Spatial and Temporal Framework, Evolution of Magma Sources, and Tectonic Settings of Paleozoic Magmatic Rocks in West Tianshan, China
-
摘要:
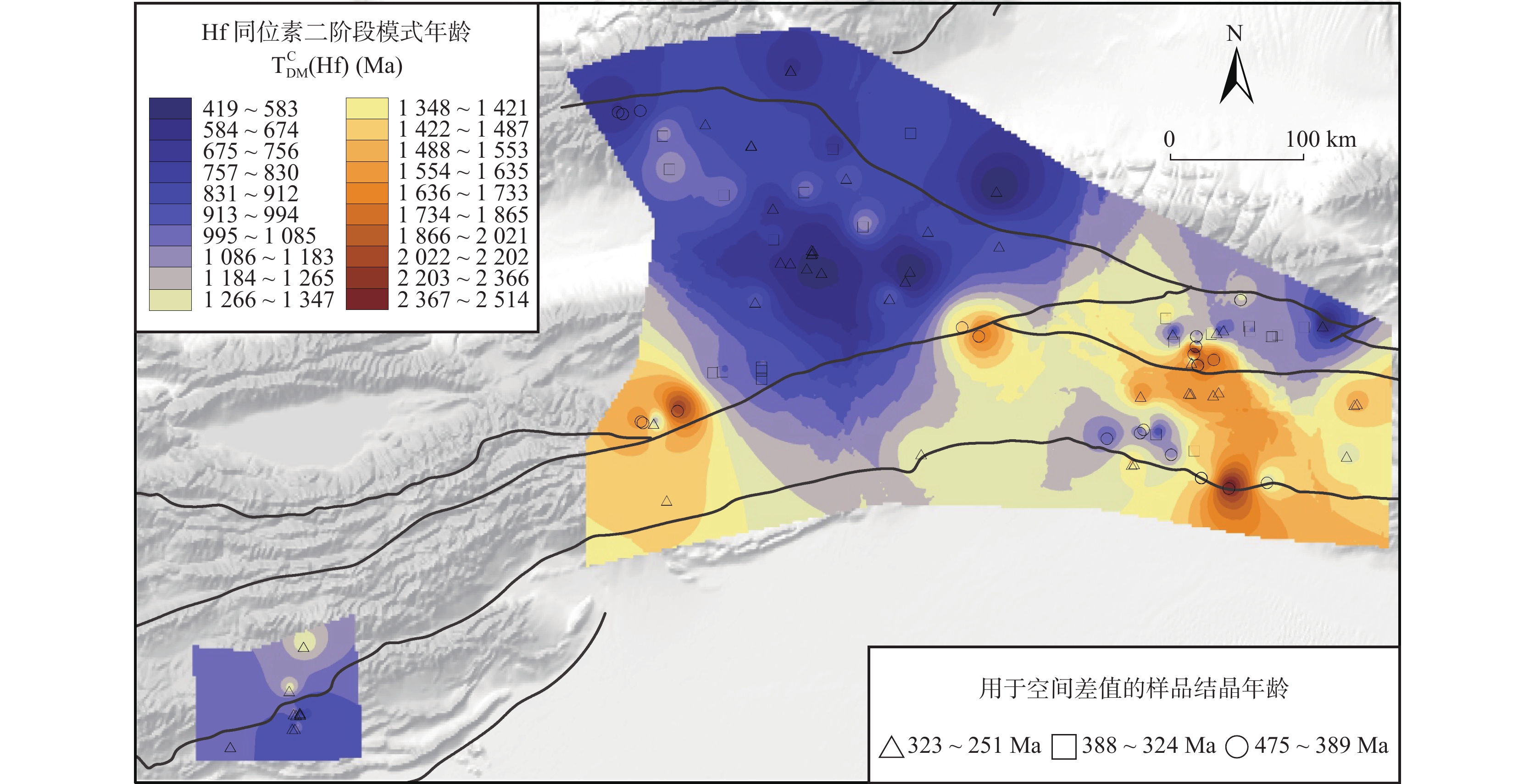
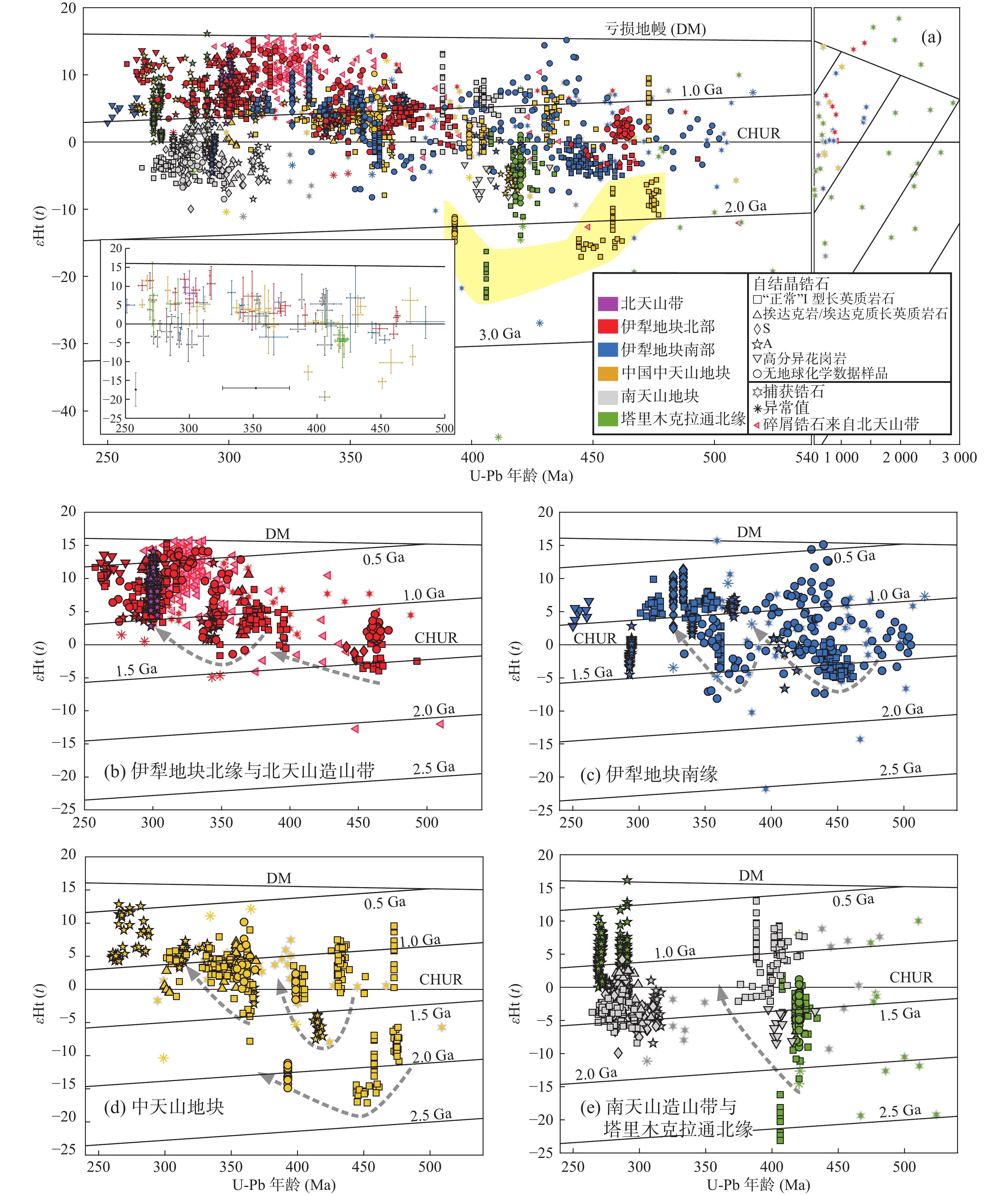
中亚造山带是全球最大、最典型的增生造山带,是全球显生宙陆壳生长最显著的地区之一。在中亚造山带形成过程中,伴随古亚洲洋的闭合,以及不同性质构造块体的拼贴碰撞,形成了巨量的岩浆岩。笔者以中亚造山带西段西天山出露的古生代岩浆岩为研究对象,系统总结了岩浆岩的时空格架、成因类型、源区特征和构造背景等特征。区内岩浆岩主要形成于3个阶段:寒武纪早期—中泥盆世早期(497~388 Ma)、晚泥盆世—早石炭世(375~323 Ma)、晚石炭世—中二叠世(322~263 Ma)。第一阶段和第二阶段的侵入岩组合主要为钙碱性I型花岗岩,以及具有“岛弧”地球化学特征的中、基性岩石,部分岩体具有埃达克质岩石的性质,并发育少量A型花岗岩。晚石炭世—中二叠世花岗岩等侵入岩以多样性的成分为特征,包括“正常的”钙碱性I型花岗岩、埃达克质岩石、A型花岗岩,以及局部出露的S型花岗岩,基性岩石中也出现较多具洋岛玄武岩特征的辉长岩和玄武岩。结合其他地质证据,笔者认为寒武纪早期—中泥盆世早期、晚泥盆世—早石炭世岩浆岩形成于与古亚洲洋洋分支洋盆俯冲有关的构造环境中,且岩浆活动的迁移和地球化学成分演化趋势均揭示俯冲过程中发生了多次从前进型、低角度俯冲到后撤型、高角度俯冲的转化。西天山南北洋盆的最终闭合均发生在晚石炭世。在南侧,古南天山洋的闭合跟随着大陆板块之间的“硬碰撞”。而在北侧,伊犁地块和中天山地块北缘与一不成熟/新生岛弧发生了“软碰撞”。就地壳演化的方式而言,基于Hf同位素资料所揭示的长英质岩浆岩源区物质演化,识别出西天山地区在在古生代交替发生大陆地壳物质再循环(continental reworking)和大陆生长(continental growth)。在俯冲阶段,大洋板片后撤(回卷)占据了主导性地位,导致了微陆块中增生造山作用开始之前形成的古老物质大量被同增生阶段形成的新生物质所置换,伊犁地块、中天山地块等块体是在古生代被显著“再更新(rejuvenation)”的古老微陆块。后碰撞伸展阶段大范围幔源岩浆底侵进一步造成了显著的地壳生长。整个古生代,西天山及邻区以地壳生长为主导。
Abstract:The Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB) is Earth's largest and most representative accretionary belt and records the most extensive growth and reworking of the continental crust. Accompanying the closure of the giant Paleo-Asian Ocean and the amalgamation of tectonic blocks in the CAOB regime, with different origins and evolutionary histories, voluminous magmatic rocks were formed. This study focuses on Paleozoic magmatic rocks exposed in West Tianshan and systemically summarizes the spatiotemporal frameworks, genetic types, evolution of their magma sources in space and time, and tectonic settings of these rocks. Paleozoic magmatic rocks in West Tianshan were mainly formed at three stages, i.e., Early Cambrian to Middle Devonian (~479 to ~388 Ma), Late Devonian to Early Carboniferous (~375 to ~372 Ma), and Late Carboniferous to Middle Permian (~322 to ~263 Ma). Magmatic rocks formed at the first and second stages are mainly of calc-alkaline I-type granite and intermediate and mafic rocks with "arc-like" geochemical fingerprints, with a few rocks bearing "adakite-like" features; a few A-type granites are also found. By contrast, Late Carboniferous to Middle Permian magmatic rocks show a diversity in rock types, including calc-alkaline I-type, adakite-like, and A-type felsic rocks, with a few locally exposed S-type granites; OIB-like mafic rocks formed in this period, such as gabbros and basalts, occur locally. In combination with other geological evidence, this study proposes that Early Cambrian to early Middle Devonian and Late Devonian to Early Carboniferous magmatic activities took place in convergent continental margin settings, which were associated with the subduction of branches of the Paleo-Asian Ocean. Besides, both magmatic migration and secular changes in geochemical proxies indicate the transition from advancing low-angle to retreating high-angle subduction. The final closure of oceanic basins plausibly occurred in the Late Carboniferous. Following the closure of the South Tianshan Ocean, a "hard" collision with the arriving Tarim Craton occurred; by contrast, in the north, the northern margin of the Yili-Central Tianshan Block amalgamated with an immature/nascent island arc. In terms of continental evolution, based on Hf isotopic datasets, this study identifies alternating occurrences of growth and reworking. During subduction stages, retreating subduction (slab rollback) played a predominant role, resulting in large-scale replacement of ancient, pre-accretionary materials by new-formed, syn-accretionary materials. Therefore, Yili and Central Tianshan blocks, can be viewed as ancient microcontinents that were significantly rejuvenated during accretionary processes. In the post-collisional stage, large-scale underplating of mantle-derived magmas represents another phase of continental growth. During the Paleozoic, West Tianshan and adjacent regions were characterized dominantly by continental growth.
-
Key words:
- Central Asian Orogenic Belt /
- West Tianshan /
- Paleozoic /
- magmatic rock /
- continental crustal growth
-

-
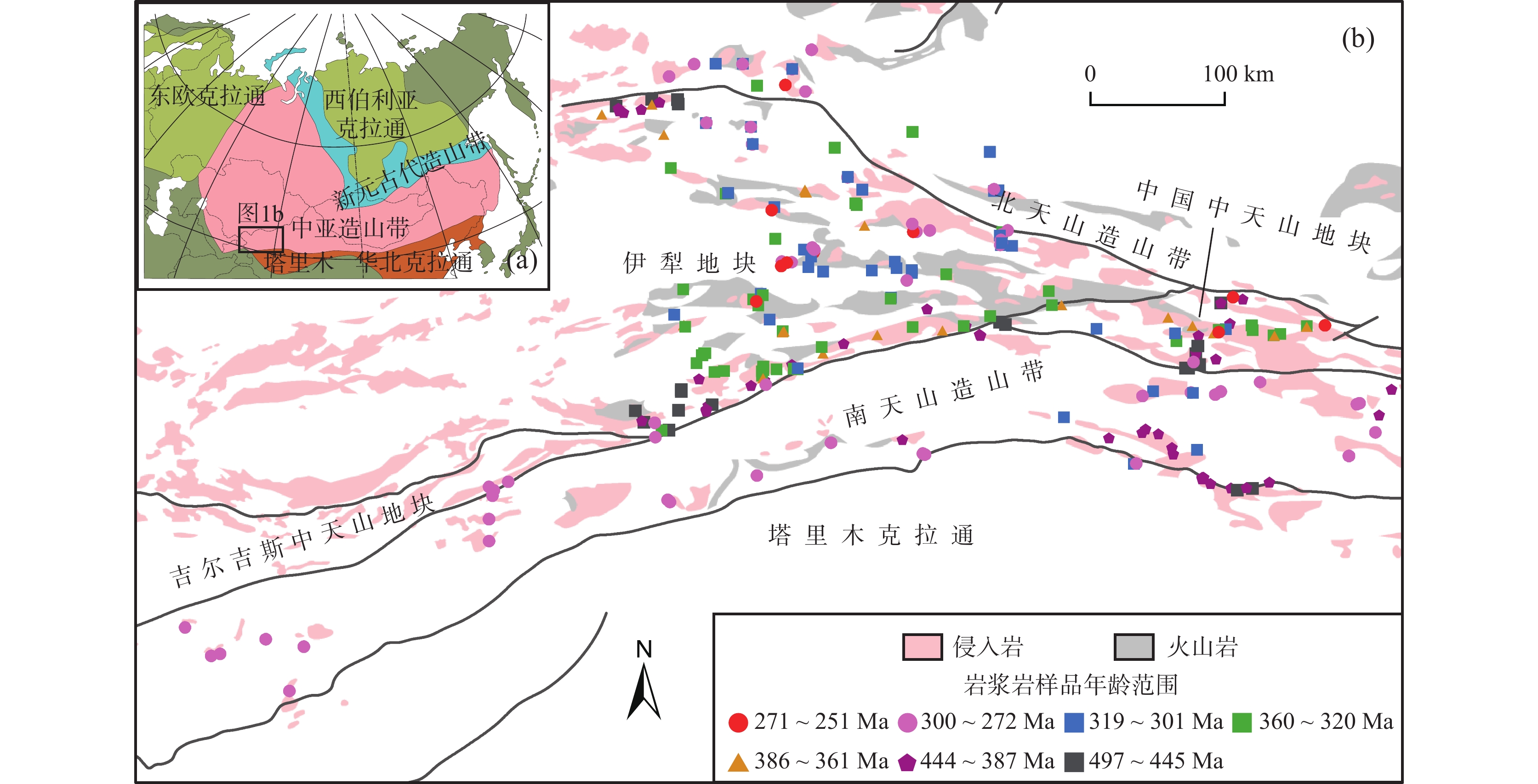
图 1 中亚造山带及相邻克拉通位置略图(a)(据Şengör et al.,2018;Xiao et al., 2015修改)、中国西天山主要构造单元岩浆岩图(b)
Figure 1.
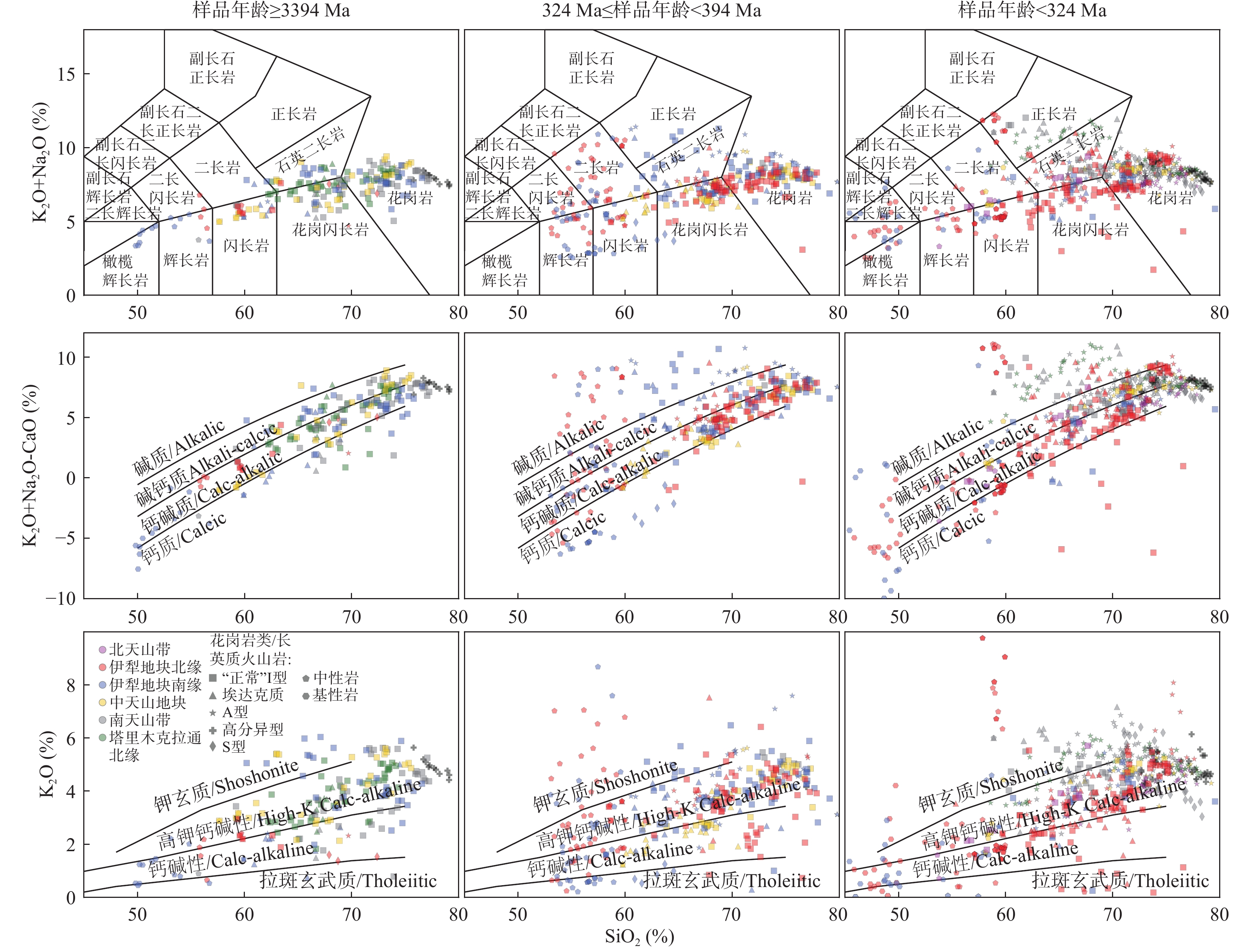
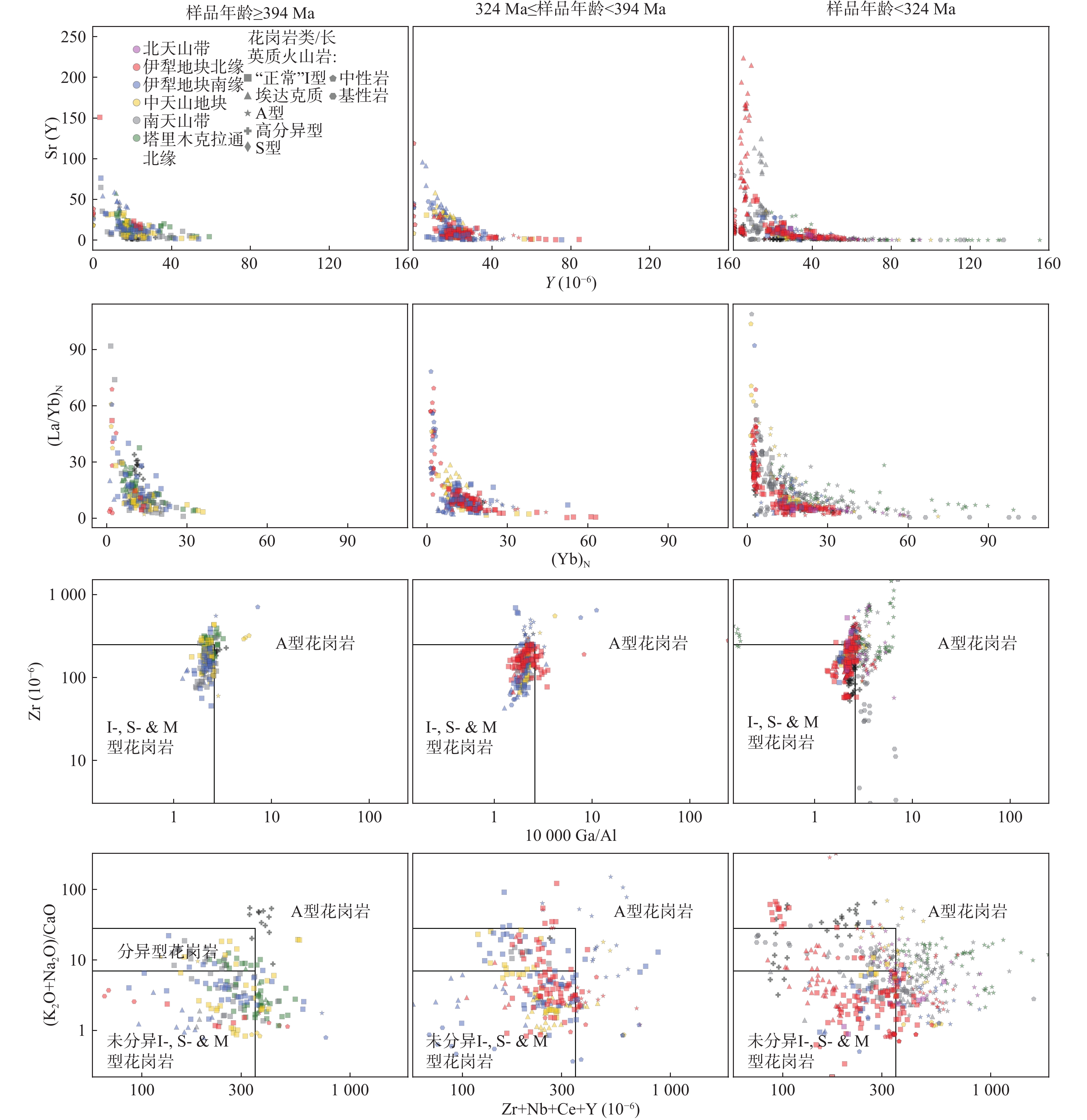
图 2 西天山各期岩浆岩的K2O+Na2O-SiO2图解(底图据Middlemost,1994)、K2O+Na2O-CaO-SiO2图解(底图据Frost et al.,2001)和K2O-SiO2图解(底图据Peccerillo et al.,1976)
Figure 2.
-
[1] 陈新跃, 王岳军, 孙林华, 等. 天山冰达坂和拉尔敦达坂花岗片麻岩SHRIMP锆石年代学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球化学, 2009, 38(5): 424−431. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2009.05.002
CHEN Xinyue, WANG Yuejun, SUN Linhua, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of the granitic gneisses from Bingdaban and Laerdundaban (Tianshan Orogen) and their geological significances[J]. Geochimica,2009,38(5):424−431. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2009.05.002
[2] 陈建, 王欣, 孟元库, 等. 北天山巴音沟石炭纪安山岩岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 西北地质, 2024, 57(3): 91−112.
CHEN Jian,WANG Xin,MENG Yuanku,et al. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of the Carboniferous Andesites from Bayingou in the North Tianshan Belt, Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology,2024,57(3):91−112.
[3] 李锦轶, 何国琦, 徐新, 等. 新疆北部及邻区地壳构造格架及其形成过程的初步探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(1): 148−168. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.01.017
LI Jinyi, HE Guoqi, XU Xin, et al. Crustal tectonic framework of northern Xinjiang and adjacent regions and its formation[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2006,80(1):148−168. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.01.017
[4] 李锦轶, 曲军峰, 张进, 等. 中国北方造山区显生宙地质历史重建与成矿地质背景研究进展[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(2−3): 207−219.
LI Jinyi, HE Guofeng, ZHANG Jin, et al. Reconstruction of Phanerozoic Geological History and Research of Metallogenic Geological Settings of the Northern China Orogenic Region[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2013,32(2−3):207−219.
[5] 李平, 朱涛, 吕鹏瑞, 等. 西天山早寒武世夏特辉长岩: 南天山洋早期俯冲的岩浆记录[J]. 西北地质, 2024, 57(3): 44−58. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023146
LI Ping, ZHU Tao, LÜ Pengrui, et al. Early Cambrian Xiate Gabbro in Western Tianshan: Magmatic Records of Initial Subduction of the South Tianshan Ocean[J]. Northwestern Geology,2024,57(3):44−58. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023146
[6] 孙吉明, 马中平, 贠杰, 等. 西天山乌孙山花岗岩和闪长岩年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 西北地质, 2024, 57(3): 59−72. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2024010
SUN Jiming, MA Zhongping, YUN Jie, et al. Geochronology Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Granite and Diorite in Wusun Mountain Western Tianshan[J]. Northwestern Geology,2024,57(3):59−72. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2024010
[7] 徐学义, 夏林圻, 马中平, 等. 北天山巴音沟蛇绿岩斜长花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及蛇绿岩成因研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(1): 83−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.01.009
XU Xueyi, XIA Linqi, MA Zhongping. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronology of the plagiogranites from Bayingou ophiolite in North Tianshan Mountains and the petrogenesis of the ophiolite[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2006,22(1):83−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.01.009
[8] 杨天南, 李锦轶, 孙桂华, 等. 中天山早泥盆世陆弧: 来自花岗质糜棱岩地球化学及 SHRIMP-U/Pb 定年的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(1): 41−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.01.004
YANG Tiannan, LI Jinyi, SUN Guihua, et al. Earlier Devonian active continental arc in Central Tianshan: evidence of geochemical analyses and Zircon SHRIMP dating on mylonitized granitic rock[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2006,22(1):41−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.01.004
[9] 张作衡, 王志良, 王彦斌, 等. 新疆西天山菁布拉克基性杂岩体闪长岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2007, 26(4): 353−360. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.04.001
ZHANG Zuoheng, WANG Zhiliang, WANG Yanbin, et al. Shrimp zircon U-Pb dating of diorite from Qingbulake basic complex in western Tianshan Mountains of Xinjiang and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits,2007,26(4):353−360. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.04.001
[10] Aitchison J C, Buckman S. Accordion vs. quantum tectonics: Insights into continental growth processes from the Paleozoic of eastern Gondwana[J]. Gondwana Research,2012,22(4):674−680.
[11] Antonijevic S K, Wagner L S, Kumar A, et al. The role of ridges in the formation and longevity of flat slabs[J]. Nature,2015,524(7564):212−215.
[12] Axen G J, Van Wijk J W, Currie C A. Basal continental mantle lithosphere displaced by flat-slab subduction[J]. Nature Geoscience,2018,11:961−964. doi: 10.1038/s41561-018-0263-9
[13] Cao Y C, Wang B, Jahn B M, et al. Late Paleozoic arc magmatism in the southern Yili Block (NW China): Insights to the geodynamic evolution of the Balkhash–Yili continental margin, Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Lithos,2017,278−281:111−125. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.01.023
[14] Carroll A, Graham S, Hendrix M, et al. Late Paleozoic tectonic amalgamation of northwestern China: sedimentary record of the northern Tarim, northwestern Turpan, and southern Junggar basins[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America,1995,107:571−594. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1995)107<0571:LPTAON>2.3.CO;2
[15] Cheng Z G, Zhang Z C, Santosh M, et al. Late Carboniferous to early Permian partial melting of the metasedimentary rocks and crustal reworking in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Evidence from garnet-bearing rhyolites in the Chinese South Tianshan[J]. Lithos,2017,282−283:373−387. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.03.017
[16] Collins W J. Hot orogens, tectonic switching, and creation of continental crust[J]. Geology,2002,30(6):535−538. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0535:HOTSAC>2.0.CO;2
[17] Collins W J, Huang H Q, Bowden P, et al. Repeated S-I-A-type granite trilogy in the Lachlan Orogen, and geochemical contrasts with A-type granites in Nigeria: Implications for petrogenesis and tectonic discrimination[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications,2019,491:SP491−2018-2159.
[18] Collins W J, Belousova E A, Kemp A I, et al. Two contrasting Phanerozoic orogenic systems revealed by hafnium isotope data[J]. Nature Geoscience,2011,4:333−337.
[19] Feng W, Zhu Y. Petrology and geochemistry of mafic and ultramafic rocks in the north Tianshan ophiolite: Implications for petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J]. Lithos,2018,318−319:124−142. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2018.08.012
[20] Frost B R. A Geochemical Classification for Granitic Rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology,2001,42:2033−2048. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033
[21] Gao J, Klemd R, Zhu M, et al. Large-scale porphyry-type mineralization in the Central Asian metallogenic domain: A review[J]. [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2018,165:7−36. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.10.002
[22] Gao J, Long L, Klemd R, et al. Tectonic evolution of the South Tianshan orogen and adjacent regions, NW China: geochemical and age constraints of granitoid rocks[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences,2009,98:1221−1238.
[23] Gazel E, Hayes J L, Hoernle K, et al. Continental crust generated in oceanic arcs[J]. Nature Geoscience,2015,8:321−327. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2392
[24] Gao J, Klemd R, Qian Q, et al. The collision between the Yili and Tarim blocks of the Southwestern Altaids: Geochemical and age constraints of a leucogranite dike crosscutting the HP–LT metamorphic belt in the Chinese Tianshan Orogen[J]. Tectonophysics,2011,499:118−131.
[25] Ge R, Zhu W, Wilde S A, et al. Neoproterozoic to Paleozoic long‐lived accretionary orogeny in the northern Tarim Craton[J]. Tectonics,2014,33:302−329. doi: 10.1002/2013TC003501
[26] Ge R, Zhu W, We H, et al. The Paleozoic northern margin of the Tarim Craton: Passive or active?[J]. Lithos,2012,142-143:1−15. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.02.010
[27] Gutscher M A, Eissler J, Bourdon E. Can slab melting be caused by flat subduction?[J]. Geology,2000,28:535−538.
[28] Guy A, Schulmann K, Janousek V, et al. Geophysical and geochemical nature of relaminated arc-derived lower crust underneath oceanic domain in southern Mongolia[J]. Tectonics,2015,34(5):1030−1053. doi: 10.1002/2015TC003845
[29] Han B F, He G Q, Wang X C, et al. Late Carboniferous collision between the Tarim and Kazakhstan–Yili terranes in the western segment of the South Tian Shan Orogen, Central Asia, and implications for the Northern Xinjiang, western China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2011,109:74−93. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.09.001
[30] Han Y, Zhao G. Final amalgamation of the Tianshan and Junggar orogenic collage in the southwestern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Constraints on the closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2018,186:129−152. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.09.012
[31] Han Y, Zhao G, Cawood P A, et al. Plume-modified collision orogeny: The Tarim–western Tianshan example in Central Asia[J]. Geology,2019,47(11):1001−1005.
[32] Hao L L, Wang Q, Zhang C, et al. Oceanic plateau subduction during closure of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean: insights from central Tibetan volcanic rocks[J]. GSA Bulletin,2018,131:864−880.
[33] He P L, Huang X L, Xu Y G, et al. Plume-orogenic lithosphere interaction recorded in the Haladala layered intrusion in the Southwest Tianshan Orogen, NW China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth,2016,121:1525−1545. doi: 10.1002/2015JB012652
[34] Hegner E, Alexeiev D V, Willbold M, et al. Early Silurian tholeiitic-boninitic Mailisu ophiolite, South Tianshan, Kyrgyzstan: a geochemical record of subduction initiation[J]. International Geology Review,2019,61(1):1−18. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2018.1440646
[35] He Z Y, Klemd R, Yan L L, et al. The origin and crustal evolution of microcontinents in the Beishan orogen of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2018,185:1−14.
[36] Hou Z, Duan L, Lu Y, et al. Lithospheric Architecture of the Lhasa Terrane and Its Control on Ore Deposits in the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen[J]. Economic Geology,2015,110:1541−1575. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.110.6.1541
[37] Hu A Q, Jahn B M, Zhang G X, et al. Crustal evolution and Phanerozoic crustal growth in northern Xinjiang: Nd isotopic evidence. Part. I. Isotopic characterization of basement rocks[J]. [J]. Tectonophysics,2000,328:15−51. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00176-1
[38] Huang H, Wang T, Guo L, et al. Crustal modification influenced by multiple convergent systems: Insights from Mesozoic magmatism in northeastern China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2024,252:104737. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2024.104737
[39] Huang H, Wang T, Tong Y, et al. Rejuvenation of ancient micro-continents during accretionary orogenesis: Insights from the Yili Block and adjacent regions of the SW Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2020,208:103255. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103255
[40] Huang H, Zhang Z, Kusky T, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Chuanwulu complex in the South Tianshan, western Xinjiang, NW China: Implications for petrogenesis and Phanerozoic continental growth[J]. Lithos,2012,140-141:65−84.
[41] Huang H, Zhang Z, Santosh M, et al. Crustal evolution in the South Tianshan Terrane: Constraints from detrital zircon geochronology and implications for continental growth in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Geological Journal,2019,54:1379−1400. doi: 10.1002/gj.3235
[42] Jahn B M, Wu F, Chen B. Granitoids of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and continental growth in the Phanerozoic[J]. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh,2000a,91:181−193. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300007367
[43] Jahn B M, Wu F, Chen B. Massive granitoid generation in Central Asia: Nd isotope evidence and implication for continental growth in the Phanerozoic[J]. Episodes Journal of International Geoscience,2000b,23:82−92.
[44] Jiang T, Gao J, Klemd R, et al. Paleozoic ophiolitic mélanges from the South Tianshan Orogen, NW China: Geological, geochemical and geochronological implications for the geodynamic setting[J]. Tectonophysics,2014,612-613:106−127. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.11.038
[45] Kemp A I S, Hawkesworth C J, Collins W J, et al. Isotopic evidence for rapid continental growth in an extensional accretionary orogen: the Tasmanides, eastern Australia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2009,284(3-4):455−466. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2009.05.011
[46] Kröner A, Kovach V, Belousova E, et al. Reassessment of continental growth during the accretionary history of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research,2014,25(1):103−125.
[47] Kröner A, Windley B F, Badarch G, et al. Accretionary growth and crust formation in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and comparison with the Arabian-Nubian shield[J]. Geological Society of America Memoirs,2007,200:181−209. doi: 10.1130/2007.1200(11)
[48] Kröner A, Kovach V, Alexeiev D, et al. No excessive crustal growth in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Further evidence from field relationships and isotopic data[J]. Gondwana Research,2017,50:135−166.
[49] Li C, Xiao W J, Han C M, et al. Late Devonian-early Permian accretionary orogenesis along the North Tianshan in the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. International Geology Review,2015b,57:1023−1050. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.913268
[50] Li P, Sun M, Rosenbaum G, et al. Geometry, kinematics and tectonic models of the Kazakhstan Orocline, Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2018,153:42−56. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.07.029
[51] Li Y J, Wen L, Yang H J, et al. New discovery and geological significance of Late Silurian–Carboniferous extensional structures in Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2015,98:304−319. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.020
[52] Liu Y J, Li W M, Ma Y F, et al. An orocline in the eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2021,221:103808. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103808
[53] Long L, Gao J, Klemd R, et al. Geochemical and geochronological studies of granitoid rocks from the Western Tianshan Orogen: Implications for continental growth in the southwestern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Lithos,2011,126:321−340. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.07.015
[54] Ma X, Shu L, Meert J G, et al. The Paleozoic evolution of Central Tianshan: Geochemical and geochronological evidence[J]. Gondwana Research,2014,25:797−819. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.015
[55] Ma X, Shu L, Meert J G. Early Permian slab breakoff in the Chinese Tianshan belt inferred from the post-collisional granitoids[J]. Gondwana Research,2015,27:228−243. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.09.018
[56] Mao Q, Wang J, Xiao W, et al. Mineralization of an intra-oceanic arc in an accretionary orogen: Insights from the Early Silurian Honghai volcanogenic massive sulfide Cu-Zn deposit and associated adakites of the Eastern Tianshan (NW China)[J]. GSA Bulletin,2019,131(3-4):803−830.
[57] Middlemost E A. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,1994,37:215−224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
[58] Mišković A, Schaltegger U. Crustal growth along a non-collisional cratonic margin: A Lu-Hf isotopic survey of the Eastern Cordilleran granitoids of Peru[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2009,279(1-2):303−315.
[59] Niu Y L. Geological understanding of plate tectonics: basic concepts, illustrations, examples and new perspectives[J]. Global Tectonics and Metallogeny,2018,10:23−46. doi: 10.1127/gtm/2014/0009
[60] Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1976,58:63−81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
[61] Qin Q, Wang T, Huang H, et al. Late Carboniferous and Early Permian garnet-bearing granites in the South Tianshan Belt, NW China: Two Late Paleozoic magmatic events and implications for crustal reworking[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2021,220:104923. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2021.104923
[62] Safonova I. Juvenile versus recycled crust in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Implications from ocean plate stratigraphy, blueschist belts and intra-oceanic arcs[J]. Gondwana Research,2017,47:6−27. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.09.003
[63] Safonova I, Krutikova A, Perfilova A, et al. Early Paleozoic juvenile crustal growth in the Paleo-Asian Ocean: A contribution from the Zasur'ya accretionary complex of NW Altai[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2024,249:104648. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2023.104648
[64] Song D F, Xiao W J, Windley B F, et al. A Paleozoic Japan-type subduction-accretion system in the Beishan orogenic collage, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Lithos,2015,224-225:195−213. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.03.005
[65] Şengör A, Natal'in B, Sunal G, et al. The tectonics of the Altaids: crustal growth during the construction of the continental lithosphere of Central Asia between∼ 750 and∼ 130 Ma ago[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2018, 46: 439-494.
[66] Tan Z, Agard P, Monié P, et al. Architecture and P-T-deformation-time evolution of the Chinese SW-Tianshan HP/UHP complex: Implications for subduction dynamics[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2019,197:102894. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102894
[67] Tan Z, Xiao W, Mao Q, et al. Final closure of the Paleo Asian Ocean basin in the early Triassic[J]. Communications Earth & Environment,2022,3:259.
[68] Tang G J, Wang Q, Wyman D A, et al. Genesis of pristine adakitic magmas by lower crustal melting: A perspective from amphibole composition[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth,2017,122:1934−1948. doi: 10.1002/2016JB013678
[69] Wang B, Chen Y, Zhan S, et al. Primary Carboniferous and Permian paleomagnetic results from the Yili Block (NW China) and their implications on the geodynamic evolution of Chinese Tianshan Belt[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2007,263(1−2):288−308.
[70] Wang B, Liu H, Shu L, et al. Early Neoproterozoic crustal evolution in northern Yili Block: Insights from migmatite, orthogneiss and leucogranite of the Wenquan metamorphic complex in the NW Chinese Tianshan[J]. Precambrian Research,2014a,242:58−81. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.12.006
[71] Wang B, Shu L, Faure M, et al. Paleozoic tectonics of the southern Chinese Tianshan: Insights from structural, chronological and geochemical studies of the Heiyingshan ophiolitic mélange (NW China)[J]. Tectonophysics,2011,497:85−104. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2010.11.004
[72] Wang B, Shu L, Liu H, et al. First evidence for ca. 780Ma intra-plate magmatism and its implications for Neoproterozoic rifting of the North Yili Block and tectonic origin of the continental blocks in SW of Central Asia[J]. Precambrian Research,2014b,254:258−272. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.09.005
[73] Wang M, Zhang J, Pei X, et al. Detrital zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopes study of the Lower Carboniferous Anjihai Formation from the northern margin of the Yili Block, NW China[J]. Geological Journal,2018a,53:223−236. doi: 10.1002/gj.3210
[74] Wang Q, Wyman D, Zhao Z, et al. Petrogenesis of Carboniferous adakites and Nb-enriched arc basalts in the Alataw area, northern Tianshan Range (western China): Implications for Phanerozoic crustal growth in the Central Asia orogenic belt[J]. Chemical Geology,2007,236:42−64. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.08.013
[75] Wang T, Huang H, Zhang J, et al. Voluminous continental growth of the Altaids and its control on metallogeny[J]. National Science Review,2023a,10:nwac283. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwac283
[76] Wang T, Xiao W, Collins W J, et al. Quantitative characterization of orogens through isotopic mapping[J]. Communications Earth & Environment,2023b,4:110.
[77] Wang X S, Cai K D, Sun M, et al. Two contrasting late Paleozoic magmatic episodes in the northwestern Chinese Tianshan Belt, NW China: Implication for tectonic transition from plate convergence to intra-plate adjustment during accretionary orogenesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2018b,153:118−138. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.03.013
[78] Wang Z P, Li Y J, Yang G X, et al. Petrogenesis and geochemical characteristics of Early Carboniferous sanukitic high‐Mg andesite from Atengtao Mountain, Yili Block: Implications for the tectonic setting during Late Palaeozoic in Chinese West Tianshan[J]. Geological Journal,2020,55:517−532. doi: 10.1002/gj.3427
[79] Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1987,95:407−419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
[80] Wilhem C, Windley B F, Stampfli G M. The Altaids of Central Asia: A tectonic and evolutionary innovative review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2012,113:303−341. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.04.001
[81] Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W, et al. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society,2007,164:31−47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022
[82] Xiao W J, Song D F, Windley B F, et al. Accretionary processes and metallogenesis of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Advances and perspectives[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2020,63:1−33. doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9474-4
[83] Xiao W, Santosh M. The western Central Asian Orogenic Belt: A window to accretionary orogenesis and continental growth[J]. Gondwana Research,2014,25:1429−1444. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.01.008
[84] Xiao W J, Windley B F, Sun S, et al. A Tale of Amalgamation of Three Permo-Triassic Collage Systems in Central Asia: Oroclines, Sutures, and Terminal Accretion[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2015, 43: 477-507.
[85] Xiao W, Windley B F, Allen M B, et al. Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Chinese Tianshan orogenic collage[J]. Gondwana Research,2013,23:1316−1341. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.01.012
[86] Xu Q, Ji J, Zhao L, et al. Tectonic evolution and continental crust growth of Northern Xinjiang in northwestern China: Remnant ocean model[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2013,126:178−205. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.08.005
[87] Xu X Y, Wang H L, Li P, et al. Geochemistry and geochronology of Paleozoic intrusions in the Nalati (Narati) area in western Tianshan, Xinjiang, China: Implications for Paleozoic tectonic evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2013,72:33−62. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.023
[88] Xu Y X, Yang B, Zhang S, et al. Magnetotelluric imaging of a fossil paleozoic intraoceanic subduction zone in western Junggar, NW China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth,2016,121:4103−4117. doi: 10.1002/2015JB012394
[89] Yang G X, Li Y J, Tong L L, et al. An overview of oceanic island basalts in accretionary complexes and seamounts accretion in the western Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2019,179:385−398. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.04.011
[90] Yang S H, Zhou M F. Geochemistry of the 430-Ma Jingbulake mafic–ultramafic intrusion in Western Xinjiang, NW China: implications for subduction related magmatism in the South Tianshan orogenic belt[J]. Lithos,2009,113:259−273. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.07.005
[91] Zhang C L, Zou H B. Comparison between the Permian mafic dykes in Tarim and the western part of Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB), NW China: Implications for two mantle domains of the Permian Tarim Large Igneous Province[J]. Lithos,2013,174:15−27. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.11.010
[92] Zhang X R, Zhao G C, Han Y G, et al. Differentiating advancing and retreating subduction zones through regional zircon Hf isotope mapping: A case study from the Eastern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Gondwana Research,2019,66:246−254. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.10.009
[93] Zhang X R, Zhao G C, Sun M, et al. Tectonic evolution from subduction to arc-continent collision of the Junggar ocean: Constraints from U-Pb dating and Hf isotopes of detrital zircons from the North Tianshan belt, NW China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,2016,128:644−660. doi: 10.1130/B31230.1
[94] Zhao Z Y, Zhang Z C, Santosh M, et al. Early Paleozoic magmatic record from the northern margin of the Tarim Craton: Further insights on the evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research,2015,28:328−347. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.04.007
[95] Zhao Z, Xiong X, Wang Q, et al. Late Paleozoic underplating in North Xinjiang: Evidence from shoshonites and adakites[J]. Gondwana Research,2009,16:216−226. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2009.03.001
[96] Zhong L L, Wang B, Alexeiev D V, et al. Paleozoic multi-stage accretionary evolution of the SW Chinese Tianshan: New constraints from plutonic complex in the Nalati Range[J]. Gondwana Research,2017,45:254−274. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.12.012
[97] Zhou J B, Wilde S A. The crustal accretion history and tectonic evolution of the NE China segment of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research,2013,23:1365−1377. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.05.012
[98] Zhu D, Wang Q, Zhao Z, et al. Magmatic record of India-Asia collision[J]. Scientific Reports,2015,5:14289. doi: 10.1038/srep14289
[99] Zhu D, Wang Q, Zhao Z. Constraining quantitatively the timing and process of continent-continent collision using magmatic record: Method and examples[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2017,60(6):1040−1056. doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-9041-x
[100] Zhu X, Wang B, Chen Y, et al. First Early Permian Paleomagnetic Pole for the Yili Block and its Implications for Late Paleozoic Postorogenic Kinematic Evolution of the SW Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Tectonics,2018,37(6):1709−1732. doi: 10.1029/2017TC004642
[101] Zhu Y, Guo X, Song B, et al. Petrology, Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry and zircon chronology of the Late Palaeozoic volcanic rocks in the southwestern Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Journal of the Geological Society,2009,166:1085−1099. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492008-130
-



 下载:
下载: