渠、吊沟及排水抗滑设计等综合治理措施。为保证滑坡影响范围内的居民、建筑及交通安全,应加强滑坡群风险管控,在滑坡治理前需加强监测预警,动态掌握滑体的稳定状态。
Abstract:On August 24, 2018, obvious cracks appeared in Beishan mountain, Hanji Town, Linxia County, Gansu Province, part of the mountain slide in different direction and landslide group formed.It is very urgent to carry out stability evaluation of the landslide groups.Field geological survey, limit equilibrium analysis and finite element numerical simulation were used to systematically evaluate the stability of each secondary landslide in Beishan landslide group.The results show that: ①Continuous rainfall or heavy rainfall was the main inducing factor that caused such a large area of deformation and the formation of multiple secondary landslides.The topography of the landslide area, the structure of the slope body and the unreasonable human engineering activities creat conditions for the formation of landslide.②According to the quantitative stability evaluation of different blocks of the landslide group, under the self-weight condition, the landslide group is in a better stable state.Under the rainfall condition, except for the H10 landslide, the rest of the secondary landslides will be further destabilized.If the area is subjected to an earthquake that exceeds its basic seismic intensity, the stability coefficient of the landslide group will decrease rapidly.All secondary landslides will experience rapid instability.③According to the deformation characteristics and disaster patterns of different secondary landslides in the landslide group, it is recommended to take targeted management measures such as retaining walls at the slope foot, slope cutting and load reduction, anchor frames, intercepting and draining channels, hanging ditches drainage anti-skid design.In order to ensure the safety of residents, buildings and traffic within the affected area of landslides, it is recommended to further strengthen the risk management and control of landslide groups, strengthen monitoring and early warning before landslide treatment, and dynamically grasp the stability of landslide groups.
-

-
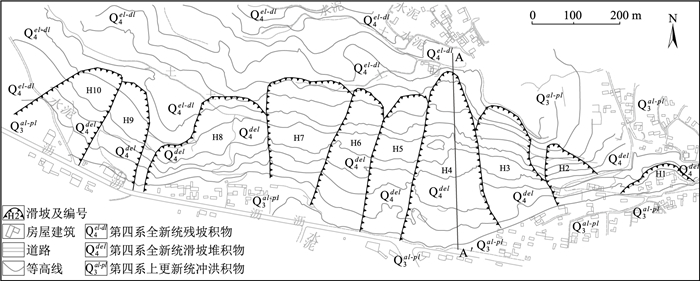
表 1 滑坡群基本特征
Table 1. Plane general characteristics of landslide group
滑坡编号 长/m 宽/m 厚/m 体积/104 m3 规模 变形模式 宏观判断稳定状态 H1 170 85 6 8.67 小型 牵引式 欠稳定 H2 115 130 6 8.97 小型 推移式 基本稳定 H3 140 255 10 35.7 中型 推移式 不稳定 H4 255 415 18 190.5 大型 推移式 不稳定 H5 95 335 12 38.2 中型 推移式 基本稳定 H6 145 315 14 63.95 中型 推移式 基本稳定 H7 130 250 8 26.0 中型 推移式 基本稳定 H8 235 200 6 28.2 中型 牵引式 基本稳定 H9 145 215 8 24.9 中型 推移式 基本稳定 H10 165 195 7 22.5 中型 推移式 基本稳定 表 2 滑坡土体重度试验值
Table 2. Soil weight test values of the landslide
类别 天然重度/(kN·m-3) 干燥重度/(kN·m-3) 饱和重度/(kN·m-3) 滑坡堆积体 17.9 14.8 18.8 滑床 20.12 17.35 22.17 滑带 18.7 15.0 19.0 表 3 滑带土体抗剪强度参数
Table 3. Shear strength parameters of soil in slip zone
岩性 自重工况 暴雨工况 地震工况 粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/° 粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/° 粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/° 试验值 强风化泥岩 50.3 33.42 20.1 34.43 50.3 33.42 经验值 碎石土 12.5 32.6 9.6 33.8 12.5 32.6 综合取值 滑带土 17.2 22.6 10.2 18.8 17.2 20.6 表 4 新近系泥岩物理力学参数
Table 4. Physical and mechanical parameters of Neogene mudstone
泥岩参数 天然重度/(kN·m-3) 饱和重度/(kN·m-3) 天然抗压强度/MPa 饱和抗压强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/° 承载力特征值/MPa 基底摩擦系数 水平抗力系数/(MN·m-3) 取值 20.17 22.24 1.44 0.52 0.39 50.3 33.42 0.55 0.4 80 表 5 滑坡稳定性评价标准
Table 5. Evaluation criteria for landslide stability
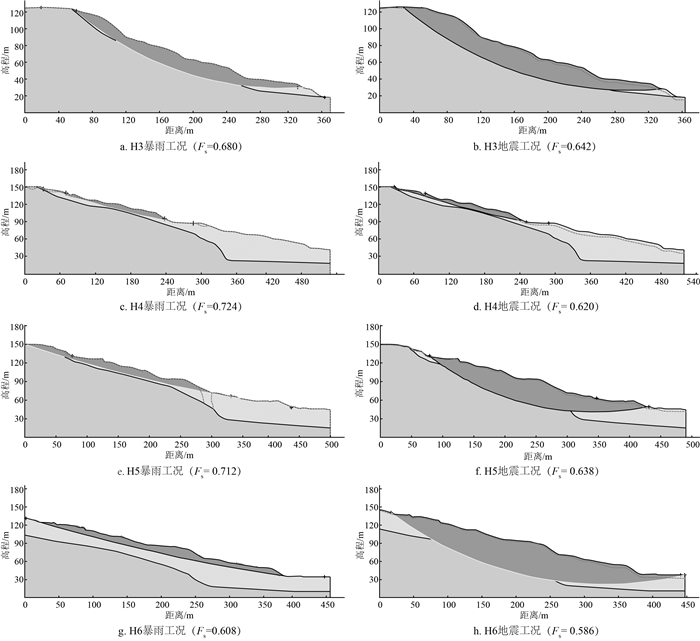
稳定状态 不稳定 欠稳定 基本稳定 稳定 稳定系数 K<1.0 1.0≤K<1.05 1.05≤K<1.15 K≥1.15 表 6 各次级滑坡在不同工况下的稳定系数
Table 6. Stability coefficient of each secondary landslide under different working conditions
滑坡编号 自重工况 暴雨工况 地震工况 稳定系数 稳定状态 稳定系数 稳定状态 稳定系数 稳定状态 H1 1.012 欠稳定 0.766 不稳定 0.738 不稳定 H2 1.008 欠稳定 0.720 不稳定 0.821 不稳定 H3 0.782 不稳定 0.680 不稳定 0.642 不稳定 H4 1.010 欠稳定 0.724 不稳定 0.620 不稳定 H5 1.001 欠稳定 0.712 不稳定 0.638 不稳定 H6 0.911 不稳定 0.608 不稳定 0.586 不稳定 H7 1.011 欠稳定 0.462 不稳定 0.558 不稳定 H8 1.011 欠稳定 0.932 不稳定 0.910 不稳定 H9 1.332 稳定 0.872 不稳定 0.922 不稳定 H10 1.090 基本稳定 1.001 欠稳定 0.681 不稳定 -
[1] Gian Q A, Tran D T, Nguyen D C, et al. Design and implementation of site-specific rainfall-induced landslide early warning and monitoring system: A case study at Nam Dan landslide(Vietnam) [J]. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 2017, 28(2) : 15-32.
[2] Ogbonnaya I, Chidinma C. Slope stability analysis of mine waste dumps at a mine site in Southeastern Nigeria[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2019, 78(4) : 20-35.
[3] 安玉科, 樊江, 马胜午, 等. 堆积阶地古老滑坡识别方法及其在线状工程地质勘察中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(6) : 1787-1794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202006014.htm
[4] 蔡广珍, 杨子和, 王东平, 等. 甘肃临夏州地质灾害成因分析及防御对策[J]. 农业灾害研究, 2015, 5(4) : 32-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NZYJ201504014.htm
[5] 窦晓东, 张泽林. 甘肃舟曲垭豁口滑坡复活机理及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2021, 32(2) : 9-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202102002.htm
[6] 方汕澳, 许强, 修德皓, 等. 基于斜率模型的突发型黄土滑坡失稳时间预测[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2021, 48(4) : 169-179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202104022.htm
[7] 冯学才, 王家鼎. 甘肃省滑坡泥石流灾害及其减灾对策[J]. 灾害学, 1991, 6(4) : 43-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU199104007.htm
[8] 耿清友, 康志强, 张雪岩, 等. 地震作用下某矿山排土场边坡稳定性分析[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2017, 46(12) : 50-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKJ201712013.htm
[9] 高孟潭, 陈国星, 谢富仁, 等. 中国地震动参数区划图(GB18306—2015) [S]. 中国标准出版社, 2015.
[10] 郭富赟. 甘肃地质灾害风险管理思考[J]. 甘肃地质, 2021, 30(1) : 16-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ202101002.htm
[11] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(3) : 433-453. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200703000.htm
[12] 李彩虹, 李雪, 郭长宝, 等. 青藏高原东部鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡危险性评价[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(8) : 1473-1486. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20220813&flag=1
[13] 刘传正, 沈伟志, 黄帅. 中国地质灾害预防应对战略思考[J]. 灾害学, 2022, 37(3) : 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU202203001.htm
[14] 裴惠娟, 陈晋, 李雯, 等. 甘肃省地质灾害风险评估[J]. 灾害学, 2017, 32(2) : 97-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU201702017.htm
[15] 冉林, 马鹏辉, 彭建兵, 等. 甘肃黑方台"10·5"黄土滑坡启动及运动特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(6) : 1-9.
[16] 任克峰. 边坡稳定性评估方法及应用[D]. 宁夏大学硕士学位论文, 2008.
[17] 申怀飞, 董雨, 杨梅, 等. 基于AHP与信息量法的甘肃省滑坡易发性评估[J]. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(6) : 412-419. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY202106053.htm
[18] 田尤, 陈龙, 黄海, 等. 西藏澜沧江流域察雅县城滑坡群成因及现状稳定性[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(12) : 2034-2042. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20211206&flag=1
[19] 铁永波, 张宪政, 卢佳燕, 等. 四川省泸定县Ms6.8级地震地质灾害发育规律与减灾对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2022, 49(6) : 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202206001.htm
[20] 王伟, 王卫, 戴雄辉. 四川美姑拉马阿觉滑坡复活特征与影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(4) : 9-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202204002.htm
[21] 汪美华, 赵慧, 倪天翔, 等. 基于不连续布局优化法的那勒寺古滑坡稳定性分析[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(1) : 234-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI202001023.htm
[22] 吴瑞安, 马海善, 张俊才, 等. 金沙江上游沃达滑坡发育特征与堵江危险性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2021, 48(5) : 120-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202105013.htm
[23] 闫茂华, 魏云杰, 李亚民, 等. 云南德钦日因卡滑坡孕灾背景及形成机理[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(12) : 1971-1980. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20201211&flag=1
[24] 张佳佳, 田尤, 陈龙, 等. 澜沧江昌都段滑坡发育特征及形成机制[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(12) : 2024-2033. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20211205&flag=1
[25] 张永双, 刘筱怡, 吴瑞安, 等. 青藏高原东缘深切河谷区古滑坡: 判识、特征、时代与演化. [J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(2) : 94-105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202102009.htm
[26] 中国建筑科学研究院. 建筑抗震设计规(B50011—2016) [S]. 北京: 建筑工业出版社, 2016.
[27] 周伟杰, 徐卫亚, 王如宾, 等. 暴雨及久雨作用下东岭信滑坡堆积体的渗流特性及稳定性分析[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(2) : 28-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHYC202002006.htm
-




 下载:
下载: