Spatial-Temporal Distribution Characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 in the Northeast Xizang Plateau and the Influence of Meteorological Factors
-
摘要:
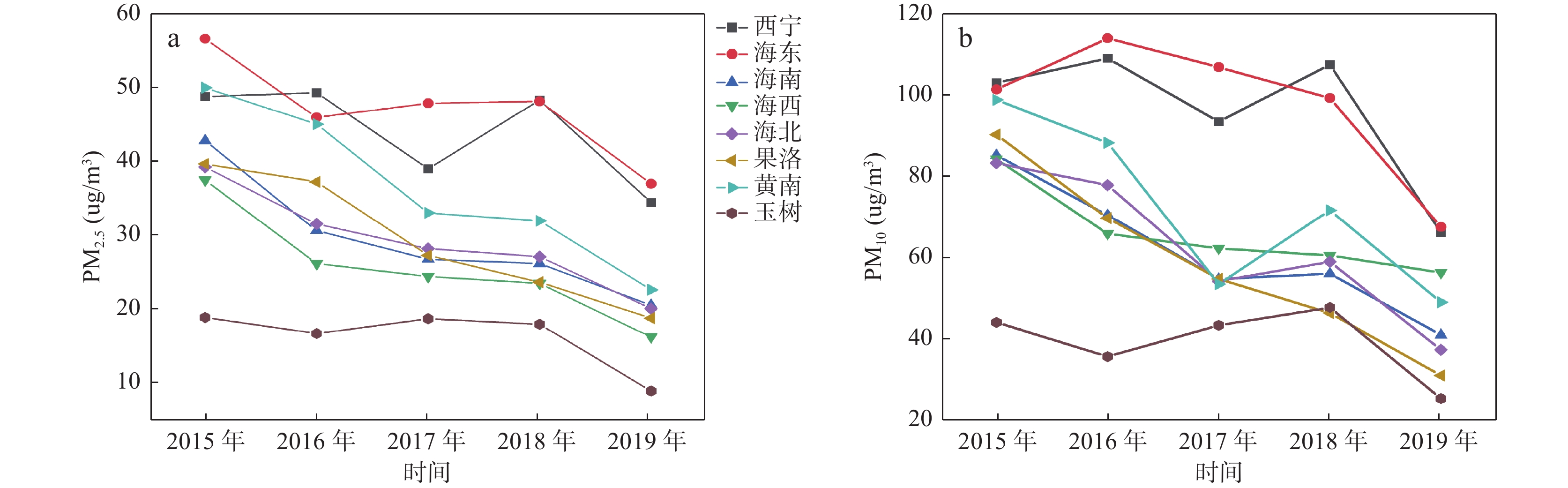
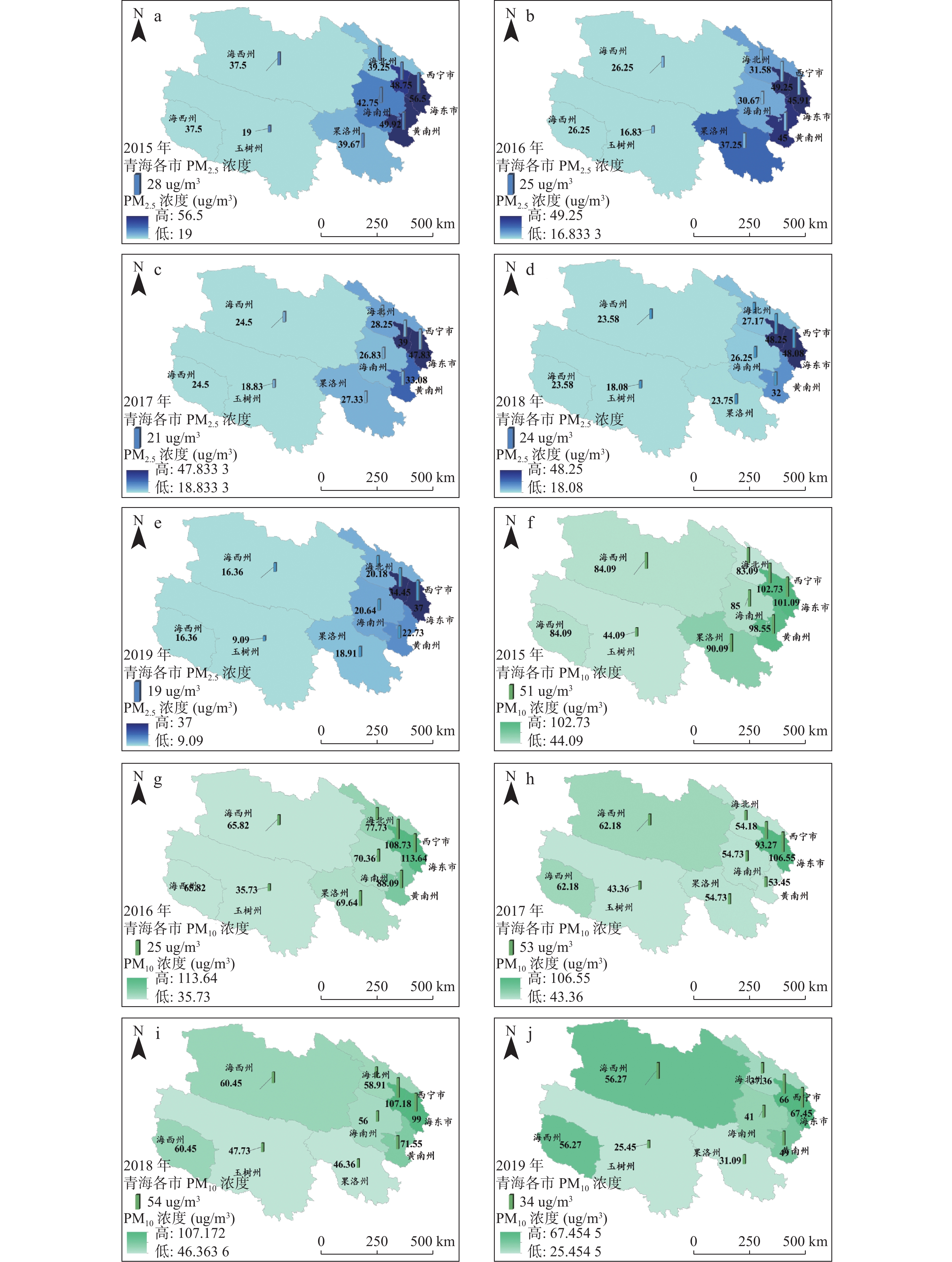
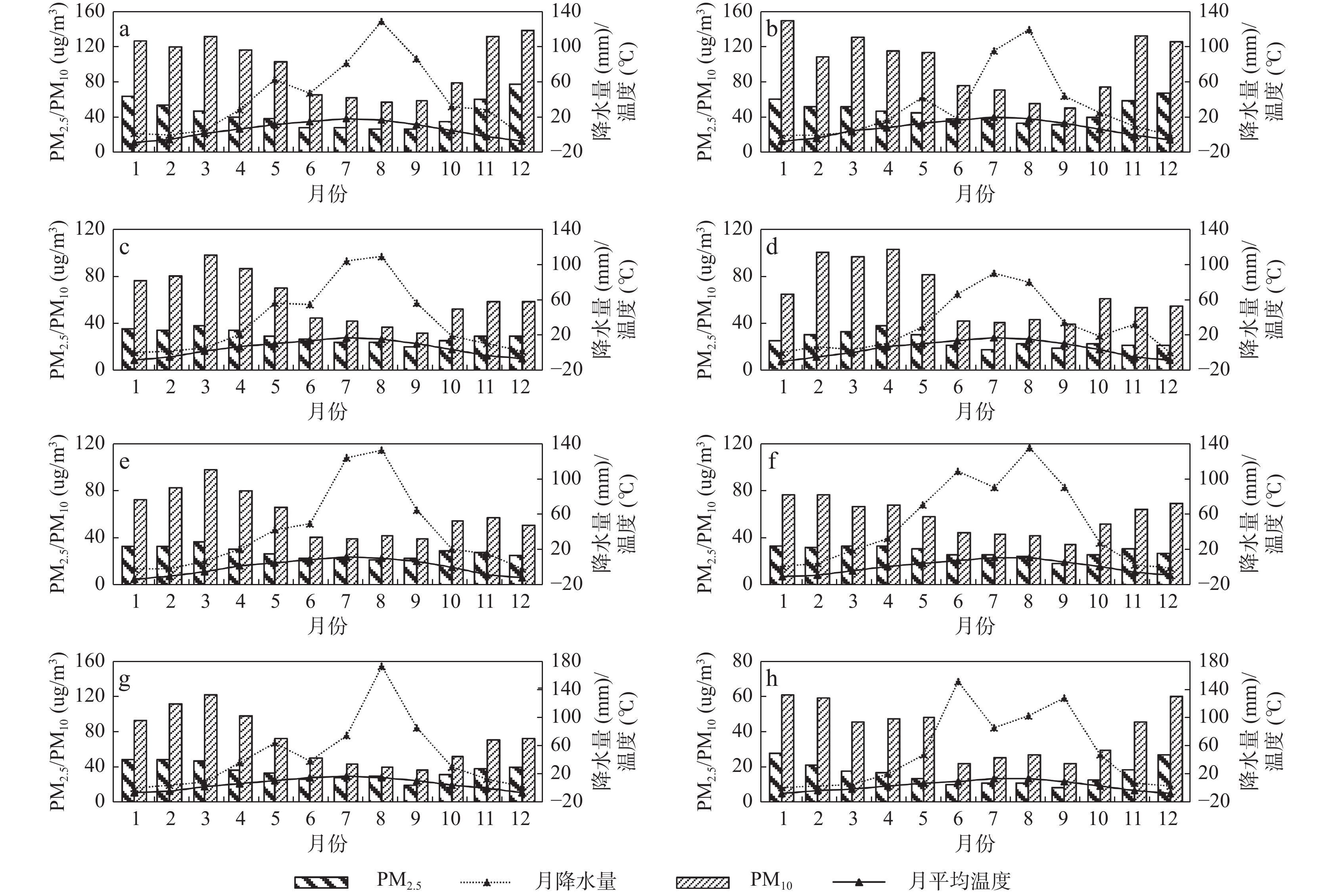
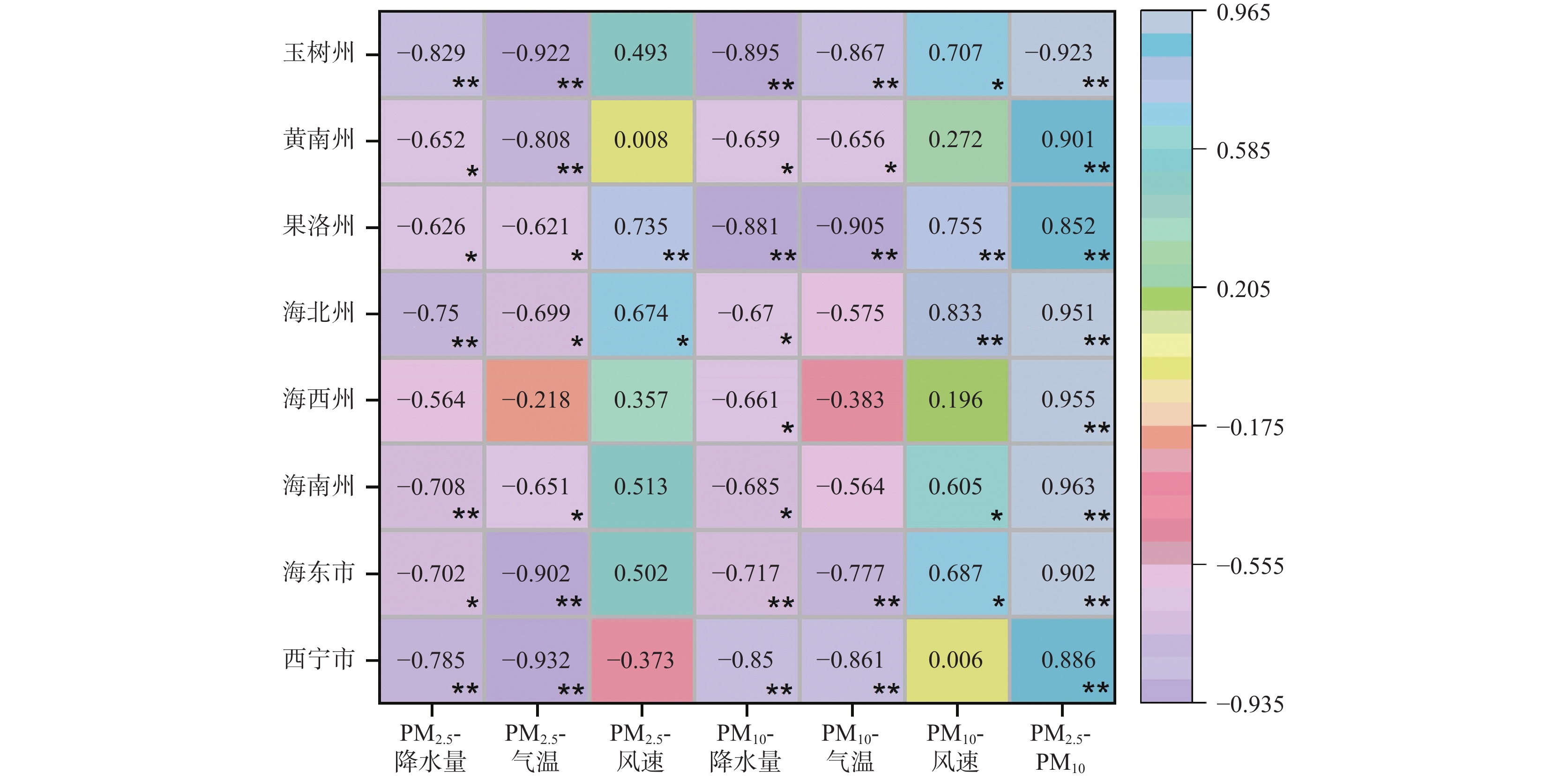
随着工业化进程的迅速发展,大气污染问题已不容忽视,青藏高原东北部作为中国重要的生态安全战略地区,由于其常年多风的地理特点导致土地荒漠化,而土地荒漠化会带来颗粒物污染的问题。笔者以青藏高原东北部地区逐月可吸入颗粒物(PM10)和细颗粒物(PM2.5)浓度为基础,分析了大气颗粒物PM2.5和PM10时空分布特征,与气象因素(降水量、气温和风速)之间的相关性及受气象因素的影响程度。结果表明:①东部人口密集和经济发达的西宁市、海东市和黄南州PM2.5和PM10较高,以上3个市州的PM2.5平均水平分别为44.2 μg/m3,44.7 μg/m3和36.5 μg/m3,PM10平均水平分别为99.1 μg/m3,99.7 μg/m3和72.2 μg/m3;2015~2019年的时间分布上各地区颗粒物浓度呈现逐年下降的趋势;空间分布表明PM2.5呈现从西到东逐渐升高的趋势,PM10则呈东高西低分布。②各地区气温和降水量的峰值均出现在夏季,呈现出“Λ”型的分布规律;而各地区的PM2.5、PM10逐月浓度变化整体呈现出“V”型的分布规律,非采暖季颗粒物浓度最低、采暖季颗粒物浓度最高。③各种气象因素的影响中,PM2.5和PM10与降水量、气温、风速均呈负相关,并且PM2.5浓度受到风速的负向影响,而PM10浓度受到风速的显著正向影响,表明风起扬尘对该区域大气污染贡献突出但风速与污染物浓度的作用机制复杂。本研究可为典型地区空气质量的改善与预测提供理论基础与参考依据。
Abstract:With the rapid development of industrialization, the problem of air pollution can not be ignored. As an important ecological security strategic area in China, the Northeast Xizang Plateau had prominent particulate pollution caused by soil desertification. Based on the monthly concentrations of inhalable particulate matter (PM10) and fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in 8 cities (prefectures) from 2015 to 2019 and the meteorological data, this study analyzed the spatial-temporal distribution characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10, the relationships between them and meteorological factors (precipitation, temperature and wind speed) and the degree of influence of meteorological factors. The results showed that: ①Xining city, Haidong city and Huangnan prefecture, which were densely populated and economically developed in the east of Qinghai province, had higher PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations, with an average level of 44.2 μg/m3 (99.1 μg/m3)、44.7 μg/m3 (99.7 μg/m3) and 36.5 μg/m3 (72.2 μg/m3) respectively. In terms of time distribution, the concentration of particulate matter in each region showed a downward trend year by year. The spatial distribution showed that PM2.5 gradually increased from the west to the east, and PM10 was high in the east and low in the west. ② The peak values of temperature and precipitation appeared in summer, showing a "Λ" distribution law. While the monthly concentration changes of PM2.5 and PM10 in various regions showed a "V" distribution law. The particle concentration in non-heating season was the lowest and that in heating season was the highest. ③ Among the effects of various meteorological factors, the concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 were strongly or moderately negatively correlated with precipitation and temperature, and were negatively affected by temperature. The concentration of particulate matter was negatively correlated with wind speed. The concentration of PM2.5 was negatively affected by wind speed, while the concentration of PM10 was significantly positively affected by wind speed, indicating that wind-induced dust had a prominent contribution to air pollution, but the action mechanism between wind speed and pollutant concentration was complex. The results of this study could provide reference and theoretical basis for the improvement and prediction of air quality in typical regions.
-
Key words:
- PM2.5 /
- PM10 /
- air pollution /
- meteorological factors /
- cause analysis /
- Northeast Xizang Plateau
-

-
表 1 PM2.5与PM10多元线性回归结果
Table 1. Results of multiple linear regression between PM2.5 and PM10
污染物 地区 多元回归模型 R2 调整后R2 p值 PM2.5 西宁 24.269+0.466*×PM10−0.021×气温+0.005×降水−25.996·×风速 0.946 0.915 0.000 海东 21.599**+0.133*×PM10−0.566*×气温+0.029×降水+8.849×风速 0.968 0.950 0.000 海北 26.564***+0.242***×PM10−0.093×气温−0.013×降水−4.361·×风速 0.973 0.957 0.000 黄南 17.730+0.169·×PM10−0.857·×气温+0.053×降水+5.044×风速 0.921 0.876 0.001 海南 14.512+0.236*×PM10−0.277×气温+0.041×降水+0.370×风速 0.955 0.929 0.000 果洛 11.575+0.183×PM10+0.069×气温−0.027×降水+4.387×风速 0.793 0.675 0.015 玉树 5.463+0.413**×PM10−0.392·×气温+0.034×降水−4.285×风速 0.948 0.918 0.000 海西 8.175*+0.176**×PM10+0.038×气温−0.095×降水+4.216×风速 0.954 0.928 0.000 青海 15.047**+0.184*×PM10−0.630**×气温+0.063·×降水+2.971×风速 0.984 0.975 0.000 PM10 西宁 −12.793+1.456**×PM2.5−1.145×气温−0.006×降水+54.761*×风速 0.954 0.928 0.000 海东 −87.131·+3.667*×PM2.5+0.818×气温−0.120×降水+8.639×风速 0.931 0.892 0.000 海北 −101.720***+3.498***×PM2.5+0.200×气温+0.046×降水+22.352**×风速 0.975 0.961 0.000 黄南 −75.280·+2.232·×PM2.5−0.486×气温−0.034×降水+33.545×风速 0.885 0.819 0.002 海南 −32.042·+2.624*×PM2.5+0.377×气温−0.187×降水+14.860×风速 0.964 0.943 0.000 果洛 0.990+0.288×PM2.5−1.209*×气温−0.028×降水+29.034**×风速 0.970 0.953 0.000 玉树 1.168+1.692**×PM2.5+0.359×气温−0.086×降水+10.561*×风速 0.959 0.935 0.000 海西 −30.355+3.972**×PM2.5−0.429×气温+0.110×降水−3.438×风速 0.938 0.902 0.000 青海 −42.628+2.835×PM2.5+0.813×气温−0.207×降水+14.313×风速 0.974 0.959 0.000 注:·为p<0.1, *为p<0.05, **为p<0.01, ***为p<0.001。 -
[1] 蔡春霞, 贾晓丹, 鲍国臣, 等. 典型燃煤电厂大气污染物沉降对周边水源地的影响及贡献研究[J]. 西北地质, 2024, 57(1):64-72.
CAI Chunxia, JIA Xiaodan, BAO Guochen, et al. Impact and contribution of atmospheric pollutant deposition from a typical power plant on surrounding water sources[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2024, 57(1):64–72.
[2] 蔡振媛, 覃雯, 高红梅, 等. 三江源国家公园兽类物种多样性及区系分析[J]. 兽类学报, 2019, 39(4): 410-420
CAI Zhenyuan, QIN Wen, GAO Hongmei, et al. Species diversity and fauna of mammals in Sanjiangyuan National Park[J]. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 2019, 39(4): 410-420.
[3] 郭立平, 乔林, 石茗化, 等. 河北廊坊市连续重污染天气的气象条件分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(3): 497-504
GUO Liping, QIAO Lin, SHI Minghua, et al. Analysis about meteorological conditions of continuous heavy pollution episodes in Langfang of Hebei province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(3): 497-504.
[4] 韩福财. 西宁市空气质量指数AQI现状分析[J]. 青海环境, 2017, 27(1): 36-38
HAN Fucai. Analysis on current situation of air quality index AQI in Xining. Journal of Qinghai Environment[J], 2017, 27(1): 36-38.
[5] 韩婧, 代志光, 李文韬. 西安市灰霾天气下PM2.5浓度与气象条件分析[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2014, 36(2): 52-56
HAN Jing, DAI Zhiguang, LI Wentao. Analysis of PM2.5 concentration and meteorological conditions in haze weather of Xi’an city[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2014, 36(2): 52-56.
[6] 贺博文, 聂赛赛, 王帅, 等. 承德市PM2.5中碳质组分的季节分布特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(11): 5152-5161
HE Bowen, NIE Saisai, WANG Shuai, et al. Seasonal Variation and Source Apportionment of Carbonaceous Species in PM2.5 in Chengde[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(11): 5152-5161.
[7] 李江苏, 段良荣, 张天娇. 中国城市PM2.5和PM10时空分布特征和影响因素分析[J/OL]. 环境科学, 2023, 1-18
LI Jiangsu, DUAN Liangrong, ZHANG Tianjiao. Analysis of Spatio-temporal Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of PM2.5 and PM10 in Chinese Cities[J/OL]. Environmental Science, 2023, 1-18. doi:10.13227/j.hjkx.202305037
[8] 李同昇, 陈谢扬, 芮旸, 等. 西北地区生态保护与高质量发展协同推进的策略和路径[J]. 经济地理, 2021, 41(10): 154-164
LI Tongsheng, CHEN Xieyang, RUI Yang, et al. Strategy and path of cooperative promotion of ecological protection and high-quality development in northwest China. Economic Geography[J], 2021, 41(10): 154-164.
[9] 李轶冰. 江河源区生态环境演变与时空格局[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2007
LI Yibing. Environment evolvement and spatio-temporal pattern in the source regions of Yangtze, Yellow and Lancang River[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2007.
[10] 刘娜, 余晔, 张莉燕, 等. 2016—2018年西宁市颗粒物来源及输送差异分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(10): 4212-4227
LIU Na, YU Ye, ZHANG Liyan, et al. Difference analysis of source and transportation in particulate matter in Xining during 2016-2018[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(10): 4212-4227.
[11] 刘彦春, 靳聪丽, 王雨薇, 等. 校园3种植被类型对春季空气PM2.5含量的影响[J]. 河南科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 41(3): 88-92
LIU Yanchun, JIN Congli, WANG Yuwei, et al. Effects of campus 3 vegetation types on air PM2.5 content in spring[J]. Journal of Henan University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 41(3): 88-92.
[12] 刘妍妍. 湖南省2021年春节期间PM2.5重污染特征及来源分析[J]. 江西科学, 2021, 39(05): 893-900
LIU Yanyan. Analysis on the characteristics and source of heavy pollution process of PM2.5 during the Spring Festival in 2021 in Hunan province[J]. Jiangxi science, 2021, 39(05): 893-900.
[13] 刘震. 黄河流域9市空气质量与社会经济及人群健康效应研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021
LIU Zhen. Study on the air quality, social economic development and population health effect in 9 cities of the Yellow River Basin[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021.
[14] 毛旭, 张涛. 2018年4月大气环流和天气分析[J]. 气象, 2018, 44(07): 977-984
MAO Xu, ZHANG Tao. Analysis of the April 2018 atmosphere circulation and weather[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2018, 44(07): 977-984.
[15] 聂赛赛, 王帅, 崔建升, 等. 石家庄市大气污染物的季节性时空特征及潜在源区[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(11): 5131-5142
NIE Saisai, WANG Shuai, CUI Jiansheng, et al. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Potential Source Areas of Seasonal Atmospheric Pollution in Shijiazhuang[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(11): 5131-5142.
[16] 彭丽思, 孙涵, 聂飞飞. 中国大气污染时空格局演变及影响因素研究[J]. 环境经济研究, 2017, (1): 48-56.
[17] 裘阅, 汪家权, 胡淑恒. 2015-2016年安徽省PM2.5和PM10时空分布特征[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43(1): 113-118
QIU Yue, WANG Jiaquan, HU Shuheng. Spatial-temporal distribution of PM2.5 and PM10-2.5 in Anhui Province, 2015-2016[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 43(1): 113-118.
[18] 石春娥, 邓学良, 吴必文, 等. 降水和风对大气PM2.5、PM10的清除作用分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(12), 4620-4629
SHI Chune, DENG Xueliang, WU Biwen, et al. The scavenging effect of precipitation and wind on PM2.5 and PM10[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(12), 4620-4629.
[19] 孙蓉花, 陈学刚, 魏疆, 等. 乌鲁木齐市PM2.5浓度与气象条件耦合分析[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2017, 39(12): 1353-1357
SUN Ronghua, CHEN Xuegang, WEI Jiang, et al. Coupling analysis of PM2.5 concentrations and meteorological conditions in Urumqi[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2017, 39(12): 1353-1357.
[20] 唐家翔, 符传博, 杨仁勇, 等. 海口市PM2.5演变特征及其与气象因素的关系[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2018, 40(4): 445-449
TANG Jiaxiang, FU Chuanbo, YANG Renyong, et al. Evolution of PM2.5 in Haikou and its relationship with weather factors[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2018, 40(4): 445-449.
[21] 王冰玉, 蔡颖, 郑凯, 等. PM2.5对HBE细胞致癌致突变相关基因表达的影响[J]. 癌变·畸变·突变, 2020, 32(1): 33-38
WANG Bingyu, CAI Ying, ZHENG Kai, et al. Effect of PM2.5 on expression of genes related to carcinogenesis and mutagenesis in HBE cells[J]. Carcinogenesis, Teratogenesis & Mutagenesis, 2020, 32(1): 33-38.
[22] 王涛, 邵田田. 2017年上海市PM2.5和PM10变化特征及来源分析[J]. 河南科学, 2018, 36(11): 1752-1758
WANG Tao, SHAO Tiantian. Characteristics and sources of PM2.5 and PM10 in Shanghai in 2017[J]. Henan science, 2018, 36(11): 1752-1758.
[23] 王遵娅, 柳艳菊, 丁婷, 等. 2018年春季气候异常及可能成因分析[J]. 气象, 2018, 44(10): 1360-1369
WANG Zunya, LIU Yanju, DING Ting, et al. Features and possible causes for climate anomalies in spring 2018[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2018, 44(10): 1360-1369.
[24] 魏玉香, 童尧青, 银燕, 等. 南京SO2, NO2和PM 10变化特征及其与气象条件的关系[J]. 大气科学学报, 2009, 32(3): 451-457
WEI Yuxiang, TONG Yaoqing, YIN Yan, et al. The variety of main air pollutants concentration and its relationship with meteorological condition in Nanjing city[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Science, 2009, 32(3): 451-457.
[25] 魏旖梦. 西北五省(区)大气污染物特征及其影响因素研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2021
WEI Yimeng. Study on the characteristics of air pollutants and its influencing factors in northwest of China[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2021.
[26] 许文轩, 田永中, 肖悦, 等. 华北地区空气质量空间分布特征及成因研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(8), 3085-3096
XU Wenxuan, TIAN Yongzhong, XIAO Yue, et al. Study on the spatial distribution characteristics and the drivers of AQI in North China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(8), 3085-3096.
[27] 薛澜, 翁凌飞. 中国实现联合国2030年可持续发展目标的政策机遇和挑战[J]. 中国软科学, 2017, (1): 1-12
XUE Lan, WENG Lingfei. The policy opportunities and challenges in China's implementation of 2030 sustainable development goals[J]. China Soft Science, 2017, (1): 1-12.
[28] 杨洪斌, 李元宜, 邹旭东等. 辽宁空气中度污染和重污染天气类型分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2009, 25(6): 15-17.
[29] 杨淼. 以幸福的名义建设生态西宁[J]. 青海科技, 2014, (04): 12-14.
[30] 杨稳强. 西北地区大气污染特征及其影响因素分析[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2023
YANG Wenqiang. Characteristics of air pollution in Northwest China and its influencing factors[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2023.
[31] 杨文涛, 谯鹏, 刘贤赵, 等. 2011~2017年中国PM2.5多尺度时空分异特征分析[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12): 5236-5244
YANG Wentao, QIAO Peng, LIU Xianzhao, et al. Analysis of Multi-scale Spatio-temporal Differentiation Characteristics of PM2.5 in China from 2011 to 2017[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12): 5236-5244.
[32] 姚振, 田兴元, 姬丙艳, 等. 西宁—乐都地区土地质量地球化学评估[J]. 西北地质, 2012, 45(1): 317-323.
[33] 中国气象局. 2019年全国生态气象公报[EB/OL]. 2020, [2020-06-30].
[34] 张红. 典型沿江城市空气污染物特征及与气象条件的耦合关系研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2018
ZHANG Hong. Study on Relationship & Characteristics of Atmospheric Pollution and Meteorological Conditions of Cities along the Yangtz River[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2018.
[35] 张天先, 陈长彬, 姚洪发. 天津市大气环境中PM2.5与PM10时空分布特征研究[J]. 洛阳理工学院学报(自然科学版), 2020, 30(04): 8-13.
[36] 章异平, 徐军亮, 赵西平, 等. 基于灰色关联的洛阳市空气质量影响因素分析[J]. 河南科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 33(1): 100-104.
[37] 周安琪, 刘建伟, 周旭, 等. 北京大气PM2.5载带金属浓度、来源及健康风险的城郊差异[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(06): 2595-2603
ZHOU Anqi, LIU Jianwei, ZHOU Xu, et al. Concentrations, sources, and health risks of PM2.5 carrier metals in the Beijing urban area and suburbs[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(06): 2595-2603.
[38] 邹佳乐, 林尧林, 杨薇. 中国近年PM2.5污染研究进展[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2019, 41(3): 357-361
ZOU Jiale, LIN Yaolin, YANG Wei. Advances on PM2.5 pollution research in China in recent years[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2019, 41(3): 357-361.
[39] Cao Q, Rui G, Liang Y. Study on PM2.5 pollution and the mortality due to lung cancer in China based on geographic weighted regression model[J]. BMC Public Health. 2018, 18(1): 925.
[40] Gaio V, Roquette R, Dias CM, et al. Ambient air pollution and lipid profile: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 254(Pt B): 113036.
[41] Han X, Xiao J, Wang L, et al. Identification of areas vulnerable to soil erosion and risk assessment of phosphorus transport in a typical watershed in the Loess Plateau[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 758.
[42] Hsu CY, Chiang HC, Lin SL, et al. Elemental characterization and source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in the western coastal area of central Taiwan[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 541: 1139-1150. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.122
[43] Hwang SH, Park WM. Radon and PM10 concentrations in underground parking lots and subway stations with health risks in South Korea[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(35): 35242-35248. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3428-6
[44] Li R, Zhou R, Zhang J. Function of PM2.5 in the pathogenesis of lung cancer and chronic airway inflammatory diseases[J]. Oncology Letters, 2018, 15(5): 7506-7514.
[45] Menard, S, Standards for standardized logistic regression coefficients[J]. The Journal of Social Forces, 2011, 89 (4), 1409-1428.
[46] Pham, TG, Degener, J, Kappas, M. Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and geographical information system (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in a Sap basin: central Vietnam[J]. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 2018, 6: 99-110. doi: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2018.01.001
[47] Qiu X, Duan L, Gao J, et al. Chemical composition and source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in different functional areas of Lanzhou, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 40: 75-83.
[48] Raaschou-Nielsen O, Beelen R, Wang M, et al. Particulate matter air pollution components and risk for lung cancer[J]. Environment International, 2016, 87: 66-73. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.11.007
[49] Shen F, Ge X, Hu J, et al. Air pollution characteristics and health risks in Henan Province, China[J]. . Environmental Research, 2017, 156: 625-634. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2017.04.026
[50] Wu F, Wang W, Man YB, et al. Levels of PM2.5/ PM10 and associated metal(loid)s in rural households of Henan Province, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 512-513: 194-200. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.041
-



 下载:
下载: