Identification of Nitrate Sources and Main Controlling Factors in Shallow Groundwater Based on MixSIAR and Random Forest Model
-
摘要:
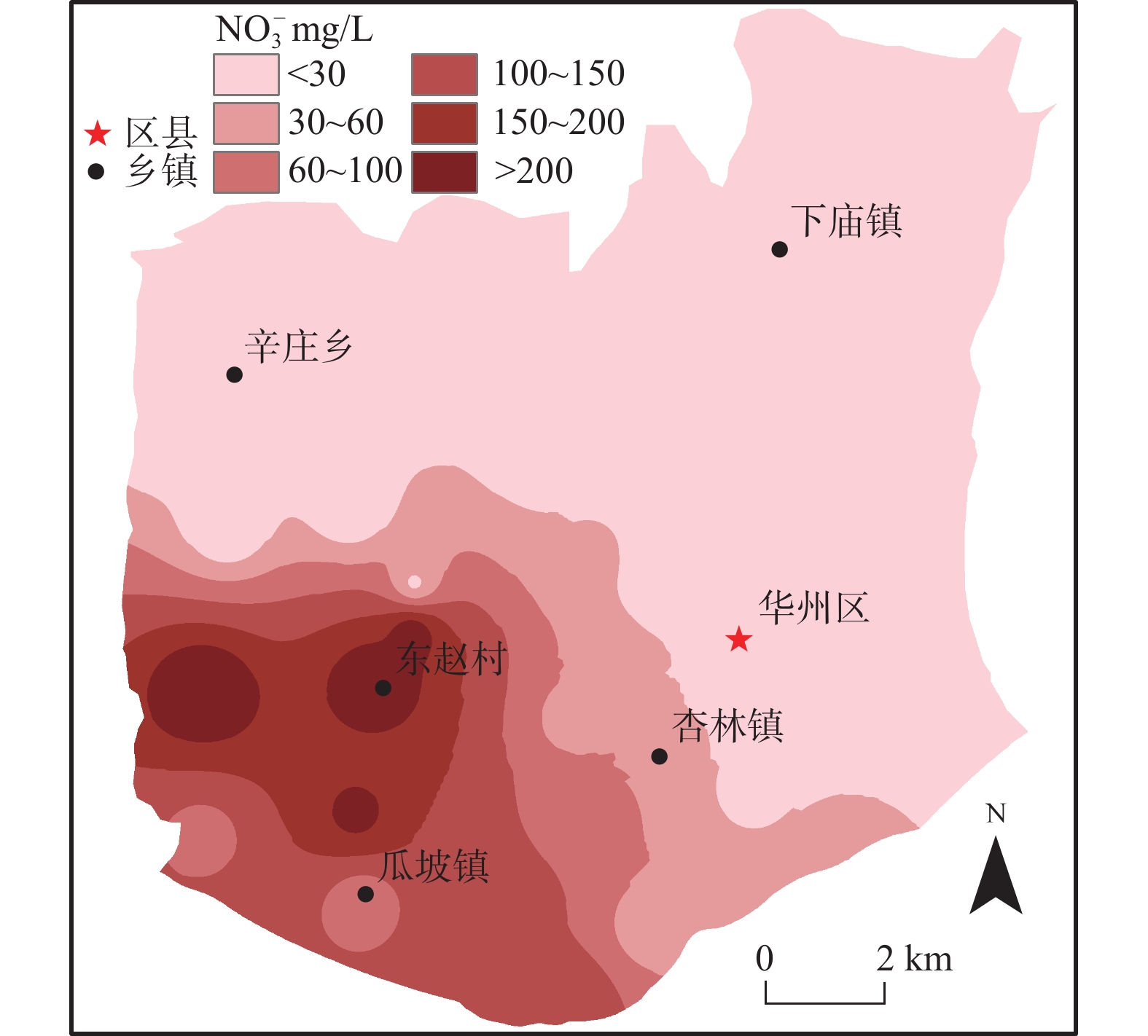
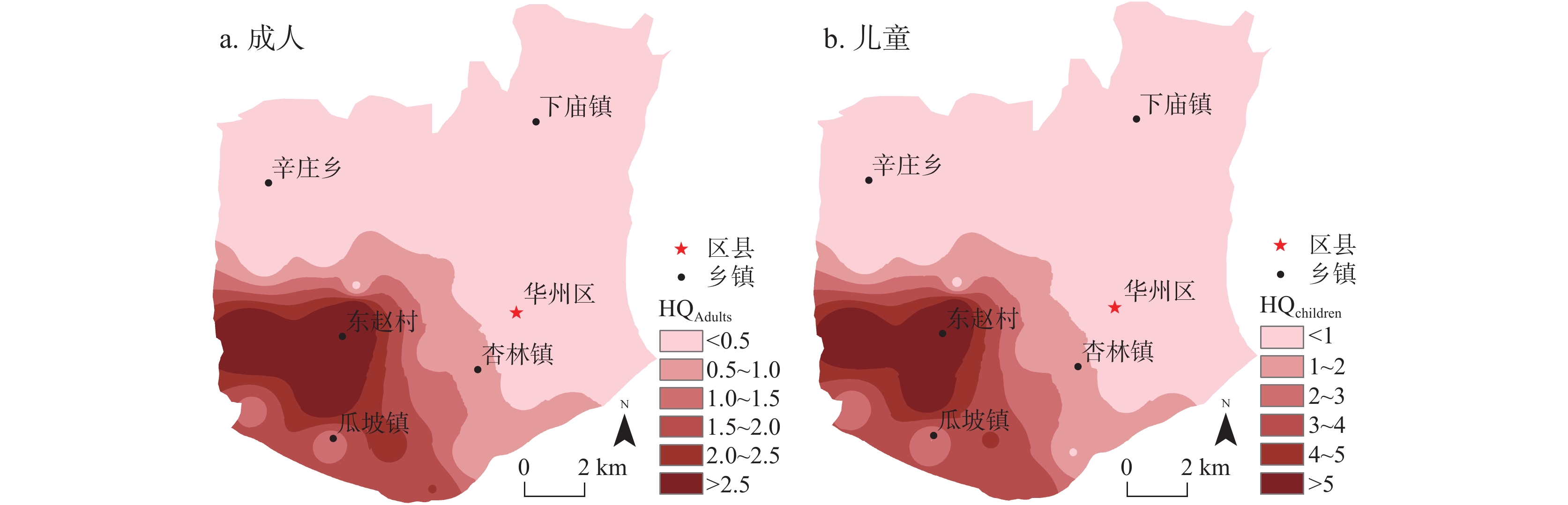
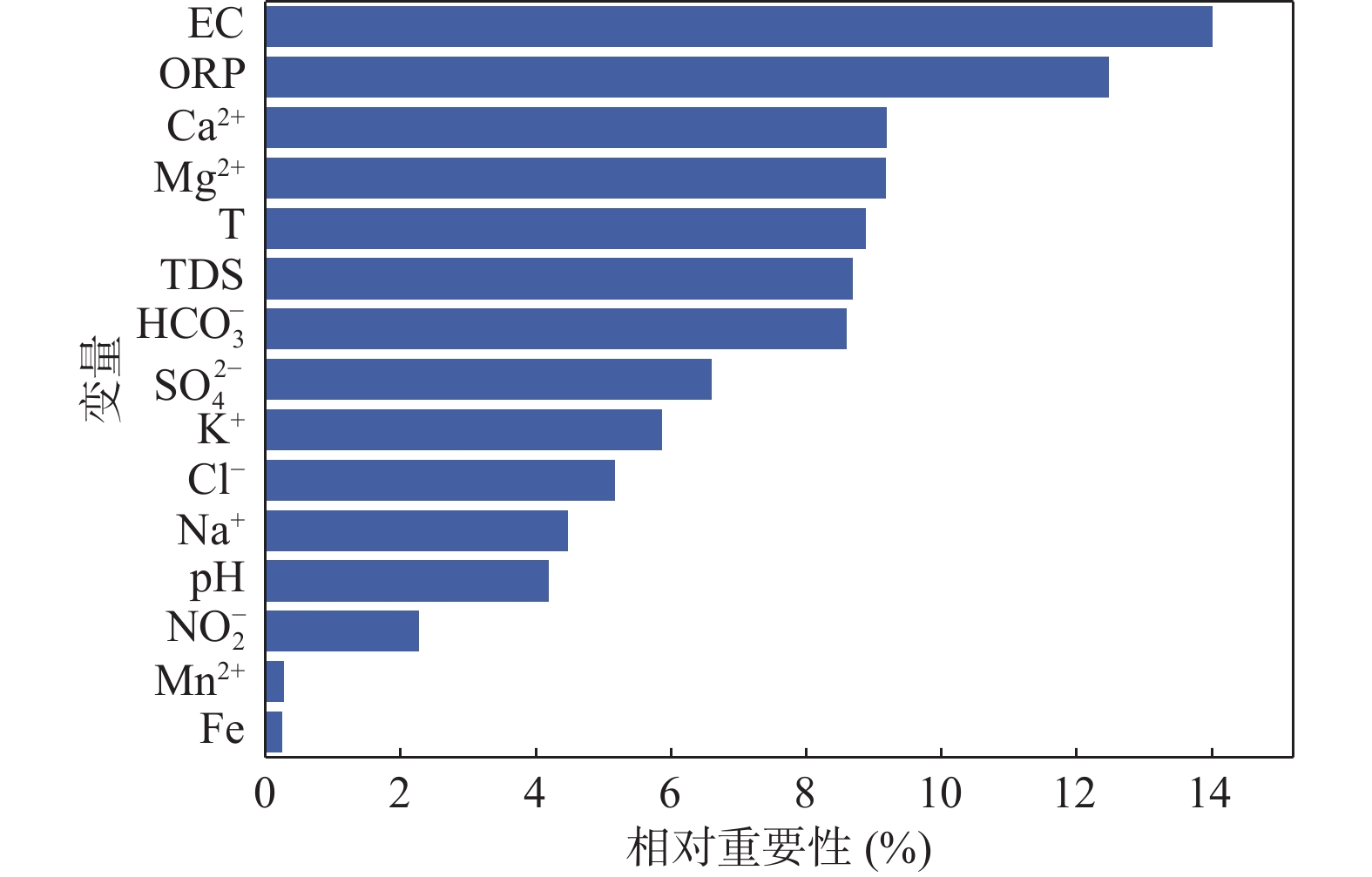
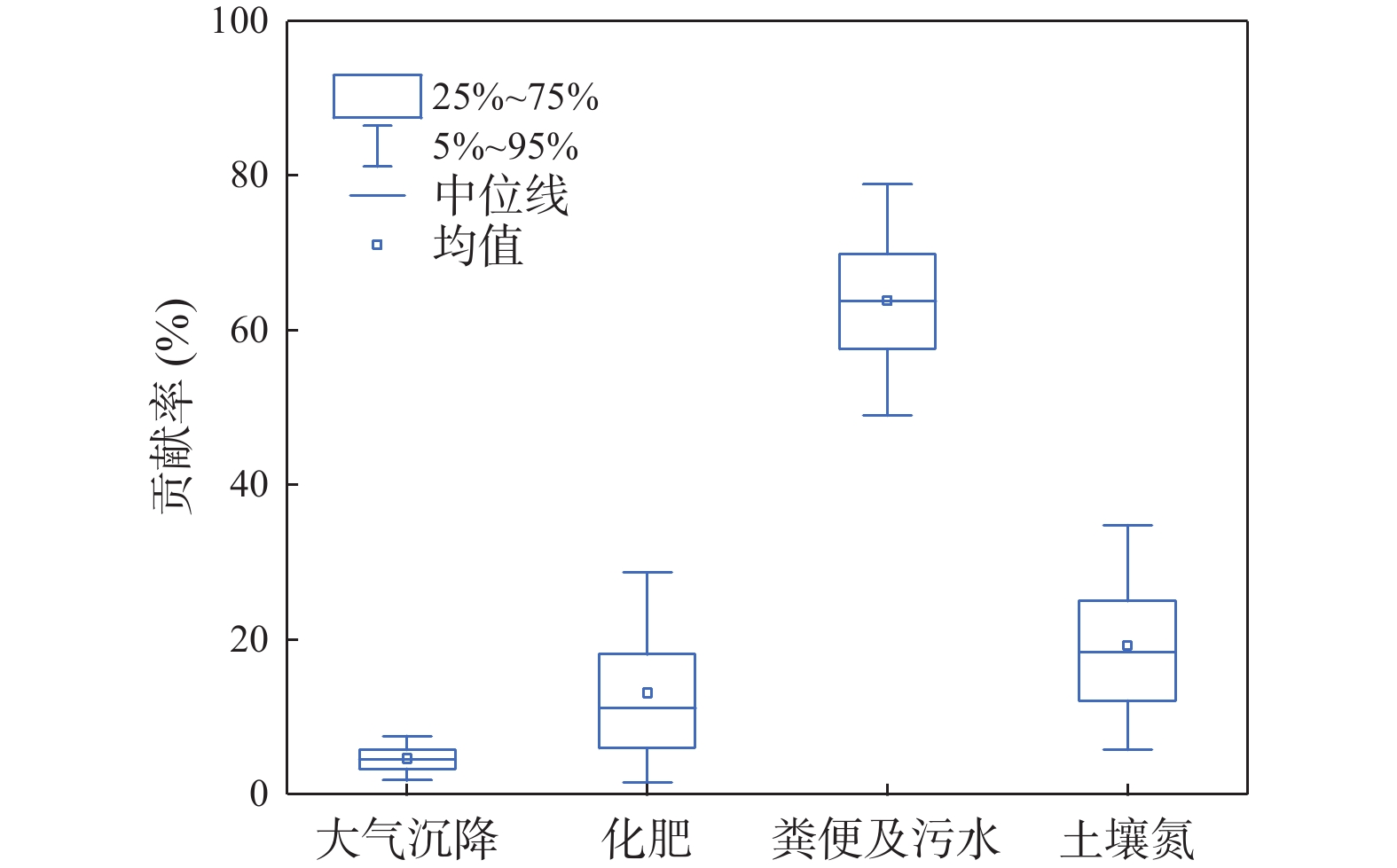
作为全球水资源中最普遍的污染物,NO3−主控因素和来源的识别对NO3−污染控制至关重要。本研究基于人体健康风险、随机森林模型、同位素和MixSIAR模型等方法,分析了华州区浅层地下水NO3−分布特征和潜在风险,揭示了浅层地下水NO3−的重要因素和主要来源。结果表明:华州区浅层地下水NO3−浓度呈西高东低趋势分布,西南部尤为显著,NO3−浓度高达271mg/L。主要控制NO3−浓度的指标依次为:EC>ORP>Ca2+>Mg2+>T>TDS>HCO3−。NO3−来源以土壤氮和粪肥及污水为主,且粪便及污水对NO3−含量贡献率最大(63.8%),其次是土壤氮(19%)和化肥(12.7%)。长期饮用研究区NO3−浓度较高的浅层地下水对人类健康具有潜在风险,特别是儿童,其HHRA评估风险值高达7.904。
Abstract:As the most common pollutant in global water resources, the identification of the main controlling factors and sources of NO3− is crucial to the control of NO3− pollution. Based on methods such as human health risk model, random forest model, isotope and MixSIAR model, this study analyzed the distribution characteristics and potential risks of shallow groundwater NO3− in Huazhou District, and revealed the main controlling factors and main sources of shallow groundwater NO3−. The results show that the shallow groundwater NO3− concentration in Huazhou District is high in the west and low in the east, especially in the southwest. The NO3− concentration is as high as 271 mg/L. The main factors controlling NO3− concentration being EC>ORP>Ca2+>Mg2+>T>TDS>HCO3−. The main sources of NO3− are soil nitrogen and manure & sewage. The manure & sewage contributes the most to the NO3− content (63.8%), followed by soil nitrogen (19%) and chemical fertilizer (12.7%). Long-term drinking of shallow groundwater with high NO3− concentration in the study area has potential risks to human health, especially for children, whose HHRA assessment risk is as high as 7.904.
-

-
表 1 模型中使用的双同位素值(Jin et al., 2023)
Table 1. Dual isotope values used in the model
来源 平均值δ15N 标准差δ15N 平均值δ18O 标准差δ18O 大气沉降 −3.7 1.5 77.4 4.8 土壤氮 6.4 0.6 −6.2 0.4 化肥 −2.1 0.7 −4.1 2.7 粪肥及污水 17.4 3.9 6.1 1.6 表 2 HHRA中用于评估浅层地下水硝酸盐污染潜在风险的参数
Table 2. Parameters used to assess the potential risk of shallow groundwater nitrate in HHRA
参数 单位 成人 儿童 引用文献 IR摄入率 L/day 1.5 0.7 (吉玉洁,2022) ED暴露持续时间 days 365 365 EF暴露频率 Year 32 12 (Wang et al., 2022) BW平均体重 kg 60 15 (Wu et al., 2020) AT平均暴露时间 days 11680 4380 (Wang et al., 2022) RfDNO3− mg/kg/day 1.6 1.6 (USEPA, 2001) 表 3 浅层地下水水化学参数统计
Table 3. Statistics of the hydrochemical parameters of shallow groundwater
指标 单位 最大值 最小值 平均值 样品数量 pH / 8.39 7.81 8.08 37 TDS mg/L 2612 180 647.95 37 ORP mV 852 −97 93.54 37 Na+ mg/L 211 9.2 50.2 37 K+ mg/L 25.7 0.82 5.59 37 Ca2+ mg/L 321 28.1 114.76 37 Mg2+ mg/L 243 2.43 27.85 37 Cl− mg/L 355 4 59.24 37 HCO3− mg/L 1062 97.6 351.61 37 SO42− mg/L 624 19.2 123.51 37 NO3− mg/L 271 <2.0 68.46 37 δ15N-NO3− ‰ 40.28 −1.61 10.83 32 δ18O-NO3− ‰ 22.56 −10.12 5.60 32 表 4 浅层地下水NO3−经口服摄入的潜在风险值
Table 4. Potential risk value of oral ingestion of shallow groundwater NO3−
HQoral 2023旱季 2018旱季
(Wang et al., 2022)2013旱季
(Wu et al., 2016)成人 儿童 成人 儿童 成人 儿童 最大值 4.234 7.904 7.975 14.887 13.34 24.89 最小值 0.031 0.058 0.126 0.236 0.04 0.07 平均值 0.817 1.525 1.141 2.129 1.44 2.69 -
[1] 曹胜伟, 费宇红, 田夏, 等 . 硝酸盐污染氮氧同位素溯源及贡献率分析——以南阳地区为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019 ,46 (2 ):82 −91 .CAO Shengwei, FEI Yuhong, TIAN Xia, et al . Using isotopes of nitrogen and oxygen to trace groundwater nitrate contamination and contribution analysis: exemplified by the Nanyang District[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019 ,46 (2 ):82 −91 .[2] 成世才 . 济南市新旧动能转换区浅层地下水硝酸盐污染特征[J]. 中国煤炭地质,2021 ,33 (2 ):53 −59 .CHENG Shicai . Shallow Groundwater Nitrate Pollution Features in Jinan City Zone to Replace Old Growth Drivers with New Ones[J]. Coal Geology of China,2021 ,33 (2 ):53 −59 .[3] 崔静思, 刘树锋, 高延康, 等 . 土地利用变化下湛江市地下水硝酸盐含量评估[J]. 环境化学,2022 ,41 (7 ):2264 −2275 .CUI Jingsi, LIU Shufeng, GAO Yankang, et al . Assessment of groundwater nitrate content under land use changes in Zhanjiang City[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2022 ,41 (7 ):2264 −2275 .[4] 党学亚, 张俊, 常亮, 等 . 西北地区水文地质调查与水资源安全[J]. 西北地质,2022 ,55 (3 ):81 −95 .DANG Xueya, ZHANG Jun, CHANG Liang, et al . Hydrogeological Survey and Water Resources Security in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology,2022 ,55 (3 ):81 −95 .[5] 董海彪, 卢文喜, 安永凯, 等 . 基于对应分析法的鄂尔多斯盆地东北部地下水污染分析[J]. 中国环境科学,2015 ,35 (11 ):3371 −3378 .DONG Haibiao, LU Wenxi, AN Yongkai, et al . Groundwater pollution assessment in northeastern Ordos Basin based on correspondence analysis method[J]. China Environmental Science,2015 ,35 (11 ):3371 −3378 .[6] 范祖金, 魏兴, 周育琳, 等 . 典型山地农业区浅层地下水硝酸盐来源及转化过程解析[J]. 环境科学研究,2023 ,36 (10 ):1946 −1956 .FAN Zujin, WEI Xing, ZHOU Yulin, et al . Analysis of Nitrate Sources and Transformation Processes in Shallow Groundwater in Typical Mountainous Agricultural Area[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2023 ,36 (10 ):1946 −1956 .[7] 高燕燕. 关中平原地下水化学成分时空演化规律及人体健康风险评价[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021. GAO Yanyan. Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Hydrochemical Components and Human Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater in Guanzhong Plain [D]. Xi’an: Chang’an Univeristy, 2021. [8] 韩聪, 高宗军, 刘久潭, 等 . 郯城地区地下水化学特征及针对硝酸盐的健康风险评价[J]. 地球与环境,2021 ,49 (4 ):436 −446 .HAN Cong, GAO Zongjun, LIU Jiutan, et al . Chemical Characteristics of Groundwater and Health Risk Assessment of Nitrate in Tancheng Area[J]. Earth and Environment,2021 ,49 (4 ):436 −446 .[9] 何松. 卫宁平原地下水环境对气候因子与土地利用/覆被模式变化的响应研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2023. HE Song. Response of Groundwater Environment to the Changes ofClimatic Factors and Land Use/Land Cover Patterns inthe Weining Plain, China [D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2023. [10] 黄颖, 江涛, 丁杰, 等 . 城镇化流域地下水氮素组成特征及来源解析[J]. 热带地理,2023 ,43 (7 ):1400 −1410 .HUANG Ying, JIANG Tao, DING Jie, et al . Composition and Source Identification of Nitrogen in Groundwater in an Urbanized Basin[J]. Tropical Geography,2023 ,43 (7 ):1400 −1410 .[11] 吉玉洁. 韩城市饮水型氟病区改水前后水质及健康风险评价[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2022. JI Yujie. Water Quality and Health Risk Assessment before and after Water Improvement Project for the Endemic Fluorosis Areas in Hancheng [D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2022. [12] 贾林春. 碳纤维强化零价铁生物反硝化去除地下水硝态氮效能与机制[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2023. JIA Linchun. Carbon fiber facilitates zero-valent iron basedbiological denitrification to remove nitrate in groundwater: performance and mechanism [D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2023. [13] 李捷, 姜颖, 刘玉莲, 等 . 凉水河流域地下水水化学特征和时空变化规律[J]. 中国环境科学,2022 ,42 (4 ):1847 −1853 .LI Jie, JIANG Ying, LIU Yulian, et al . Hydrolochemical characteristics and spatial temporal variations of groundwater in the Liangshui River basin, Beijing[J]. China Environmental Science,2022 ,42 (4 ):1847 −1853 .[14] 李依鸿, 于瑞莲, 张瑞琦, 等 . 海峡西岸典型城市大气降尘稀土元素生态风险及来源——基于钕同位素MixSIAR模型解析[J]. 中国环境科学,2023 ,43 (11 ):5663 −5670 .LI Yihong, YU Ruilian, ZHANG Ruiqi, et al . The ecological risks and sources of rare earth elements in the dustfall in typical cities of West China Strait: based on neodymium isotope tracing combined with MixSIAR model[J]. China Environmental Science,2023 ,43 (11 ):5663 −5670 .[15] 刘芳盈, 赵志强, 孟超, 等 . 淄博市生活饮用水中硝酸盐暴露及其健康风险的时空分布特征[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版),2021 ,59 (12 ):50 −57 .LIU Fangying, ZHAO Zhiqiang, MENG Chao, et al . Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of nitrates and health risks in drinking water in Zibo City[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Health Sciences),2021 ,59 (12 ):50 −57 .[16] 裴东艳, 谢磊, 徐斌, 等 . 基于氮氧同位素技术的黄河上游清水河硝酸盐来源解析[J]. 中国环境科学,2022 ,42 (9 ):4115 −4121 .PEI Dongyan, XIE Lei, XU Bin, et al . Analysis of nitrate sources in the Qingshui River of the Yellow River with nitrogen and oxygen isotope technique[J]. China Environmental Science,2022 ,42 (9 ):4115 −4121 .[17] 任坤, 潘晓东, 彭聪, 等 . 氮氧同位素和水化学解析昭通盆地地下水硝酸盐来源及对环境的影响[J]. 中国地质,2022 ,49 (2 ):409 −419 .REN Kun, PAN Xiaodong, PENG Cong, et al . Identification of nitrate sources of groundwaters in the Zhaotong basin using hydrochemistry, nitrogen and oxygen isotopes and its impact on the environment[J]. Geology in China,2022 ,49 (2 ):409 −419 .[18] 盛丹睿, 温小虎, 冯起, 等 . 张掖盆地地下水硝酸盐污染与人体健康风险评价[J]. 中国沙漠,2019 ,39 (5 ):37 −44 .SHENG Danrui, WEN Xiaohu, FENG Qi, et al . Groundwater Nitrate Pollution and Human Health Risk Assessment in the Zhangye Basin, Gansu, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2019 ,39 (5 ):37 −44 .[19] 苏东, 龚绪龙, 杨磊, 等 . 常州市地下水化学特征与成因分析[J]. 地质论评,2023 ,69 (3 ):1039 −1049 .SU Dong, GONG Xulong, YANG Lei, et al . Hydrogeochemical characteristics and controlling factors of groundwater in Changzhou City[J]. Geological Review,2023 ,69 (3 ):1039 −1049 .[20] 苏凤梅. 卫宁平原农业灌溉对地下水环境的影响研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2023. SU Fengmei. Influence of Agricultural Irrigation on GroundwaterEnvironment in Weining Plain, China[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2023. [21] 苏贺, 康卫东, 杨永康 . 基于水化学和稳定同位素的黄土区地下水硝酸盐来源示踪[J]. 太原理工大学学报,2021 ,52 (5 ):775 −788 .SU He, KANG Weidong, YANG Yongkang . Tracing of Nitrate Sources in Groundwater of Loess Area Based on Hydrochemistry and Stable Isotopes[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology,2021 ,52 (5 ):775 −788 .[22] 王斌, 张俊, 龙睿, 等 . 40年来新疆阿克苏河流域地下水流场演化及成因模式[J]. 西北地质,2024 ,57 (4 ):252 −261 .WANG Bin, ZHANG Jun, LONG Rui, et al . Evolution and Genetic Pattern of Groundwater Flow Field in the Aksu River Basin of Xinjiang Over the Past 40 Years[J]. Northwestern Geology,2024 ,57 (4 ):252 −261 .[23] 王凯霖. 雄安新区地下水资源和湿地的共同可持续研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020. WANG Kailin. Research on Commonjunctive Sustainbility of Groundwater Resources and Wetlands in Xiongan New Area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020. [24] 吴庭雯, 袁磊, 韩双宝, 等 . 安固里淖内陆河流域地下水硝酸盐污染时空分布特征及成因分析[J]. 环境化学,2021 ,40 (8 ):2515 −2523 .WU Tingwen, YUAN Lei, HAN Shuangbao, et al . Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and origin analysis of nitrate pollution in groundwater in Angulinao inland river basin[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2021 ,40 (8 ):2515 −2523 .[25] 张航, 樊荣, 李超, 等 . 基于氮氧同位素的北洛河流域硝酸盐来源及其空间分布解析[J]. 环境污染与防治,2024 ,46 (1 ):43 −49 .ZHANG Hang, FAN Rong, LI Chao, et al . Spatial distribution and sources analysis of nitrate in the Beiluo River Watershed based on nitrogen and oxygen stable isotope[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2024 ,46 (1 ):43 −49 .[26] 张奇莹. 交口抽渭灌区地下水环境时空演化及预警与应对研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2023. ZHANG Qiying. Study on Spatial-Temporal Evolution Analysis as well as Early Warning and Response of Groundwater Environment in Jiaokou Irrigation District[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2023. [27] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 地下水质量标准(GB/T 14848−2017)[S]. 中国标准出版社, 北京, 2017. [28] Chen T, Zhu L, Niu R, et al . Mapping landslide susceptibility at the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, using gradient boosting decision tree random forest and information value models[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2020 ,17 :670 −685 .[29] Deng L, Xu B, Yang X T, et al . Water quality and health risk assessment based on hydrochemical characteristics of tap and large-size bottled water from the main cities and towns in Guanzhong Basin, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2021 ,80 :139 .[30] Gao Y Y, Chen J, Qian H, et al . Hydrogeochemical characteristics and processes of groundwater in an over 2260 year irrigation district: A comparison between irrigated and nonirrigated areas[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022 ,606 :127437 .[31] Gholami V, Booij M . Use of machine learning and geographical information system to predict nitrate concentration in an unconfined aquifer in Iran[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2022 ,360 :131847 .[32] Gibrilla A, Fianko J R, Ganyaglo S, et al . Nitrate contamination and source apportionment in surface and groundwater in Ghana using dual isotopes (15N and 18O-NO3−) and a Bayesian isotope mixing model[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2020 ,233 :103658 .[33] Jia H, Howard K, Qian H . Use of multiple isotopic and chemical tracers to identify sources of nitrate in shallow groundwaters along the northern slope of the Qinling Mountains, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2020 ,113 :104512 .[34] Jiang C L, Li M, Li C, et al . Combining hydrochemistry and 13C analysis to reveal the sources and contributions of dissolved inorganic carbon in the groundwater of coal mining areas, in East China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health,2023 ,45 :7065 −7080 .[35] Jin Z F, Xiao J Z, Ye H Y, et al . Determination of nitrogen sources and losses in surface runoff from different lands at a watershed scale[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2023 ,30 :63052 −63064 .[36] Karlović I, Posavec K, Larva O, et al . Numerical groundwater flow and nitrate transport assessment in alluvial aquifer of Varaždin region, NW Croatia[J]. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies,2022 ,41 :101084 .[37] Li P Y, Wu J H, Qian H . Preliminary assessment of hydraulic connectivity between river water and shallow groundwater and estimation of their transfer rate during dry season in the Shidi River, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016 ,75 :99 .[38] Niu X Q, Jia X X, Yang X F, et al . Tracing the Sources and Fate of NO3− in the Vadose Zone–Groundwater System of a Thousand-Year-Cultivated Region[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2022 ,56 (13 ):9335 −9345 .[39] Ransom K, Nolan B, Stackelberg P, et al . Machine learning predictions of nitrate in groundwater used for drinking supply in the conterminous United States[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022 ,807 (3 ):151065 .[40] Podlasek A, Bujakowski F, Koda E. The spread of nitrogen compounds in an active groundwater exchange zone within a valuable natural ecosystem [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2020, 146: 105746. [41] Ruan D M, Bian J M, Wang Y, et al . Identification of groundwater pollution sources and health risk assessment in the Songnen Plain based on PCA-APCS-MLR and trapezoidal fuzzy number-Monte Carlo stochastic simulation model[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2024 ,632 :130897 .[42] Singh O, Kasana A, Bhardwaj P. Long-Term Groundwater Behaviour Over an Agriculturally Developed State of North-West India: Trend and Impact on Agriculture[M]. Groundwater and Society, Springer, Cham, 2021: 318−406. [43] Stock B C, Jackson A L, Ward E J, et al . Analyzing mixing systems using a new generation of Bayesian tracer mixing models[J]. Peerj,2018 ,6 :e5096 .[44] Torres-Martínez J, Mora A, Knappett P, et al . Tracking nitrate and sulfate sources in groundwater of an urbanized valley using a multi-tracer approach combined with a Bayesian isotope mixing model[J]. Water Research,2020 ,182 :115962 .[45] Torres-Martínez J A, Mora A, Mahlknecht J, et al . Determining nitrate and sulfate pollution sources and transformations in a coastal aquifer impacted by seawater intrusion: A multi-isotopic approach combined with self-organizing maps and a Bayesian mixing model[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021 ,417 :126103 .[46] United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund, Vol I, Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A)[S]. Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, Washington, DC, 1989. [47] United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Risk assessment guidance for Superfund: volume III part A, process for conducting probabilistic risk assessment (EPA/540-R-02-002)[S]. Washington DC: Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, U. S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2001. [48] Wang Y H, Li P Y . Appraisal of shallow groundwater quality with human health risk assessment in different seasons in rural areas of the Guanzhong Plain (China)[J]. Environmental Research,2022 ,207 :112210 .[49] Wilson S, Close M, Abraham P, et al . Achieving unbiased predictions of national-scale groundwater redox conditions via data oversampling and statistical learning[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020 ,705 :135877 .[50] Wu J H, Sun B . Evaluation of Shallow Groundwater Contamination and Associated Human Health Risk in an Alluvial Plain Impacted by Agricultural and Industrial Activities, Mid-west China[J]. Exposure and Health,2016 ,8 :311 −329 .[51] Wu J H, Zhang Y X, Zhou H . Groundwater chemistry and groundwater quality index incorporating health risk weighting in Dingbian County, Ordos basin of northwest China[J]. Geochemistry,2020 ,80 (4 ):125607 .[52] Xue D M, Botte J, Baets B D, et al . Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface- and groundwater[J]. Water Research,2009 ,43 (5 ):1159 −1170 .[53] Zhang M, Huang G, Liu C, et al . Distributions and origins of nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium in various aquifers in an urbanized coastal area, south China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020 ,582 :124528 .[54] Zhang Q X, Li P Y, Lyu Q F, et al . Groundwater contamination risk assessment using a modified DRATICL model and pollution loading: A case study in the Guanzhong Basin of China[J]. Chemosphere,2022a ,291 :132695 .[55] Zhang Q Y, Shu W, Li F D, et al . Nitrate source apportionment and risk assessment: A study in the largest ion-adsorption rare earth mine in China[J]. Environmental Pollution,2022b ,302 :119052 .[56] Zhang X, Zhang Y, Shi P, et al . The deep challenge of nitrate pollution in river water of China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021 ,770 :144674 .[57] Zhao Y Y, Zheng B H, Jia H F, et al . Determination sources of nitrates into the Three Gorges Reservoir using nitrogen and oxygen isotopes[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019 ,687 :128 −136 . -




 下载:
下载: