Migration and Enrichment of Heavy Metals During the Weathering Pedogenesis of Rocks in the Ningzhen Ore Cluster Area
-
摘要:
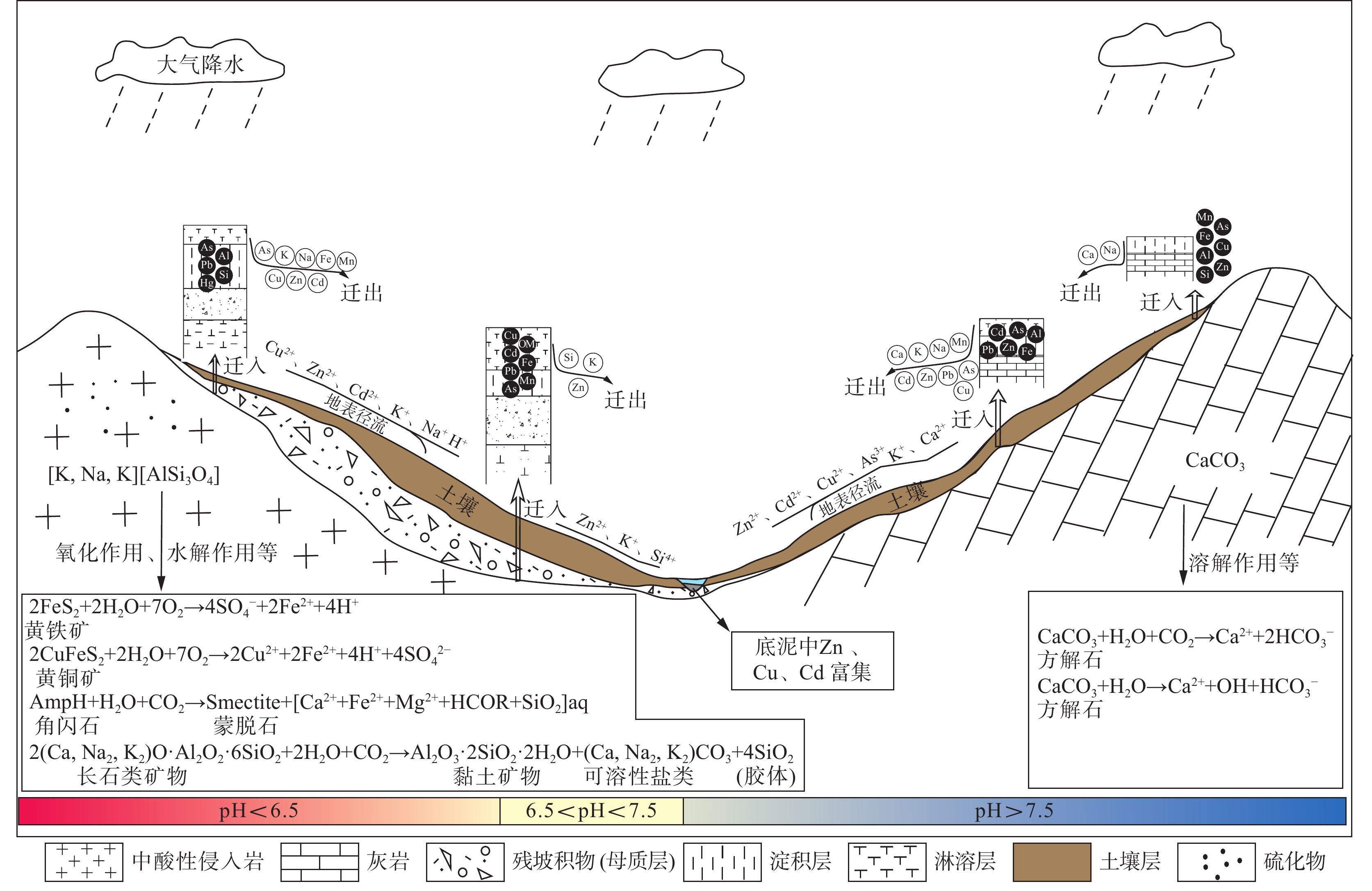
岩石的风化成土作用造成重金属富集并导致土壤超标是一类特殊的地质成因土壤重金属污染现象,也被称为地质高背景问题,近年来受到学术界的高度关注。为弄清岩石风化成土过程中的重金属的物质来源、释放迁移和富集规律,本研究以宁镇矿集区代表性碳酸盐岩、岩浆岩和碎屑岩风化成土剖面为对象,通过野外调查、岩矿鉴定、相关性分析、上陆壳标准化蛛网图解、化学蚀变指数和质量平衡系数计算等方法,系统研究了重金属在岩石风化成土过程中迁移富集规律。结果表明:各剖面土壤与其下伏母岩具有物源继承关系;在同一气候条件下,重金属在风化剖面中的迁移规律受岩石岩性、剖面化学风化程度和重金属元素在岩石中赋存状态等多因素控制;岩浆岩和碎屑岩剖面土壤重金属表现出继承母岩化学成分组成和含量特征,重金属迁移能力与化学风化程度呈正比。而碳酸盐岩剖面重金属迁移能力与化学风化程度呈反比,导致碳酸盐岩剖面重金属呈现出(岩石)低背景、(土壤)高富集的地球化学特征,其中Cd、As的含量甚至超农用地土壤污染风险管制值,需要加以重视。在上述研究基础上,建立了重金属在岩石风化成土过程中的释放迁移模式。
Abstract:Weathering pedogenesis of rocks can release heavy metals to soil, and further accumulation of heavy metals in soil may exceed the national standard for safety soils. To understand the source, release, transport, and enrichment of heavy metals in the process of weathering pedogenesis, we systematically studied the migration and enrichment of heavy metals during rock weathering in the representative weathering pedogenesis profiles (carbonate rock, magmatic rock, and clastic rock) of the Ningzhen ore cluster area using a combination of field survey, rock and mineral identification, geochemical analysis and statistical analysis. The results showed that the soil of each profile has a provenance inheritance relationship with its underlying parent rock. The heavy metals in the soil of magmatic rock and clastic rock profiles showed similar chemical composition and content characteristics to the inherited parent rock. In contrast, the carbonate rock profile showed the geochemical characteristics of a low content of heavy metals in rocks and a high content in soil. In particular, the contents of Cd and As even exceeded the risk intervention values for soil contamination of agricultural land. It was revealed that the migration of heavy metals in weathering profiles of rocks under the same climatic conditions is controlled by multiple factors, such as rock lithology, the degree of chemical weathering of the profiles, and the occurrence state of heavy metals in rocks. The migration ability of heavy metals in magmatic rock and clastic rock profiles is proportional to the degree of chemical weathering, while the migration ability of heavy metals in carbonate rock profiles is inversely proportional to the degree of chemical weathering, leading to a higher potential for enrichment of heavy metals. Based on the above research, the release and migration pattern of heavy metals in the processes of rock weathering and soil formation was established.
-
Key words:
- soil heavy metals /
- the chemical weathering /
- enrichment /
- mining areas /
- Ningzhen
-

-
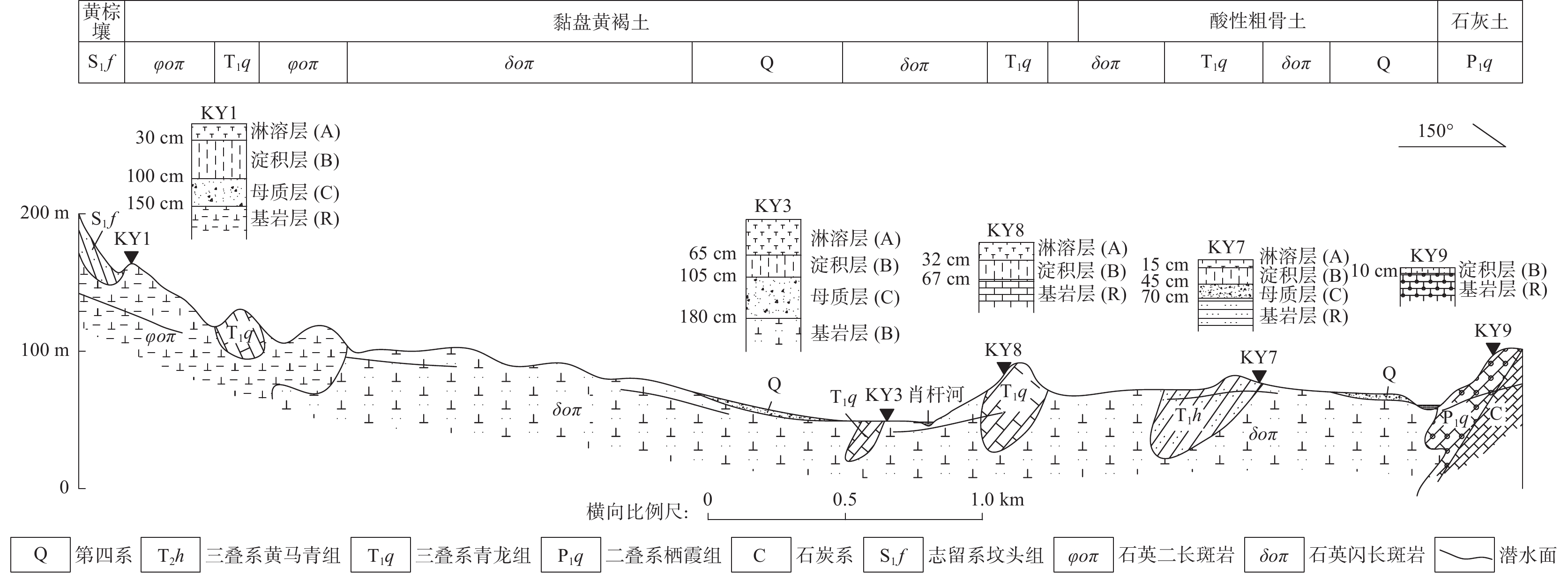
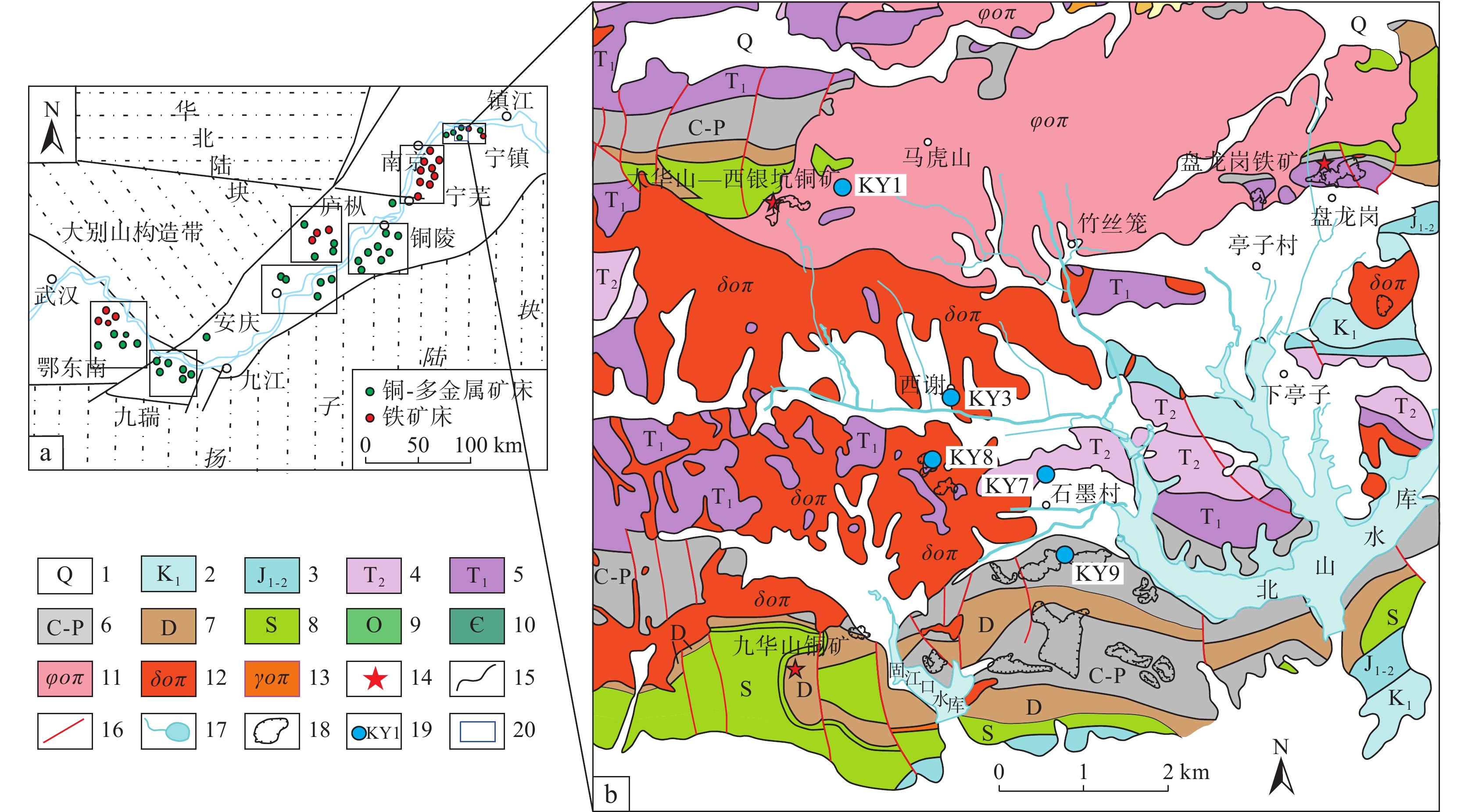
图 1 长江中下游成矿带矿集区分布图(a)(据张明超等, 2018)及研究区地质简图和采样位置分布(b)
Figure 1.
表 1 宁镇矿集区岩石−土壤剖面特征
Table 1. Characters of the rock-soil profiles in Ningzhen ore cluster area
剖面 基岩 岩石特征 剖面特征 海拔(m) 坡度(°) 土地利用方式 KY1 石英二长斑岩 斑状结构,块状构造。斑晶为斜长石(25%)、钾长石(20%),次为黑云母(10%)及少量角闪石和石英,含黄铁矿和黄铜矿等硫化物 剖面厚度(指岩-土界面以上部分,下同)150 cm,其中土壤层厚100 cm,呈黄棕色黏土状,下伏50 cm厚的粉状岩母质层,向下逐渐过渡到弱风化-新鲜母岩 145 5~10 林地 KY3 石英闪长斑岩 斑状结构,块状构造。斑晶为斜长石(35%)、黑云母(3%)以及少量石英和角闪石 剖面厚度约180 cm,土壤层厚105 cm,风化壳成棕色黏土状,下伏75 cm厚的砂糖状母质层,向下逐渐过渡到弱风化-新鲜母岩 66 8 林地 KY7 中三叠统黄马青组
长石石英砂岩细粒结构。主要矿物成分为石英(70%)、长石(20%)及少量灰岩、泥岩碎屑和云母碎片 剖面厚度70 cm,其中土壤层厚45 cm,下伏25 cm厚的砂糖状母质层,向下逐渐过渡到弱风化母岩 83 3~5 林地 KY8 中三叠统青龙组灰岩
(简称“青龙灰岩”)细晶结构。矿物主要为方解石(98%)和少量黏土、石英等,见铁质分布于方解石上及晶粒间 岩-土界面清晰,剖面发育较薄(67 cm),其呈红棕色黏土状,缺失C层,土壤体(A+B层)直接与下伏基岩接触 90 5 林地 KY9 下二叠统栖霞组含生物碎屑灰岩(简称“栖霞灰岩”) 微晶-细晶结构。矿物为方解石(80%)和生物碎屑(12%)。生物碎屑由纤维状方解石、泥晶方解石组成。矿物间充填铁质、泥质 岩-土界面清晰,剖面发育极薄(10 cm),土层呈红棕色黏土状,顶部有机质层和腐殖质层已被侵蚀,缺A层和残存部分B层,C层不发育,下伏基岩 97 2 林地 表 2 岩石风化剖面主量元素(%)、惰性元素(m/kg)含量及CIA值
Table 2. Concentrations of major (%), immobile (mg/kg) elements and CIA values in rock weathering profles
剖面
(母岩)KY1
(石英二长斑岩)KY3
(石英闪长斑岩)KY8
(青龙灰岩)KY9
(栖霞灰岩)(KY7)
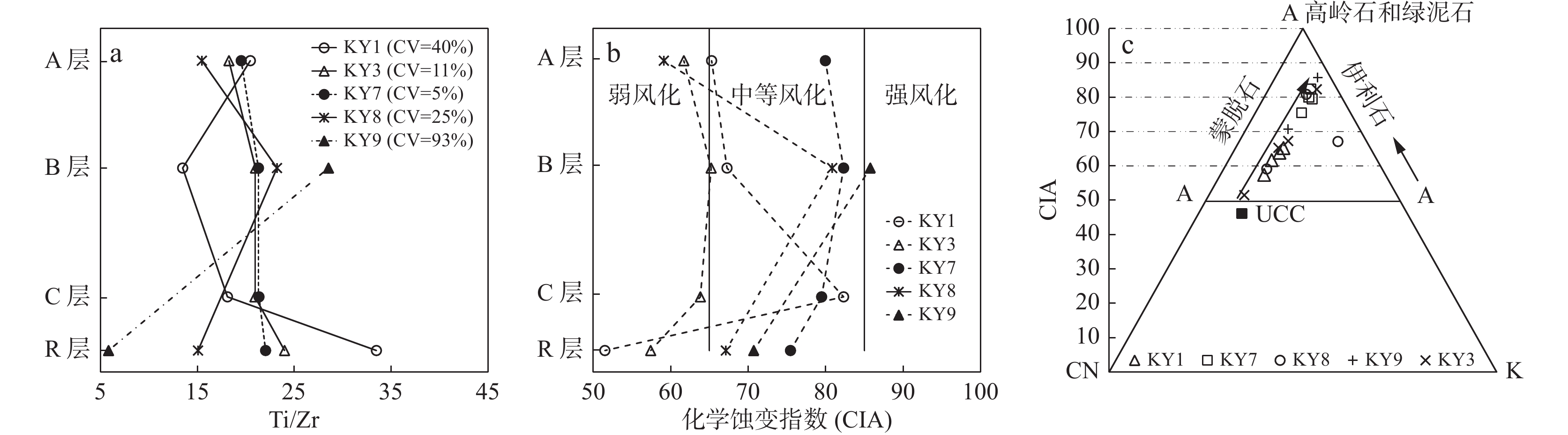
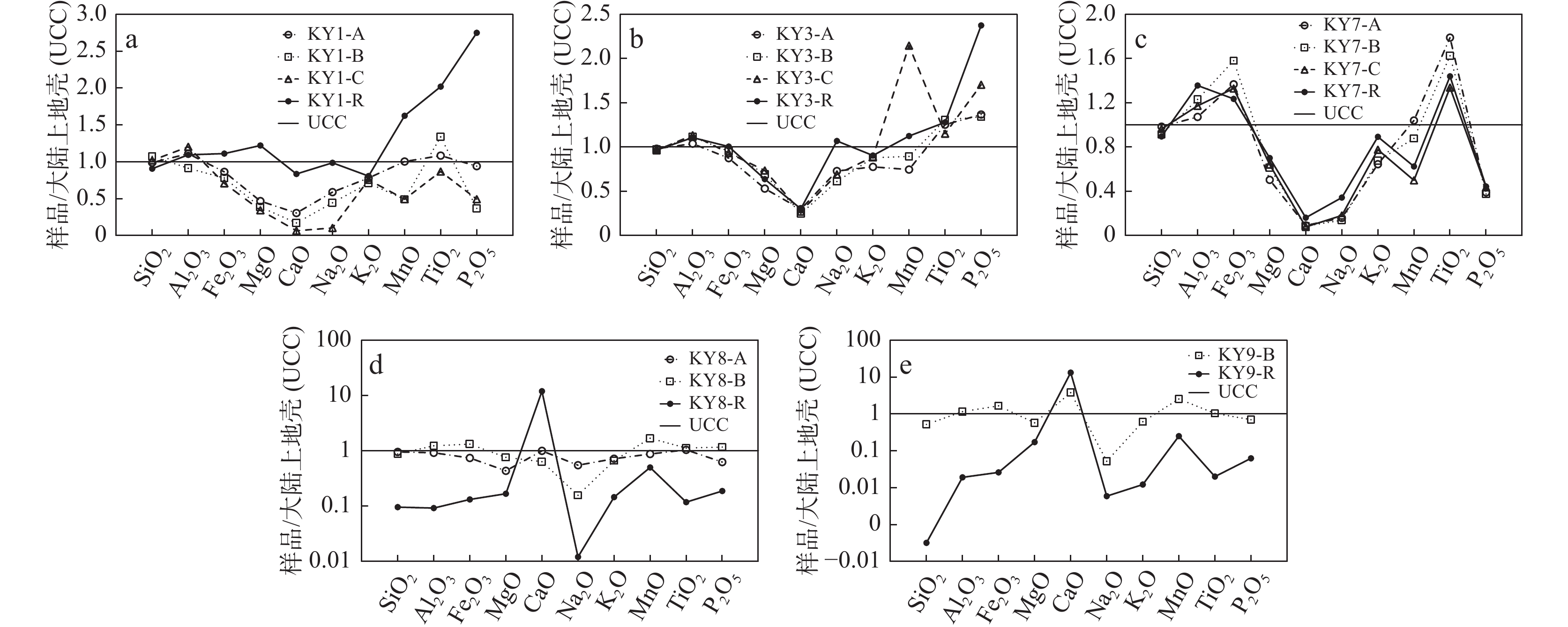
长石石英砂岩UCC 发生层 A层 B层 C层 R层 A层 B层 C层 R层 A层 B层 R层 B层 R层 A层 B层 C层 R层 SiO2 65.21 70.82 67.22 59.79 64.70 64.22 63.51 63.73 62.85 57.87 6.32 34.18 0.02 64.89 60.28 63.53 59.05 66* Al2O3 16.87 13.87 18.29 16.64 15.78 16.93 17.23 16.82 13.99 18.72 1.40 17.55 0.29 16.29 18.70 17.82 20.61 15.2* Fe2O3 2.71 2.97 3.10 5.04 1.49 3.49 4.11 4.81 0.91 5.36 0.44 7.11 0.03 5.64 6.70 6.10 6.00 5* FeO 1.61 0.94 0.44 0.52 2.89 1.28 0.56 0.22 2.80 1.25 0.22 1.17 0.10 1.20 1.20 0.55 0.18 MgO 1.03 0.86 0.76 2.70 1.17 1.53 1.63 1.41 0.96 1.68 0.37 1.27 0.38 1.11 1.36 1.42 1.55 2.2* CaO 1.29 0.72 0.28 3.51 1.25 1.04 1.14 1.27 4.19 2.67 50.23 15.87 55.44 0.39 0.36 0.33 0.68 4.2* Na2O 2.30 1.73 0.40 3.85 2.85 2.38 2.70 4.17 2.14 0.61 0.05 0.20 0.02 0.62 0.54 0.71 1.34 3.9* K2O 2.63 2.39 2.55 2.72 2.62 2.97 3.00 3.05 2.42 2.23 0.49 2.07 0.04 2.17 2.28 2.62 3.01 3.4* MnO 0.08 0.04 0.04 0.13 0.06 0.07 0.17 0.09 0.07 0.14 0.04 0.20 0.02 0.08 0.07 0.04 0.05 0.08* TiO2 0.54 0.67 0.43 1.01 0.63 0.65 0.58 0.64 0.52 0.56 0.06 0.52 0.01 0.89 0.81 0.67 0.72 0.5* P2O5 0.15 0.06 0.08 0.44 0.22 0.21 0.27 0.38 0.10 0.19 0.03 0.11 0.01 0.06 0.06 0.07 0.07 0.16* LOI 5.27 4.63 6.11 3.30 6.05 4.92 4.80 3.09 8.74 8.42 40.02 19.44 43.53 6.34 7.33 5.85 6.41 — Zr 159.0 298.0 144.0 181.0 206.0 187.0 165.0 160.0 202.0 145.0 23.50 109.00 10.30 275.0 229.0 188.0 196.0 190* Th 9.89 11.60 9.73 6.05 9.13 7.56 7.02 7.47 9.14 10.40 1.00 10.31 0.48 14.20 12.60 12.60 13.30 10.7* U 2.62 2.80 2.19 1.76 2.25 2.23 1.93 1.79 2.82 4.02 2.69 5.34 2.07 2.75 2.93 3.06 3.19 2.8* CIA 65.26 67.25 82.30 51.49 61.68 65.20 63.81 57.40 59.10 80.83 67.10 85.74 70.70 79.94 82.30 79.46 75.44 40.2 注:*上陆壳元素平均含量(UCC)(Taylor et al., 1985);LOI.烧失量;R.基岩;C.母质层;B.淀积层;A.淋溶层;CIA.化学蚀变指数,CIA=Al2O3/[(Al2O3+K2O+Na2O+CaO*)]×100,摩尔比,CaO*采用S.M. Mclennan(1993)方法校正。 表 3 岩石风化剖面重金属(mg/kg)、有机质(%)含量及pH值
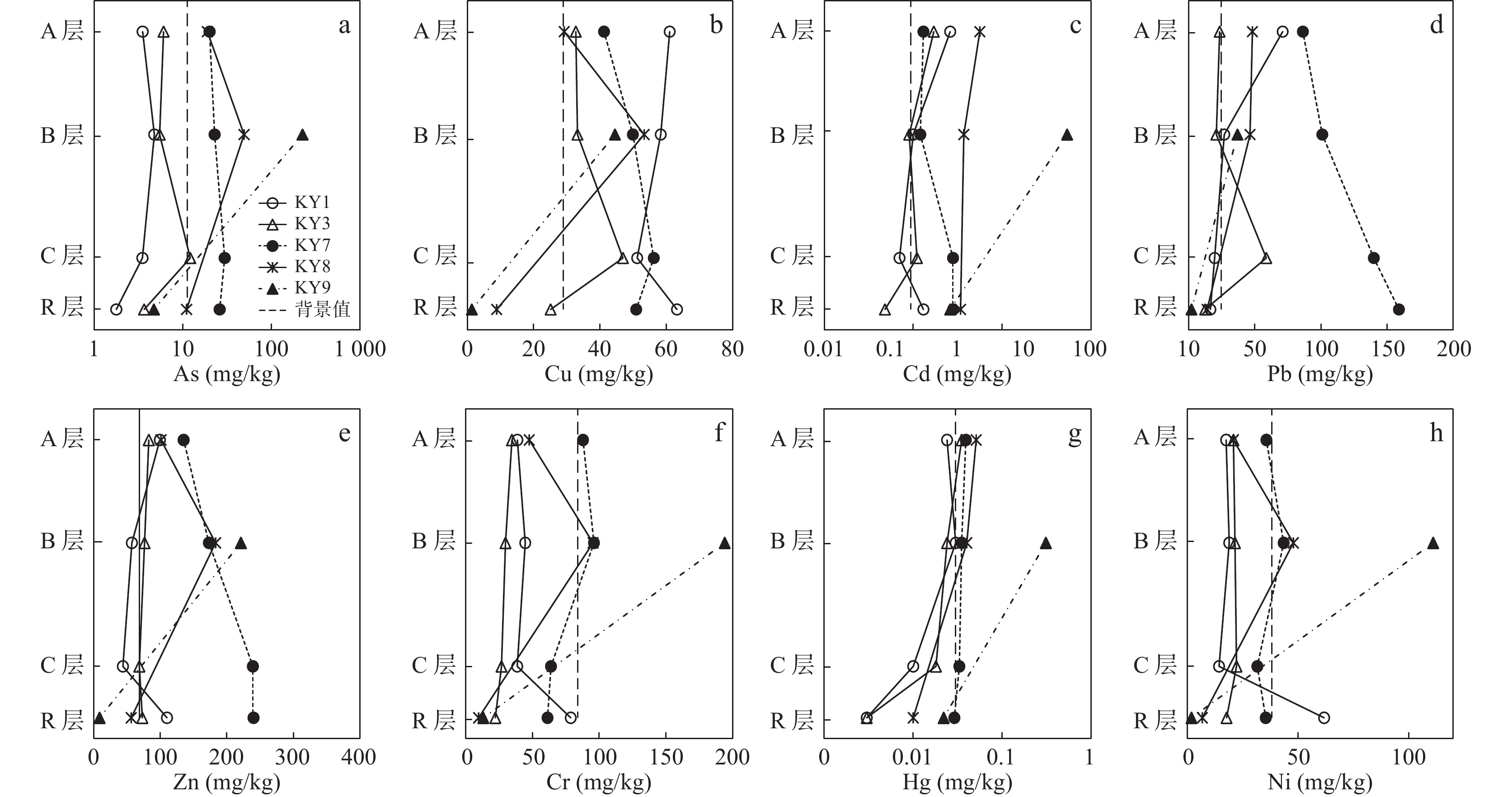
Table 3. Characteristics of average contents of heavy metals in soils from rocks Concentrations of heavy metals (mg/kg), organic matter (%) and pH value in rock weathering profles
母岩 剖面 分层 重金属元素 pH值 有机质 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Zn Ni Pb 石英二长斑岩 KY1 A 3.51 0.26 38.60 61.00 0.024 99.30 17.40 71.00 6.38 1.26 B 4.76 0.10 44.50 58.30 0.03 57.30 18.80 26.80 5.06 0.98 C 3.49 0.07 38.50 51.20 0.01 43.80 14.20 19.50 5.45 0.35 R 1.77 0.13 78.60 63.20 0.003 110.00 61.70 16.30 — — 石英闪长斑岩 KY3 A 6.05 0.17 34.5 32.7 0.035 82.7 20.7 23.3 7.13 2.25 B 5.46 0.09 29.7 33.2 0.024 76.3 21.4 20.8 7.83 0.71 C 12.1 0.11 26.7 46.9 0.018 68.5 22.1 58.6 7.44 0.47 R 3.65 0.05 22.10 25.10 0.003 73.00 17.6 12.30 — — 长石石英砂岩 KY7 A 20.00 0.13 87.80 41.20 0.039 135.00 35.60 86.30 5.58 0.83 B 22.80 0.12 96.00 49.90 0.035 173.00 43.40 101.00 5.53 0.81 C 29.60 0.28 63.8 56.20 0.033 239.00 31.50 140.00 5.66 0.40 R 26.00 0.28 61.2 50.9 0.029 240 35.3 159 — — 细晶灰岩 KY8 A 18.9 0.56 47.5 29.2 0.051 101.00 20.70 48.10 8.09 2.51 B 49.00 0.37 95.3 53.3 0.04 183.00 47.80 46.30 8.15 0.77 R 11 0.34 9.53 8.83 0.01 56.30 6.65 13.80 — — 含生物屑微晶-
细晶灰岩KY9 B 224.00 5.37 194.00 44.50 0.31 221.00 111.00 36.80 8.35 0.89 R 4.70 0.26 13.10 1.35 0.022 8.76 1.74 1.99 — — 宁镇扬丘陵深层(150~200 cm)
土壤背景值(廖启林,2004)11.3 0.094 84 29 0.03 69 38 24.5 — — 农用地土壤风险筛选值
(GB 15618-2018)5.5<pH≤6.5 30 0.4 250 50 0.5 200 70 100 — — 6.5<pH≤7.5 25 0.6 300 100 0.6 250 100 140 — — 表 4 重金属与主量元素含量相关系数(r)
Table 4. The correlation coeficient (r) between heavy metals and major elements content
SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO MgO CaO Na2O K2O MnO OM pH CIA As −0.975** 0.226 0.564 −0.079 0.164 0.960** −0.486 −0.542 0.711** −0.091 0.458 0.512 Cd −0.948** 0.114 0.435 −0.010 0.042 0.983** −0.380 −0.477 0.670* −0.004 0.459 0.397 Cr −0.901** 0.328 0.738** −0.113 0.164 0.814** −0.703* −0.772** 0.596* −0.150 0.256 0.710** Cu 0.108 0.346 0.356 −0.642* −0.055 −0.167 −0.357 −0.126 −0.048 −0.580* −0.531 0.394 Hg −0.949** 0.087 0.456 0.023 0.050 0.978** −0.390 −0.522 0.657* 0.024 0.447 0.403 Zn −0.634* 0.460 0.776** −0.140 0.444 0.446 −0.622* −0.523 0.328 −0.202 0.144 0.633* Ni −0.965** 0.330 0.701* −0.106 0.272 0.886** −0.572 −0.623* 0.709** −0.150 0.400 0.612* Pb 0.039 0.310 0.532 −0.266 0.264 −0.229 −0.325 −0.117 −0.129 −0.269 −0.383 0.325 OM 0.050 −0.659* −0.664* 0.971** −0.329 0.117 0.508 −0.105 −0.153 1 0.342 −0.624* pH −0.564 0.015 −0.100 0.416 0.487 0.583* 0.264 0.08 0.674* 0.342 1 −0.245 CIA −0.481 0.695* 0.839** −0.574 0.104 0.291 −0.963** −0.621* 0.202 −0.624* −0.245 1 注:**. 在 0.01 水平(双侧)上显著相关,*. 在 0.05 水平(双侧)上显著相关。 表 5 剖面土壤重金属元素质量平衡系数
Table 5. The mass-balance calculation of heavy metal elements in profiles
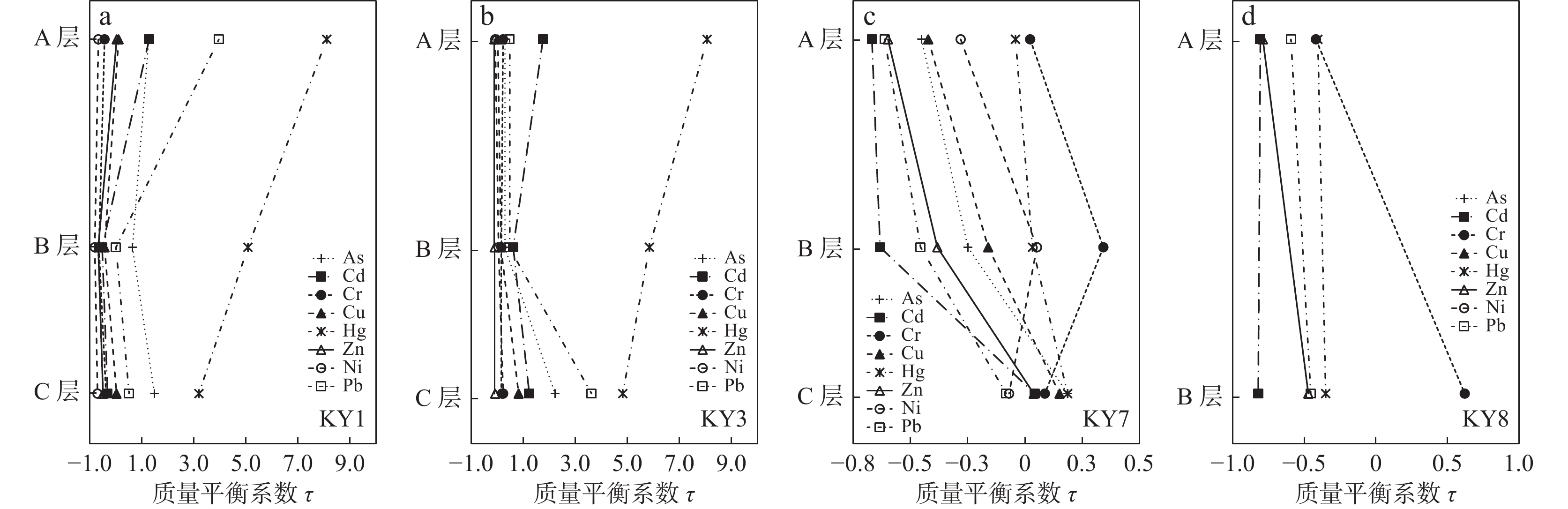
岩石 剖面 τAs τCd τCr τCu τHg τZn τNi τPb 平均值 石英二长斑岩 KY1-A 1.26 1.28 −0.44 0.10 8.11 0.03 −0.68 3.96 1.70 KY1-B 0.63 −0.53 −0.66 −0.44 5.07 −0.68 −0.81 0.00 0.32 KY1-C 1.48 −0.32 −0.38 0.02 3.19 −0.50 −0.71 0.50 0.41 平均值 1.12 0.14 −0.49 −0.11 5.46 −0.39 −0.73 1.49 0.81 石英闪长斑岩 KY3-A 0.29 1.75 0.21 0.01 8.06 −0.12 −0.09 0.47 1.32 KY3-B 0.28 0.60 0.15 0.13 5.84 −0.11 0.04 0.45 0.92 KY3-C 2.21 1.22 0.17 0.81 4.82 −0.09 0.22 3.62 1.62 平均值 0.93 1.19 0.18 0.32 6.24 −0.11 0.06 1.51 1.29 长石石英砂岩 KY7-A −0.45 −0.67 0.02 −0.42 −0.04 −0.60 −0.28 −0.61 −0.38 KY7-B −0.25 −0.63 0.34 −0.16 0.03 −0.38 0.05 −0.46 −0.18 KY7-C 0.19 0.04 0.09 0.15 0.19 0.04 −0.07 −0.08 0.07 平均值 −0.17 −0.42 0.15 −0.14 0.06 −0.31 −0.10 −0.38 −0.17 青龙灰岩 KY8-A −0.80 −0.81 −0.42 −0.62 −0.41 −0.79 −0.64 −0.59 −0.63 KY8-B −0.28 −0.82 0.62 −0.02 −0.35 −0.47 0.16 −0.46 −0.20 平均值 −0.54 −0.82 0.10 −0.32 −0.38 −0.63 −0.24 −0.53 −0.42 栖霞灰岩 KY9-B 3.50 0.95 0.40 2.11 0.33 1.38 5.03 0.75 1.81 -
[1] 陈静生, 洪松, 邓宝山, 等. 中国东部花岗岩、玄武岩及石灰岩上土壤微量元素含量的纬向分异[J]. 土壤与环境, 1999(3): 161-167
CHEN Jingsheng, HONG Song, DENG Baoshan, et al. Geographical tendencies of trace element contents in soils derived from granite, basalt and limestone of Eastern China[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 1999(3): 161-167.
[2] 陈留美, 张甘霖. 滨海沉积物发育的水稻土时间序列母质均一性判定与特性演变[J]. 土壤学报, 2009, 46(5): 753-763 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2009.05.001
CHEN Liumei, ZHANG Ganlin. Parent material uniformity and evolution of soil characteristics of a paddy soil chronosequence derived from marine sediments[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2009, 46(5): 753-763. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2009.05.001
[3] 冯连君, 储雪蕾, 张启锐, 等. 化学蚀变指数(CIA)及其在新元古代碎屑岩中的应用[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(4): 539-544 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.04.019
FENG Lianjun, CHU Xuelei, ZHANG Qirui, et al. CIA (chemical index of alteration)and its applications in the Neoproterozoic clastic rocks[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(4): 539-544. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.04.019
[4] 冯志刚, 刘威, 张兰英, 等. 贫Cd碳酸盐岩发育土壤Cd的富集与超常富集现象——以贵州岩溶区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(4): 533-544 doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.04.002
FENG Zhigang, LIU Wei, ZHANG Lanying, et al. Enrichment and supernormal enrichment phenomenon of Cd in soils developed on Cd-poor carbonate rocks: a case study of karst areas in Guizhou, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(4): 533-544. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.04.002
[5] 冯志刚, 刘炫志, 韩世礼, 等. 碳酸盐岩风化过程中高场强元素的地球化学行为研究: 来自碳酸盐岩淋溶实验的证据[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(3): 315-329 doi: 10.11932/karst20180301
FENG Zhigang, LIU Xuanzhi, HAN Shili, et al. Study on geochemical behavior of high field strength elements during weathering of carbonate rocks: Evidence from leaching experiment on carbonate rock[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(3): 315-329. doi: 10.11932/karst20180301
[6] 高雅, 胡晨, 张春雷, 等. 安徽石台地区富硒土壤分布及硒的富集迁移规律探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(2): 284-291
GAO Ya, HU Chen, ZHANG Chunlei, et al. Study on the distribution of selenium-rich soil and the regularity of selenium enrichment-migration in Shitai area, Anhui, China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(2): 284-291.
[7] 龚慧山, 徐友宁, 陈华清, 等. 某地陈家沟河水中重金属元素时空变化及影响因素研究[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 169−184.
GONG Huishan, XU Youning, CHEN Huaqing, et al. Temporal and Spatial Variation and Influencing Factors of Heavy Metals in the Water of the Chenjiagou River in a Certain Place[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4): 169−184.
[8] 顾会, 赵涛, 高月, 等. 贵州省典型铅锌矿区土壤重金属污染特征及来源解析[J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(4): 506-515
GU Hui, ZHAO Tao, GAO Yue, et al. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in soils of a typical lead-zinc mining area in guizhou province[J]. Earth and Environment, 2022, 50(4): 506-515.
[9] 韩宝华, 胡永浩, 段星星, 等. 西北地区重金属元素累积现状及典型地区成因分析[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3): 318-325
HAN Baohua, HU Yonghao, DUAN Xing xing, et al. Accumulation status of heavy metals in northwest China and analysis of causes in typical areas[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 318-325.
[10] 贾晓丹, 王晖, 徐友宁. 某钼矿集中开采区尾矿库排水重金属环境风险等级及其贡献率分析[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 152−161.
JIA Xiaodan, WANG Hui, XU Youning. Analysis of Heavy Metal Environmental Risk Level and Contribution Rate of Tailings Storerooms of A Molybdenum Mine[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4): 152-161.
[11] 李杰, 战明国, 钟晓宇, 等. 广西典型岩溶地区重金属在土壤-农作物系统中累积特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(2): 597-606 doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0235
LI Jie, ZHAN Mingguo, ZHONG Xiaoyu, et al. Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in soil⁃crop systems from a typical carbonate rocks area in Guangxi[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021.41(2): 597-606. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0235
[12] 李娟. 黄铁矿表生氧化及其微生物相互作用关系研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2015
LI Juan. Supergenic oxidation of pyrite and the study for microbial oxidation mechanism [D].Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2015.
[13] 廖启林, 吴新民, 金洋. 南京—镇江地区多目标地球化学调查初步成果[J]. 物探与化探, 2004(3): 257-260
LIAO Qilin, WU Xin Min, JIN Yang. Preliminary achievements of multi-objective geochemical survey in Nanjing-Zhenjiang area[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2004, 28(3): 257-260.
[14] 刘南. 宁镇中段矽卡岩型铜多金属矿床成矿物质来源及找矿方向[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010
LIU Nan. Ore sources and prospecting direction of skarn-typecopper-polymetallic deposit in the middle of ningzhen mountains [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010.
[15] 刘鹏, 张德会, 吴鸣谦, 等. 浅谈花岗岩浆热液的形成及成矿作用[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(3): 699-719 doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2020.03.012
LIU Peng, ZHANG Dehui, WU Mingqian, et al. Discussion on magma-hydrothermal formation and mineralization of granites[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(3): 699-719. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2020.03.012
[16] 季文兵, 杨忠芳, 尹爱经, 等. 地质高背景地区土壤中铁锰结核形成机理——以广西桂中地区为例[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(8): 2302-2314 doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202108.006
JI Wenbing, YANG Zhongfang, YIN Aijing, et al. Formation mechanisms of iron-manganese nodules in soils from high geological back-ground area of central Guangxi[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(8): 2302-2314. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202108.006
[17] K. H. 马尔夫. 层控矿床河层状矿床(第三卷)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1979
K. H. 马尔夫. 层控矿床河层状矿床(第三卷)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1979. K. H. Wolfed. Hndbook of strt-bound nd strtiform ore deposits(Vol. 3)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1979.
[18] 曲向荣. 土壤环境学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2010
QU Xiangrong. Soil environmental science[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2010.
[19] 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(GB 15618-2018)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018
The Ministry of Ecology and Environment P. R. C. Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land(GB 15618-2018) [S]. Beijing: China Quality and Standards Publishing & Media Co. Ltd, 2018.
[20] 涂光炽, 高振敏, 胡瑞忠, 等. 分散元素地球化学及成矿机制[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004
TU Guangchi, GAO Zhenmin, HU Ruizhong, et al. Disperse element geochemistry and metallogenic mechanism [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004.
[21] 王浩贤. 江苏盱眙和雷琼地区玄武岩地质高背景农田重金属污染研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2019
WANG Haoxian. Study on heavy metals in agricultural land of basaltic area in xuyi county, jiangsu province and leiqiong area, eastern china[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2019.
[22] 王孝, 叶青, 李建武, 等. 新嵊盆地玄武岩发育土壤的母质均一性判定[J]. 土壤通报, 2021, 52(2): 253-260 doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2020060201
WANG Xiao, YE Qing, LI Jianwu, et al. Determination for the uniformity of parent material of basalt-developed soil in the Xinsheng Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2021, 52(2): 253-260. doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2020060201
[23] 王云, 魏复盛. 土壤环境元素化学[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. 1995.
WANG Yun, WEI Fusheng. Soil environmental element chemistry [M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1995.
[24] 肖高强, 向龙洲, 代达龙, 等. 花岗质岩浆岩土壤重金属地球化学特征及生态风险评价——以云南盈江旧城一姐冒地区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5): 1135-1146
XIAO Gaoqiang, XIANG Longzhou, DAI Dalong, et al. Geochemical characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in granitic magmatic soil: A case study of the Jiucheng-Jiemao area in Yingjiang County, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1135-1146.
[25] 徐颖菲, 张耿苗, 张丽君, 等. 亚热带不同母岩成壤过程中金属元素的迁移和积累特点[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(12): 2064-2072 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2019.12.16
XU Yingfei, ZHANG Gengmiao, ZHANG Lijun, et al. Migration and accumulation of metal elements during formation of soils derived from different parent rocks in subtropical zone[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2019, 31(12): 2064-2072. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2019.12.16
[26] Xu Youning, Zhang Jianghua. Ke Hailing, et al. An assessment methodfor heavy metal cumulative risk on farmland soil in the miningarea: A case study of the Xiaoqinling gold mining area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(8): 1097-1105(in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] 徐争启. 攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿区重金属元素地球化学特征[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009
XU Zhengqi. Geochemical Characteristics of heavy metals in different media in Panzhihua V-Ti-Magnetite zone[D].Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2009.
[28] 阎长虹, 许宝田, 吴澄宇, 等. 宁镇地区山前缓坡地层结构及其稳定性分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2019, 27(1): 48-54 doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-007
YAN Changhong, XU Baotian, WU Chengyu, et al. The stratigraphic structure and stability analysis in gentle slopes of piedmontat Ningzhen area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(1): 48-54. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-007
[29] 曾昭华. 长江中下游地区地下水的Ni, Ti, Mo元素的形成及其分布规律[J]. 江西科学, 1998(1): 28-32
ZENG Zhaohua. Formation and distribution of Ni, Ti, Mo elements in groundwater in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Jiangxi Science, 1998 (1): 28-32.
[30] 张立娟. 热带土壤剖面风化成壤过程中的元素地球化学特征[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2011
ZHANG Lijuan. The element geochemistry characteristic of weathering and soil forming processes in tropical soil profiles—take soil profiles developed from basalts in leiqiong area for example[D].Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2011.
[31] 张明超, 陈仁义, 叶天竺, 等. 宁镇矿集区安基山花岗闪长斑岩和韦岗花岗闪长岩的锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(11): 2248-2268
ZHANG Mingchao, CHEN Renyi, YE Tianzhu, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic compositions of the Anjishan granodiorite porphyry and Weigang granodiorite in the Ningzhen ore cluster area and their geological implications. ACTA GEOLOGICA SINICA, 2018, 92(11): 2248-2268.
[32] 张术根, 徐莺, 余旭辉. 宁镇中段岩浆带杂岩体的斜长石矿物学研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2010, 30(3): 15-22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2010.03.002
ZHANG Shugen, XU Ying, YU Xuhui. Research on the mineralogy of plagioclase from the magmatic complex in the middle segment of nanjing-zhenjiang mesozoic magmatic belt[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2010, 30(3): 15-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2010.03.002
[33] 张远根, 周木林, 吴行国. 江苏省句容县土壤志[R]. 句容: 句容县土壤普查办公室, 1987.
[34] 周正. 碎屑岩储层成岩作用影响因素研究[J]. 石化技术, 2020, 27(2): 115+135 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2020.02.072
ZHOU Zheng. Study on the influencing factors of diagenesis of clastic reservoir[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 2020, 27(2): 115+135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2020.02.072
[35] 朱继保, 陈繁荣, 卢龙, 等. 广东凡口Pb-Zn尾矿中重金属的表生地球化学行为及其对矿山环境修复的启示[J]. 环境科学学报, 2005(3): 414-422 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2005.03.025
ZHU Jibao, CHEN Fanrong, LU Long, et al. Heavy metal geochemistry behavior during the oxidation of the Fankou Pb-Zn minetailings in Guangdong province and the implications for environmental remediation of the mines[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2005(3): 414-422. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2005.03.025
[36] Brimhall G H, Dietrich W E. Constitutive mass balance relations between chemical composition, volume, density, porosity, and strain in metasomatic hydrochemical systems: results on weathering and pedogenesis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51: 567-587. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90070-6
[37] Chapman S L, Horn M E. Parent material uniformity and origin of silty soils in northwest Arkansas based on zirconium-titanium contents[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1968, 32: 265−271.
[38] Drees L R, Wilding L P. Elemental distribution in the light isolate of soil separates[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1978, 42: 976-978. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1978.03615995004200060031x
[39] Fralick P W, Kronberg B I. Geochemical discrimination of clastic sedimentary rock sources[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1997, 113: 111-124.31-33. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(97)00049-3
[40] Hao Q Z, Guo Z T, Qiao Y S, et al. Geochemical Evidence for the provenance of middle pleistocene loess depositsin Southern China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29: 3317−3326.
[41] Mahmoodi M, Khormali F, Amini A, et al. Weathering and soils formation on different parent materials in Golestan Province, Noethern Iran[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2016, 13(5). : 870-881. doi: 10.1007/s11629-015-3567-x
[42] McLennan S M. Weathering and global denudation[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1993. 101: 295−303.
[43] Morse J W, Arvidson R S. The dissolution kinetics of major sedimentary carbonate minerals[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2002, 58: 51−84.
[44] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(7): 1523-1534. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90408-3
[45] Sheoran A S, Sheoran V.Heavy metal removal mechanism of acid mine drainage in wetlands:A critical review[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2006,19: 105-116.
[46] Taylor S R , McLeman S M. The continental crust: its composition and evolutio [M]. London: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1985.
-



 下载:
下载: