Geological Hazard Failure Mode and Risk Control of Slopes along the Yellow River Highway: Taking the Suide Qingjian Section in Shaanxi Province as an Example
-
摘要:
沿黄公路位于黄土高原黄河中游区,区域滑坡崩塌等地质灾害多发,对沿黄公路的道路安全造成威胁。笔者通过1∶
10000 地质灾害野外调查,总结了沿黄公路陕西绥德–清涧段边坡地质灾害变形破坏演化模式,定量评估了边坡地质灾害财产风险和人员风险。结果表明:①沿黄公路陕西绥德–清涧段共发育地质灾害51处,以小型基岩崩塌为主;崩塌包括岩质和土质崩塌,其破坏模式分为倾倒式、滑移式和坠落式3种;滑坡均为黄土滑坡,为拉裂–剪切滑移式破坏模式。②51处地质灾害财产年损失为0.0005 ~3.375万元/a,单人年死亡概率为4.16×10−5~4.40×10−2,其中低风险源12个,中风险源9个,高风险源18个,极高风险源12个。③根据边坡破坏模式及风险评估结果,对研究区边坡地质灾害制定了搬迁避让、专业监测、工程防治、群策群防等相应的风险管控措施建议。该研究结果为沿黄公路沿线地质灾害防灾减灾提供了技术支撑。Abstract:The Yellow River Highway is located in the middle reaches of the Yellow River on the Loess Plateau, where geological hazards such as landslides and collapses occur frequently, posing a threat to the road safety along the Yellow River Highway. This article summarizes the deformation and failure evolution patterns of geological hazards along the Suide Qingjian section of the Yellow River Highway in Shaanxi Province through a 1∶
10000 field survey, and quantitatively evaluates the property and personnel risks of slope geological hazards. The results show that: ① 51 geological hazards have developed along the Yellow River Highway in the Suide Qingjian section of Shaanxi Province, mainly small-scale bedrock collapses; Collapse includes rock collapse and soil collapse, and its failure modes are divided into three categories: toppling, sliding, and falling; The landslides are all loess landslides, with a tensile shear sliding failure mode. ② 51 geological hazards result in annual property losses ranging from0.0005 to 3.375 million yuan per year, with an annual mortality probability of 4.16 × 10−5 to 4.40 × 10−2 per person. Among them, there are 12 low-risk sources, 9 medium risk sources, 18 high-risk sources, and 12 extremely high-risk sources. ③ Based on the failure mode and risk assessment results of the slope, corresponding risk control measures and suggestions have been formulated for the geological hazards of the slope in the study area, including relocation avoidance, professional monitoring, engineering prevention and control, and group strategy and prevention. The research results provide technical support for geological hazard prevention and reduction along the Yellow River Highway.-
Key words:
- the Yellow River Highway /
- geological Hazards /
- failure mode /
- risk evaluation /
- risk control
-

-
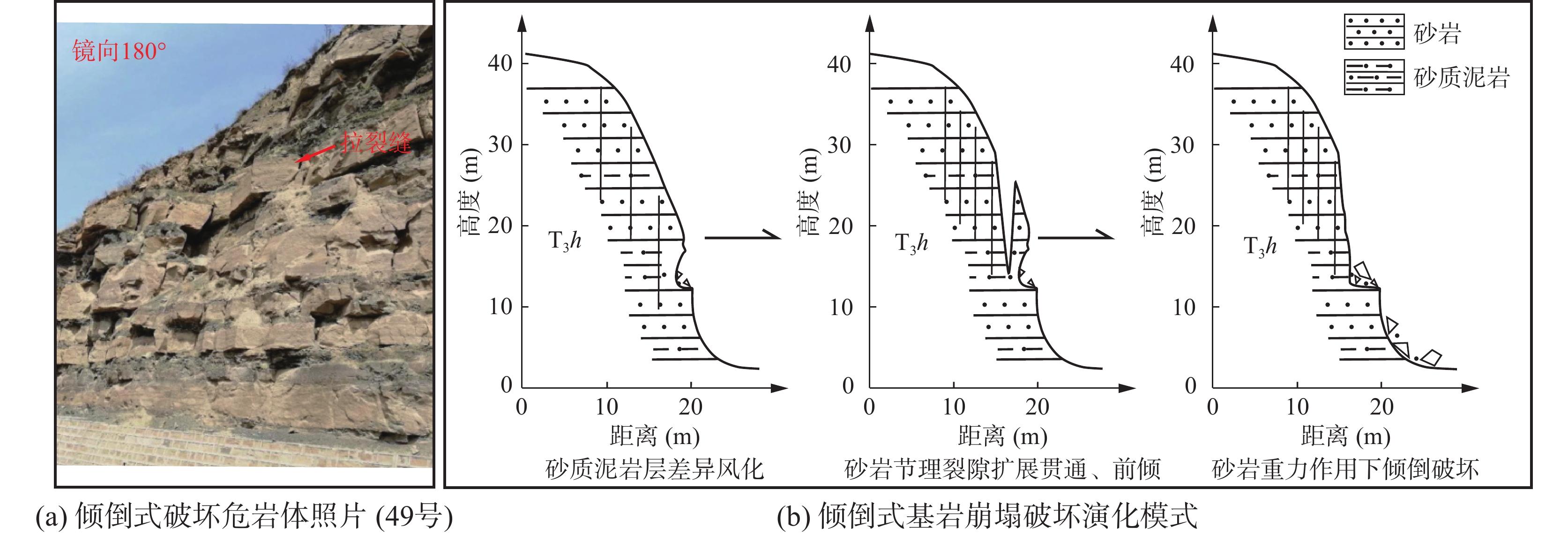
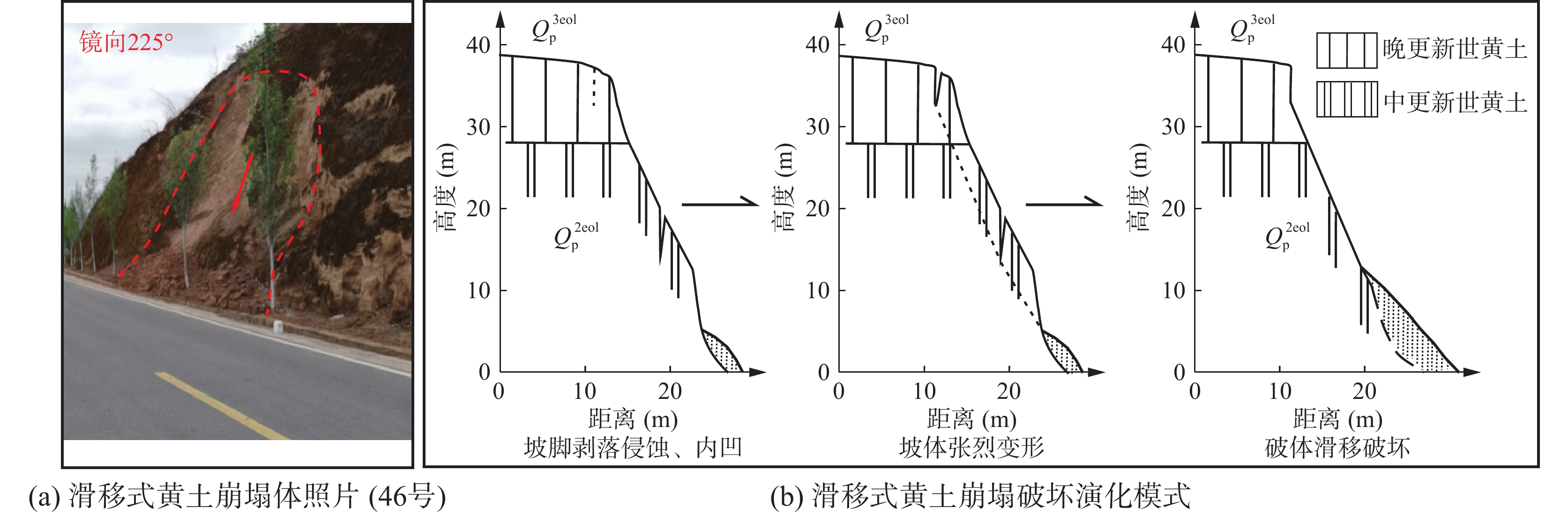
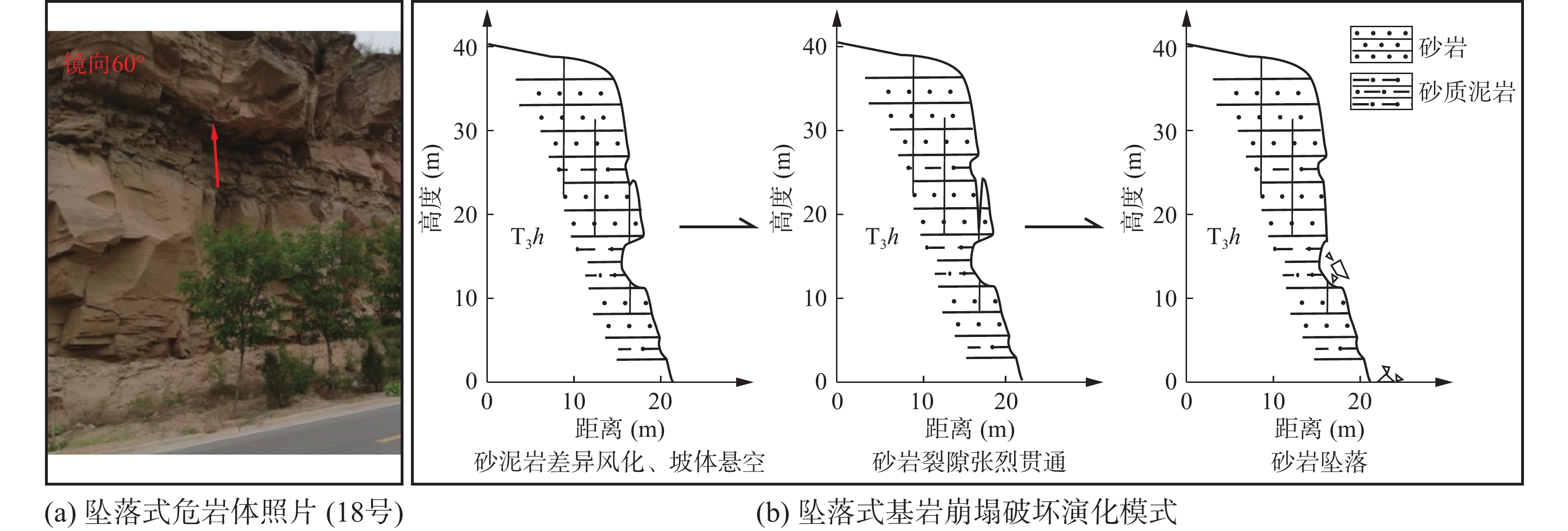
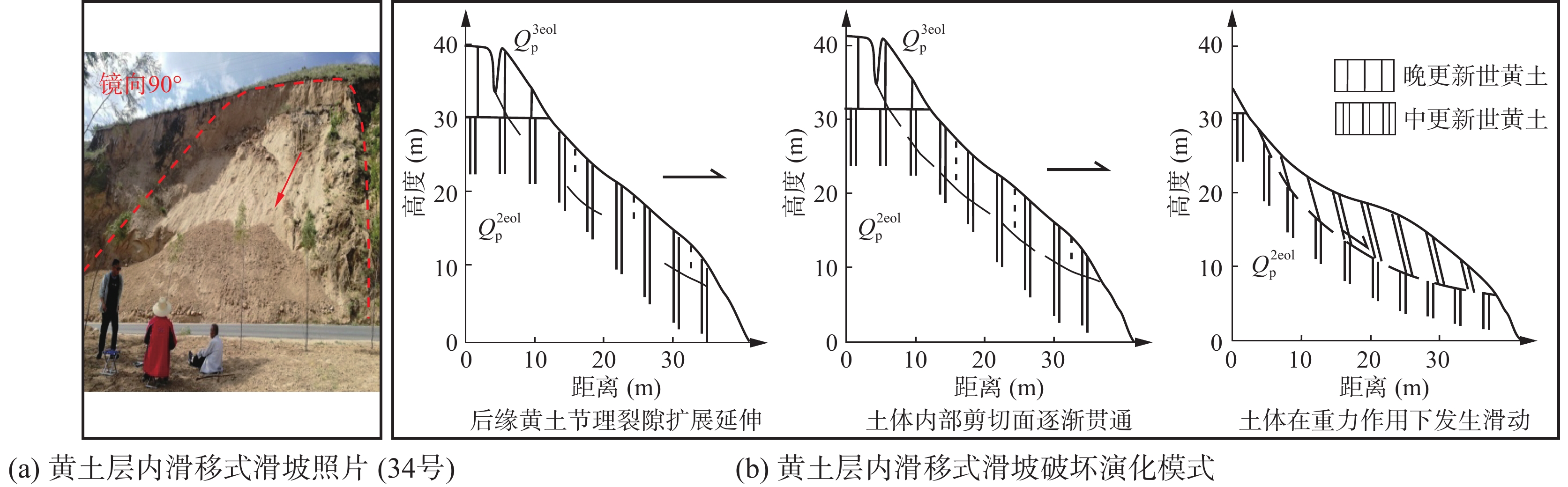
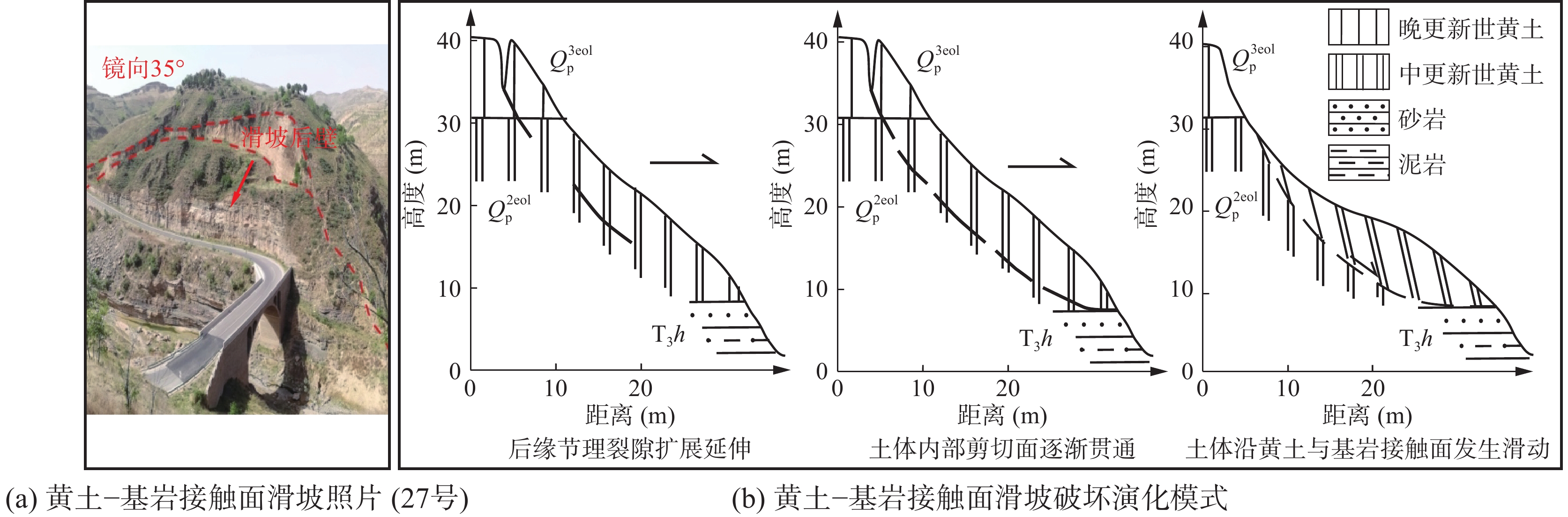
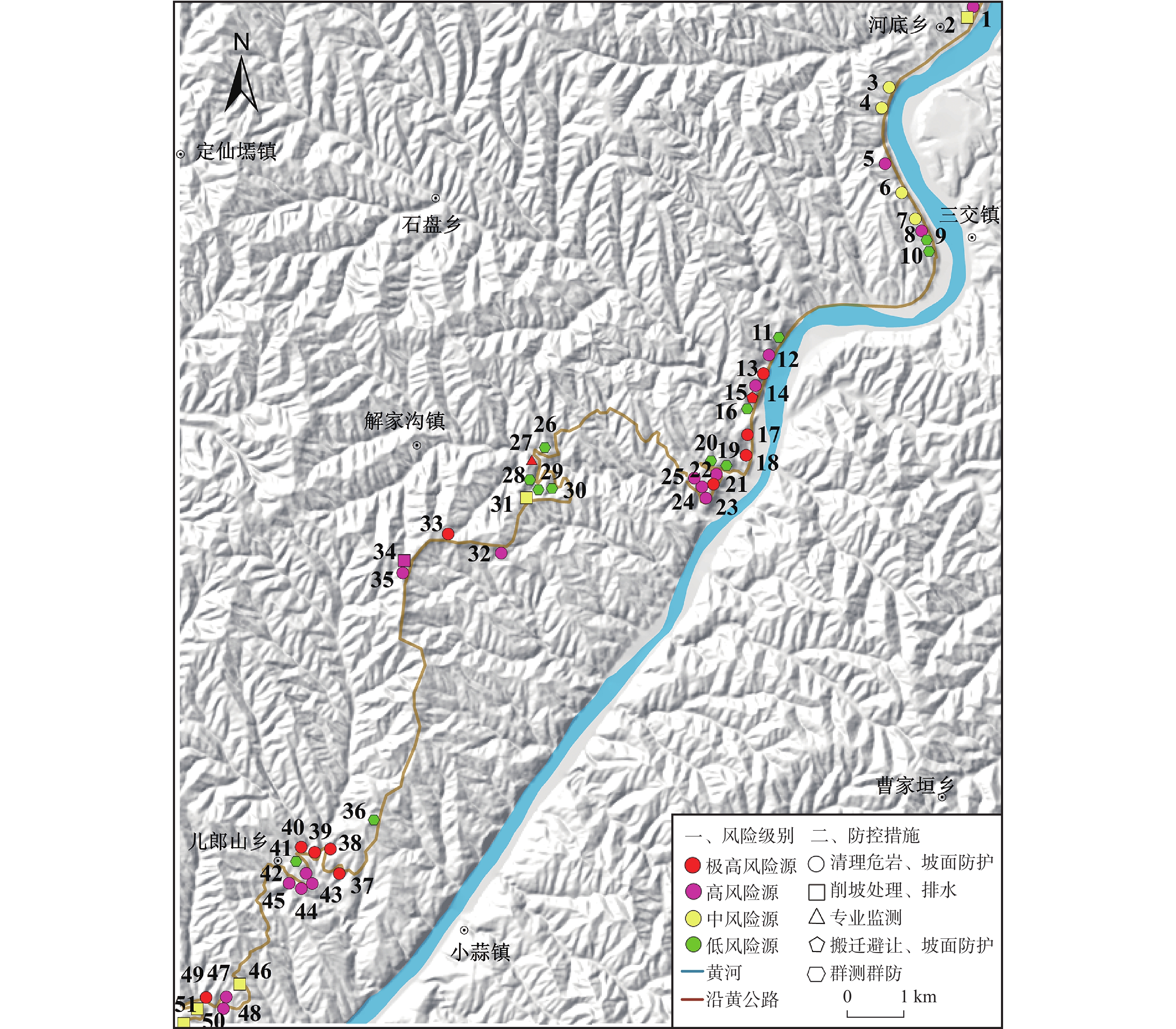
表 1 研究区边坡灾害变形破坏模式分类
Table 1. Classification of deformation and failure modes of slope disasters in the study area
编号 灾害类型 破坏模式 地层岩性及灾害体特征 编号 灾害类型 破坏模式 地层岩性及灾害体特征 1 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高18 m,宽200 m 27 滑坡 拉裂-滑移 黄土+基岩,厚15~20 m,
坡高120 m,宽270 m2 崩塌 倾倒 黄土,坡高13 m,宽50 m 28 崩塌 滑移 黄土,坡高66 m,宽100 m 3 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高60 m,宽150 m 29 崩塌 滑移 黄土,坡高20 m,宽50 m 4 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高50 m,宽150 m 30 滑坡隐患 拉裂–滑移 黄土,坡高45.5 m,宽100 m 5 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高80 m,宽650 m 31 滑坡 拉裂–滑移 黄土,坡高45.5 m,
宽100 m,厚1~2 m6 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高100 m,宽500 m 32 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高33 m,宽100 m 7 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高96 m,宽250 m 33 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高18.4 m,宽70 m 8 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高65 m,宽150 m 34 滑坡 拉裂–滑移 黄土,坡高23 m,
宽100 m,厚约4 m9 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高65 m,宽250 m 35 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高21 m,宽20 m 10 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高70 m,宽300 m 36 崩塌 滑移 黄土,坡高23 m,宽100 m 11 崩塌隐患 滑移 基岩,坡高108 m,宽150 m 37 崩塌隐患 倾倒 黄土,坡高29 m,宽7 m 12 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高114 m,宽300 m 38 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高29.5 m,宽105 m 13 崩塌隐患 滑移 基岩,坡高115 m,宽150 m 39 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高18 m,宽50 m 14 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高105 m,宽100 m 40 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高20 m,宽150 m 15 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高106 m,宽200 m 41 崩塌隐患 滑移 黄土+基岩,坡高30 m,宽120 m 16 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高90 m,宽500 m 42 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高18 m,宽60 m 17 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高26 m,宽300 m 43 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高19 m,宽100 m 18 崩塌隐患 坠落 基岩,坡高30 m,宽200 m 44 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高13 m,宽70 m 19 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高60 m,宽100 m 45 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高11 m,宽93 m 20 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高45 m,宽100 m 46 崩塌 滑移 黄土,坡高17 m,宽10 m 21 崩塌隐患 坠落 基岩,坡高17 m,宽50 m 47 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高18 m,宽200 m 22 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高35 m,宽30 m 48 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高19 m,宽50 m 23 崩塌隐患 坠落 基岩,坡高15 m,宽100 m 49 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高21 m,宽75 m 24 崩塌隐患 坠落 基岩,坡高23 m,宽70 m 50 崩塌 滑移 黄土,坡高17 m,宽100 m 25 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高20 m,宽60 m 51 崩塌 滑移 黄土,坡高22 m,宽100 m 26 崩塌隐患 倾倒 基岩,坡高25 m,宽250 m 表 2 沿黄公路段边坡灾害风险评估结果
Table 2. Results of slope disaster risk assessment along the Yellow Highway section
风险源
编号发生概
率P(L)到达概
率P(T:L)固定承载体时
空概率P(S:T)流动承灾体时
空概率P(S:T)财产易损
性V(prop:S)人员易损
性V(D:T)承灾体
价值E(万元)财产年损失
P(prop)(万元/a)单人年死亡
概率P(LOL)1 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.60 0.60 45.00 0.270 1.25×10−3 2 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.20 0.20 11.25 0.023 4.16×10−4 3 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.40 11.25 0.034 8.32×10−4 4 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.40 22.50 0.090 8.32×10−4 5 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.50 146.25 0.585 1.04×10−3 6 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.40 112.50 0.338 8.32×10−4 7 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.40 56.25 0.169 8.32×10−4 8 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.50 33.75 0.135 1.04×10−3 9 10−3 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.20 0.30 56.25 0.011 6.24×10−5 10 10−3 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.40 67.50 0.020 8.32×10−5 11 10−3 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.40 33.75 0.010 8.32×10−5 12 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.60 67.50 0.270 1.25×10−3 13 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.60 0.70 33.75 2.025 1.46×10−2 14 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.50 22.50 0.090 1.04×10−3 15 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.55 0.60 0.80 55.00 3.300 4.40×10−2 16 10−3 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.40 112.50 0.034 8.32×10−5 17 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.50 0.70 67.50 3.375 1.46×10−2 18 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.50 0.60 45.00 2.250 1.25×10−2 19 10−3 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.30 22.50 0.009 6.24×10−5 20 10−3 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.20 0.30 22.50 0.005 6.24×10−5 21 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.60 11.25 0.045 1.25×10−3 22 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.60 6.75 0.270 1.25×10−2 23 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.60 0.60 22.50 0.135 1.25×10−3 24 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.50 15.75 0.063 1.04×10−3 25 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.40 13.50 0.540 8.32×10−3 26 10−3 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.20 0.30 33.75 0.007 6.24×10−5 27 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.50 0.70 60.75 3.038 1.46×10−2 28 10−3 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.40 22.50 0.007 8.32×10−5 29 10−2 0.3 1.0 0.208 0.20 0.10 11.25 0.007 6.24×10−5 30 10−3 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.30 22.50 0.007 6.24×10−5 31 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.20 22.50 0.068 4.16×10−4 32 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.5 0.60 15.75 0.079 1.25×10−3 33 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.50 15.75 0.630 1.04×10−2 34 10−1 0.5 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.20 9.00 0.135 2.08×10−3 35 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.5 0.70 4.50 0.225 1.46×10−2 36 10−3 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.20 1.58 0.0005 4.16×10−5 37 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.50 22.50 0.900 1.04×10−2 38 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.5 0.60 23.63 1.181 1.25×10−2 39 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.50 0.60 11.25 0.563 1.25×10−2 40 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.5 0.50 33.75 1.688 1.04×10−2 41 10−3 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.20 27.00 0.008 4.16×10−5 42 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.5 0.60 13.50 0.675 1.25×10−3 43 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.50 22.50 0.900 1.04×10−3 44 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.40 15.75 0.630 8.32×10−3 45 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.40 0.40 20.93 0.837 8.32×10−3 46 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.30 2.25 0.068 6.24×10−4 47 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.60 0.70 45.00 0.270 1.46×10−3 48 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.60 0.70 11.25 0.068 1.46×10−3 49 10−1 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.50 0.50 16.88 0.844 1.04×10−2 50 10−2 1.0 1.0 0.208 0.30 0.40 22.50 0.068 8.32×10−4 51 10−2 0.3 1.0 0.208 0.20 0.20 22.50 0.014 1.25×10−4 -
[1] 毕银强, 唐亚明, 张茂省, 等. 公路沿线危岩崩塌风险定量评估-以甘肃S306沿线磨石咀崩塌为例[J]. 防灾科技学院学报, 2016, 18(2): 35−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2016.02.005
BI Yinqiang, TA Yaming, ZHANG Maosheng, et al. The Quantitative Risk Assessment for Perilous Rockfall of Cut Slope along Road-A Case Study on the Moshiju Rockfall in Gansu along S306[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention,2016,18(2):35−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2016.02.005
[2] 陈晓刚, 李红卫, 张乾翼. 重庆某高速公路危岩崩塌变形特征及治理措施[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2024, 35(3): 43−51.
CHEN Xiaogang, LI Hongwei, ZHANG Qianyi. Deformation Characteristics and Treatment Measures of Dangerous Rock Collapae in an Expressway in Chongqing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Contrlo,2024,35(3):43−51.
[3] 冯凡, 唐亚明, 潘学树, 等. 不同尺度下地质灾害风险评价方法探讨—以陕西吴堡县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(2): 115−124.
FENG Fan, TANG Yaming, PAN Xueshu, et al. An Attempt of Risk Assessment of Geological Hazards in Different Scales: A Case Study in Wubao County of Shaanxi Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):115−124.
[4] 黄强兵, 康孝森, 王启耀, 等. 山西吕梁黄土崩滑类型及发育规律[J]. 工程地质学报, 2016, 24(1): 64−72.
HUANG Qiangbing, KANG Xiaosen, WANG Qiyao, et al. Types and Characteristics of Loess Landslides and Collapses in Luliang Area of Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(1):64−72.
[5] 蒋瑜阳, 向波, 王东, 等. 震后山区公路地质灾害风险评估体系研究-以川九公路震后恢复重建为例[J]. 地震工程学报, 2023, 45(5): 1026−1034.
JIANG Yuyang, XIANG Bo, WANG Dong, et al. Risk Evaluation System for Geological Disasters of Highways in Mountainous Regions after Earthquakes: A Case Study of the Postearthquake Restoration and Reconstruction of the Chuanzhusi-Jiuzhaigou Highway[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2023,45(5):1026−1034.
[6] 李同录, 龙建辉, 李新生. 黄土滑坡发育类型及其空间预测方法[J]. 工程地质学报, 2007, 15(4): 500−505. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.04.012
LI Tonglu, LONG Jianhui, LI Xinsheng. Types of Loess Landslides and Methods for Their Movement Forecast[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2007,15(4):500−505. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.04.012
[7] 廖小平, 徐风光, 蔡旭东, 等. 香丽高速公路边坡地质灾害发育特征与易发性区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2021, 32(5): 121−129.
LIAO Xiaoping, XU Fengguang, CAI Xudong, et al. Development Characteristics and Susceptibality Zoning of Slope Geological Hazards in Xiangli Expressway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Contrlo,2021,32(5):121−129.
[8] 马红娜, 刘江, 冯卫, 等. 地质灾害风险评估在国土空间规划中的应用-以陕北榆林高西沟为例[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(3): 223−231. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023058
MA Hongna, LIU Jiang, FENG Wei, et al. Application of Geological Hazard Risk Assessment in Territorial Space Planning: A Case Study of Gaoxigou Village in Yulin City of Northen Shaanxi Province[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023,56(3):223−231. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023058
[9] 彭建兵, 林鸿州, 王启耀, 等. 黄土地质灾害研究中的关键问题与创新思路[J]. 工程地质学报, 2014, 22(4): 684−691.
PENG Jianbing, LIN Hongzhou, WANG Qiyao, et al. The Critical Issues and Creative Concepts in Mitigation of Loess Eeological Hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(4):684−691.
[10] 彭军, 李翔宇, 闫蕊鑫, 等. 陕北地区黄土崩塌破坏模式分类及防控对策研究[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2015, 32(10): 11−16.
PENG Jun, LI Xiangxu, YAN Ruixin, et al. Failure Modes Classification and Counterm Easures of Loess Collapse in Northern Shaanxi Area[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2015,32(10):11−16.
[11] 孙萍萍, 张茂省, 程秀娟, 等. 黄土高原地质灾害发生规律[J]. 山地学报, 2019, 37(5): 737−746.
SUN Pingping, ZHANG Maosheng, CHENG Xiujuan, et al. On the Eegularity of Geological Hazard on the Loess Plateau in China[J]. Mountain Research,2019,37(5):737−746.
[12] 唐亚明, 冯卫, 毕银强, 等. 基于风险评价的黄土滑坡分类及特征[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(11): 2092−2099. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.11.015
TANG Yaming, FENG Wei, BI Yinqiang, et al. The Classification and Features of Loess Landslide Based on Risk Assessment[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2015,34(11):2092−2099. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.11.015
[13] 王根龙, 张茂省, 苏天明, 等. 黄土崩塌破坏模式及离散元数值模拟分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2011, 19(4): 541−549. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.015
WANG Genlong, ZHANG Maosheng, SU Tianming, et al. Collapse Failure Modes and Dem Numerical Simulation for Loess Slopes[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(4):541−549. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.015
[14] 伍运霖, 刘天翔, 王丰, 等. 考虑长期蠕变劣化的昔格达黏土岩公路路堑边坡稳定性评价及防护对策建议—以西攀高速公路边坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2024, 35(4): 56−66.
WU Yunlin, LIU Tianxiang, WANG Feng, et al. Stability Assessment of the Road Cut Slopes in the Xigeda Mudstone Considering Long-term Creep Deterioration and Suggestion for Countermeasures: A Case Study of Cut Slopes along the Xichang-Panzhihua Expressway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Contrlo,2024,35(4):56−66.
[15] 许领, 戴福初, 邝国麟, 等. 黑方台黄土滑坡类型与发育规律[J]. 山地学报, 2008, 26(3): 364−371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2008.03.018
XU Ling, DAI Fuchu, KUANG Guolin, et al. Types and Characteristics of Loess Landslides at Heifang Loess Plateau, China[J]. Mountain Research,2008,26(3):364−371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2008.03.018
[16] 徐继维, 张茂省. 中国地质灾害风险允许标准[J]. 灾害学, 2016, 31(3): 127−130.
XU Jiwei, ZHANG Maosheng. Risk Criteria of Geohazards in China[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2016,31(3):127−130.
[17] 薛强, 唐亚明, 白轩. 吕梁山区大宁县城地质灾害破坏模式及风险管控[J]. 山地学报, 2021, 39(1): 151−162.
XUE Qiang, TANG Yaming, BAI Xuan. Failure Modes and Risk Control of Geohazards in the County Town of Daning in the Lüliang Mountains, China[J]. Mountain Research,2021,39(1):151−162.
[18] 杨柳, 牟鑫亮, 李晨, 等. 延安市宝塔区地质灾害风险评价[J]. 山地学报, 2020, 38(5): 679−690.
YANG Liu, MOU Xinliang, LI Chen, et al. Risk Assessment of Geological Hazards in Baota District, Yan’an City, Shaanxi, China[J]. Mountain Research,2020,38(5):679−690.
[19] 岳中琦. 梅大高速公路路基边坡失稳条件与滑坡机理初探[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2024, 35(3): 1−12.
YUE Zhongqi. Study on the Instability Condition and Landslide Mechanism of Subgrade Slope in Mei-Da Expressway[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Contrlo,2024,35(3):1−12.
[20] 张茂省, 薛强, 贾俊, 等. 山区城镇地质灾害调查与风险评价方法及实践[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(2): 125−135.
ZHANG Maosheng, XUE Qiang, JIA Jun, et al. Methods and Practices for the Investigation and Risk Assessment of Geo-hazards in Mountainous Towns[J]. Northwestern Geology,2019,52(2):125−135.
-




 下载:
下载: