Precise Calculation for Characteristic Parameters of Valley-type Debris Flow Using a Methed of Recursive Equivalent Area Substitution
-
摘要:
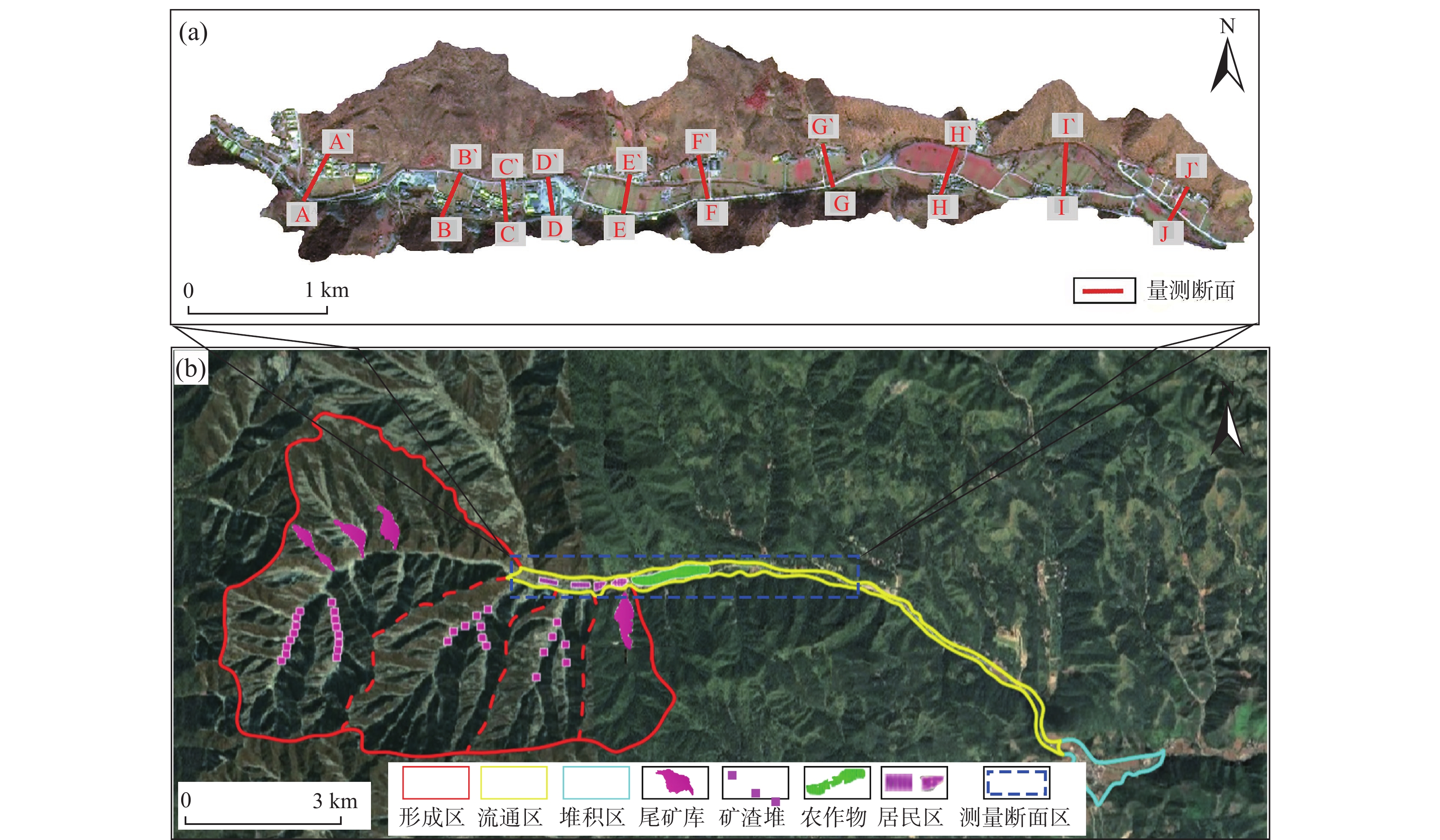
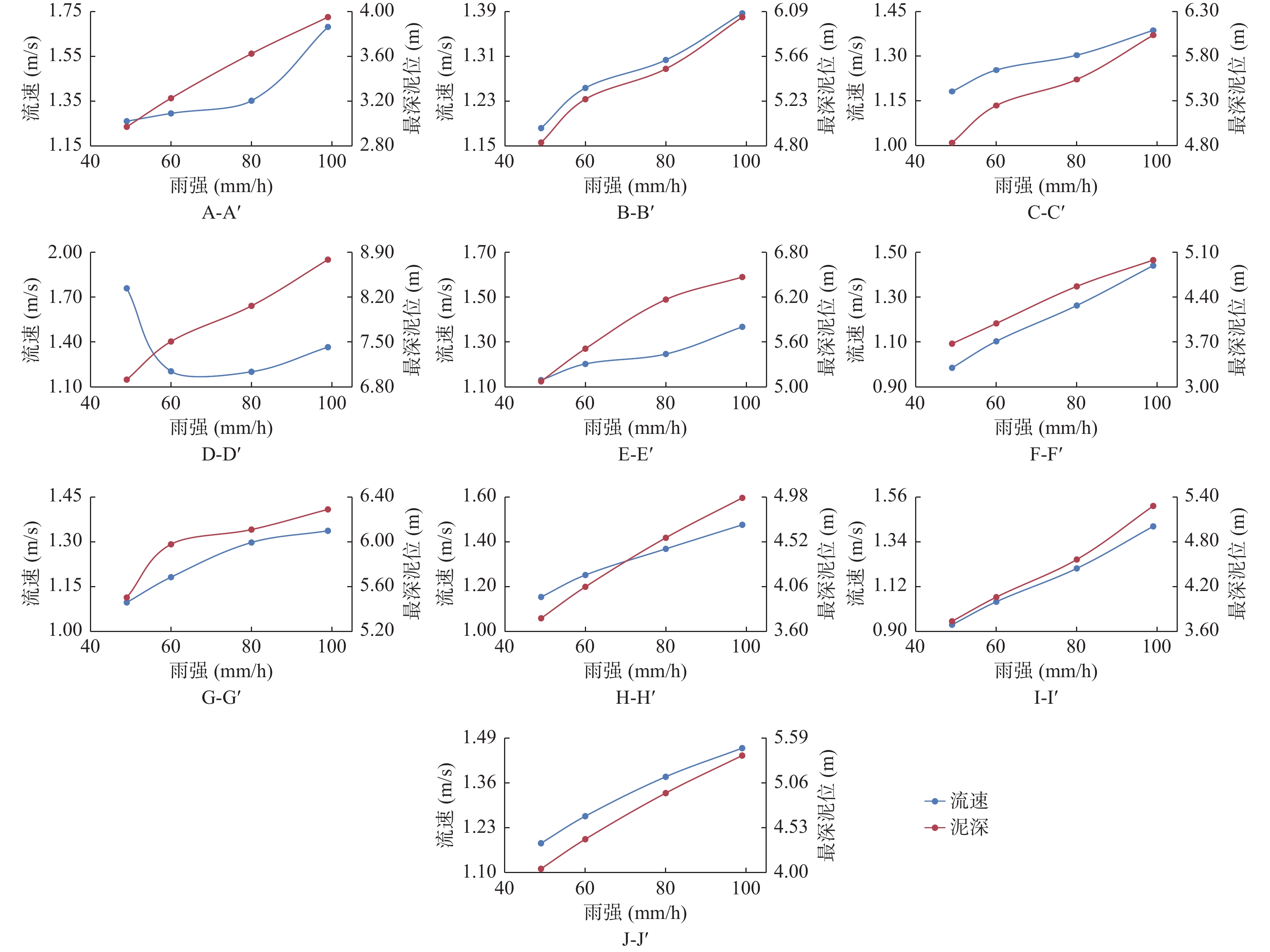
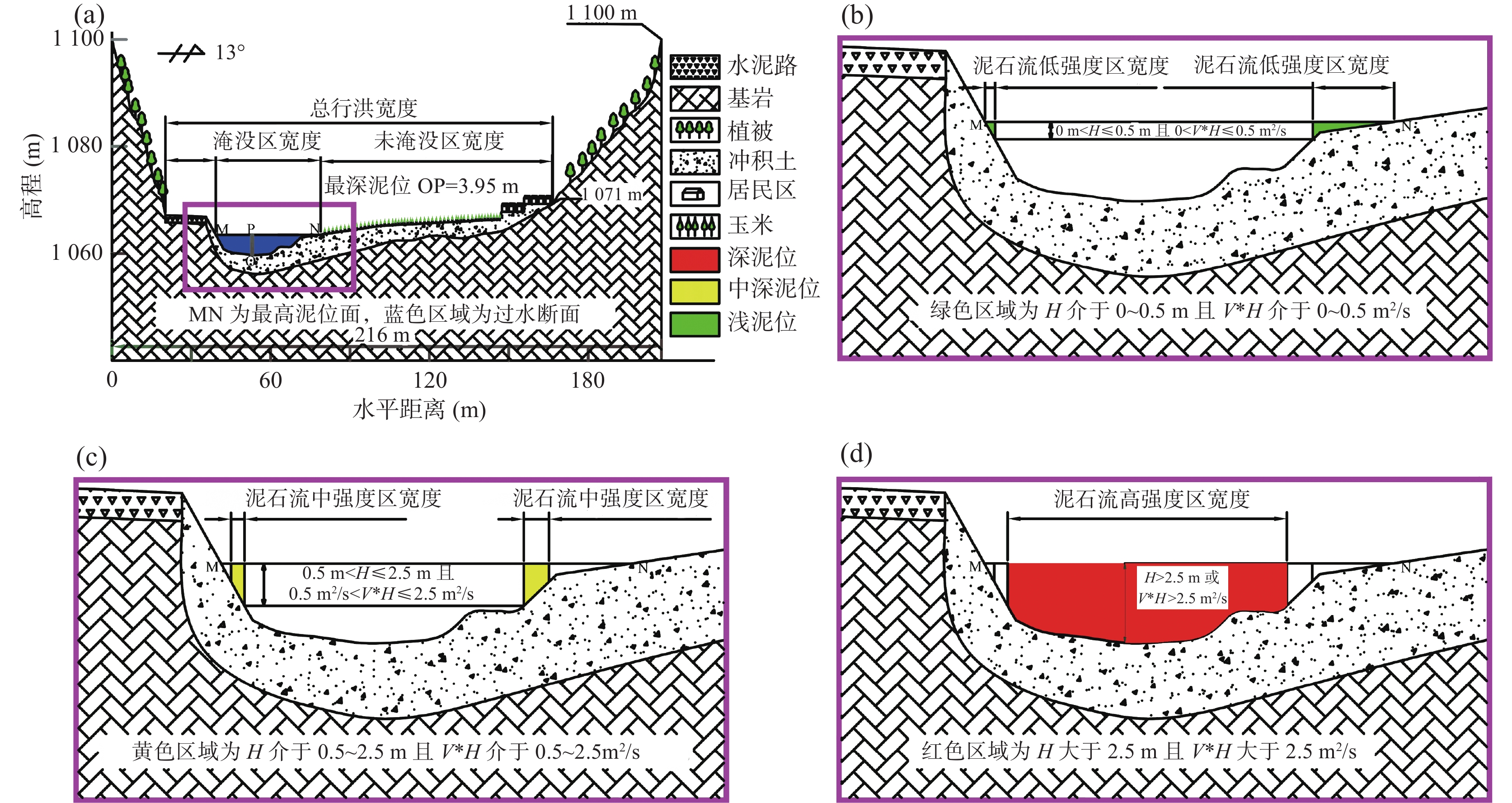
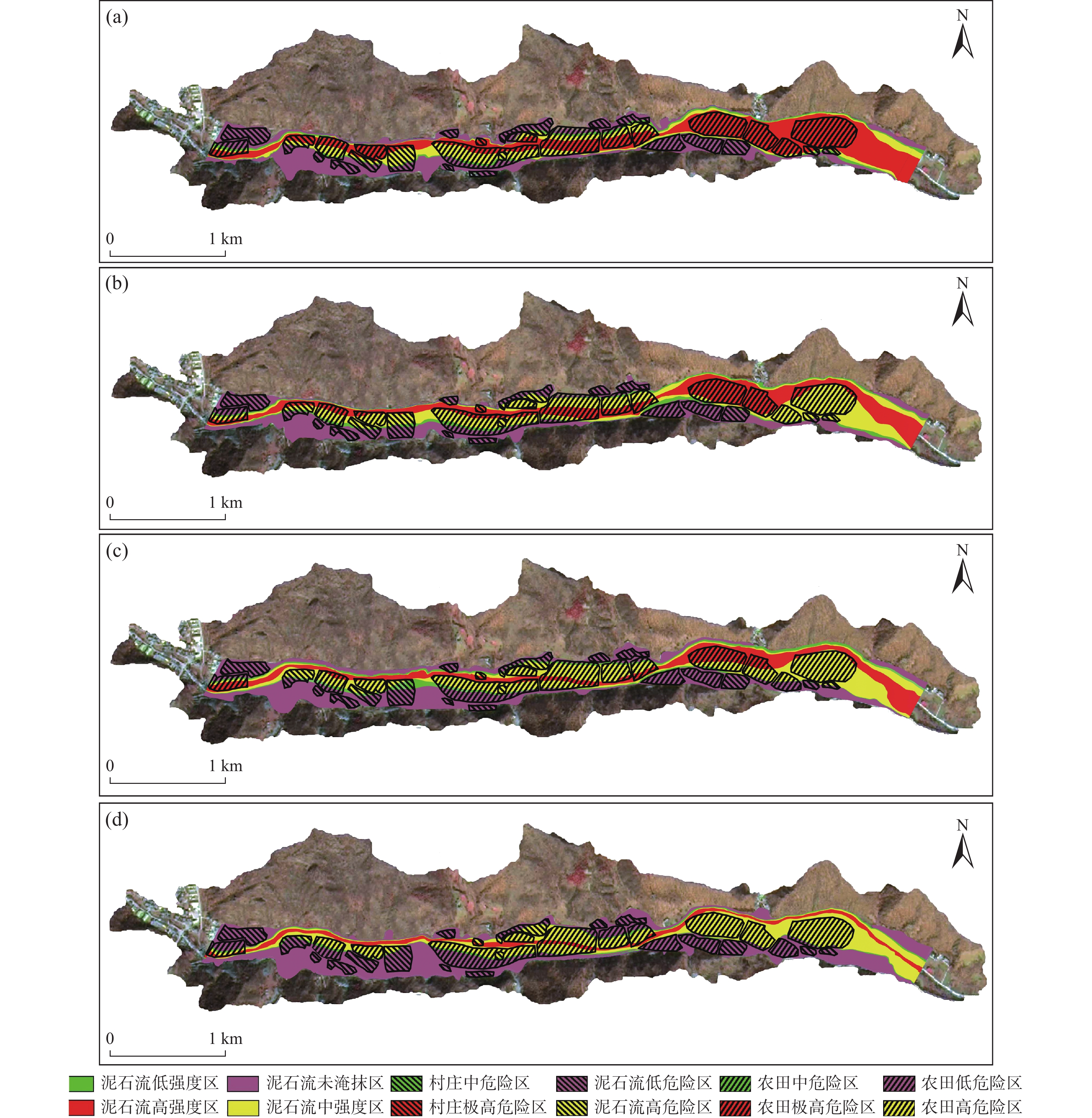
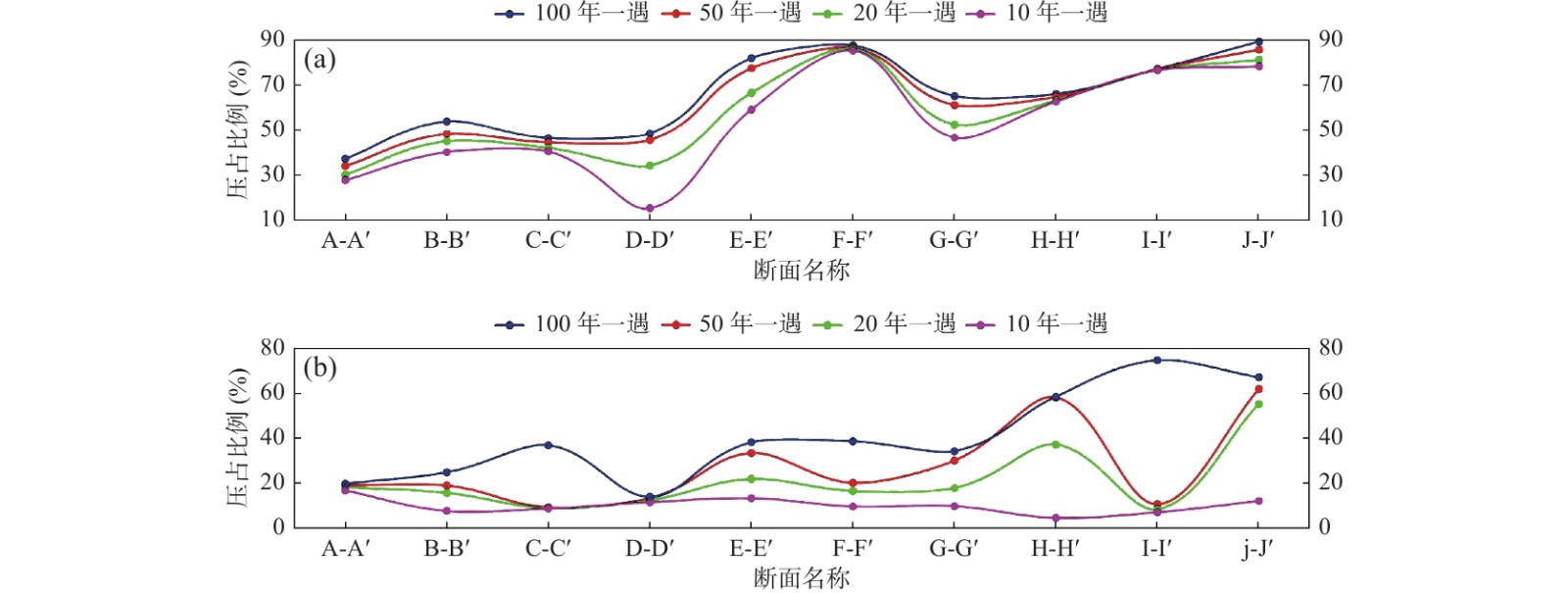
为解决“沟谷型”泥石流在不规则断面处特征参数的精细求解问题,笔者以曼宁公式为基础,建立“等代”面积递归逼近的数学模型,实现了最深泥位、流体速度、威胁范围的求解计算,其结果比较符合实际。利用该模型在豫西某泥石流受威胁对象段任取10个断面进行研究分析:①计算出10年一遇、20年一遇、50年一遇、100年一遇等降水概率工况下最深泥位、流速、行洪断面大小,研究其随雨强大小的演变规律。②定量分析了各断面泄洪能力强弱。③结合泥石流强度判定标准对所选区域进行危险度分区,划分了极高危险区、高危险区、中危险区、低危险区。该模型不仅可以为预测泥石流各项指标提供基本参数,而且可为灾害防治提供科学依据。研究成果对泥石流的精细化防治方面具有重要支撑作用。
Abstract:In order to solve the problem of key parameters in predicting "valley-type" debris flow at irregular profiles, based on Manning's formula, this paper establishes an approaching mathematical model of "equivalent area substitution method", which completed calculation for the deepest mud level, the flow rate and the threat range. The result is close to reality. This paper select 10 profiles randomly in the affected area by debris flow in western Henan, by this model: ① the deepest mud level was calculated, the flow velocity, and the area size of the cross-flood profiles under the probability of rainfall once in 10 years, and in 20 years, 50 years, in 100 years. ② Moreover, this paper has done some research for the law of evolution with different rain intensity, and quantitatively analyzed the flood discharge capacity of each profile. ③ Combined with the judgment standard of debris flow intensity, the selected areas were classified into extermely high-risk areas, high-risk areas, medium-risk areas, and low-risk areas. Furthermore, the model can not only provide basic parameters for predicting various indicators of debris flow, but also provide scientific basis for preventing and controlling disaster of debris flow. Finally, the results of this research have a certain significance in the refined prevention and control of debris flow.
-

-
表 1 AA`断面测量数据表
Table 1. The table of measurement data for AA` profiles
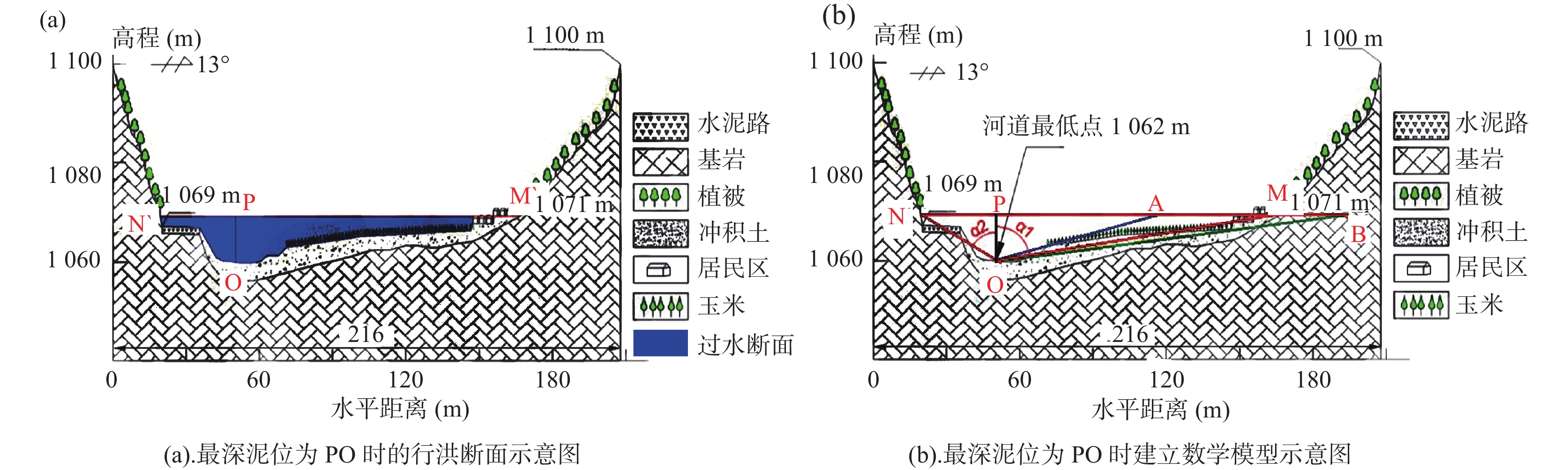
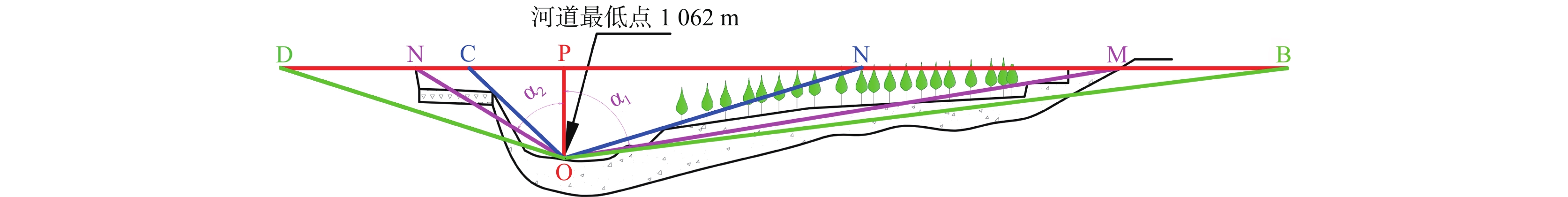
点号 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 X 3770586 3770593 3770601 3770608 3770629 3770635 3770638 3770669 3770715 3770735 Y 533751 533752 533754 533755 533758 533759 533759 533765 533772 533776 H 1069 1069 1068 1062 1063 1063 1064 1067 1068 1071 表 2 不同雨强条件下各断面的泥位、流速计算表
Table 2. Calculation table for mud level and flow velocity of each profiles under various rain conditions
降水概率 断面名称 A-A` B-B` C-C` D-D` E-E` F-F` G-G` H-H` I-I` J-J` 100年一遇 最深泥位(m) 3.95 6.03 6.11 8.48 6.45 4.45 7.05 4.97 5.28 5.38 流速(m/s) 1.68 1.39 1.54 1.37 1.37 1.44 1.34 1.48 1.42 1.46 断面面积(m2) 189 224 229 195 246 249 287 395 460 481 50年一遇 最深泥位(m) 3.62 5.54 5.61 8.06 6.17 4.57 6.72 4.56 4.56 4.94 流速(m/s) 1.35 1.30 1.41 1.20 1.25 1.26 1.30 1.37 1.21 1.38 断面面积(m2) 117 190 194 160 218 284 236 333 402 406 20年一遇 最深泥位(m) 3.23 5.25 4.99 7.51 5.51 3.99 5.98 4.06 4.06 4.39 流速(m/s) 1.30 1.25 1.23 1.20 1.20 1.10 1.18 1.25 1.05 1.26 断面面积(m2) 93 145 153 124 159 228 188 264 319 320 10年一遇 最深泥位(m) 2.97 4.83 4.60 6.91 5.07 3.67 5.50 3.74 3.74 4.04 流速(m/s) 1.26 1.18 1.11 1.76 1.13 0.99 1.10 1.15 0.93 1.18 断面面积(m2) 78 123 130 105 135 193 159 224 271 271 表 3 泥石流强度判定准则
Table 3. Judgment criteria for debris flow intensity
泥石流强度 泥深H(m) 关系 泥深H与最大流速V的乘积(m2/s) 高 H≥2.5 或 V*H≥2.5 中 0.5<H≤2.5 且 0.5<V*H≤2.5 低 0<H≤0.5 且 0<V*H≤0.5 表 4 模型递归的最终角度以及面积误差表
Table 4. Final angle and area error table for model iterations
断面名称 A-A` B-B` C-C` D-D` E-E` F-F` G-G` H-H` I-I` J-J` 100年一遇 α1(°) 86.57 84.97 37 53 83 83 70.88 88.14 88.24 87.7 α2(°) 47.96 45.23 85.05 74.44 74 87 85.51 51 27 83.17 CAD测量实际面积(m2) 175 214 237 202 244 278 279 380 501 468 模型求解的理论面积(m2) 189 224 229 195 246 249 287 395 460 481 面积误差(%) 6 4.7 3.5 3.5 6.1 2.1 3 4.1 8 3 断面名称 A-A` B-B` C-C` D-D` E-E` F-F` G-G` H-H` I-I` J-J` 50年一遇 α1(°) 86.57 84.97 37 53 82 83 67 88.14 88.5 87.7 α2(°) 47.96 45.23 85.05 74.44 74 87 83 51 27 83.17 CAD测量实际面积(m2) 116 175 199 157 202 265 251 332 392 409 模型求解的理论面积(m2) 117 190 194 160 218 284 236 333 402 406 面积误差(%) 0.90 8.42 2.61 2.00 8.02 7.30 5.66 0.22 2.64 0.77 断面名称 A-A` B-B` C-C` D-D` E-E` F-F` G-G` H-H` I-I` J-J` 20年一遇 α1(°) 86.57 84 37 53 82 84 67 88.14 88.5 87.7 α2(°) 47.96 45.23 85.05 72 73.53 87 83 51 27 83.17 CAD测量实际面积(m2) 96 154 153 119 162 215 184 282 312 338 模型求解的理论面积(m2) 93 145 153 124 159 228 188 264 319 320 面积误差(%) 3.52 5.60 0.28 4.21 1.98 5.66 2.04 6.39 2.13 5.10 断面名称 A-A` B-B` C-C` D-D` E-E` F-F` G-G` H-H` I-I` J-J` 10年一遇 α1(°) 86.57 84 37 53 82 84 67 88.14 88.5 87.7 α2(°) 47.96 45.23 85.05 72 73.53 87 83 51 27 83.17 CAD测量实际面积(m2) 85 125 125 99 130 179 146 246 262 294 模型求解的理论面积(m2) 78 123 130 105 135 193 159 224 271 271 面积误差(%) 7.22 2.07 4.03 6.16 3.78 7.40 8.71 9.04 3.48 7.86 -
[1] 柴春岭, 陈守煜. 模糊优选神经网络模型在泥石流平均流速预测中应用研究[J]. 大连理工大学学报, 2008, 48 ((6): 887-891
CHAI Chunling, CHEN Shouyu. Research on application of fuzzy optimization neural network model to debris flow average velocity forecasting[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2008, 48 ((6): 887-891.
[2] 常士骠, 张苏民. 工程地质手册(第五版)[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018,691
CHANG Shibiao, ZHANG Sumin. Geological Engineering Handbook(The fifth Edition)[M]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2018,691.
[3] 丛凯, 李瑞冬, 毕远宏. 基于FLO-2D模型的泥石流治理工程效益评价[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(3): 209-216
CONG Kai, LI Ruidong, BI Yuanhong. Benefit Evaluation of Debris Flow Control Engineering Based on the FLO-2D Model[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(3): 209-216.
[4] 杜榕桓, 李鸿琏, 唐邦兴, 等. 三十年来的中国泥石流研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 1995(01): 64-73
DU Ronghuan, LI Honglian, TANG Bangxing, et al. Research on debris flow for thirty years in China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 1995(01): 64-73.
[5] 高东光. 桥涵水文[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2005: 76-87
GAO Dongguang. Hydrology and Hydraulics for Bridge Engineering[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2005: 76-87.
[6] 韩征, 徐林荣, 苏志满, 等. 基于流域形态完整系数的泥石流容重计算方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2012, 39(2): 100-105
HAN Zheng, XU Linrong, SU Zhiman, et al. Research on the method for calculating the bulk density of debris flow based on the integrity coefficient of watershed morphology[J]. Hydrogeology&Engineering Geology, 2012, 39(2): 100-105.
[7] 黄崇福. 自然灾害基本定义的探讨[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2009, 18(5): 41-50 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2009.05.007
HUANG Chongfu. A discussion on basic definition of natural disaster[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2009, 18(5): 41-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2009.05.007
[8] 康志成, 李焯芬, 马蔼乃, 等. 中国泥石流研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004
KANG Zhicheng, LI Chuofen, MA Ainai, et al. Research on debris flow in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004.
[9] 刘波, 胡卸文, 何坤, 等. 西藏洛隆县巴曲冰湖溃决型泥石流演进过程模拟研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2021, 48(5): 150-160
LIU Bo, HU Xiewen, HE Kun, et al. Characteristics and evolution process simulation of the Baqu gully debris flow triggered by ice-lake outburst in Luolong County of Tibet, China[J]. Hydrogeology&Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 150-160.
[10] 刘星宇, 刘向东, 赵浩, 等. 豫西某金矿矿渣转化为泥石流物源的危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(5): 29-39
LIU Xingyu, LIU Xiangdong, ZHAO Hao, et al. Risk assessment of source of debris flow from a gold slag heap in western Henan[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(5): 29-39.
[11] 倪化勇, 唐川. 中国泥石流起动物理模拟试验研究进展[J]. 水科学进展, 2014, 25(4): 606-613
NI Huayong, TANG Chuan. Advances in the physical simulation experimeng on debris flow initiation in China[J]. Advance in Water Science, 2014, 25(4): 606-613.
[12] 唐亚明, 武立, 冯凡, 等. 泥石流风险减缓措施及经济决策—以山西吉县城北沟为例[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(4): 227-238
TANG Yaming, WU Li, FENG Fan, et al. Risk Mitigation Measures and Economic Decisions on Debris Flow -Taking Beigou of Jixian County, Shanxi Province as an Example[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(4): 227-238.
[13] 唐川, 周钜乾, 朱静等. 泥石流堆积扇危险度分区评价的数值模拟研究[J]. 灾害学, 1994(04): 7-13
TANG Chuan, ZHOU Juqian, ZHU Jing, et al. A Study on the risk zoning debris flow on alluvial fans by applying technology of numerical simulation[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 1994(4): 7-13.
[14] 王喜安, 陈剑刚, 陈华勇, 等. 考虑浆体黏度的泥石流流速计算方法[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2020, 37(4): 56-61
WANG Xi`an, CHEN Jiangang, CHEN Huayong, et al. Calculation of Debris Flow Velocity in Consideration of Viscosity of Slurry[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2020, 37(4): 56-61.
[15] 韦方强, 胡凯衡. 泥石流流速研究现状与发展方向[J]. 山地学报, 2009, 27(5): 545-550 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2009.05.005
WEI Fangqiang,HU Kaiheng, Review and Trends on Debris Flow Velocity Research[J]. Jounal of Mountain Science, 2009, 27(5): 545-550. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2009.05.005
[16] 徐黎明, 王清, 陈剑平, 等. 基于BP神经网络的泥石流平均流速预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013, 43(1): 186-191
XU Liming, WANG Qing, CHEN Jianping, et al. Forcast for Average Velocity of Debris Flow Based on BP Neural Network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2013, 43(1): 186-191.
[17] 徐士彬, 钱德玲, 姚兰飞, 等. 基于结构两相流模型计算泥石流对路基的冲击力[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 41(3): 373-376+394
XU Shibin, QIAN Deling, YAO Lanfei, et al. Calculation of impact force of debris flow on subgrade based on the model of conceptual two phase flow[J]. Journal of HeFei University of technology( natural science edition), 2018, 41(3): 373-376+394.
[18] 杨晓宇. 合作市砂子沟泥石流形成条件及危险度评价[J]. 河北地质大学学报, 2018, 41(3): 37-42
YANG Xiaoyu. Forming Conditions and Risk Assessment on Debris Flow of Shazigou in the Hezuo City[J]. Journal of Hebei GEO University, 2018, 41(3): 37-42.
[19] 于国强, 张茂省, 王根龙, 等. 支持向量机和BP神经网络在泥石流平均流速预测模型中的比较与应用[J]. 水利学报, 2012, 43(S2): 105-110 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9350.2012.z2.019
YU Guoqiang, ZHANG Maosheng, WANG Genglong, et al. Application and comparison of prediction models of support vector machines and back-propagation artificial neural network for debris flow average velocity[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2012, 43(S2): 105-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9350.2012.z2.019
[20] 朱立峰, 赵成, 于国强等. 三眼峪特大泥石流堆积特征[J]. 西北地质, 2011, 44(3): 30-37
ZHU Lifeng, ZHAO Cheng, YU Guoqiang, et al. Accumulation Characteristics of Sanyanyu Extremely Big Debris Flow[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2011, 44(3): 30-37.
[21] 张罗号, 张红武, 张锦方, 等. 泥石流流速计算与模型设计方法[J]. 人民黄河, 2015, 37(4): 18-24
ZHANG Luohao, ZHANG Hongwu, ZHANG Jingfang, et al. Calculation Method of Debris Flow Velocity and Debris Flow Model Design[J]. Yellow River, 2015, 37(4): 18-24.
[22] 中国科学院水利部成都山地灾害与环境研究所. 中国泥石流[M]. 北京: 商务印书馆, 2000
Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, CAS. China debris flow[M]. Beijing: The Commercial Press, 2000.
[23] ASCH, TH. W. J. VAN, TANG, C. , ALKEMA, D. , et al. An integrated model to assess critical rainfall thresholds for run-out distances of debris flows. [J]. Natural Hazards, 2014, 70(1): 299-311. doi: 10.1007/s11069-013-0810-z
[24] Iverson, Richard M. The physics of debris flows[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1997, 35(3): 245-296. doi: 10.1029/97RG00426
-



 下载:
下载: