Genetic Analysis of Chenjiazhuang Spring in Yongding River, Beijing
-
摘要:
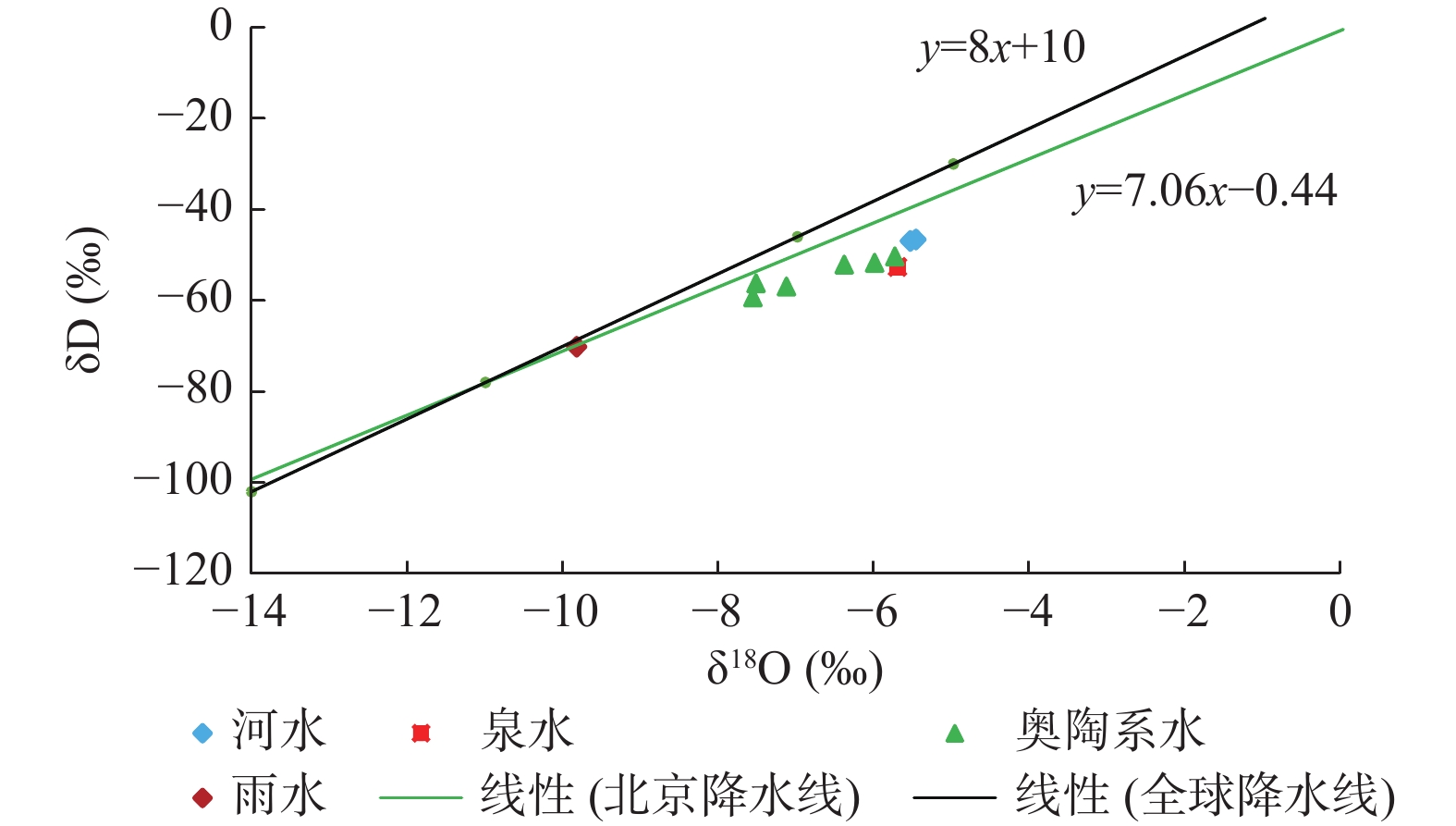
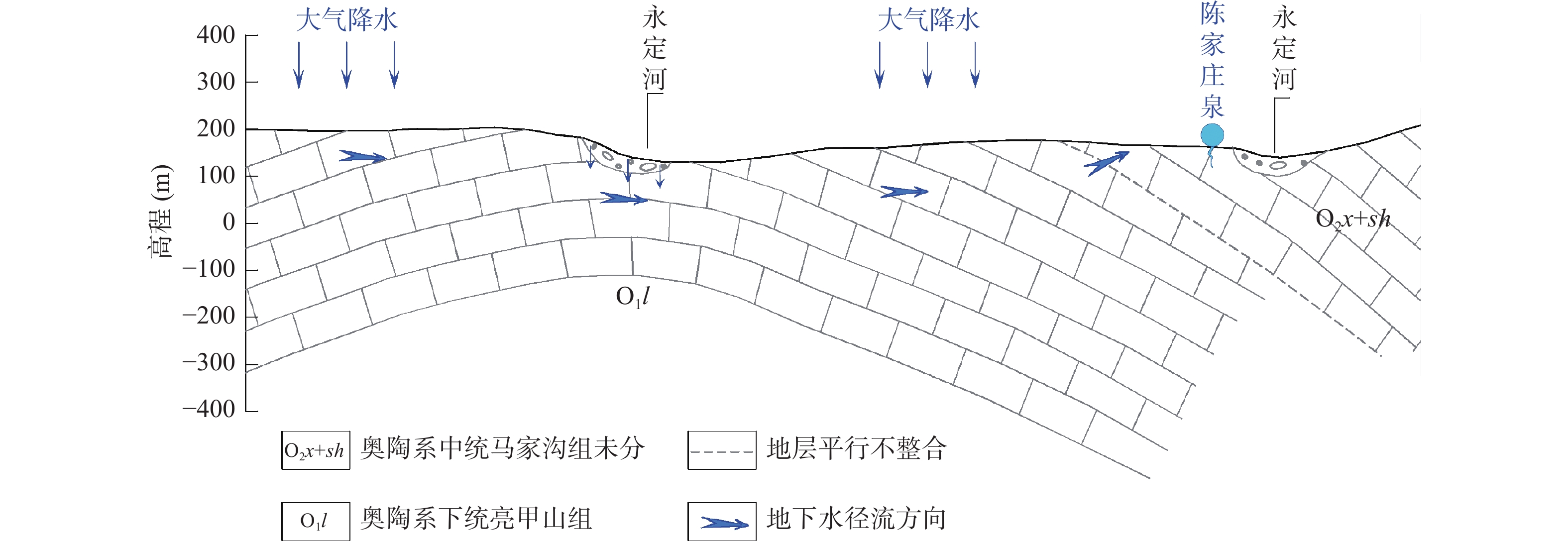
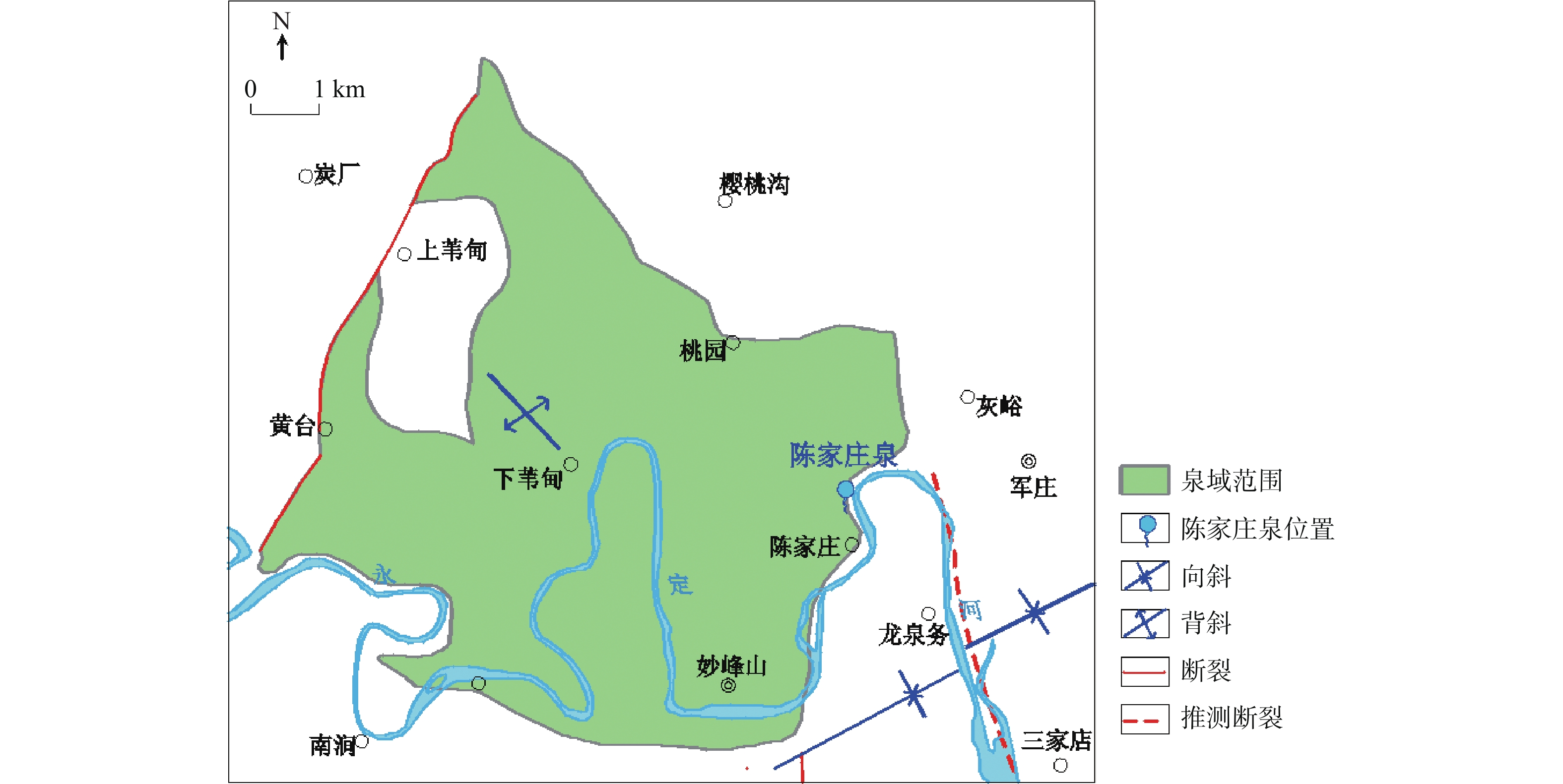
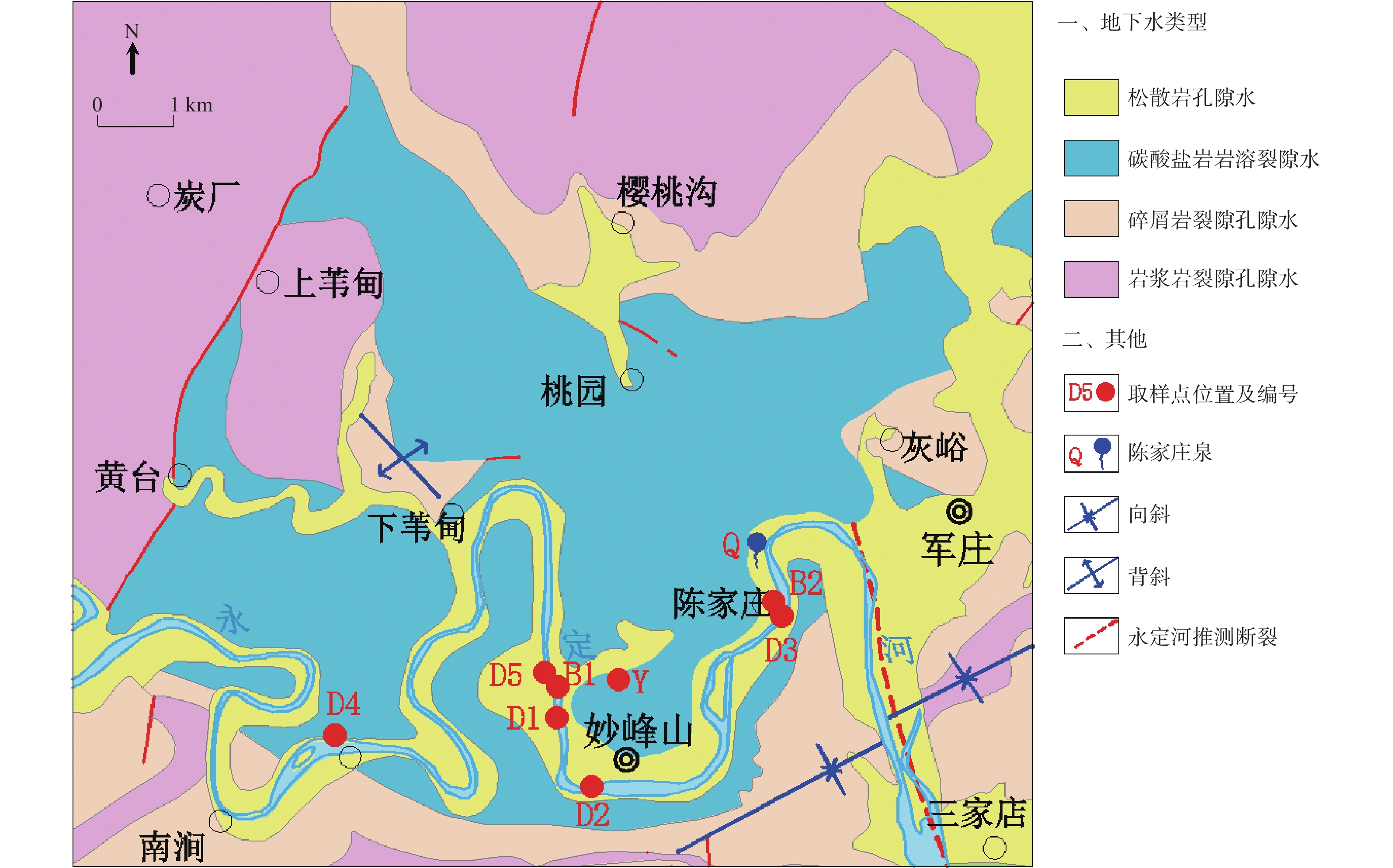
陈家庄泉位于永定河畔,在永定河生态环境治理工程开展以来至2019年,泉水复涌。为更好的管理和保护陈家庄泉,实现永定河生态环境治理及区域水资源战略储备,开展泉水成因分析及泉域划分研究。通过泉域范围雨水、河水、地下水同位素和水化学样测试分析,获取泉水的补给来源、补给高程及补给温度;在以上分析的基础上,结合区域地质、水文地质条件,划定泉水汇水面积(泉域范围)。分析结果表明陈家庄泉赋存于奥陶系灰岩含水层中,区域岩溶地下水补给来源为大气降水和永定河河水,泉水为一裸露型侵蚀溢流泉,泉水补给高程为736 m,补给温度为13.12 ℃,泉域汇水面积为30.6 km2。
Abstract:Chenjiazhuang Spring is located on the Yongding River. Since the ecological environment improvement project of Yongding River was carried out, the spring flowed out in 2019. In order to protect and manage Chenjiazhuang Spring, realize the ecological environment management of Yongding River and regional water resources strategic reserve, spring origin analysis and spring domain division were carried out.The recharge source, recharge elevation and recharge temperature of the spring were obtained by testing and analyzing the isotope and hydrochemistry samples of rainwater, river water and groundwater in the spring area; On the basis of the above analysis, combined with the regional geological and hydrogeological conditions, delimit the spring catchment area. The results show that the Chenjiazhuang spring exists in the Ordovician limestone aquifer,the regional karst groundwater recharge source is atmospheric precipitation and Yongding River water, the spring is an exposed erosion overflow spring, the spring recharge elevation is 736 m, the recharge temperature is 13.12 ℃, the catchment area of the spring is 30.6 km2.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- spring /
- isotope /
- hydrochemical /
- formation mechanism /
- Beijing
-

-
表 1 陈家庄泉区域水样点及测试结果表
Table 1. Water sample point test result in Chenjiazhuang Spring area
样品
编号位置 取样
日期取样
类型δ2H
(‰)δ18O
(‰)T
(TU)K+
(Mg/L)Na+
(Mg/L)Ca+
(Mg/L)Mg2+
(Mg/L)HCO3-
(Mg/L)Cl−
(Mg/L)SO42−
(Mg/L)TDS
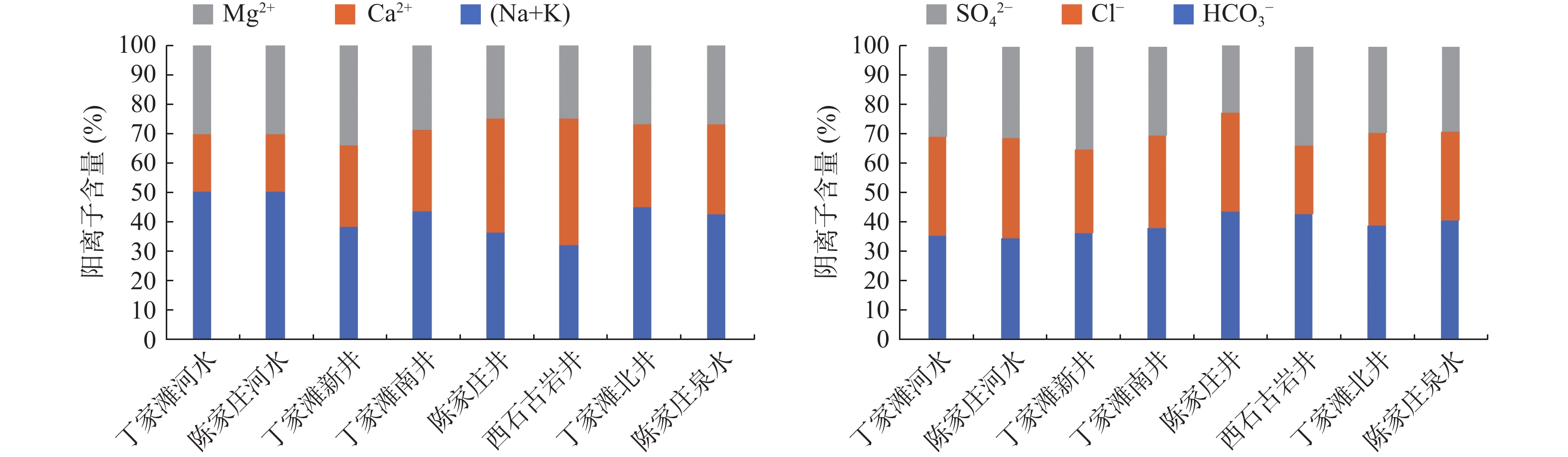
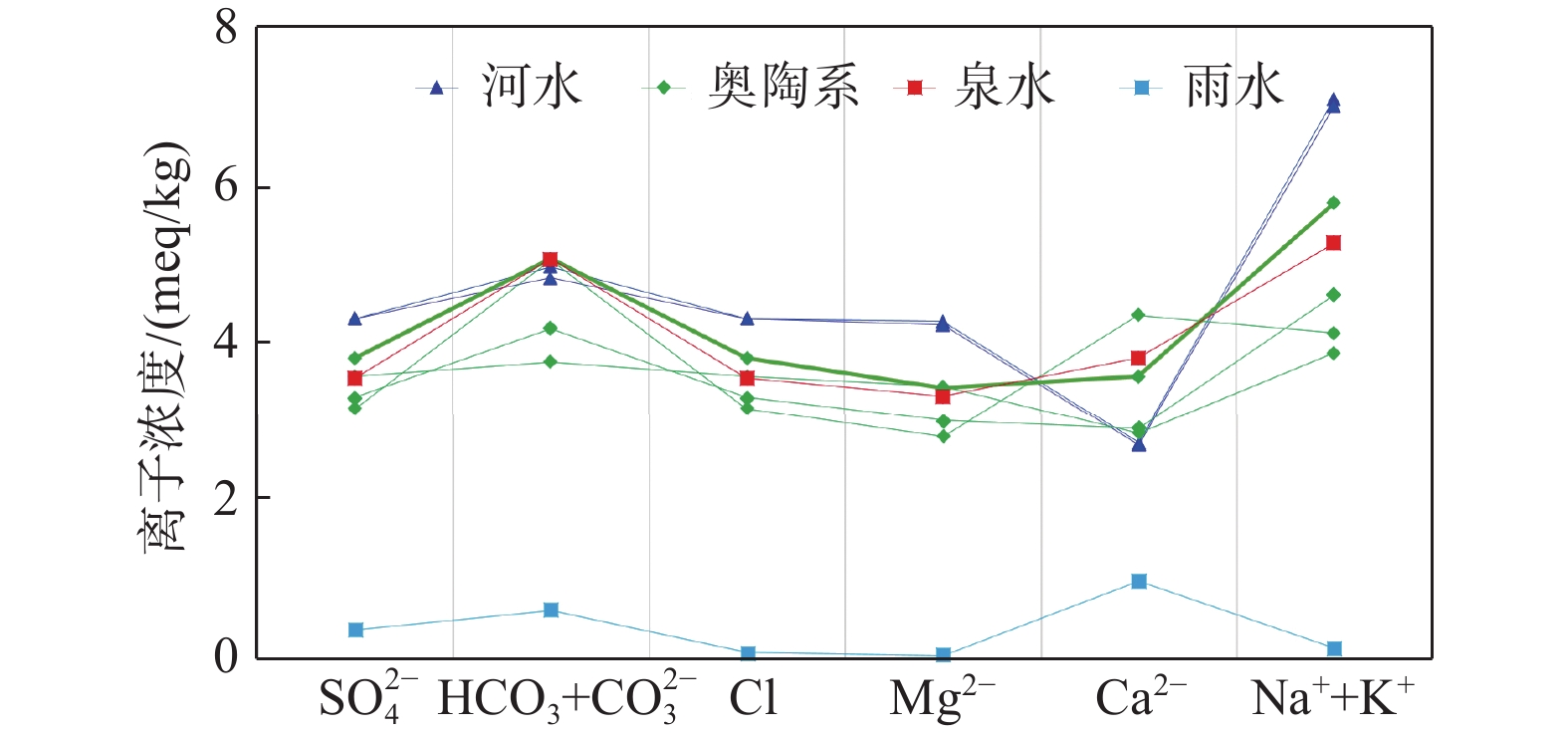
(Mg/L)pH 水化学类型 B1 丁家滩新
井边河水2021/5/14 河水 −46.9 −5.55 7.6±0.4 12 156 54.7 51.4 298 165 207 811 8.31 HCO3·Cl·SO4-
Na·MgB2 陈家庄
泉边河水2021/5/14 河水 −46.6 −5.48 8.8±0.5 11.7 154 54.2 50.8 290 164 207 806 8.34 HCO3·Cl·SO4-
Na·MgD1 丁家滩
新打井2021/5/14 奥陶系 −50.3 −5.75 6.3±0.4 3.68 87 57 41.5 226 102 172 505 9.12 HCO3·Cl·SO4-
Na·Ca.MgD2 丁家滩
南井2021/5/14 奥陶系 −52.1 −6.4 4.7±0.4 11.5 99.3 58.4 32.6 251 122 159 613 7.96 HCO3·Cl·SO4-
Na.·Ca·MgD3 陈家庄
村井2021/5/14 奥陶系 −51.6 −6.01 6.3±0.5 3.42 92.9 87 33.8 303 116 152 682 7.17 HCO3.Cl·SO4-
Ca.Na.MgD4 西石古
岩井2021/5/14 奥陶系 −57.6 −7.57 3.29 95.7 115 39.8 331 104 205 933 7.7 HCO3·SO4.-
Ca.Na.MgD5 丁家滩
北井2021/5/14 奥陶系 −56.2 −7.53 4.62 130 71.6 41.2 304 144 183 557 8.05 HCO3·SO4.Cl-
Na·Mg·Ca.Q 陈家庄泉
边河水2021/5/14 泉水 −52.6 −5.72 5.7±0.5 5.19 118 76.2 39.9 304 132 171 703 7.51 HCO3·Cl·SO4-
Na·Ca.MgY 雨水 2021/8/20 雨水 −70.16 −9.83 2.85 1.49 19.5 0.49 36.8 2.65 17.6 89 6.24 HCO3-Ca.Mg 表 2 泉水和奥陶系灰岩地下水接受降水及河水补给比例情况表
Table 2. The proportion of precipitation and water recharge in spring water and Ordovician limestone groundwater
补给来源 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 Q 降水 14.62 22.36 21.22 46.00 39.98 24.51 河水 85.38 77.64 78.78 54.00 60.02 75.49 表 3 陈家庄泉区域地下水和泉水补给高程和补给温度计算结果
Table 3. Calculation results of recharge elevation and temperature of groundwater and spring in Chenjiazhuang Spring area
编号 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 Q 补给高程(m) 664 731 452 757 557 736 补给温度(℃) 12.64 13.3 13.43 10.9 11.93 13.12 -
[1] 北京市地质矿产局. 北京市区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 1991
[2] 冯炳兴, 周启顺, 田树润, 等. 北京西山能源基地供水水文地质勘察报告[R]. 北京: 北京市地质工程勘察院, 1982.
[3] 韩行瑞. 岩溶水文地质学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015, 83−89.
[4] 梁永平, 王维泰. 中国北方岩溶水系统划分与系统特征. 地球学报, 2010, 31(6): 860-868
LIANG Yongping, WANG Weitai. The Division and Characteristics of Karst Water Systems in Northern China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, Vol. 31 No. 6: 860-868.
[5] 龙 汨, 周 训, 李 婷等. 北京延庆县松山温泉的特征与成因[J], 现代地质, 2014, 28(5), 1053-1060
LONG Mi, ZHOU Xun, LI ting, et al. Characteristics and Formation of the Songshan Hot Spring in Yanqing County of Beijing[J], Geoscience, 2014, Vol. 28 No. 5, 1053-1060
[6] 刘启仁, 张凤奇、秦毅苏等. 中国北方岩溶水资源的形成、分布与开发利用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1992, (04), 41-44
LIU Qiren, ZHANG Fengqi, QIN Yisu, et al. The formation, distribution, and development and utilization of karst water resources in northern China[J]. Hydrogeology engineering Geology, 1992, No. 04, 41-44
[7] 刘存富, 王佩仪, 周炼等. 河北平原地下水氢、氧、碳、氯同位素组成的环境意义[J]. 地学前缘, 1997, 4(1-2): 267-274 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1997.02.018
LIU Chunfu, Wang Peiyi, ZHOU Lian, et al. The environment signifincance of H O C and Cl isotopic composition in groundwater of hebei plane[J]. Earth Sciences Fronters, 1997, 4(1-2): 267-274. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1997.02.018
[8] 马传明, 刘存富, 周爱国. 同位素水文学新技术新方法[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2010
[9] 钱会, 马致远, 李培月,等. 水文地球化学[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 2012.
[10] 宋献方, 李发东, 于静洁等. 基于氢氧同位素与水化学的潮白河流域地下水循环特征[J]. 地理研究, 2007, 26(1)12-21.
SONG Xian fang, LI Fa dong, YU Jing jie, et al. Characteristics of groundwater cycle using deuterium, oxygen-18 and hydrochemistry in Chaobai River Basin, Geography research, 2007 26(1)12-21.
[11] 宋献方, 唐 瑜, 张应华等. 北京连续降水水汽输送差异的同位素示踪[J], 水科学进展, 2017, 28(4): 488-495.
SONG Xianfang, TANG Yu, ZHANG Yinghua, et al. Using stable isotopes to study vapor transport of continuous precipitation in Beijing[J], Advances in water sciencs, 2017, 28(4): , 488-495
[12] 唐春雷, 梁永平, 韩凯等. 玉泉山泉九龙山一香峪向斜的水文地质意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 5(43): 432-437
TANG Chunlei, LIANG Yongping, Han Kai, et al. Hydrogeological significance of the Jiulongshan-Xiangyu syncline at Yuquanshan sping[J]. Carsologica sinica, 2015, Vol. 43 No. 5: 432-437
[13] 唐春雷, 梁永平, 王维泰等. 龙子祠泉域岩溶水水化学 - 同位素特征[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2020, 37(1): 53-58
TANG Chunlei, LIANG Yongping, WANG Weitai, et al. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of the karst groundwater systems in Longzici spring basin[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2020, Vol. 37 No. 1: 53-58
[14] 王恒纯. 同位素水文地质概论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991
[15] 周训, 胡伏生, 何江涛, 等. 地下水科学概论[M].北京, 地质出版社, 2009, 71−73.
[16] 周训, 李晓露, 王蒙蒙等. 浅循环泉简析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2017, 5(44): 1-5
ZHOU Xun, LI Xiaolu, Wang Mengmeng, et al. A preliminary analysis of the springs of shallow groundwater circulation[J]. Hydrogeology engineering Geology, 2017, Vol 5 No. 44: 1-5
[17] 赵春红, 李强, 梁永平等. 北京西山黑龙关泉域岩溶水系统边界与水文地质意义[J]. 地球科学进展, 2014, 29(3): 412-419 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.03.0412
ZHAO Chunhong, LI Qiang, LIANG Yongping, et al. KarstWater System Boundaries and Hydrogeological Properties of Heilongguan Springshed in Xishan Region, Beijing[J]. Advances in earth science, 2014, Vol. 29 No. 3: 412-419 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.03.0412
[18] 赵春红, 梁永平, 王维泰等. 北京西山泉域岩溶水系统特征探讨[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(5): 641-647
ZHAO Chunhong, LIANG Yongping, WANG Weitai, et al. Discussion on the characteristic of water systems in the Xishan area of Beijing[J]. Carsologica sinica, 2017, Vol. 36 No. 5: 641-647
[19] Yurtsever Y. Worldwide survey of stable isotopes in precipitation[R]. Vienna: Isotope Hydrology International Atomic Energy Agency, 1975.
-



 下载:
下载: