OIL-BEARING PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION AND RESOURCE CALCULATION OF THE SHALE OIL IN QIJIA AND GULONG SAGS, SONGLIAO BASIN
-
摘要:
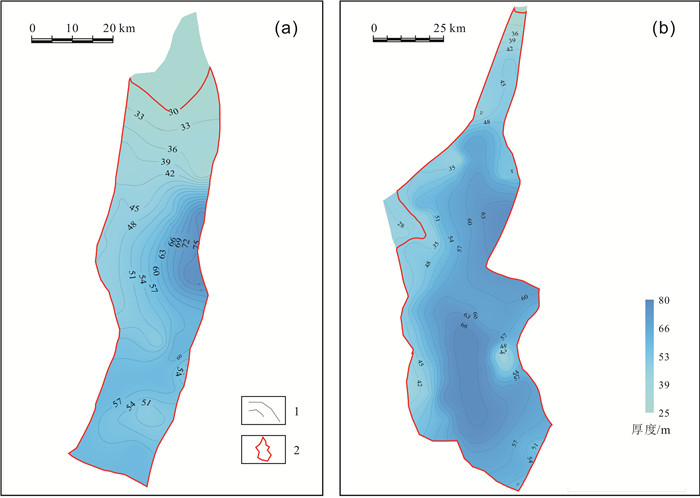
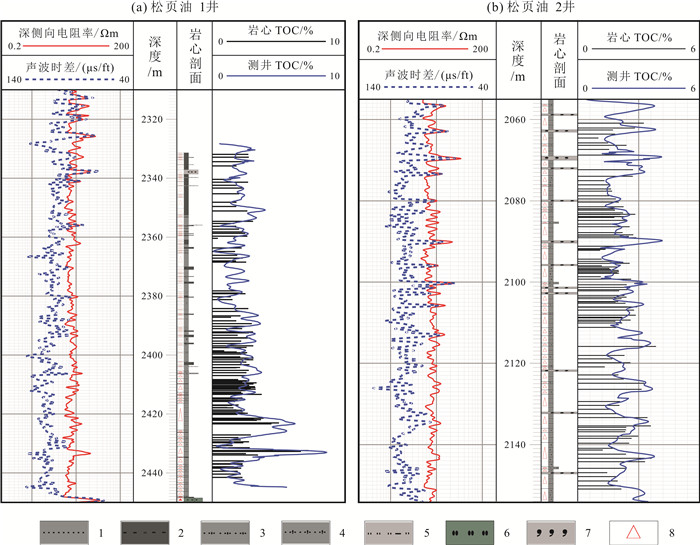
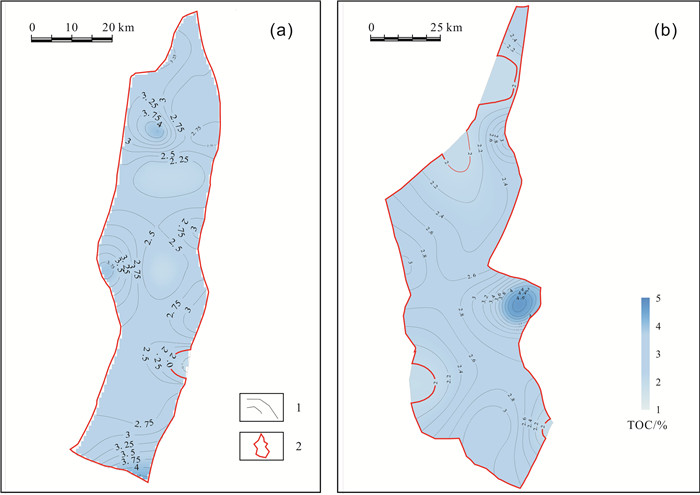
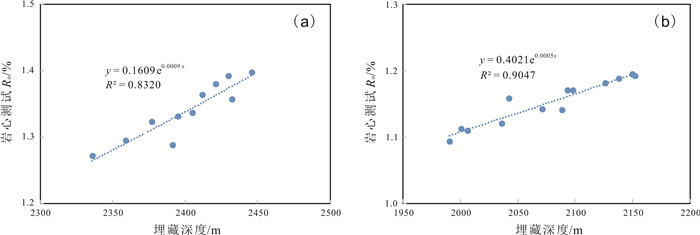
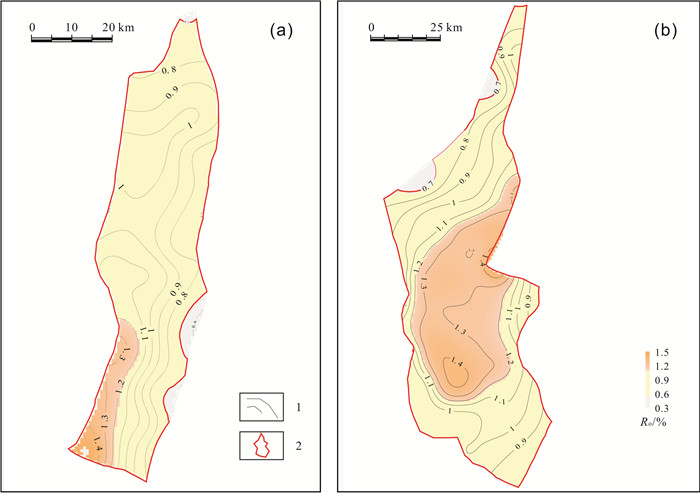
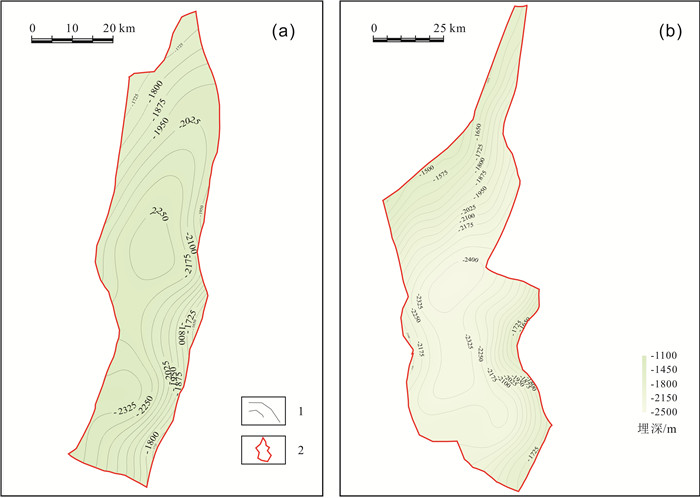
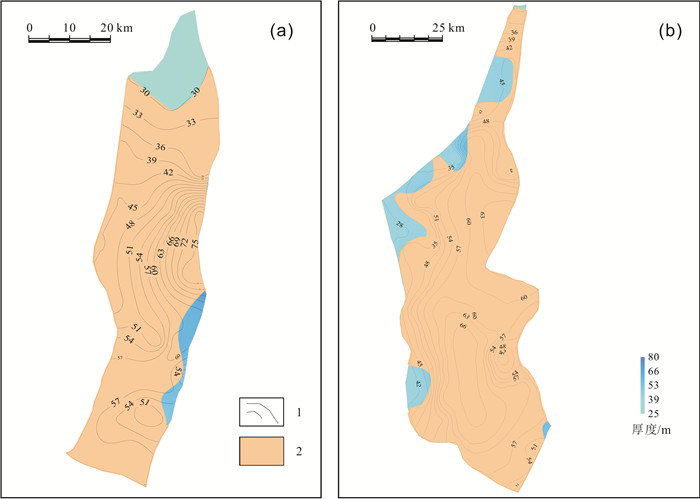
松辽盆地齐家和古龙凹陷青山口组一段页岩油资源丰富.以往主要基于不完整的老岩心资料,以校正后的热解S1或氯仿沥青"A"作为含油性参数计算页岩油资源量,校正参数的准确性受样品新鲜程度、测试手段及校正方法等多种因素影响,导致上述参数的应用存在一定的局限性.根据最新页岩油勘探进展,对比分析了页岩油资源量计算的含油性参数(包括热解S1、氯仿沥青"A"和含油饱和度)的应用差异,认为含油饱和度可反映游离油和溶解烃含量,不用考虑吸附油影响,且无需进行轻烃、重烃和NSO化合物校正,在具有新鲜样品测试数据的条件下,更适合作为研究区页岩油资源量计算的含油性参数.基于最新页岩油参数井钻探成果和测试数据,明确了有效泥页岩厚度、有机质丰度(TOC)、有机质成熟度(Ro)和埋深的平面分布.通过多因素叠合法查明了齐家和古龙凹陷青山口组一段页岩油富集区面积分别为1 957.23 km2和4 509.09 km2.结合密闭冷冻样品的含油饱和度、页岩油密度实测数据和有效孔隙度测井解释数据,通过体积法计算出齐家和古龙凹陷青山口组一段页岩油富集区资源量分别为19.79×108 t和27.29×108 t,表明研究区基质型页岩油具有很好的勘探前景.
Abstract:There are abundant shale oil resources in the first member of Qingshankou Formation in Qijia and Gulong sags of Songliao Basin. In the past, the shale oil resources were calculated mainly based on incomplete old core data with corrected pyrolysis S1 or chloroform asphalt "A" as oil-bearing parameters. The accuracy of corrected parameters was affected by multiple factors including sample freshness, testing means and correction method, leading to certain limitations in the application of the above parameters. According to the latest development in shale oil exploration, the paper compares the applications of different oil-bearing parameters (pyrolysis S1, chloroform bitumen "A" and oil saturation) in shale oil resource calculation. The result shows that oil saturation can reflect the content of free oil and dissolved hydrocarbon, without considering the influence of adsorbed oil and correction of light hydrocarbon, heavy hydrocarbon and NSO compound. This parameter is more suitable for the calculation of shale oil resources under the condition of fresh sample test data. The plane distribution of effective shale thickness, TOC, organic maturity(Ro) and burial depth are determined on the basis of latest drilling results and test data of shale oil parameter well. The shale oil enrichment areas in the first member of Qingshankou Formation in Qijiahe and Gulong sags are 1957.23 km2 and 4509.09 km2 respectively by multifactor overlap method. Combined with the measured data of oil saturation, density and effective porosity logging interpretation data of sealed frozen samples, the resources of shale oil enriched areas in Qijia and Gulong sags are calculated as 19.79×108 t and 27.29×108 t respectively, indicating the matrix shale oil in the study area has a good exploration prospect.
-
Key words:
- Songliao Basin /
- Qijia sag /
- Gulong sag /
- first member of Qingshankou Formation /
- oil saturation /
- shale oil /
- resource calculation
-

-
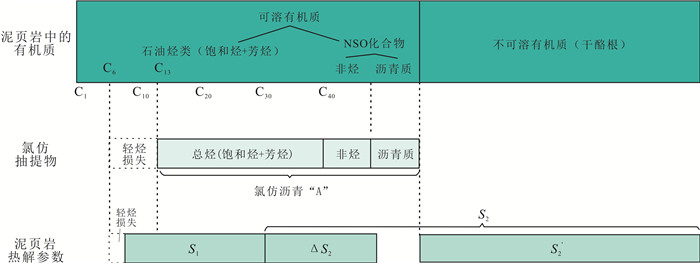
图 1 氯仿沥青"A"和热解S1组分对比示意图(改编自文献[15])
Figure 1.
表 1 页岩油资源量计算含油性参数综合评价表
Table 1. Comprehensive evaluation of oil-bearing parameters for shale oil resource calculation
含油性参数 计算公式 关键参数 适用性 有利因素 不利因素 研究区情况 可信度 氯仿沥青"A" Q=S×h×ρ×(A+K轻×A-TOC×K吸)
Q:页岩油资源量, t;
S:泥页岩面积, km2;
h:泥页岩厚度, m;
ρ:泥页岩密度, g/cm3;
TOC:总有机碳, %A:氯仿沥青"A", ‰;
K轻:轻烃校正系数;
K吸:吸附系数适合氯仿沥青"A"数据较多地区的页岩油资源评价 ①比较接近页岩油组分; ②参数获取技术成熟 ①抽提过程中C6-13轻烃损失殆尽, 需进行轻烃校正; ②含有部分吸附烃, 需去除; ③受样品热演化程度影响大; ④实验所需样品量较大 氯仿沥青"A"分析化验资料较少 中等, 受轻烃校正和吸附烃去除准确性影响 热解S1 Q=S×h×ρ×(S1+K轻× S1+K重×S1)
Q:页岩油资源量, t;
S:泥页岩面积, km2;
h:泥页岩厚度, m;
ρ:泥页岩密度, g/cm3;
TOC:总有机碳, %S1:热解S1, 10-3;
K轻:轻烃校正系数;
K重:重烃校正系数(包含NSO化合物裂解烃)适合热解数据较多地区的页岩油资源量评价 ①基本属于游离油组成; ②参数获取技术成熟; ③实验所需样品量小 ①损失C6-13轻烃, 需进行轻烃校正; ②缺失高碳数重烃和NSO化合物, 需进行校正; ③受样品热演化程度影响大 热解S1分析化验资料较多 中等, 受轻烃、重烃和NSO化合物校正准确性影响 含油饱和度 Q=S×h×Φ×So×ρoi
Q:页岩油资源量, t;
S:泥页岩面积, km2;
h:泥页岩厚度, m;
ρoi:页岩油密度, g/cm3So:含油饱和度, %;
Φ:有效孔隙度, %适合具有密闭取心岩心样品地区的页岩油资源量评价 ①主要参数获取方法成熟; ②含油饱和度代表游离油和溶解烃, 无需进行轻烃、重烃校正及吸附烃去除 ①测试方法对岩心样品大小、样品纹层或裂缝发育程度以及后期保存情况要求较高; ②需进行密闭取心获取实验样品 新钻页岩油井密闭取心测试数据齐全 较高, 主要反映了潜在可采的游离油组分 -
[1] US Energy Information Administration. Technically recoverable shale oil and shale gas resources: An assessment of 137 shale formations in 41 countries outside the United States[EB/OL]. http://www.eia.gov/analysis/studies/worldshalegas/pdf/overview.pdf, 2013.
[2] 张林晔, 李钜源, 李政, 等.北美页岩油气研究进展及对中国陆相页岩油气勘探的思考[J].地球科学进展, 2014, 29(6):700-711. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201406008.htm
Zhang L Y, Li J Y, Li Z, et al. Advances in shale oil/gas research in North America and considerations on exploration for continental shale oil/gas in China[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2014, 29(6):700-711. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201406008.htm
[3] 柳波, 石佳欣, 付晓飞, 等.陆相泥页岩层系岩相特征与页岩油富集条件——以松辽盆地古龙凹陷白垩系青山口组一段富有机质泥页岩为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(5):828-838. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201805009.htm
Liu B, Shi J X, Fu X F, et al. Petrological characteristics and shale oil enrichment of lacustrine fine-grained sedimentary system:A case study of organic-rich shale in first member of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in Gulong Sag, Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(5):828-838. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201805009.htm
[4] 宋明水.济阳坳陷页岩油勘探实践与现状[J].油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(1):1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201901001.htm
Song M S. Practice and current status of shale oil exploration in Jiyang Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(1):1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201901001.htm
[5] 赵贤正, 周立宏, 赵敏, 等.陆相页岩油工业化开发突破与实践——以渤海湾盆地沧东凹陷孔二段为例[J].中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(5):589-600. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.006
Zhao X Z, Zhou L H, Zhao M, et al. Breakthrough and practice of industrial development on continental shale oil:A case study on Kong-2 Member in Cangdong sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5):589-600. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.006
[6] 杨华, 牛小兵, 徐黎明, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系长7段页岩油勘探潜力[J].石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(4):511-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201604003.htm
Yang H, Niu X B, Xu L M, et al. Exploration potential of shale oil in Chang7 Member, Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(4):511-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201604003.htm
[7] 支东明, 唐勇, 杨智峰, 等.准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷陆相页岩油地质特征与聚集机理[J].石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(3):524-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201903009.htm
Zhi D M, Tang Y, Yang Z F, et al. Geological characteristics and accumulation mechanism of continental shale oil in Jimusaer sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(3):524-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201903009.htm
[8] 杨建国, 李士超, 姚玉来, 等.松辽盆地北部陆相页岩油调查取得重大突破[J].地质与资源, 2020, 29(3):300. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.03.015 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10208.shtml
Yang J G, Li S C, Yao Y L, et al. Significant breakthrough in the continental shale oil survey in northern Songliao Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(3):300. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.03.015 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10208.shtml
[9] 崔宝文, 蒙启安, 白雪峰, 等.松辽盆地北部石油勘探进展与建议[J].大庆石油地质与开发, 2018, 37(3):1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201803001.htm
Cui B W, Meng Q A, Bai Y F, et al. Petroleum exploration progress and suggestions for north Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2018, 37(3):1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201803001.htm
[10] 吴河勇, 林铁锋, 白云风, 等.松辽盆地北部泥(页)岩油勘探潜力分析[J].大庆石油地质与开发, 2019, 38(5):78-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201905011.htm
Wu H Y, Lin T F, Bai Y F, et al. Analyses of the mudstone (shale) oil exploration potential in North Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2019, 38(5):78-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201905011.htm
[11] 宋国奇, 张林晔, 卢双舫, 等.页岩油资源评价技术方法及其应用[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(4):221-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304021.htm
Song G Q, Zhang L Y, Lu S F, et al. Resource evaluation method for shale oil and its application[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4):221-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304021.htm
[12] 陈小慧.页岩油赋存状态与资源量评价方法研究进展[J].科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(3):136-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.03.020
Chen X H. Advances in the research on the occurrence state and resources assessment of shale oil[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(3):136-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.03.020
[13] 朱日房, 张林晔, 李政, 等.陆相断陷盆地页岩油资源潜力评价——以东营凹陷沙三段下亚段为例[J].油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(1):129-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201901014.htm
Zhu R F, Zhang L Y, Li Z, et al. Evaluation of shale oil resource potential in continental rift basin:A case study of Lower Es3 member of Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(1):129-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201901014.htm
[14] 柳波, 何佳, 吕延防, 等.页岩油资源评价指标与方法——以松辽盆地北部青山口组页岩油为例[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(11):3846-3852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201411019.htm
Liu B, He J, Lv Y F, et al. Parameters and method for shale oil assessment:Taking Qinshankou Formation shale oil of Northern Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(11):3846-3852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201411019.htm
[15] 薛海涛, 田善思, 王伟明, 等.页岩油资源评价关键参数——含油率的校正[J].石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(1):15-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201601004.htm
Xue H T, Tian S S, Wang W M, et al. Correction of oil content-One key parameter in shale oil resource assessment[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(1):15-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201601004.htm
[16] 薛海涛, 田善思, 卢双舫, 等.页岩油资源定量评价中关键参数的选取与校正——以松辽盆地北部青山口组为例[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(1):70-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.008
Xue H T, Tian S S, Lu S F, et al. Selection and verification of key parameters in the quantitative evaluation of shale oil:A case study at the Qingshankou Formation, Northern Songliao Basin[J] Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(1):70-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.008
[17] 张金川, 林腊梅, 李玉喜, 等.页岩油分类与评价[J].地学前缘, 2012, 9(5):322-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205032.htm
Zhang J C, Lin L M, Li Y X, et al. Classification and evaluation of shale oil[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 9(5):322-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205032.htm
[18] 宁方兴, 王学军, 郝雪峰, 等.济阳坳陷页岩油赋存状态和可动性分析[J].新疆石油天然气, 2015, 11(3):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2677.2015.03.001
Ning F X, Wang X J, Hao X F, et al. An analysis in occurrence state and mobility of shale oil in Jiyang Depression[J]. Xinjiang Oil & Gas, 2015, 11(3):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2677.2015.03.001
[19] 卢双舫, 张敏.油气地球化学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2008:19-20.
Lu S F, Zhang M. Petroleum geochemistry[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press, 2008:19-20. (in Chinese)
[20] 肖飞, 杨建国.湖相泥页岩密闭冷冻测试与现场地化录井热解参数对比研究[C].福州: 第十二届全国石油地质实验技术学术会议, 2020.
Xiao F, Yang J G. Comparative study of the pyrolysis parameters between laboratory test of airtight freezing samples and geochemical mud logging in the well site[C]. Fuzhou: The 12th National Academic Conference of Petroleum Geology Experimental Technology, 2020. (in Chinese)
[21] 李延钧, 张烈辉, 冯媛媛, 等.页岩有机碳含量测井评价方法及其应用[J].天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(1):169-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201301026.htm
Li Y J, Zhang L H, Feng Y Y, et al. Logging evaluation method and its application for measuring the total organic carbon content in shale gas[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(1):169-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201301026.htm
[22] Dow W G. Kerogen studies and geological interpretations[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1977, 7:79-99. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(77)90078-4
-



 下载:
下载: