Quantitative Determination of Calcium Rare Earth Fluoro-carbonate Minerals by Electron Probe Microanalyzer
-
摘要:
稀土氟碳酸盐矿物是工业开发利用轻稀土元素的主要赋存矿物。钙稀土氟碳酸盐矿物化学成分的准确测定,是快速鉴别其种属的前提,也是研究稀土矿床的成因和高效开发利用稀土矿产的必然要求。通过测试条件优选、C含量直接测定并校正计算,完善了利用电子探针准确分析钙稀土氟碳酸盐矿物化学成分的定量分析方法。采用理论分子式法和电荷平衡法对样品中C含量进行校准计算,结果显示理论分子式法计算结果更合理。笔者对赋存在金川正长花岗岩中的钙稀土氟碳酸盐矿物化学成分进行电子探针分析和结构拉曼光谱分析。结果表明,该矿物组合存在多种物相,以新奇钙铈矿为主,氟碳钙铈矿和伦琴钙铈矿呈微细针状分布于新奇钙铈矿中。结合矿物共生关系,认为金川正长花岗岩中钙稀土氟碳酸盐矿物为岩浆作用晚期,富F−、CO2、REE3+流体与磷灰石交代反应生成。
Abstract:Rare earth fluoro-carbonate minerals are the most important LREE-bearing minerals in industrial development. Accurate determination of the chemical composition of calcium rare earth fluoro-carbonates is a prerequisite for rapid identification of their species and an essential requirement for studying the genesis of rare earth deposits and the efficient development and utilization of rare earth resources. In this study, by optimizing the experimental conditions, direct determination of carbon content with a subsequent calibration, we have improved the quantitative analytical method for accurately analyzing the chemical composition of calcium rare earth fluoro-carbonate minerals using an EPMA. The calibration calculation of carbon content in the samples was performed using both theoretical crystallochemical formula and charge balance methods, and the results showed that the theoretical crystallochemical formula method yielded more reasonable results. Based on compositional analysis by EPMA and structural analysis by Laser Raman Spectroscopy, Jinchuan syenogranite comprises at least two species of calcium rare earth fluoro-carbonate minerals. The predominant phase is synchysite, the minor phase that exhibited as radial needles is parasite or roentgenite-(Ce). Based on the mineral paragenesis, it is believed that the calcium rare earth fluoro-carbonate minerals in the Jinchuan syenogranite are formed during the post-magmatic stage due to the metasomatism of apatite by F−, CO2, and REE3+-rich fluids.
-

-
表 1 4种常见钙稀土氟碳酸盐矿物的化学特征(据张培善,1998;Donnay等,1953修改)
Table 1. Chemical composition of four common calcium rare earth fluoro-carbonate Minerals
矿物名称 英文名称 代号 理想化学式 化学成分(%) REE2O3 CaO CO2 F 氟碳铈矿 Bastnaesite B (Ce,La) [CO3]F 74.77 − 20.17 8.73 氟碳钙铈矿 Parisite BS (Ce,La)2Ca[CO3]3F2 60.97 10.42 24.58 7.07 伦琴钙铈矿 Roentgenite-Ce BS2 (Ce,La)3Ca2[CO3]5F3 57.24 13.12 25.77 6.63 新奇钙铈矿 Synchysite S (Ce,La) Ca[CO3]2F 51.25 17.62 27.67 5.97 表 2 钙稀土氟碳酸盐矿物电子探针分析晶体选择及检出限
Table 2. Analytical crystal selection and element detection limits for calcium rare earth fluoro-carbonate in EPMA analysis
分析元素 选择晶体 检出限(10–6) 分析元素 选择晶体 检出限(10–6) F LDE1 344 Ce LiF 819 C LDE2 1654 Pr LiFH 913 Mg TAP 96 Nd LiFH 812 Fe LiF 303 Sm LiFH 871 Ca PETH 80 Eu LiFH 916 U PETH 226 Gd LiFH 972 Th PETH 206 Y TAP 272 La LiF 923 Zr PETH 233 表 3 金川正长花岗岩中钙稀土氟碳酸盐矿物电子探针分析结果表(%)
Table 3. EPMA results of calcium rare earth fluoro-carbonates in Jinchuan syenogranite
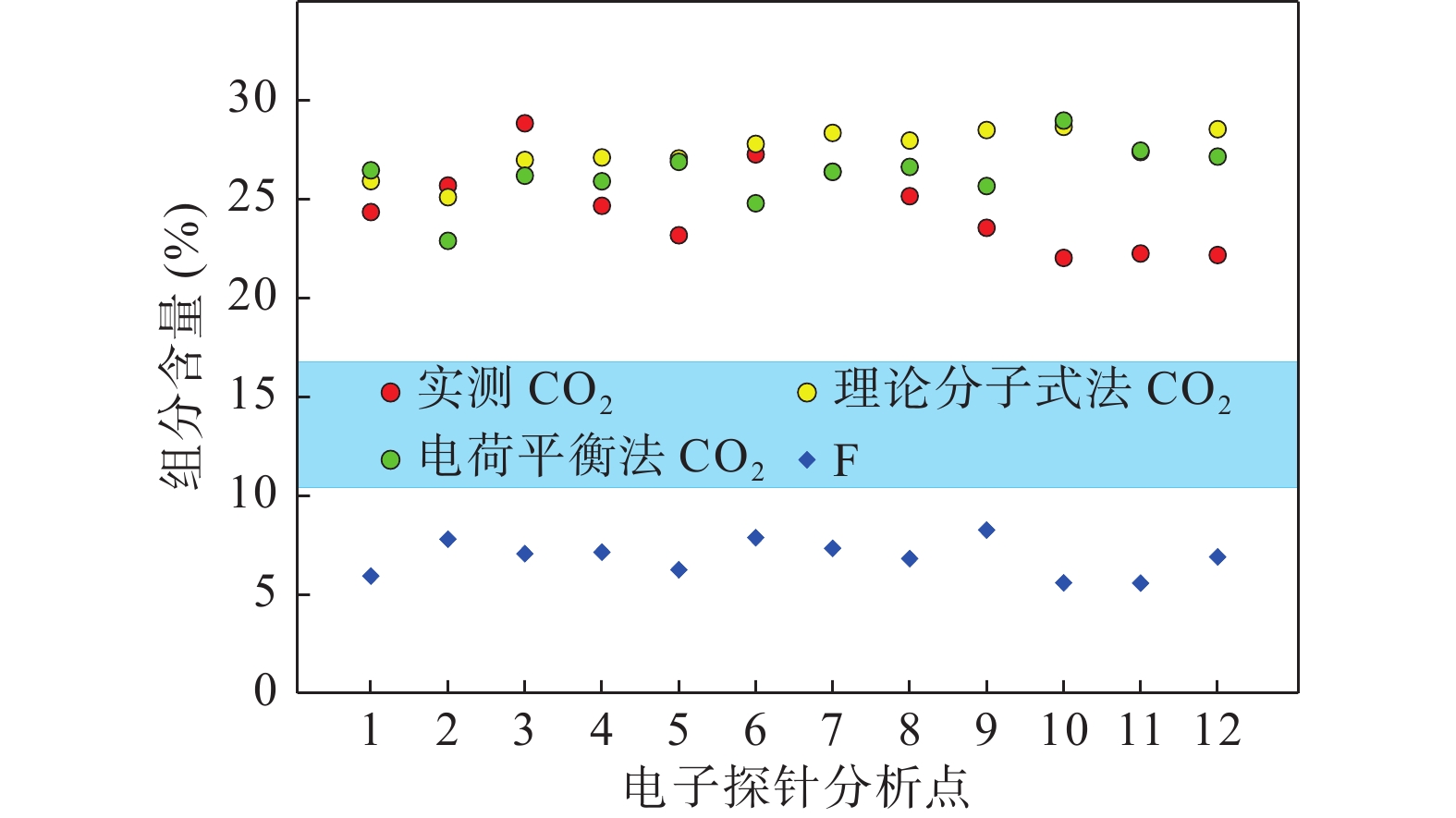
化学成分 点1 点2 点3 点4 点5 点6 点7 点8 点9 点10 点11 点12 实测值 F 5.97 7.83 7.10 7.18 6.29 7.91 7.37 6.85 8.29 5.63 5.61 6.94 CO2 24.34 25.68 28.83 24.66 23.17 27.26 26.37 25.14 23.55 22.03 22.25 22.18 MgO − 0.06 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.10 0.02 − 0.02 − 0.02 0.02 Gd2O3 0.31 0.22 1.84 1.82 1.66 − 0.59 0.42 0.64 0.31 − − Eu2O3 − 0.26 − − − − − − − − − 0.11 FeO 3.02 8.23 0.35 1.95 1.48 1.87 1.17 0.62 2.86 0.55 3.03 3.03 Sm2O3 0.64 0.10 40.88 0.74 0.47 0.59 1.19 0.47 1.11 1.03 0.13 0.92 Pr2O3 2.04 2.09 3.11 2.19 2.74 2.03 2.23 2.17 2.58 2.57 2.28 2.52 Ce2O3 26.26 23.80 24.01 20.86 22.98 21.69 21.43 25.14 22.58 24.23 22.91 24.53 La2O3 15.21 11.75 9.07 15.31 13.10 11.48 10.09 12.87 7.91 11.51 11.97 10.97 CaO 12.19 8.98 15.62 15.83 15.91 18.59 18.75 18.55 17.53 19.04 16.32 17.17 UO2 0.04 0.07 − 0.04 0.08 0.15 − 0.02 0.10 0.05 0.02 0.09 ThO2 2.54 4.61 2.23 4.44 3.42 2.19 1.56 1.03 3.41 1.75 2.31 0.60 Nd2O3 7.22 6.85 12.74 5.98 7.47 6.61 9.62 6.33 10.37 8.23 7.92 8.24 ZrO2 − 0.06 − 0.06 − − − − 0.06 0.02 0.07 − Y2O3 0.63 0.24 1.03 0.45 0.39 0.55 1.55 0.43 0.81 0.73 0.48 1.12 Total 97.88 97.52 103.81 98.52 96.52 97.69 98.83 97.16 98.33 95.30 92.99 95.50 ∑REE2O3 52.29 45.30 52.66 47.35 48.81 42.95 46.70 47.84 46.00 48.61 45.74 48.41 理论分子式法 CO21 25.90 25.09 26.97 27.10 27.05 27.79 28.34 27.95 28.48 28.65 27.38 28.52 Total1 99.44 96.93 101.95 100.96 100.40 98.22 100.80 99.97 103.26 101.92 98.12 101.85 电荷平衡法 CO22 26.45 22.89 26.18 25.90 26.88 24.79 26.38 26.62 25.66 28.96 27.44 27.14 Total2 99.99 94.72 101.16 99.76 100.24 95.23 98.84 98.64 100.44 102.24 98.18 100.46 矿物种属判别 Par/Roe Par/Roe Syn Syn Syn Syn Syn Syn Syn Syn Syn Syn 注:−表示低于检出限; 上角标1与 2分别表示按照理论分子式法(方法1)与电荷平衡法(方法2)计算得到的值。 -
[1] 陈其慎, 张艳飞, 邢佳韵, 等. 国内外战略性矿产厘定理论与方法[J]. 地球学报, 2021, 42(2): 137−144.
CHEN Qishen,ZHANG Yanfei,XING Jiayun,et al. Methods of Strategic Mineral Resources Determination in China and Abroad[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2021,42(2): 137−144.
[2] 程秀花, 李艳广, 叶美芳, 等. 西北地区地质实验测试技术研究进展及其在地质调查中的应用[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3): 170–190.
CHENG Xiuhua, LI Yanguang, YE Meifang, et al. Progress in the Research on Geochemical Analytic Technique and Its Application in Geological Survey in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 170–190.
[3] 范晨子, 詹秀春, 曾普胜, 等. 白云鄂博稀土氟碳酸盐矿物的 LA-ICP-MS 多元素基体归一定量分析方法研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2015, 34(6): 609−616.
FAN Chenzi, ZHAN Xiuchun, ZENG Pusheng, et al. Multi-element Content Analysis of Rare Earth Fluorocarbonates from Bayan Obo Deposit by Laser Ablation- Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis,2015,34(6):609−616.
[4] 龚大兴, 田恩源, 肖斌, 等. 川滇黔相邻区古陆相沉积型稀土的发现及意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2023, 42(5): 1025−1033.
GONG Daxing, TIAN Enyuan, XIAO Bin, et al. Significance and discovery of sedimentary REE deposits in adjacent areas of Sichuan, Yunnan and Guizhou[J]. Meneral Deposits,2023,42(5):1025−1033.
[5] 黄舜华, 王中刚, 章钟嵋, 等. 氟碳铈矿形成条件的实验研究[J]. 矿物学报, 1986, (6)2: 155−160. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1986.02.010
HUANG Shunhua, WANG Zhonggang, ZHANG Zhongmei, et al. Experimental studies of the conditions of formation of Bastnaesite[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,1986,(6)2:155−160. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1986.02.010
[6] 李献华, 苏犁, 宋彪, 等. 金川超镁铁侵入岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(4): 401−402. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.04.018
LI Xianhua, SU Li, SONG Biao, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating and geological significance of the Jinchuan ultramafic rocks[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2004,49(4):401−402. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.04.018
[7] 毛景文, 袁顺达, 谢桂青, 等. 21世纪以来中国关键金属矿产找矿勘查与研究新进展[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(5): 935−969.
MAO Jingwen, YUAN Shunda, XIE Guiqing, et al. New advances on metallogenic studies and exploration on critical minerals of China in 21st century[J]. Meneral Deposits,2019,38(5):935−969.
[8] 毛景文, 宋世伟, 刘敏, 等. 稀土矿床: 基本特点与全球分布规律[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(11): 3675−3697. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.11.001
MAO Jingwen, SONG Shiwei, LIU Min, et al. REE deposits: basic characteristics and global metallogeny[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2022,96(11):3675−3697. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.11.001
[9] 孟大维, 吴秀玲, 杨光明, 等. 氟碳钙铈矿6R2新多型的高分辨电镜研究[J]. 地球科学, 1994, 19(5): 655−661+719−720.
MENG Dawei,WU Xiuling,YANG Guangming,et al. A study of new polytype 6R2 in parasite by high resolution transmission electron microscopy[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences,1994,19(5): 655−661+719 −720.
[10] 孟大维, 吴秀玲, 潘兆橹, 等. 钙稀土氟碳酸盐矿物中三种B8S6型新规则混层结构的高分辨电镜研究[J]. 中国稀土学报, 1996, 14(, 1): 59−63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.1996.01.011
MENG Dawei, WU Xiuling, PAN Zhaolu, et al. HRTEM study of three new regular mixed-layer structures with type in calcium-rare earth fluorocarbonate minerals[J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society,1996,14(,1):59−63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.1996.01.011
[11] 万建军, 潘春蓉, 严杰, 等. 应用电子探针-扫描电镜研究陕西华阳川铀稀有多金属矿床稀土矿物特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(1): 145−155.
WAN Jianjun, PAN Chunrong, YAN Jie, et al. EMPA-SEM study on the rare earth minerals from the Huayangchuan uranium rare polymetallic deposit, Shaanxi Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis,2021,40(1):145−155.
[12] 王登红, 王瑞江, 孙艳, 等. 我国三稀(稀有稀土稀散)矿产资源调查研究成果综述[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37(5): 569−580. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.05.06
WANG Denghong, WANG Ruijiang, SUN Yan, et al. A Review of Achievements in the Three-type Rare Mineral Resources (Rare Resources, Rare Earth and Rarely Scattered Resources) Survey in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2016,37(5):569−580. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.05.06
[13] 王鲜华, 潘兆橹. 牦牛坪稀土矿区氟碳铈矿与氟碳钙铈矿矿物学[J]. 河北地质学院学报, 1996, 19(3−4): 307−313+479−480.
WANG Xianhua, PAN Zhaolu. The study on mineralogy of Bastnaesite and Paristie in Maoniuping ore deposite[J]. Journal of Hebei College of Geology,1996,19(3−4):307−313+479−480.
[14] 吴秀玲, 杨光明, 潘兆橹, 等. 钙-铈氟碳酸盐矿物系列中新规则混层矿物的晶格象研究[J]. 矿物学报, 1991, 11(3): 193−199+289−290. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1991.03.001
WU Xiuling, YANG Guangming, PAN Zhaolu, et al. Lattice image study of new regular mixed-layer minerals in the calcium-cerium Fluoro-carbonate mineral series[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,1991,11(3):193−199+289−290. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1991.03.001
[15] 吴秀玲, 杨光明, 潘兆橹. 钙-铈氟碳酸盐矿物中BmSn型新多型的发现及其微结构研究[J]. 电子显微学报, 1992, (3): 216−221.
WU Xiuling, YANG Guangming, PAN Zhaolu. Discovery of new polytypes of the BmSn in the calcium-cerium fluoro carbonate minerals and their microstructural study[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society,1992,(3):216−221.
[16] 吴秀玲, 杨光明, 潘兆橹. 氟碳钙铈矿及B2S规则混层矿物型体间共晶格取向连生的透射电镜研究[J]. 矿物学报, 1993, 13(3): 214−219+295−296. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1993.03.001
WU Xiuling, YANG Guangming, PAN Zhaolu. A TEM study of the syntaxies formed from the polytypes of parasite (BS) and regular mixed-layer mineral B2S[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,1993,13(3):214−219+295−296. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1993.03.001
[17] 吴秀玲, 孟大维, 杨光明, 等. 钙稀土氟碳酸盐矿物中体衍交生结构的电子显微镜研究[J]. 中国稀土学报, 1996, 14(, 2): 170−174. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.1996.02.016
WU Xiuling, MENG Dawei, YANG Guangming, et al. Study of transmission electron microscopy of the syntactic intergrowth structure in the calcium rare earth fluorocarbonate minerals[J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society,1996,14(,2):170−174. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.1996.02.016
[18] 解港, 周丽, 张为, 等. 氟碳铈矿-(La)的水热合成实验[J]. 矿物学报, 2018, 38(5): 469−473.
XIE Gang, ZHOU Li, ZHANG Wei, et al. Experimental study on the hydrothermal synthesis of Bastnaesite-(La)[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2018,38(5):469−473.
[19] 修迪, 徐翠, 何丽, 等. 氟碳铈矿、氟碳钙铈矿在岩矿鉴定及电子探针上的对比分析[J]. 中国锰业, 2017, 35(6): 63−65.
XIU Di, XU Cui, HE Li, et al. A Comparative Analysis of Bastnaesite and Parisite in Rock Ore Appraisal and Electronic Probe[J]. China’s Manganese Industry,2017,35(6):63−65.
[20] 修群业, 陆松年, 于海峰, 等. 龙首山岩群主体划归古元古代的同位素年龄证据[J]. 前寒武纪研究进展, 2002, 25(2): 93−96.
XIU Qunye, LU Songnian, YU Haifeng, et al. The Isotopic age Evidence for Main Longshoushan Group Contributing to Palaeoproterozoic[J]. Progress in Precambrian Research,2002,25(2):93−96.
[21] 杨光明, 吴秀玲, 潘兆橹. 氟碳钙铈矿中6R和3R多型微双晶结构的透射电镜研究[J]. 地球科学, 1992, 17(4): 447−454.
YANG Guangming, WU Xiuling, PAN Zhaolu. A study of the microtwin structures of coexisting 6R and 3R polytypes in pariste using transmission electron microscopy[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences,1992,17(4):447−454.
[22] 杨光明, 吴秀玲, 潘兆橹. 氟碳钙铈矿的42R、48R和16H新多型[J]. 矿物学报, 1993, 13(4): 331−334. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1993.04.007
YANG Guangming, WU Xiuling, PAN Zhaolu. A TEM study of new polytypes 42R, 48R and 16H existing in Parisite[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,1993,13(4):331−334. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1993.04.007
[23] 杨学明, 张培善, 陶克捷, 等. 白云鄂博稀土氟碳酸盐矿物的共面网定向附生结构[J]. 科学通报, 1998, 43(2): 209−212. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.02.024
YANG Xueming, ZHANG Peishan, TAO Kejie, et al. Study of epitaxial intergrowth structure in the calcium rare earth fluorocarbonate minerals from Bayan Obo Deposit[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,1998,43(2):209−212. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.02.024
[24] 杨主明, Smith M, Henderson P, 等. 牦牛坪钙稀土氟碳酸盐多体矿物的成分特征及其成因意义[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2002, 20(, 1): 61−67. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2002.01.014
YANG Zhuming, Smith M, Henderson P, et al. Composition of Ca-REE fluorocarbonate minerals in Maoniuping and implications to their genesis[J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society,2002,20(,1):61−67. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2002.01.014
[25] 张迪, 陈意, 毛骞, 等. 电子探针分析技术进展及面临的挑战[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(1): 261−274. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.01.21
ZHANG Di, CHEN Yi, MAO Qian, et al. Progress and challenge of electron probe microanalysis technique[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2019,35(1):261−274. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.01.21
[26] 张培善, 陶克捷, 杨主明, 等. 中国稀土矿物学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998.
ZHANG Peishan,TAO Kejie,YANG Zhuming,et al. Mineralogy of Rare Earth Elements in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998.
[27] 张文兰, 胡欢, 刘鹏, 等. 重稀土-钒-铝硅酸盐矿物电子探针定量分析[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(5): 754−763.
ZHANG Wenlan, HU Huan, LIU Peng, et al. Electron probe quantitative analysis of HREE-V-aluminosilicate minerals[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis,2022,41(5):754−763.
[28] 张晓旭, 苏尚国, 刘美玉, 等. 甘肃金川早古生代正长花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学、岩石学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(4): 283−298.
ZHANG Xiaoxu, SU Shangguo, LIU Meiyu. Characteristics and tectonic significance of the early Paleozoic syenite granite from Jinchuan, Gansu Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2021,28(4):283−298.
[29] Batapola N M, Dushyantha N P, Premasiri H M R, et al. A comparison of global rare earth element (REE) resources and their mineralogy with REE prospects in Sri Lanka[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2020,200:104475. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104475
[30] Beland C M J, Williams-Jones A E. The genesis of the Ashram REE deposit, Quebec: Insights from bulk-rock geochemistry, apatite-monazite-bastnäsite replacement reactions and mineral chemistry[J]. Chemical Geology,2021,578:120298. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2021.120298
[31] Donnay G, Donnay J D H. The crystallography of bastnaesite, parasite, roentgenite, and synchysite[J]. American Mineralogist, 1953, 38: 932-963.
[32] Gysi A P, Williams-Jones A E. The thermodynamic properties of bastnäsite-(Ce) and parisite-(Ce)[J]. Chemical Geology,2015,392:87−101. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.11.001
[33] Landuyt J V, Amelinck S. Multiple beam direct lattice imaging of new mixed- layer compounds of the bastnaesite-syn chysite series[J]. Am. Mineral.,1975,60:351−358.
[34] Migdisov A, Williams-Jones A E, Brugger J, et al. Hydrothermal transport, deposition, and fractionation of the REE: Experimental data and thermodynamic calculations[J]. Chemical Geology,2016,439:13−42. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.06.005
[35] Pyle J M, Spear F S, Wark D A. Electron microprobe analysis of REE in apatite, monazite and xenotime: protocols and pitfalls[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry,2002,48:337−362.
[36] She H D, Fan H R, Yang K F, et al. Complex, multi-stage mineralization processes in the giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021,139:104461. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104461
[37] Williams-Jones A E, Wood S A. A preliminary petrogenetic grid for REE fluorocarbonates and associated minerals[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1992,56(2):725−738. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(92)90093-X
[38] Zeng R Y, Lai J Q, Mao X C, et al. Geochemistry, zircon U–Pb dating and Hf isotopies composition of Paleozoic granitoids in Jinchuan, NW China: Constraints on their petrogenesis, source characteristics and tectonic implication[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2016,121:20−33.
[39] Zhang X, Yang S Y, Zhao H, et al. Effect of beam current and diameter on electron probe microanalysis of carbonate minerals[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2019,30(4):834−842. doi: 10.1007/s12583-017-0939-x
[40] Zheng X, Liu Y, Zhang L. The role of sulfate-, alkali-, and halogen-rich fluids in mobilization and mineralization of rare earth elements: Insights from bulk fluid compositions in the Mianning–Dechang carbonatite-related REE belt, southwestern China[J]. Lithos, 2021, 386–387: 106008.
-




 下载:
下载: