Formation Mechanism of Acid Water and Treatment Method in Pyrite Mine: Example from Wuliba Pyrite Mine in Xixiang, Southern Shaanxi
-
摘要:
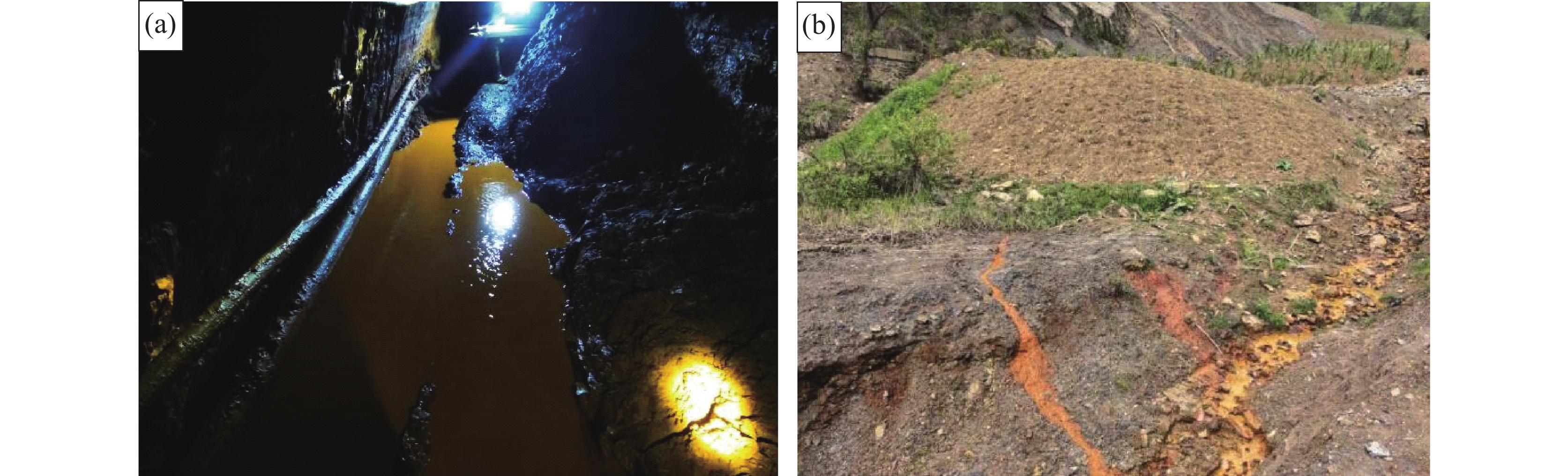
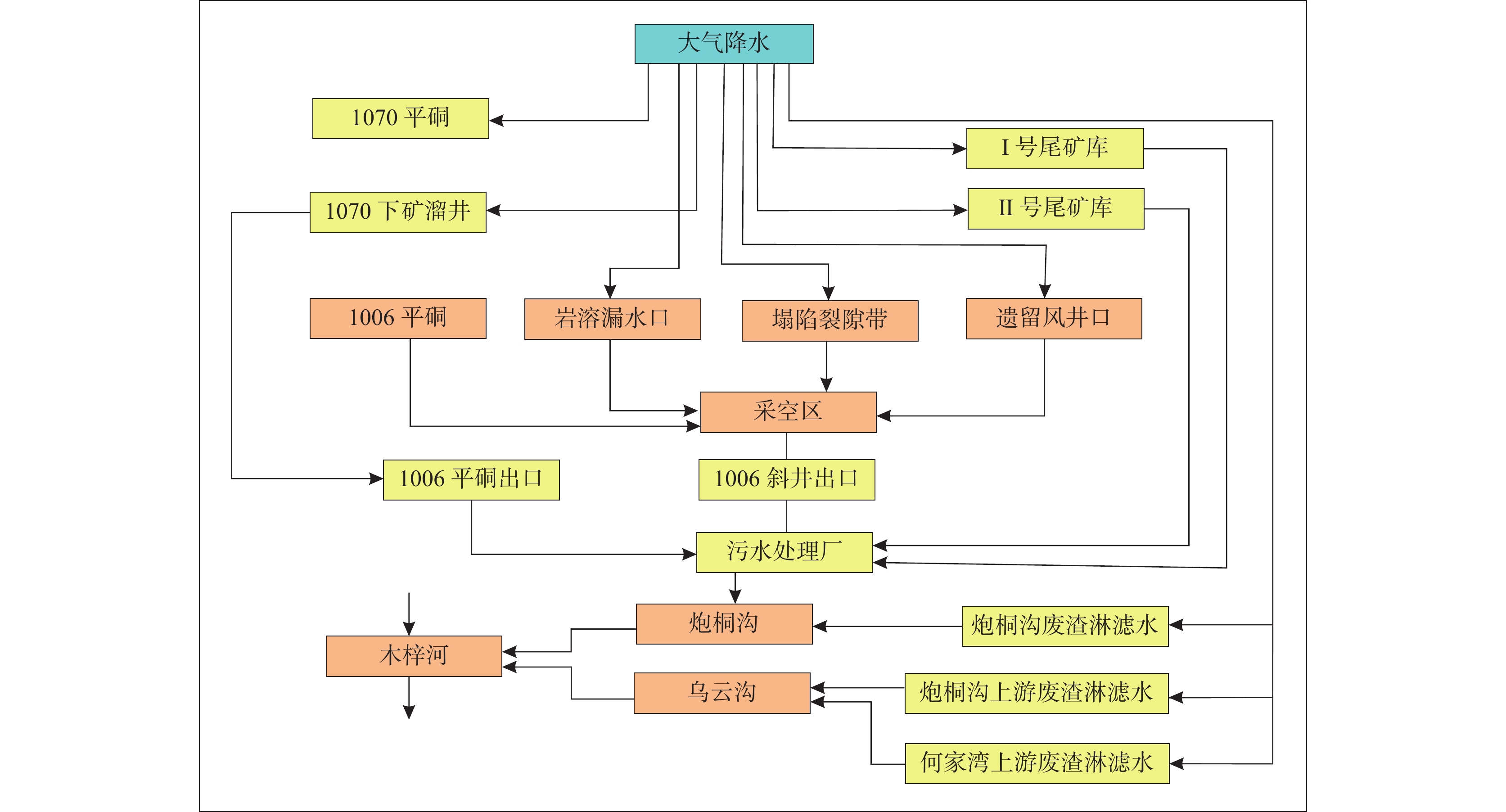
硫铁矿矿山在开采过程中往往产生含有金属硫酸盐类的酸性矿排水,不仅腐蚀管道和设备,危害工人身体健康,还会严重污染水系,影响工农业和渔业生产,因而,系统解决硫铁矿矿山环境问题是矿山环保工作亟待解决的课题之一。系统分析矿山环境问题,深入认识酸性水形成机理,因地制宜提出其中一个或多个方法生态修复治理方案,是硫铁矿酸性矿排水生态修复的有效途径。笔者以陕南西乡五里坝硫铁矿为例,在分析矿硐、废渣、地表水及地面塌陷等环境现状和生态环境问题的基础上,重点分析酸性水产生的根源,提出了“地表水治理+地下水治理+地质灾害治理+生态修复+末端治理+环境监测”综合治理技术,最后探究了矿硐改性充填、弃渣资源化利用和塌陷区注浆加固3种治理模式,以期为类似地区矿山生态修复治理提供科学参考。
Abstract:Sulphate acid water is often produced in the mining process of pyrite mines, which not only corrodes pipelines and equipment, endangers workers’ health, but also seriously pollutes water system, affects industry, agriculture and fishery production. Therefore, it is one of the urgent tasks to solve the environmental problems of pyrite mines. Systematic analysis of mine environmental problems, in-depth understanding of the formation mechanism of acid water, and proposed one or more methods of ecological restoration and treatment programs according to local conditions are effective ways for ecological restoration of acid water in pyrite mines. Taking Wuliba Pyrite Mine in Xixiang County of South Shaanxi Province as an example, based on the analysis of the environmental status and ecological environment problems of mine cave, waste residue, surface water and ground subsidence, the paper analyzes the root of acid water, puts forward the comprehensive treatment technology of "surface water treatment + groundwater treatment + geological disaster treatment + ecological restoration + end treatment + environmental monitoring", and finally explores three treatment modes of mine cave modification filling, waste residue resource utilization and grouting reinforcement in subsidence area. It provides a scientific reference for the ecological restoration of mines in similar areas.
-
Key words:
- acid mine drainage /
- formation mechanism /
- comprehensive treatment /
- Wuliba Pyrite Mine
-

-
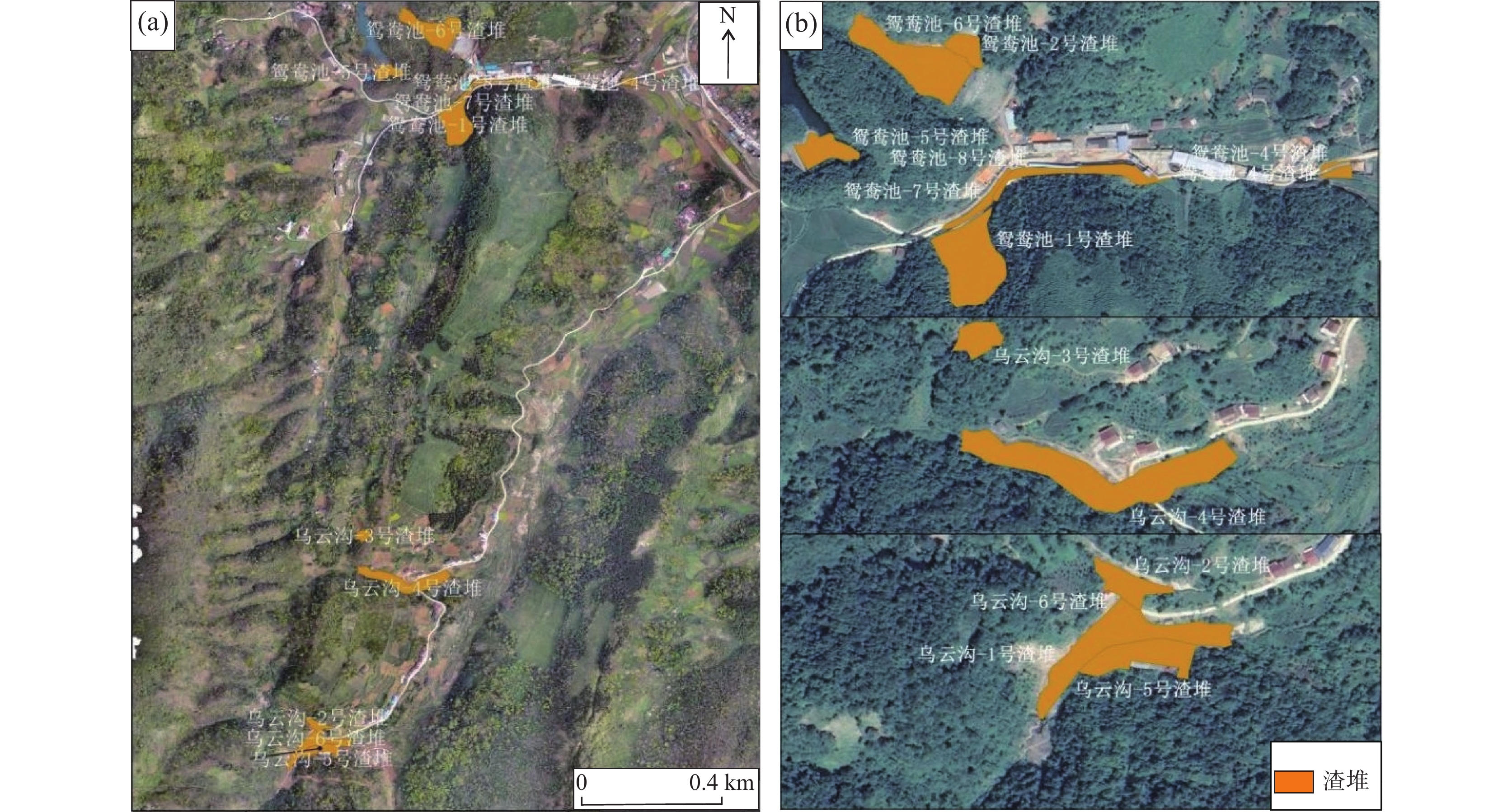
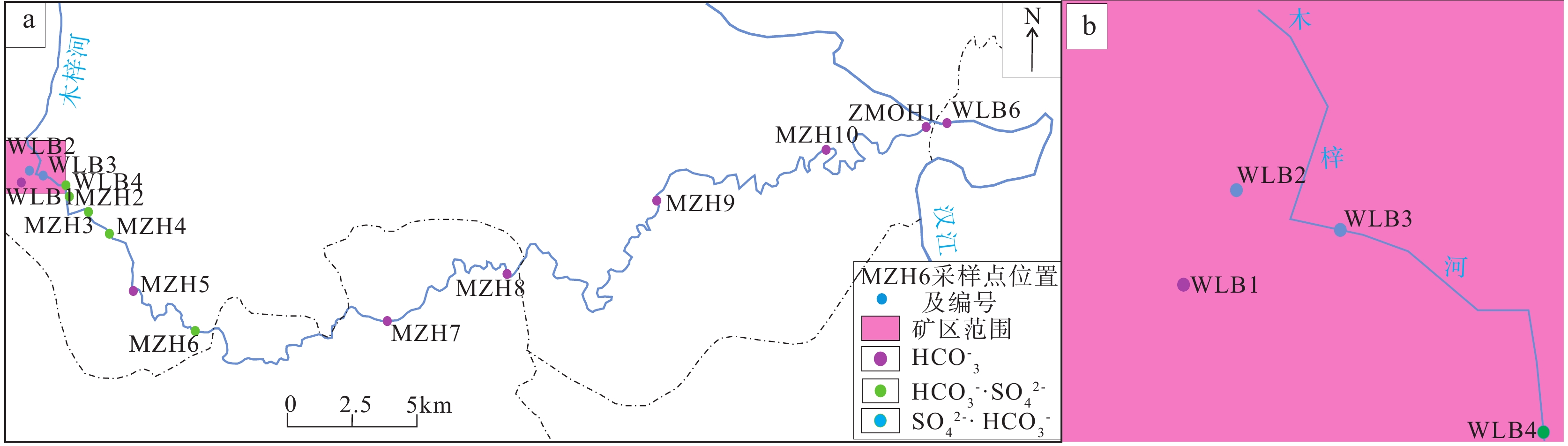
表 1 水样分析数据统计表(mg/L)
Table 1. The statistical table of water sample analysis data (mg/L)
采样地点 地表水Ⅱ类
水质标准1070
平硐1006
主井1006
斜井2#尾矿
库渗水1#尾矿
库渗水乌云沟-5
渣堆渗水乌云沟-6
渣堆渗水pH 6~9 4.17 3.02 2.96 5.4 6.42 3.32 7.12 锌 1 1.54 0.61 2.92 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.11 0.05 L 铜 1 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.05 L 锰 0.1 5.33 1.98 7.4 5.36 1.84 0.66 0.34 铁 0.3 0.91 27.8 48 19.7 0.96 1.18 0.72 镉 0.005 0.0025 0.0008 0.0021 0.0006 0.0008 0.0015 0.001 铬(六价) 0.05 0.004 L 0.005 0.004 0.004 L 0.004 L 0.004 L 0.004 L 砷 0.05 0.0003 0.0004 0.0003 L0.0003 L0.0003 L0.0003 L0.0003 L镍 0.02 0.21 0.09 0.28 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.05 L 采样
地点地表水Ⅱ类
水质标准乌云沟-4
渣堆西侧渗水乌云沟-4
渣堆东侧渗水乌云沟-4
渣堆下游地表水乌云沟-5
渣堆下游地表水鸳鸯池-8
渣堆渗水鸳鸯池-1
渣堆渗水pH 6-9 3.21 7.22 3.22 7.43 2.94 4.64 锌 1 0.19 0.05 L 0.29 0.05 L 1.67 0.05 L 铜 1 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.05 L 0.05 L 硒 0.01 0.0006 0.0008 0.0007 0.0008 0.0011 0.0006 铁 0.3 9.39 3.44 13.6 0.84 450 0.14 汞 0.00005 0.00011 0.00014 0.00008 0.00011 0.00013 0.0002 镉 0.005 0.0009 0.001 0.0007 0.0004 0.0036 0.0012 总铬 / 0.005 0.004 L 0.009 0.004 L 0.017 0.004 L 砷 0.05 0.0003 L0.0003 L0.0003 0.0003 L 0.0006 0.0005 镍 0.02 0.07 0.05 L 0.1 0.05 L 0.57 0.05 L 注:统计数据来源于2021年4月28日汉环集团陕西名鸿检测有限公司分析结果。L表示低于检出限。 表 2 地面塌陷统计表
Table 2. The table of subsidence statistics
编号 面积(m2) 深度(m) 形态特征 W-TX1 89.33 0.7 近圆形 W-TX2 79.63 1.3 近圆形 W-TX3 590.63 0.5 椭圆形,长轴呈北东东向 W-TX4 574.22 2.2 近圆形 W-TX5 716.53 2.5 不规则四边形 W-TX6 1201.81 0.6 椭圆形,长轴呈近南北向 W-TX7 667.76 2.5 近圆形 W-TX8 545.35 0.4 椭圆形,长轴呈近西北北向 W-TX9 365.62 2.1 近圆形 合计 4830.88 -
[1] 陈华清, 张天亮, 龚慧山, 等. 矿山酸性水中铝相次生矿物及环境学意义的研究进展[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 141-151 doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023129
CHEN Huaqing, ZHANG Tianliang, GONG Huishan, et al. Stable isotope characteristics and geological significance of acid wastewater in a stone coal mining area[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4): 141-151. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023129
[2] 陈宏坪, 韩占涛, 沈仁芳, 等. 废弃矿山酸性矿井水产生过程与生态治理技术[J]. 环境保护科学, 2021, 47(6): 73-80 doi: 10.16803/j.cnki.issn.1004-6216.2021.06.014
CHEN Hongping, HAN Zhantao, SHEN Renfang, et al. Production process and ecological treatment technology of acid mine drainage in abandoned mines[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2021, 47 (6): 73-80. doi: 10.16803/j.cnki.issn.1004-6216.2021.06.014
[3] 何绪文, 胡建龙, 李静文, 等. 硫化物沉淀法处理含铅废水[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(4): 1394-1398
HE Xuwen, HU Jianlong, LI Jingwen, et al. Treatment of lead-containing wastewater by sulfide precipitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 7(4): 1394-1398.
[4] 李春花, 张倩, 张文龙, 舒小华, 等. 黄铁矿氧化过程中水的作用再认识[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2022, 42(3): 695-703
LI Chunhua, ZHANG Qian, ZHANG Wenlong, et al. Reunderstanding of the role of water in pyrite oxidation [J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2022, 42(3): 695-703.
[5] 李麟, 贺俊, 高沛, 等. 略阳县硖口驿镇长沟硫铁矿矿区酸性水综合治理工程可行性研究报告[R]. 西安: 陕西矿业开发工贸有限公司, 2022.
[6] 李建民, 李晔, 董宪伟. 地质聚合物的研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 化工新型材料, 2021, 49(8): 28-32, 36 doi: 10.19817/j.cnki.issn1006-3536.2021.08.006
LI Jianmin, LI Ye, DONG Xianwei. Research progress and development trend of geopolymer [J]. New Chemical Materials, 2021, 49(8): 28-32, 36. doi: 10.19817/j.cnki.issn1006-3536.2021.08.006
[7] 黎洁, 谢贤, 李博琦, 等. 地质聚合物研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(6): 141-148 doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2020.06.020
LI Jie, XIE Xian, LI Boqi, et al. Overview of research on geopolymers[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020, 40(6): 141-148. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2020.06.020
[8] 李麟, 张俊峰, 杨苏才, 等. 西乡县五里坝硫铁矿矿山污染现状调查与环境风险评估报告[R]. 西安: 陕西矿业开发工贸有限公司, 2021.
[9] 李娟. 黄铁矿表生氧化及其与微生物相互作用关系研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2015
LI Juan. Study on surface oxidation of pyrite and its interaction with Microorganisms [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2015.
[10] 刘伟. 新型生物絮凝剂协同处理重金属废水的研究与应用[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2017
LIU Wei. Research and application of novel bioflocculating agents in the collaborative treatment of heavy metal wastewater [D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2017.
[11] 陆现彩, 李娟, 刘欢, 等. 金属硫化物微生物氧化的机制和效应[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(1): 153-163 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.01.12
LU Xiancai, LI Juan, LIU Huan, et al. Mechanism and effect of microbial oxidation of metal sulfide [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(1): 153-163. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.01.12
[12] 李强, 钟峻宏, 肖皓天, 等. 陕西省汉中市五里坝、刘家坪、麻柳铺硫铁矿区机载 LiDAR 数据釆集与解译项目成果报告[R]. 京创智慧科技有限责任公司, 2022.
[13] 聂轶苗, 牛福生, 张锦瑞. 我国矿渣综合利用的现状[J]. 建材技术与应用, 2009, (2): 6-9 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9441.2009.02.003
NIE Yimiao, NIU Fusheng, ZHANG Jinrui. Slag comprehensive utilization status of mine in our country [J]. Building Materials Technology and Application, 2009, (2): 6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9441.2009.02.003
[14] 王晓勇, 徐友宁, 赵振宏, 等. 石煤矿区酸性废水稳定同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 162-168 doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023130
WANG Xiaoyong, XU Youning, ZHAO Zhenhong, et al. Stable Isotope Characteristics and geological significance of acid wastewater in a stone coal mining area[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4): 162-168. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023130
[15] 王柱强, 胡巍. 矿山酸水成因分析及治理技术评价[J]. 中国矿业, 2010, 5(4): 37-40
WANG Zhuqiang, HU Wei. Genetic analysis and treatment technology evaluation of mine acid water [J]. China Mining, 2010, 5(4): 37-40.
[16] 徐志诚. 酸性矿井水的人工湿地处理方法综述[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2005, 32(2): 40-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2005.02.016
XU Zhicheng. Review on constructed wetland treatment of acid mine drainage [J]. Safety and Environmental Protection in Mining Industry, 2005, 32(2): 40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2005.02.016
[17] 徐友宁, 陈华清, 柯海玲, 等. 蒿坪河流域石煤矿区河流铝的白色污染及其成因分析[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 128−140.
XU Youning, CHEN Huaqing, KE Hailing, et al. Analysis of White Pollution of River Aluminum in Stone CoalMining Area in Haoping River Basin and Its Causes[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4): 128−140.
[18] 袁加巧, 柏少军, 毕云霄, 等. 国内外矿山酸性废水治理与综合利用研究进展[J]. 有色金属工程, 2022, 12(4): 131-139 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.04.019
YUAN Jiaqiao, BAI Shaojun, BI Yunxia, et al. Research progress of acid mine wastewater treatment and comprehensive utilization at home and abroad [J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2022, 12(4): 131-139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.04.019
[19] 杨程, 王广成, 王绍平, 等. 化学中和法处理含锰酸性矿山废水的工艺优化[J]. 广州化工, 2021, 49(7): 118-121 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2021.07.039
YANG Cheng, WANG Guangcheng, WANG Shaoping, et al. Optimization of chemical neutralization. Optimization of chemical neutralization process for treating manganese containing acid mine wastewater[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2021, 49(7): 118-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2021.07.039
[20] 朱爱平, 田虎伟. 浅谈金属矿山酸性废水处理工艺[J]. 现代矿业, 2020, 36(1): 204-206 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2020.01.062
ZHU Aiping, TIAN Huwei. Discussion on acid wastewater treatment technology of metal mine[J]. Modern Mining, 2020, 36(1): 204-206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2020.01.062
[21] Acharya B S, Kharel G. Acid mine drainage from coal mining in the United States-An overview[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 588(1): 125061.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125061 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125061
[22] A. P. Jarvis, P. L. Younger. Design, construction and performance of a full-Scale compost wetland for mine-spoil drainage treatment at quaking houses[J]. Water and Environmental Management Journal, 1999, 13(5): 313 - 318. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-6593.1999.tb01054.x
[23] ATA Akcil, Soner Koldas. Acid Mine Drainage (AMD): causes, treatment and case studies[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2006, 14(12/13): 1139 - 1145.
[24] CHEN Yt; LI Jt; Chen Lx; et al. Biogeochemical processes governing natural pyrite oxidation and release of acid metalliferous drainage[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(10): 5537 - 5545.
[25] FABIAND, YOUNGERPL, APLINAC. Constructed wetlands for the passive treatment of acid mine drainage allow aquantitative appraisal of the biogeochemical removal of iron, sulphur, and other pollutants[J]. Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 230: 1785 - 1786.
[26] GAYATHRI Naidu, Seongchul Ryu, RAMESH Thiruvenkatachari, et al. A critical review on remediation, reuse, and resource recovery from acid mine drainage. [J]. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987), 2019, 247: 1110 - 1124. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.085
[27] JOHNSON D. Barrie; Hallberg Kevin B. Acid mine drainage remediation options: a review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2005, 338(1): 3 - 14.
[28] Johnson D Barrie, Hallberg Kevin B. Reviews in environmental science and biotechnology[M]. Springer, 2002: 335.
[29] KEFENI K. K, MSAGATI T. A. M, MAMBA B. B. Acid mine drainage: prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: a review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 151: 475 - 493. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.082
[30] SKOUSEN J, ZIPPER C E, ROSE A, et al. Review of passive systems for acid mine drainage treatment[J]. Mine Water and the Environment, 2017, 36(1): 133 - 153. doi: 10.1007/s10230-016-0417-1
[31] YOUNGER P L. Hydro geochemistry of mine waters flowing from abandoned coal workings in County Durham[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, 1995, 28: 101 − 113.
-




 下载:
下载: