Trace Element Geochemical Characteristics of the Shangshuiqiao Fluorite Deposit in Eastern Jiangxi with Implications for the Genesis of the Deposit
-
摘要:
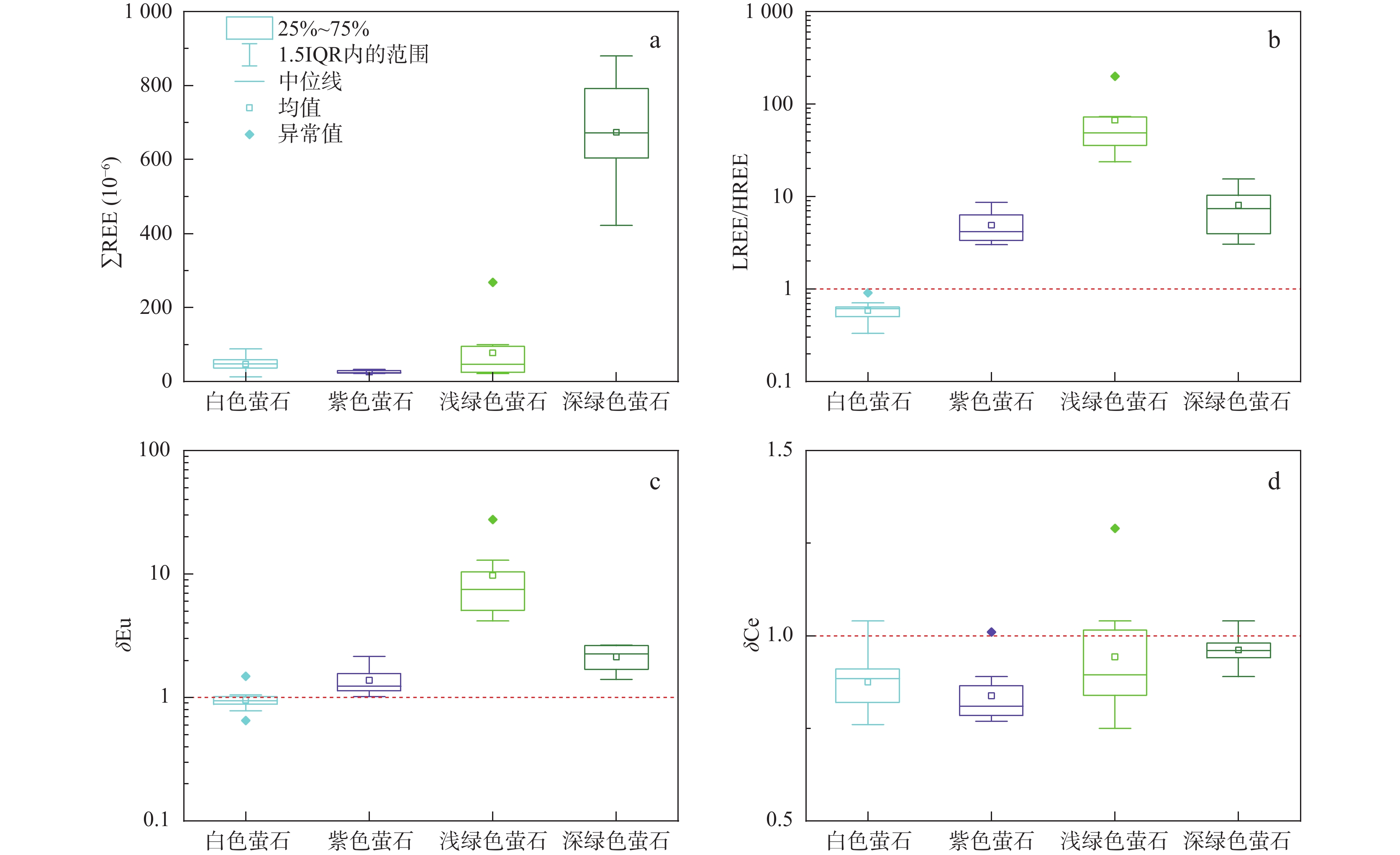
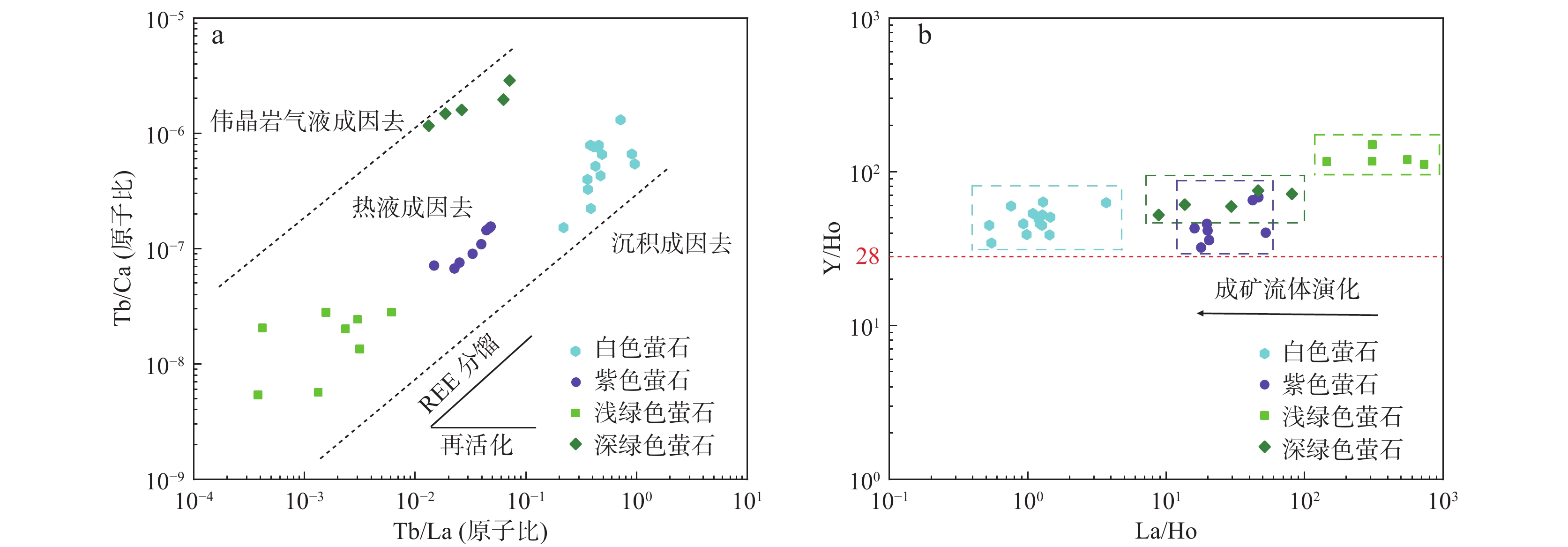
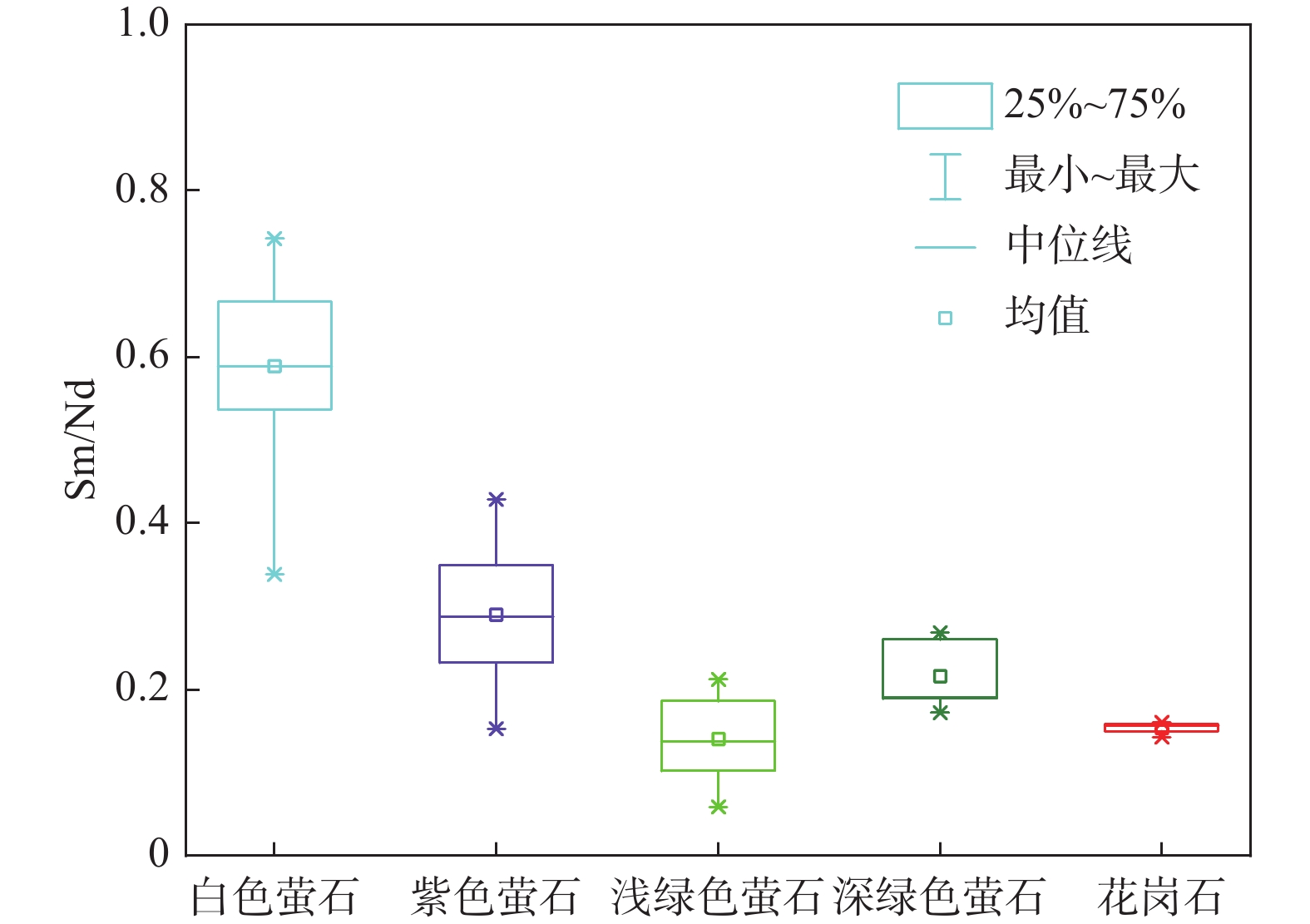
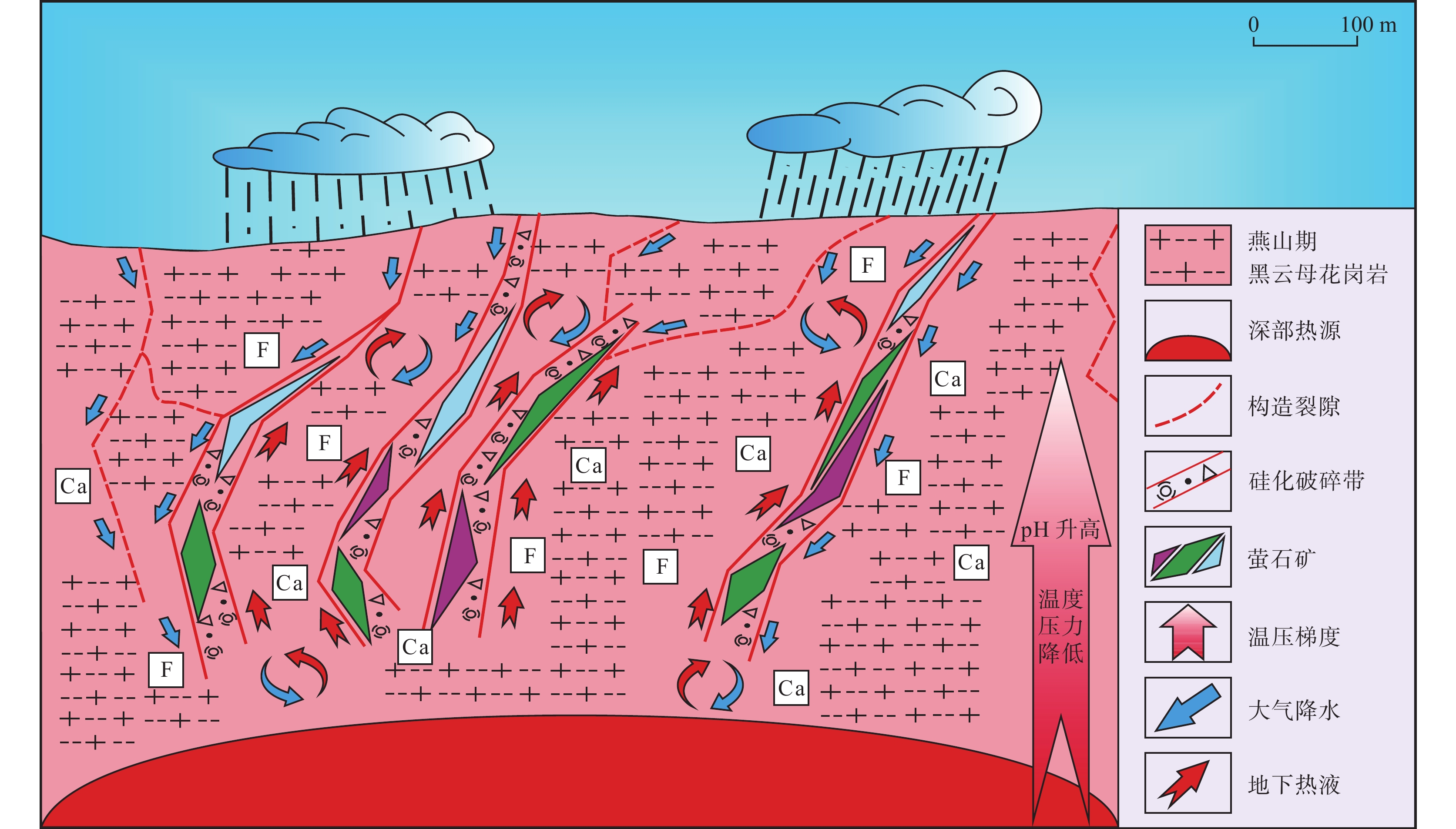
赣东黎川上水桥萤石矿床位于华南褶皱系武夷成矿带北端,产于燕山期黑云母花岗岩的断裂破碎带内。笔者对该矿床的地质特征、不同颜色萤石及围岩黑云母花岗岩的微量元素地球化学特征进行了研究。结果表明,萤石整体上呈现Eu正异常和Ce负异常,但不同颜色的萤石REE配分模式特征有差异,浅绿色、深绿色和紫色萤石为轻稀土富集型,白色萤石为重稀土富集型。围岩的REE配分模式为轻稀土富集型,整体呈现Eu负异常。Y/Ho-La/Ho关系图和REE配分模式图显示,萤石成矿过程中Y-REE发生了分馏,白色萤石成矿时期最晚。Tb/Ca-Tb/La关系图显示,研究区萤石矿床为热液成因。围岩黑云母花岗岩的微量元素配分曲线变化趋势与萤石基本一致,且围岩和萤石的Sm/Nd值十分接近。越靠近矿体的围岩F含量越高,且近矿围岩发生硅化、绢云母化等蚀变,推测萤石矿中的Ca和F主要来自围岩。矿区内萤石形成于中低温氧化环境,矿床成因类型为多期次的中低温热液充填型萤石矿床。
Abstract:The Shangshuiqiao fluorite deposit in Lichuan, eastern Jiangxi, is located at the northern end of the Wuyi metallogenic belt in the South China fold system and is produced in the fractured fracture zone of Yanshanian biotite granite. This paper investigates the geological characteristics of the deposit, as well as the trace element geochemical features of different-colored fluorites and the surrounding biotite granite. The results show that fluorite shows positive Eu anomalies and negative Ce anomalies as a whole, but the REE distribution pattern characteristics of different colors of fluorite are different. Light green, dark green and purple fluorite are light rare earth enriched types, and white fluorite is heavy rare earth enriched type. Enriched type. The REE distribution pattern of the surrounding rock is light rare earth enriched type, and the overall negative Eu anomaly is present. The Y/Ho-La/Ho relationship diagram and REE partitioning model diagram show that Y-REE fractionation occurred during the fluorite mineralization process, and the white fluorite mineralization period was the latest. The Tb/Ca-Tb/La relationship diagram shows that the fluorite deposits in the study area are of hydrothermal origin. The change trend of the trace element distribution curve of the surrounding rock biotite granite is basically the same as that of fluorite, and the Sm/Nd values of the surrounding rock and fluorite are very close. At the same time, the F content in the surrounding rocks closer to the ore body is higher, and the surrounding rocks near the ore undergo alterations such as silicification and sericitization. It is inferred that Ca and F in the fluorite ore mainly come from the surrounding rocks. The fluorite in the mining area was formed in a medium-low temperature oxidation environment, and the deposit formation type is a multi-stage medium-low temperature hydrothermal filling type fluorite deposit.
-

-
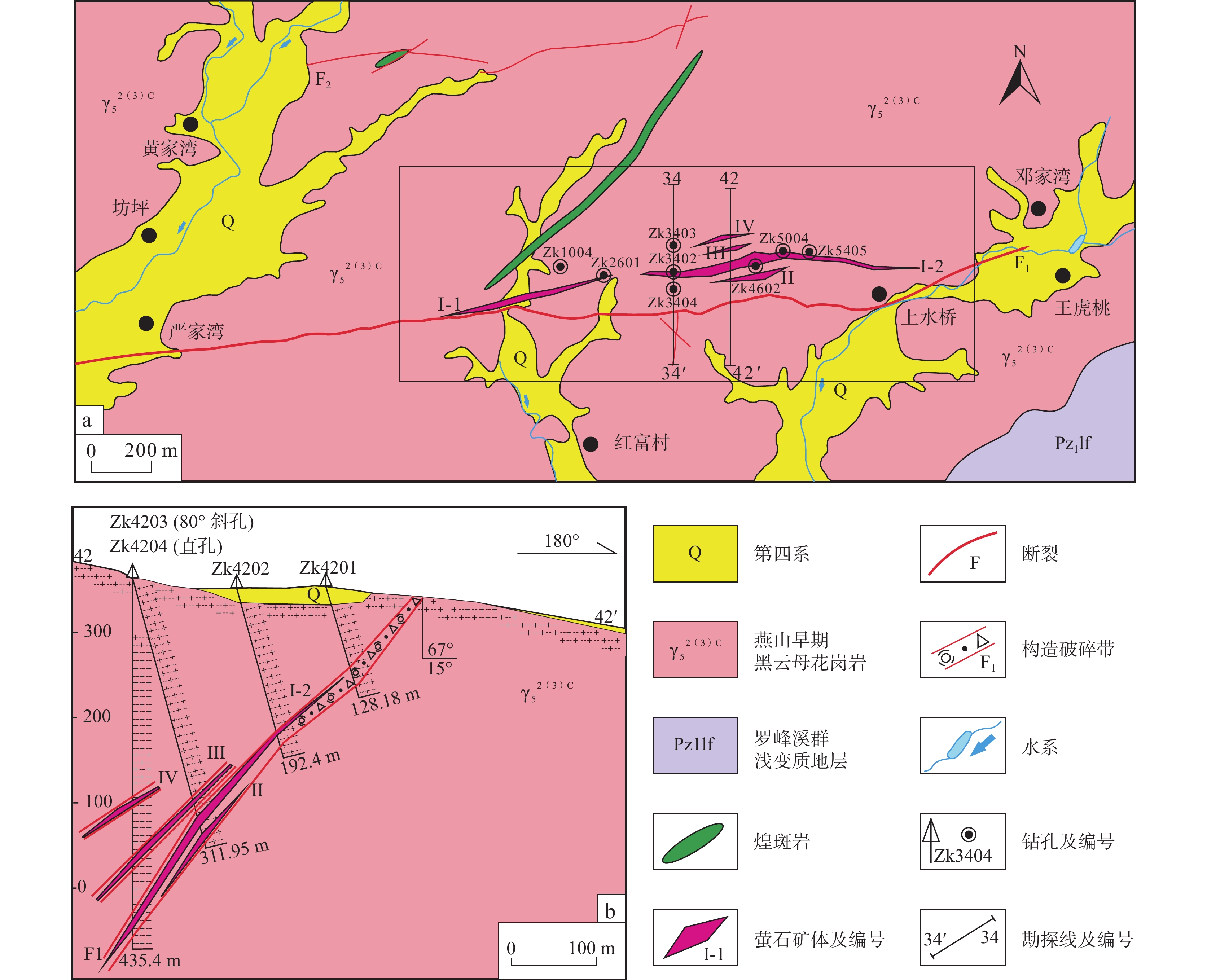
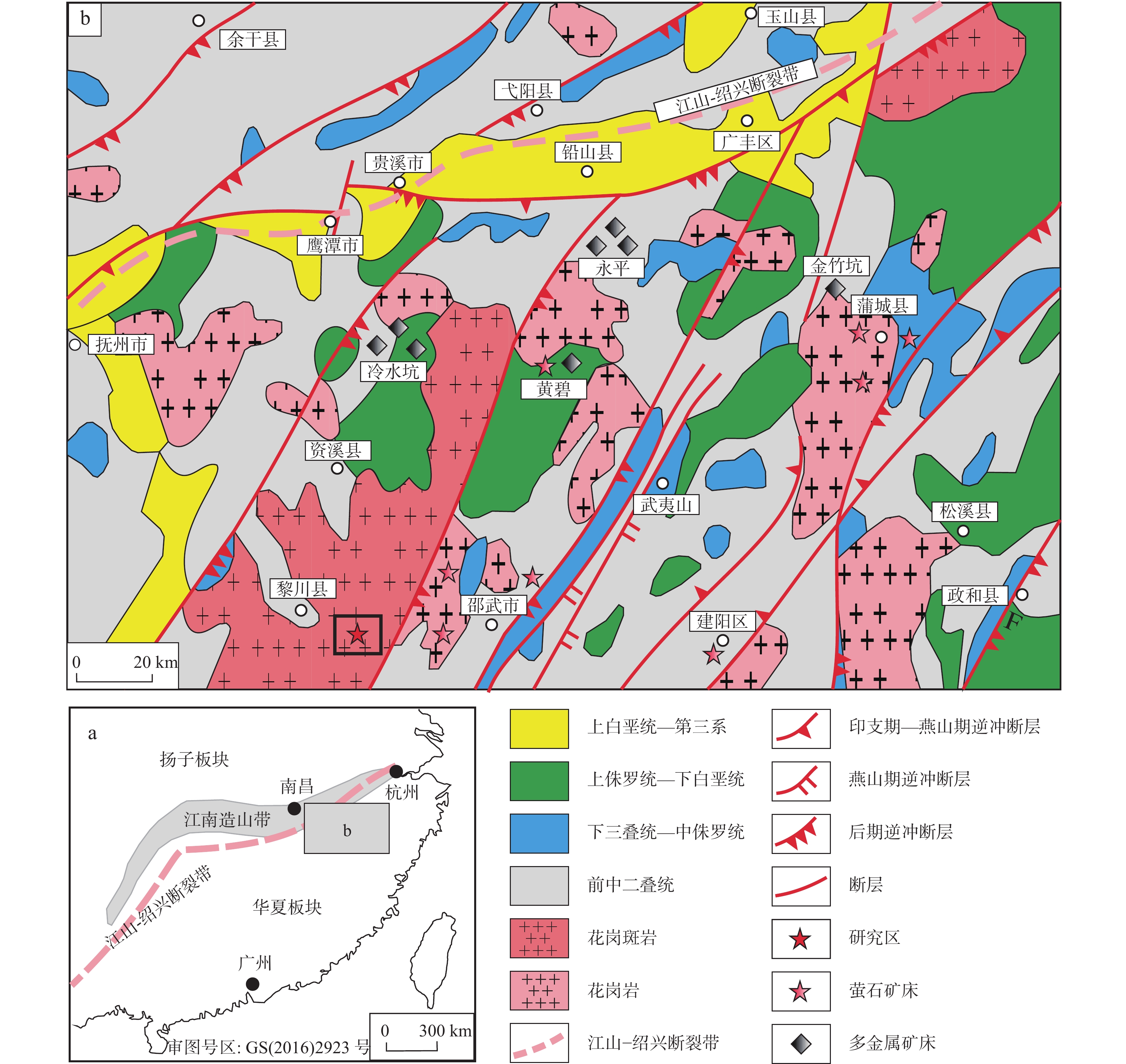
图 1 华南地区构造简图(a)与武夷北地区地质简图(b)(改自Yu et al., 2012)
Figure 1.
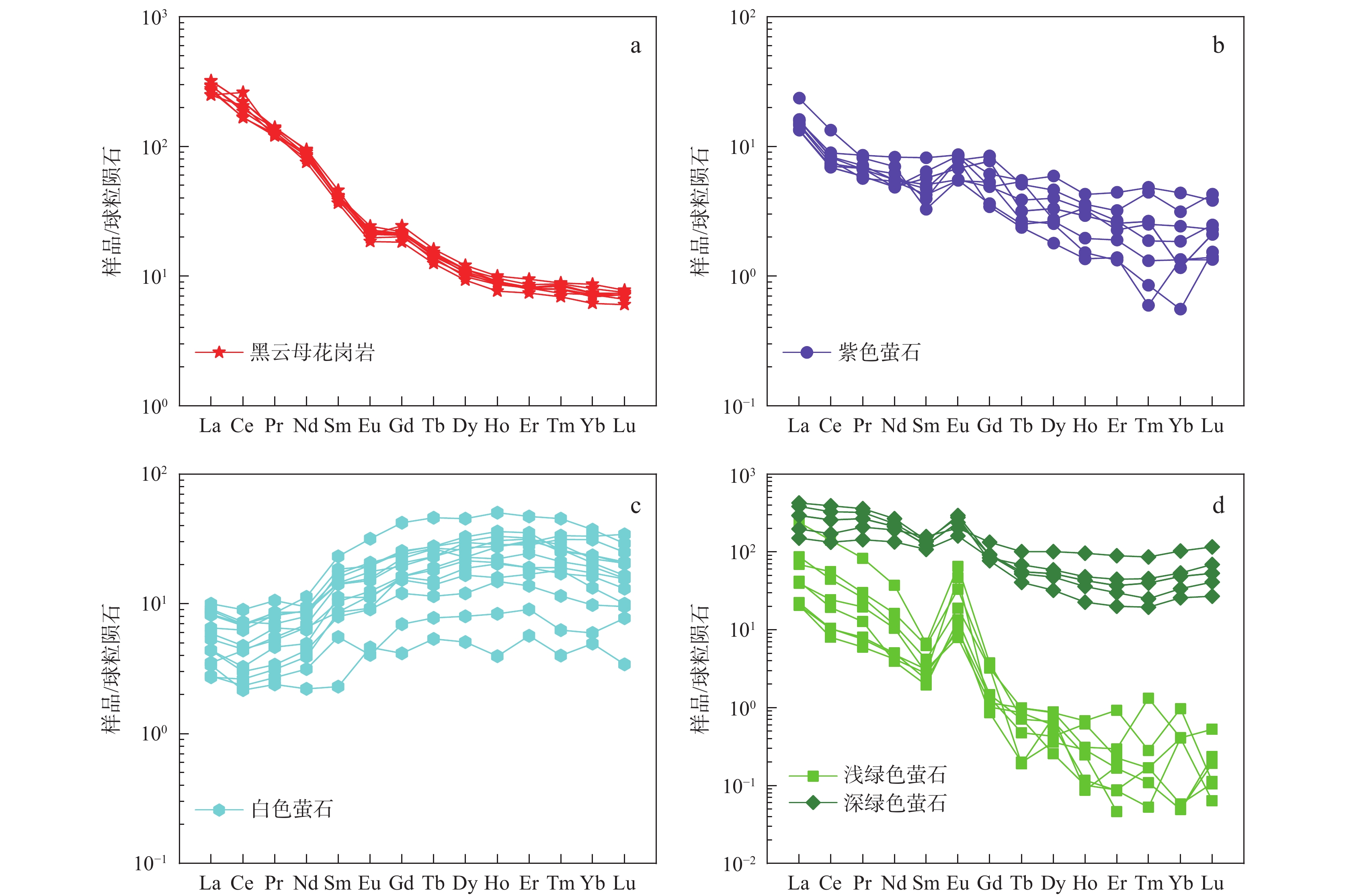
图 4 上水桥萤石矿床围岩及萤石球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线图(标准数据引自Sun et al.,1989)
Figure 4.
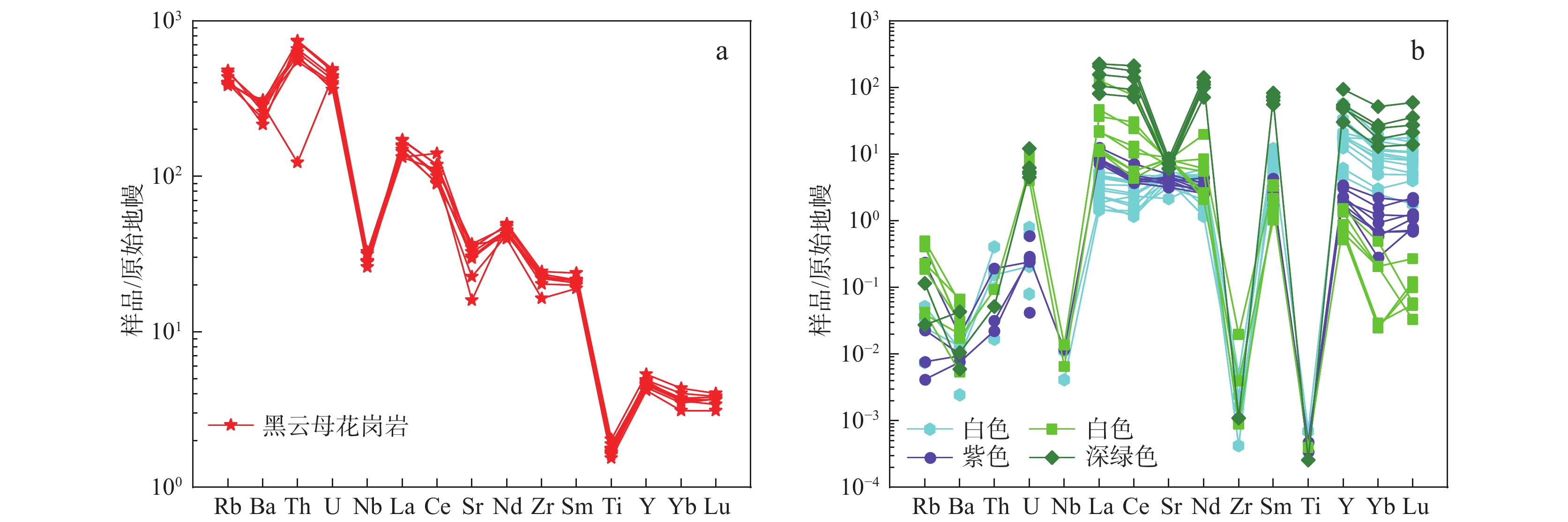
图 5 上水桥萤石矿床围岩及萤石原始地幔标准化微量元素配分曲线图(标准数据引自Taylor et al.,1985)
Figure 5.
图 7 上水桥萤石矿床不同颜色萤石Tb/Ca-Tb/La关系图(a)(底图据Möller et al.,1976)与上水桥萤石矿床不同颜色萤石La/Ho-Y/Ho关系图(b)(底图据Bau et al.,1995)
Figure 7.
表 1 黎川上水桥萤石矿床围岩微量元素(10−6)和CaF2(%)分析结果
Table 1. Analysis results of trace elements (10−6) and CaF2 (%) in the surrounding rocks of the Shangshuiqiao fluorite deposit in Lichuan
样品号 ZK4602 ZK5405 ZK3402 ZK2601 ZK5004 ZK1004 ZK3403 ZK3404 样品名 花岗岩 花岗岩 花岗岩 花岗岩 花岗岩 花岗岩 花岗岩 花岗岩 Rb 252 275 292 252 304 243 252 254 Ba 2070 1500 2020 1640 1820 2170 2080 2010 Th 50.6 63.3 46.6 48.7 55.9 53.3 62.6 10.0 U 7.56 10.3 8.10 8.36 9.25 8.83 9.93 9.14 Nb 18.6 23.2 20.0 20.4 20.3 19.9 20.4 22.5 Sr 761 336 477 625 643 777 730 689 Zr 184 274 246 227 247 263 254 251 Ti 2001 2634 2269 2144 2105 2462 2190 2302 La 102 107 98.7 109 117 91.0 118 91.6 Ce 159 186 161 178 211 196 210 250 Pr 17.1 18.9 16.5 17.6 18.6 16.6 19.3 16.7 Nd 53.6 67.3 57.1 59.6 61.0 63.9 66.0 60.9 Sm 8.44 10.60 9.16 8.87 9.50 9.57 9.41 9.63 Eu 1.61 1.83 1.72 1.83 1.91 2.11 1.87 1.97 Gd 5.59 7.46 6.15 6.31 6.55 6.70 6.41 6.52 Tb 0.72 0.94 0.80 0.77 0.82 0.88 0.85 0.85 Dy 3.54 4.60 3.76 3.89 4.12 4.30 4.03 4.28 Ho 0.65 0.85 0.73 0.76 0.77 0.78 0.74 0.82 Er 1.84 2.35 2.02 1.97 2.00 2.04 2.03 2.14 Tm 0.25 0.32 0.26 0.28 0.28 0.31 0.30 0.31 Yb 1.53 2.14 1.78 1.72 1.78 1.84 1.82 1.98 Lu 0.23 0.30 0.25 0.27 0.27 0.28 0.27 0.29 Y 19.1 24.3 22.0 19.9 20.6 21.4 20.8 22.2 ΣREE 356.10 410.58 359.94 390.88 435.61 396.30 441.03 447.99 LREE 341.75 391.63 344.18 374.90 419.01 379.18 424.58 430.80 HREE 14.35 18.95 15.76 15.98 16.60 17.12 16.45 17.19 LREE/HREE 23.81 20.67 21.84 23.46 25.24 22.14 25.82 25.07 (La/Yb)N 47.82 35.86 39.77 45.46 47.15 35.48 46.51 33.18 δEu 0.72 0.63 0.70 0.75 0.74 0.81 0.74 0.76 δCe 0.93 1.01 0.98 1.00 1.11 1.24 1.08 1.57 CaF2 2.06 9.34 5.18 1.44 3.66 0.74 1.50 0.51 表 2 黎川上水桥萤石矿床萤石微量元素(10−6)分析结果表
Table 2. Analysis results of fluorite trace elements (10−6) in the Shangshuiqiao fluorite deposit in Lichuan
样品号 样品名 Rb Ba Th U Nb Sr Zr Ti La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd ZK3402-1 白色萤石 — — 0.008 — 0.003 67.20 — — 1.00 2.51 0.43 2.78 1.99 0.81 4.97 ZK3402-2 白色萤石 — — — — — 84.23 — — 1.61 3.13 0.64 3.51 2.61 0.97 4.92 ZK3402-3 白色萤石 — 0.017 — — — 87.33 — — 2.40 5.99 1.13 6.26 3.35 1.54 6.00 ZK3402-4 白色萤石 — — — 0.002 — 45.17 — — 1.29 4.18 0.76 4.93 3.28 1.32 6.33 ZK3402-5 白色萤石 — 0.064 0.015 — — 98.35 0.026 — 3.68 8.60 1.46 6.72 4.27 1.70 7.68 ZK3402-6 白色萤石 0.023 — 0.001 — — 103.2 — — 2.16 4.54 0.89 4.49 2.41 1.09 4.96 ZK3402-7 白色萤石 0.017 — — — 0.008 84.43 0.018 — 1.24 2.07 0.33 1.58 0.53 0.40 1.27 ZK3402-8 白色萤石 — — — — — 100.6 0.012 — 1.96 4.27 0.72 4.69 2.00 1.01 4.67 ZK3402-9 白色萤石 0.016 0.092 0.013 0.004 — 100.7 — — 3.07 6.67 1.11 6.30 3.69 1.73 7.81 ZK3402-10 白色萤石 — — — 0.013 — 111.3 — — 1.60 2.88 0.47 3.12 1.84 0.79 3.69 ZK3402-11 白色萤石 — — — 0.017 — 100.2 — — 1.02 2.24 0.37 2.23 1.28 0.35 2.13 ZK3402-12 白色萤石 0.022 — — — — 86.81 0.005 0.903 3.34 6.94 0.96 5.69 3.94 1.81 7.32 ZK3402-13 白色萤石 0.005 — — — — 115.2 — — 3.01 6.51 1.18 6.14 3.31 1.36 6.83 ZK3402-14 白色萤石 0.033 0.084 0.034 — — 94.09 0.055 — 3.25 6.68 1.17 8.03 5.35 2.76 12.9 ZK3403-1 紫色萤石 0.149 0.134 0.016 0.005 — 104.4 — — 8.62 12.8 1.12 4.98 0.76 0.48 1.10 ZK3403-2 紫色萤石 — — 0.003 0.006 — 92.66 — — 5.46 7.49 0.78 3.84 0.98 0.47 1.62 ZK3403-3 紫色萤石 0.003 0.053 0.002 0.006 — 95.80 — — 5.37 7.03 0.93 4.39 0.92 0.69 1.05 ZK3403-4 紫色萤石 — — — 0.006 0.008 73.80 — 0.444 5.85 7.86 0.91 3.94 1.17 0.48 1.49 ZK3403-5 紫色萤石 0.014 0.070 — 0.012 — 83.55 — — 5.78 8.53 1.17 5.90 1.89 0.75 1.87 ZK3403-6 紫色萤石 — — — — — 84.04 — — 4.94 6.75 0.93 3.45 1.48 0.74 1.50 ZK3403-7 紫色萤石 — — — — — 67.33 — — 4.92 6.59 0.81 3.47 1.31 0.59 2.36 ZK3403-8 紫色萤石 0.005 0.065 — 0.001 — 75.19 — 0.610 5.93 7.96 0.97 3.92 1.09 0.68 2.57 ZK4602-1 深绿色萤石 — 0.074 0.004 0.114 — 152.9 0.012 — 141 314 44.0 165 31.3 25.4 27.9 ZK4602-2 深绿色萤石 0.073 0.041 — 0.255 — 180.2 — — 156 374 49.4 191 32.7 24.1 23.6 ZK4602-3 深绿色萤石 — — — 0.107 — 150.4 — 0.334 108 247 36.7 151 28.5 20.9 28.3 ZK4602-4 深绿色萤石 0.017 0.302 — 0.094 — 127.0 — — 55.4 127 19.8 95.7 24.8 13.9 25.6 ZK4602-5 深绿色萤石 — — — 0.131 — 128.5 — — 72.1 164 28.5 136 36.6 17.7 40.6 ZK4602-6 浅绿色萤石 0.258 0.192 — 0.090 — 180.2 — 0.106 7.55 9.83 1.10 3.57 0.53 0.94 0.26 ZK4602-7 浅绿色萤石 0.270 0.190 — 0.084 0.005 175.3 — — 7.63 7.69 0.82 3.00 0.63 0.85 0.42 ZK4602-8 浅绿色萤石 0.145 0.467 — 0.088 — 177.5 — 0.515 8.18 9.93 1.04 3.41 0.71 0.69 0.35 ZK4602-9 浅绿色萤石 0.314 0.410 — 0.136 — 187.8 0.045 — 15.3 18.5 1.74 2.79 0.45 1.16 0.45 ZK4602-10 浅绿色萤石 0.025 0.139 — 0.182 — 173.4 — — 87.5 135 11.4 26.5 1.55 5.66 1.15 ZK4602-11 浅绿色萤石 — 0.121 0.008 0.124 0.010 162.0 0.220 — 25.3 53.4 4.08 11.5 1.45 2.87 1.00 ZK4602-12 浅绿色萤石 0.118 0.216 — 0.211 — 173.5 — — 31.9 42.7 3.52 8.22 0.96 1.63 0.99 ZK4602-13 浅绿色萤石 0.027 0.037 — 0.120 — 141.7 0.010 — 14.5 23.3 2.69 7.44 0.64 4.05 0.31 续表2 样品号 样品名 Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y ΣREE LREE HREE LREE/
HREELaN/YbN δEu δCe ZK3402-1 白色萤石 1.10 8.71 1.89 6.11 0.75 4.80 0.598 85.1 38.46 9.52 28.94 0.33 0.15 0.78 0.94 ZK3402-2 白色萤石 0.87 7.16 1.73 4.74 0.68 4.28 0.593 79.3 37.44 12.47 24.97 0.50 0.27 0.83 0.76 ZK3402-3 白色萤石 1.34 11.3 2.45 7.06 1.12 7.72 0.952 95.5 58.60 20.67 37.94 0.54 0.22 1.05 0.89 ZK3402-4 白色萤石 1.34 10.4 2.35 7.39 1.19 8.23 1.308 80.7 54.25 15.75 38.49 0.41 0.11 0.88 1.04 ZK3402-5 白色萤石 1.61 12.5 3.07 8.78 0.92 5.85 0.801 152 67.65 26.43 41.23 0.64 0.45 0.91 0.91 ZK3402-6 白色萤石 1.06 8.20 1.77 4.73 0.61 4.03 0.500 81.5 41.46 15.59 25.86 0.60 0.39 0.96 0.80 ZK3402-7 白色萤石 0.31 1.93 0.34 1.41 0.14 1.22 0.131 21.0 12.90 6.15 6.76 0.91 0.72 1.49 0.80 ZK3402-8 白色萤石 0.81 6.33 1.35 4.21 0.65 3.29 0.381 68.5 36.35 14.66 21.69 0.68 0.43 1.01 0.88 ZK3402-9 白色萤石 1.60 11.6 2.82 7.98 0.90 5.86 0.776 151 61.90 22.57 39.32 0.57 0.38 0.98 0.89 ZK3402-10 白色萤石 0.67 4.60 1.27 3.44 0.41 2.43 0.364 56.6 27.55 10.69 16.86 0.63 0.47 0.92 0.82 ZK3402-11 白色萤石 0.45 3.05 0.71 2.26 0.22 1.48 0.295 27.7 18.10 7.49 10.60 0.71 0.50 0.65 0.89 ZK3402-12 白色萤石 1.55 9.90 2.62 7.86 1.02 5.52 0.783 137 59.25 22.68 36.57 0.62 0.43 1.03 0.95 ZK3402-13 白色萤石 1.54 8.69 2.34 7.65 0.93 5.11 0.631 148 55.24 21.51 33.73 0.64 0.42 0.88 0.85 ZK3402-14 白色萤石 2.67 17.3 4.29 11.8 1.61 9.28 1.112 257 88.22 27.25 60.97 0.45 0.25 1.02 0.84 ZK3403-1 紫色萤石 0.15 1.01 0.17 0.47 0.05 0.33 0.051 6.66 32.04 28.72 3.32 8.64 18.67 1.60 1.01 ZK3403-2 紫色萤石 0.16 0.96 0.13 0.33 0.03 0.14 0.058 8.46 22.44 19.02 3.42 5.56 28.46 1.15 0.89 ZK3403-3 紫色萤石 0.14 0.68 0.12 0.35 0.02 0.33 0.053 7.94 22.06 19.32 2.74 7.05 11.64 2.15 0.77 ZK3403-4 紫色萤石 0.31 1.04 0.29 0.66 0.07 0.46 0.094 10.3 24.63 20.22 4.41 4.59 9.15 1.12 0.84 ZK3403-5 紫色萤石 0.32 2.25 0.36 1.10 0.17 1.09 0.146 15.6 31.33 24.02 7.31 3.29 3.81 1.22 0.80 ZK3403-6 紫色萤石 0.22 1.52 0.28 0.57 0.09 0.60 0.088 8.94 23.14 18.28 4.86 3.76 5.89 1.51 0.77 ZK3403-7 紫色萤石 0.18 1.27 0.25 0.64 0.09 0.29 0.080 10.3 22.85 17.69 5.16 3.43 12.20 1.02 0.81 ZK3403-8 紫色萤石 0.30 1.76 0.30 0.80 0.16 0.78 0.162 14.0 27.37 20.55 6.82 3.01 5.48 1.25 0.81 ZK4602-1 深绿色萤石 3.03 18.1 3.06 7.43 0.90 8.33 1.565 231 791.3 721.0 70.24 10.26 12.18 2.63 0.98 ZK4602-2 深绿色萤石 2.36 12.3 1.92 4.99 0.69 6.40 1.027 138 879.7 826.4 53.27 15.51 17.48 2.66 1.04 ZK4602-3 深绿色萤石 3.24 20.1 3.64 9.21 1.42 12.1 2.027 216 671.7 591.7 79.99 7.40 6.40 2.25 0.96 ZK4602-4 深绿色萤石 3.98 22.5 4.07 11.1 1.62 13.3 2.638 249 421.6 336.8 84.81 3.97 2.98 1.69 0.94 ZK4602-5 深绿色萤石 5.85 38.4 8.19 22.3 3.08 25.6 4.408 428 603.6 455.2 148.4 3.07 2.02 1.40 0.89 ZK4602-6 浅绿色萤石 0.01 0.14 0.02 0.04 — 0.01 — 2.86 24.02 23.52 0.50 46.93 440.9 7.68 0.84 ZK4602-7 浅绿色萤石 0.03 0.16 0.05 0.06 — 0.10 — 6.13 21.44 20.62 0.82 25.03 54.14 5.04 0.75 ZK4602-8 浅绿色萤石 0.06 0.34 0.03 0.07 0.05 0.10 0.020 3.95 24.98 23.96 1.02 23.59 57.49 4.18 0.84 ZK4602-9 浅绿色萤石 0.04 0.25 0.02 0.01 — — 0.004 2.34 40.67 39.89 0.78 50.90 — 7.86 0.88 ZK4602-10 浅绿色萤石 0.04 0.10 — 0.02 — 0.01 0.004 3.40 268.5 267.2 1.34 199.1 4397 12.96 1.04 ZK4602-11 浅绿色萤石 0.01 0.29 — 0.04 — 0.01 — 3.37 99.96 98.58 1.38 71.66 1489 7.27 1.29 ZK4602-12 浅绿色萤石 0.06 0.33 0.06 0.23 0.01 0.24 0.004 6.92 90.85 88.93 1.92 46.39 95.04 5.11 0.99 ZK4602-13 浅绿色萤石 0.05 0.23 — 0.02 — 0.10 0.002 2.99 53.32 52.60 0.72 72.76 103.4 27.70 0.91 注:“—”为低于检测限。 -
[1] 敖平, 陈克昱, 李强, 等 . 江西省黎川县上水桥矿区成矿潜力研究[J]. 世界有色金属,2020 , (15 ):217 −218 .AO Ping, CHEN Keyu, LI Qiang, et al . Research on Metallogenic Potential of Shangshuiqiao Mining Area, Lichuan County, Jiangxi Province[J]. World Nonferrous Metal,2020 , (15 ):217 −218 .[2] 曹华文, 张寿庭, 高永璋, 等 . 内蒙古林西萤石矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 地球化学,2014 ,43 (2 ):131 −140 .CAO Huawen, ZHANG Shouting, GAO Yongzhang, et al . REE geochemistry of fluorite from Linxi fluorite deposit and its geological implications, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[J]. Geochimica,2014 ,43 (2 ):131 −140 .[3] 曹俊臣 . 中国萤石矿床分类及其成矿规律[J]. 地质与勘探,1987 , (3 ):12 −17 .CAO Junchen . The classification and minerogenic regularity of fluorite deposits in China[J]. Geology and Exploration,1987 , (3 ):12 −17 .[4] 曹俊臣 . 中国与花岗岩有关的萤石矿床地质特征及成矿作用[J]. 地质与勘探,1994 ,30 (5 ):1 −6 .CAO Junchen . Geological feature and mineralization of fluorite deposit related to granite in China[J]. Geology and Prospecting,1994 ,30 (5 ):1 −6 .[5] 曹俊臣 . 华南低温热液脉状萤石矿床稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学,1995 , (3 ):225 −234 .CAO Junchen . REE geochemical characteristics of epithermal vein fluorite deposits in south China[J]. Geochimica,1995 , (3 ):225 −234 .[6] 方乙, 张寿庭, 邹灏, 等 . 浅覆盖区萤石矿综合勘查方法研究——以内蒙古林西赛波萝沟门萤石矿为例[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2014 ,41 (1 ):94 −101 .FANG Yi, ZHANG Shouting, ZOU Hao, et al . Comprehensive exploration method for fluorite deposits in grassands covered area.A case study of the Saiboluogoumen fluorite deposit in Linxi, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition),2014 ,41 (1 ):94 −101 .[7] 黄鸿新, 罗平, 常斯敏, 等 . 江西簧碧萤石矿床萤石稀土元素特征与成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 矿产与地质,2018 ,32 (4 ):641 −646+654 .HUANG Hongxin, LUO Pin, CANG Siming, et al . Geological features and metallogenic perspective predictionof Shipengzi iron deposit in Fushun County of Liaonin Province[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology,2018 ,32 (4 ):641 −646+654 .[8] 金松, 王春连, 高立湧, 等 . 闽北羊角尾萤石矿成因: 来自稀土、微量元素地球化学的证据[J]. 地球学报,2022 ,43 (3 ):371 −382 .JIN Song, WANG Chunlian, GAO Liyong, et al . Evidence from REE and Trace Element Geochemistry for Genesis of Yangiaowei Fluorite Deposit in Northern Fujian[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2022 ,43 (3 ):371 −382 .[9] 李长江, 蒋叙良 . 中国东南部两类萤石矿床的成矿模式[J]. 地质学报,1991 , (3 ):263 −274 .LI Changjiang, JIANG Xuliang . The Minerogenetic Model of Two Types of Fluorite Deposits in Southeastern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,1991 , (3 ):263 −274 .[10] 栗克坤, 王春连, 陈新立, 等 . 福建邵武地区萤石矿微量、稀土元素特征及对成矿物质指示[J]. 中国地质,2021 ,50 (3 ):806 −817 .LI Kekun, WANG Chunlian, CHEN Xinli, et al . Characteristics of trace and rare earth elements and direction for ore-forming materials in Shaowu area, Fujian Province[J]. Geology in China,2021 ,50 (3 ):806 −817 .[11] 李敬, 高永璋, 张浩 . 中国萤石资源现状及可持续发展对策[J]. 中国矿业,2017 ,26 (10 ):7 −14 .LI Jing, GAO Yongzhang, ZHANG Hao . Fluorite resource status and its sustainable development countermeasures in China[J]. China Mining Magazine,2017 ,26 (10 ):7 −14 .[12] 李培铮, 邓国萍, 陶红, 等 . 赣东北壳体构造演化与铜(金)多金属成矿系列[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,1999 ,23 (4 ):300 −307 .LI Peizheng, DENG Guoping, TAO Hong, et al . Analysis of tectonic evolution and major Cu (Au) polymetallic metallogenic series in northeast Jiangxi Province[J]. Geoteetonic et Metallogenia,1999 ,23 (4 ):300 −307 .[13] 黎彤, 袁怀雨 . 大洋岩石圈和大陆岩石圈的元素丰度[J]. 地球化学,2011 ,40 (1 ):1 −5 .LI Tong, YUAN Huaiyu . Element abundance in the oceanic and the continental lithospheres[J]. Geochimica,2011 ,40 (1 ):1 −5 .[14] 刘迅, 孙知明, 马寅生, 等. 武夷山北部及周边地区控矿构造及成矿预测[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1999. [15] 刘磊, 林国宣, 谢晓亮 . 武夷成矿带闽西北部萤石矿床地质特征及成矿启示[J]. 中国矿业,2013 ,22 (S1 ):139 −142+200 .LIU Lei, LIN Guoxuan, XIE Xiaoliang . Geological characeristics of fluorite deposits, western Fujian, Wuyi metallogenic belt and their implications for mineralization[J]. China Mining Magazine,2013 ,22 (S1 ):139 −142+200 .[16] 刘英俊, 曹励明.元素地球化学导论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987. LIU Yingjun, CAO Liming. Element Geochemistry Intro duction[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987. [17] 梅勇文 . 武夷山造山带及其成矿过程[J]. 江西地质,1998 ,12 (2 ):109 −115 .MEI Yongwen . The Wuyishan orogen and its ore-forming process[J]. Jiangxi Geology,1998 ,12 (2 ):109 −115 .[18] 彭建堂, 胡瑞忠, 蒋国豪 . 萤石Sm-Nd同位素体系对晴隆锑矿床成矿时代和物源的制约[J]. 岩石学报,2003 ,19 (4 ):785 −791 .PENG Jiantang, HU Ruizong, JIANG Guohao . Samarium-Nodymium isotope system of fluorites from the Qinglong antimonydeposit, Guizhou Province:Constraints on the mineralizing age and ore-forming materials' sources[J]. Aeta Petrologiea Sinica,2003 ,19 (4 ):785 −791 .[19] 万禄进, 刘传侦, 冯德志 . 江西省黎川县上水桥金、萤石矿区控矿断裂形成的时效性及脉岩对成矿的屏蔽作用[J]. 福建地质,2000 , (4 ):197 −204 .WAN Lujin, LUI Chuanzhen, FENG Dezhi . Discussion on the Limitation Period of Forming Ore-Controlled Faults and the Shielding of Vein Rocks against Mineralizationin the Shangshuiqiao Gold and Fluorite Mining, Lichuan, Jiangxi Province[J]. Geology of Fujian,2000 , (4 ):197 −204 .[20] 王国芝, 胡瑞忠, 刘颖, 等 . 黔西南晴隆锑矿区萤石的稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石,2003 ,23 (2 ):62 −65 .WAN Guozhi, HU Ruizong, LIU Ying, et al . REE Geochemical Characteristics of Fluorite in the Qinglong Antimony Deposit, Southwestern Guizhou[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology,2003 ,23 (2 ):62 −65 .[21] 王吉平, 商朋强, 熊先孝, 等 . 中国萤石矿床成矿规律[J]. 中国地质,2015 ,42 (1 ):18 −32 .WANG Jiping, SHANG Pengqiang, XIONG Xianxiao, et al . Metallogenic regularities of fluorite deposits in China[J]. Geology in China,2015 ,42 (1 ):18 −32 .[22] 王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华. 稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989. WANG Zhonggang, YU Xueyuan, ZHAO Zhenhua. REE Chemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989. [23] 舒良树, 于津海, 贾东, 等 . 华南东段早古生代造山带研究[J]. 地质通报,2008 ,27 (10 ):1581 −1593 .SHU Liangshu, YU Jinhai, JIA Dong, et al . Early Paleozoic orogenic belt in the eastern segment of South China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2008 ,27 (10 ):1581 −1593 .[24] 孙海瑞, 黄智龙, 周家喜, 等 . 热液矿床中萤石的稀土元素地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,2014 ,33 (1 ):185 −193 .SUN Hairui, HUANG Zhilong, ZHOU Jiaxi, et al . Rare earth elements geochemistry of fluorite in hydrothermal deposits and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2014 ,33 (1 ):185 −193 .[25] 夏学惠, 韩豫川, 连卫, 等 . 浙江八面山萤石矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 化工矿产地质,2009 ,31 (4 ):193 −200 .XIA Xuehui, HAN Yuchuan, LIAN Wei, et al . Studies on genesis of unique fluorite deposit in Bamianshan Zhejiang Province[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals,2009 ,31 (4 ):193 −200 .[26] 许东青, 聂凤军, 钱明平, 等 . 苏莫查干敖包超大型萤石矿床的稀土元素地球化学特征及其成因意义[J]. 矿床地质,2009 ,28 (1 ):29 −41 .XU Dongqing, NIE Fengjun, QIAN Mingping, et al . REE geochemistry and genesis of Sumochagan Obo superlarge fluorite deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits,2009 ,28 (1 ):29 −41 .[27] 游超, 王春连, 刘殿鹤, 等 . 江西宁都坎田萤石矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 地球学报,2022 ,43 (3 ):359 −370 .YOU Chao, WANG Chunlian, LIU Dianhe, et al . REE Geochemistry of Fluorite from Kantian Fluorite Deposit and Its Geological Implications in Ningdu Area, Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2022 ,43 (3 ):359 −370 .[28] 曾勇廖, 群安 . 西武夷地区加里东期花岗岩与造山过程[J]. 地质通报,2000 ,19 (4 ):344 −349 .ZENG Yongliao, QUN An . Caledonian granite in the western Wuyi area and inversion of the orogenic process[J]. Regional Geology of China,2000 ,19 (4 ):344 −349 .[29] 邹灏, 方乙, 陈合毛, 等 . 浙江天台盆地下陈萤石矿稀土元素地球化学特征及成因[J]. 中国地质,2014 ,41 (4 ):1375 −1386 .ZOU Hao, FANG Yi, CHEN Hemao, et al . REE geochemistry and genesis of the Xiachen fluorite deposit in Tiantai basin, Zhejiang Province[J]. Geology in China,2014 ,41 (4 ):1375 −1386 .[30] 邹灏, 淡永, 张寿庭, 等 . 重庆东南部彭水地区重晶石-萤石矿床的成矿物质来源探讨: 地球化学证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2016a ,40 (1 ):71 −85 .ZOU Hao, DAN Yong, ZHANG Shouting, et al . Geochemical Evidence for Sources of Ore-forming Material of Barite-Fluorite Deposits in Pengshui Area, Southeast Chongqing[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2016a ,40 (1 ):71 −85 .[31] 邹灏, 张强, 包浪, 等 . 浙江天台盆地下陈萤石矿床地质特征及ESR年代学[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016b ,43 (1 ):86 −94 .ZOU Hao, ZHANG Qiang, BAO Lang, et al . FANG YiGeological characteristics and ESR dating of Xiachen fluorite deposit in Tiantai basin, Zhejiang, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2016b ,43 (1 ):86 −94 .[32] 张潮, 黄涛, 刘向东, 等 . 胶西北新城金矿床热液蚀变作用[J]. 岩石学报,2016 ,32 (8 ):2433 −2450 .ZHANG Chao, HUANG Tao, LIU Xiangdong, et al . Hydrothermal alteration of the Xincheng gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2016 ,32 (8 ):2433 −2450 .[33] 张成信, 商朋强, 焦森, 等 . 内蒙古喀喇沁旗地区萤石矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质调查,2019 ,6 (6 ):79 −87 .ZHANG Chengxin, SHANG Pengqiang, JIAO Sen, et al . Geological characteristics and genesis analysis of fluorite deposits in Harqin Banner area of Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Survey of China,2019 ,6 (6 ):79 −87 .[34] 张苏坤, 王辉, 冯绍平, 等 . 河南省栾川县杨山萤石矿成矿作用: 来自氢氧同位素和元素地球化学的约束[J]. 西北地质,2022 ,55 (2 ):209 −216 .ZHANG Sukun, WANG hui, FENG Shaoping, et al . Mineralization of Yangshan Fluorite Deposit in Luanchuan County, Henan Province: Constraints from H-O Isotopes and Element Geochemistry[J]. Northwestern Geology,2022 ,55 (2 ):209 −216 .[35] 赵辛敏, 高永宝, 燕洲泉, 等 . 阿尔金卡尔恰尔超大型萤石矿带成因: 来自年代学、稀土元素和Sr–Nd同位素的约束[J]. 西北地质,2023 ,56 (1 ):31 −47 .ZHAO Xinmin, GAO Yongbao, YAN Zhouquan, et al . Genesis of Kalqiaer Super–large Fluorite Zone in Altyn Tagh Area: Chronology, Rare Earth Elements and Sr–Nd Isotopes Constraints[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023 ,56 (1 ):31 −47 .[36] 朱利岗, 金松, 王春连, 等 . 福建浦城地区萤石矿床围岩和矿石地球化学特征及成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,2021 ,40 (5 ):923 −938 .ZHU Ligang, JIN Song, WANG Chunlian, et al . Geochemistry characteristic ana geriesis oi surrounding rock and ore in Pucheng fluorite deposits district Fujian Province[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2021 ,40 (5 ):923 −938 .[37] Bau M, Moeller P . Rare-earth element fractionation in metamorphogenic hydrothermal calcite, magnesite and siderite[J]. Mineralogy and petrology,1992 ,45 :231 −246 .[38] Bau M, Dulski P . Comparative study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviours in fluorine-rich hydrothermal fluids[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1995 ,119 :213 −223 .[39] Chen J, Liu Y, Yan L, et al . Research on development trend of strategic nonmetallic minerals such as graphite and fluorite[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2021 ,42 (2 ):287 −296 .[40] Constantopoulos J . Fluid inclusions and rare earth element geochemistry of fluorite from south-central Idaho[J]. Economic Geology,1988 ,83 (3 ):626 −636 .[41] Charvet J, Shu L, Faure M, et al . Structural development of the Lower Paleozoic belt of South China: genesis of an intracontinental orogen[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2010 ,39 (4 ):309 −330 .[42] Dill H G, Hansen B T, Weber B . REE contents, REE minerals and Sm/Nd isotopes of granite-and unconformity-related fluorite mineralization at the western edge of the Bohemian Massif: With special reference to the Nabburg-Wölsendorf District, SE Germany[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2011 ,40 (1 ):132 −148 .[43] Faure M, Shu L, Wang B, et al . Intracontinental subduction: a possible mechanism for the Early Palaeozoic Orogen of SE China[J]. Terra Nova,2009 ,21 (5 ):360 −368 .[44] Graf J L . Rare earth elements as hydrothermal tracers during the formation of massive sulfide deposits in volcanic rocks[J]. Economic Geology,1977 ,72 (4 ):527 −548 .[45] Irber W . The lanthanide tetrad effect and its correlation with K/Rb, Eu/Eu*, Sr/Eu, Y/Ho, and Zr/Hf of evolving peraluminous granite suites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1999 ,63 (3−4 ):489 −508 .[46] Li Z, Li J, Wu H H, et al . Effect of electric field orientation on ferroelectric phase transition and electrocaloric effect[J]. Acta Materialia,2020 ,191 :13 −23 .[47] Liu D, Wang C, Zhang X, et al. Implications for the contribution of Pacific plate subduction to fluorite mineralization in Southeast China: evidence from Nanzhou large fluorite deposit, Fujian Province[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2023: 105385. [48] Möller P, Parekh P P, Schneider H J . The application of Tb/Ca-Tb/La abundance ratios to problems of fluorspar genesis[J]. Mineralium Deposita,1976 ,11 (1 ):111 −116 .[49] Möller P. On the geochemical fractionation of ram earth elements during the formation of Ca-minerals and its application to problems of the genesis of ore deposits[J]. The significance of trace elements in solving petrogenetic problems and controversies, 1983: 747-791. [50] Paton C, Hellstrom J, Paul B, et al . Iolite: Freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry,2011 ,26 (12 ):2508 −2518 .[51] Richardson C K, Holland H D . The solubility of fluorite in hydrothermal solutions, an experimental study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1979 ,43 (8 ):1313 −1325 .[52] Rollinson H R. Using geochemical data: evaluation, presentation, interpretation[M]. Routledge, 2014. [53] Sun S S, McDonough W F . Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications,1989 ,42 (1 ):313 −345 .[54] Strong D F, Fryer B J, Kerrich R . Genesis of the St. Lawrence fluorspar deposits as indicated by fluid inclusion, rare earth element, and isotopic data[J]. Economic Geology,1984 ,79 (5 ):1142 −1158 .[55] Taylor R P . Rare earth element geochemistry as an aid to interpreting hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Metallization Associated with Acid Magmatism,1982 357 −365 .[56] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The continental crust: its composition and evolution[M]. London: Blackwell Scientific, 1985. [57] Veksler I V, Dorfman A M, Kamenetsky M, et al . Partitioning of lanthanides and Y between immiscible silicate and fluoride melts, fluorite and cryolite and the origin of the lanthanide tetrad effect in igneous rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2005 ,69 (11 ):2847 −2860 .[58] Williams-Jones A E, Samson I M, Olivo G R . The genesis of hydrothermal fluorite-REE deposits in the Gallinas Mountains, New Mexico[J]. Economic Geology,2000 ,95 (2 ):327 −341 .[59] Wan Y, Liu D, Wilde S A, et al . Evolution of the Yunkai Terrane, South China: evidence from SHRIMP zircon U–Pb dating, geochemistry and Nd isotope[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2010 ,37 (2 ):140 −153 .[60] Wang Y, Fan W, Zhao G, et al . Zircon U–Pb geochronology of gneissic rocks in the Yunkai massif and its implications on the Caledonian event in the South China Block[J]. Gondwana Research,2007 ,12 (4 ):404 −416 .[61] Wang Y, Zhang A, Fan W, et al . Kwangsian crustal anatexis within the eastern South China Block: geochemical, zircon U–Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic fingerprints from the gneissoid granites of Wugong and Wuyi–Yunkai Domains[J]. Lithos,2011 ,127 (1−2 ):239 −260 .[62] Xu X S . Late Mesozoic-Cenozoic basaltic rocks and crust-mantle interaction, SE China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2005 ,11 :318 −314 .[63] Yang S W, Feng C Y, Lou F S, et al . Origin of the Tongda fluorite deposit related to the Palaeo‐Pacific Plate subduction in southern Jiangxi Province, China: New evidence from geochronology, geochemistry, fluid inclusion, and H–O isotope compositions[J]. Geological Journal,2022 ,57 (1 ):238 −253 .[64] Yu X, Wu G, Zhao X, et al . New geochronological data from the Paleozoic and Mesozoic nappe structures, igneous rocks, and molybdenite in the North Wuyi area, Southeast China[J]. Gondwana Research,2012 ,22 (2 ):519 −533 .[65] Zhao F . The chronotectonic framework of Pre-Caledonian basements from Cathaysia block[J]. Progress in Pre-Cambrian Research,1999 ,22 (2 ):39 −46 . -



 下载:
下载: