VARIATION CHARACTERISTICS OF ORGANIC MATTERS AND NUTRIENT ELEMENTS IN TYPICAL BLACK SOIL
-
摘要:
依据2003-2008年松辽平原中南部地区多目标区域地球化学调查成果, 选择黑土类型土壤样本6553件, 研究典型黑土中有机质及养分元素碳、氮、硫、磷、钙、钾、铁、镁、锌、铜、钼、锰、硼的变化特征. 发现典型黑土中有机质结构性元素碳、氮、硫、磷以及铜、镁、铁、钙元素的含量变化与有机质的变化具有正相关性. 养分元素含量的变化与成土母质和土壤类型关系密切, 如锰在黑土中含量普遍偏高. 中国土壤以及松辽平原土壤的宏观背景是典型黑土中钾偏高和钼、硼偏低. 生物气候带是影响有机质和某些养分元素变化的重要因素. 温带-寒温带的气候条件影响着土壤的物理性质和化学性质, 如粒级、黏粒性、酸碱性, 进而影响元素含量的变化.
Abstract:Based on the results of multi-objective regional geochemical survey in central and southern Songliao Plain during 2003-2008, 6553 soil samples are selected to study the variation characteristics of organic matters and nutrient elements including C, N, S, P, Ca, K, Fe, Mg, Zn, Cu, Mo, Mn and B in typical black soil. It is found that the content variation of structural elements such as C, N, S and P, as well as other elements including Cu, Mg, Fe and Ca, has positive correlation with that of organic matters in typical black soil. The content change of nutrient elements is closely related to parent materials and soil types. For instance, Mn content is generally high in black soil. The macro-background of soil in China and Songliao Plain is characterized by high K and low Mo and B in typical black soil. Bioclimatic zone is an important factor affecting the variation of organic matters and some nutrient elements. The climatic conditions of temperate-cold temperate zones affect the physical-chemical properties of soil such as grain size, clay fraction acid-base property of soil and then the change of element content.
-
Key words:
- black soil /
- organic matter /
- nutrient element /
- soil geochemistry /
- Songliao Plain
-

-
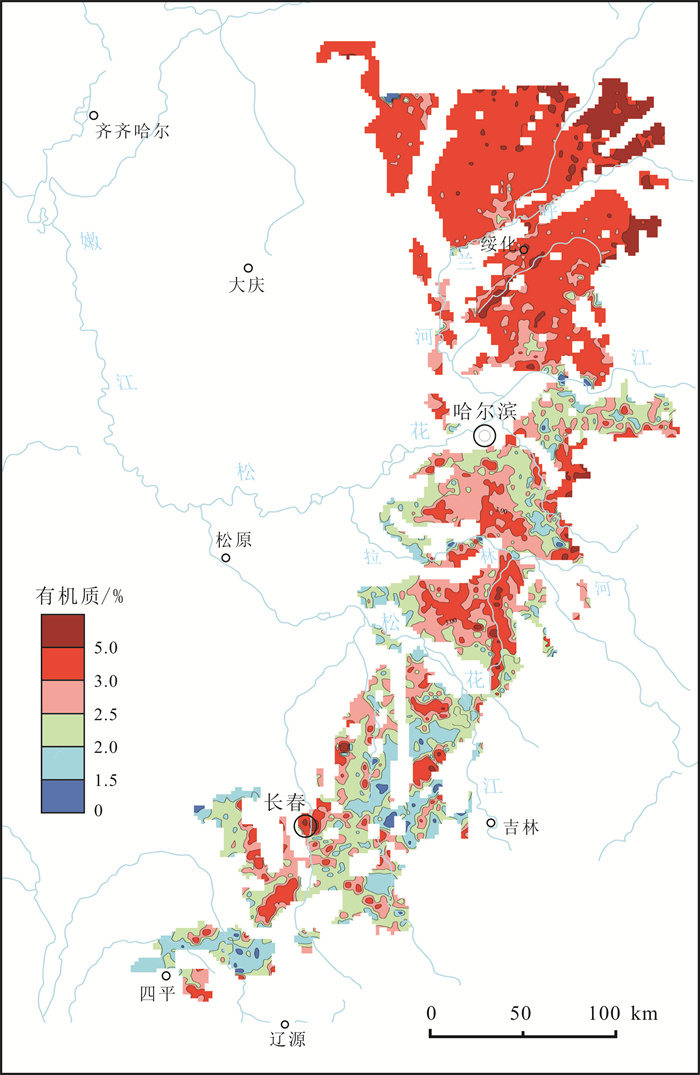
图 1 典型黑土区有机质分布图(据文献16)
Figure 1.
表 1 不同地区养分元素平均值
Table 1. Average contents of nutrient elements in different regions
指标 哈尔滨-绥化 双城-扶余 长春-四平 中国土壤元素背景值(A层) C 2.52 1.76 1.49 1.50* N 2015 1425 1236 1197* P 866 708 617 554* S 268 209 176 198* CaO 1.62 1.68 1.37 1.30 K2O 2.53 2.57 2.57 2.26 Fe2O3 4.85 4.64 4.61 4.24 MgO 1.40 1.37 1.24 1.23 B 30.89 33.48 36.11 41.0 Cu 21.83 21.13 21.44 20.7 Mn 789 768 780 540 Mo 0.62 0.62 0.69 1.10 Zn 65.37 66.26 65.50 68.0 有机质 3.93 2.71 2.39 2.0 pH 6.70 6.75 6.36 7.81* *为松辽平原中南部表层土壤背景值. 含量单位: C、氧化物、有机质为%, 其他元素为10-6. 表 2 不同有机质样本中养分元素含量高于背景值的占比率
Table 2. Percentages of soil samples with nutrient element contents over background value
指标 有机质≥3%(n=2938) 2%≤有机质<3%(n=2713) 有机质<2%(n=902) 样本量 占比/% 样本量 占比/% 样本量 占比/% C 2908 98.98 1688 62.22 90 9.98 N 2856 97.21 1978 72.91 241 26.72 P 2850 97.00 2186 80.58 410 45.45 S 2746 93.46 969 35.72 68 7.54 CaO 2504 85.23 1678 61.85 235 26.05 K2O 2873 97.79 2697 99.41 897 99.45 Fe2O3 2775 94.45 2268 83.60 647 71.73 MgO 2571 87.51 2016 74.31 537 59.53 B 107 3.64 324 11.94 249 27.61 Cu 2384 81.14 1641 60.49 388 43.02 Mn 2886 98.23 2671 98.45 854 94.68 Mo 140 4.77 56 2.06 42 4.66 Zn 1059 36.04 595 21.93 155 17.18 pH<6.5 1245 42.38 1310 48.28 573 63.52 pH≥6.5 1693 57.62 1403 51.72 329 36.48 表 3 不同土壤类型钾元素的丰度
Table 3. Abundance of potassium in different soil types
土类 样点数 平均值 土类 样点数 平均值 绵土 12 1.75 沼泽土 20 1.9 黑垆土 7 1.9 盐土 32 1.93 黑土 11 2.06 碱土 3 1.85 黑钙土 18 2.17 风沙土 13 2.06 水稻土 57 1.64 红壤 77 1.75 棕壤 51 1.88 棕漠土 14 1.68 暗棕壤 29 1.93 棕色针叶林土 10 1.76 栗钙土 34 1.91 草甸土 39 1.86 据文献[28]. 含量单位: %. -
[1] 李世泉, 王岩松. 东北黑土区水土保持监测技术[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2008: 1-3.
Li S Q, Wang Y S. Monitoring technology of soil and water conservation in black soil area of Northeast China[M]. Beijing: China Water Resources and Hydropower Press, 2008: 1-3. (in Chinese)
[2] 刘春梅, 张之一. 我国东北地区黑土分布范围和面积的探讨[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2006(2): 23-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2767.2006.02.009
Liu C M, Zhang Z Y. Discussion of the area and distribution of black soils in Northeastern China[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2006(2): 23-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2767.2006.02.009
[3] 韩晓增, 李娜. 中国东北黑土地研究进展与展望[J]. 地理科学, 2018, 38(7): 1032-1041. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201807004.htm
Han X Z, Li N. Research progress of black soil in northeast China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2018, 38(7): 1032-1041. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201807004.htm
[4] 方宏宾, 赵福岳, 姜琦刚, 等. 松辽平原第四纪地质环境与黑土退化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 158-198.
Fang H B, Zhao F Y, Jiang Q G, et al. Quaternary geological environment and black soil degradation in Songliao Plain[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009: 158-198. (in Chinese)
[5] 韩晓增, 邹文秀. 我国东北黑土地保护与肥力提升的成效与建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(2): 206-212. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX201802013.htm
Han X Z, Zou W X. Effects and suggestions of black soil protection and soil fertility increase in northeast China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(2): 206-212. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX201802013.htm
[6] 王文娟, 邓荣鑫, 张树文. 东北典型黑土区沟蚀发生风险评价研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2014, 29(12): 2058-2067. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2014.12.007
Wang W J, Deng R X, Zhang S W. Preliminary research on risk evaluation of gully erosion in typical black soil area of northeast China [J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2014, 29(12): 2058-2067. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2014.12.007
[7] 李家熙, 吴功建, 黄怀曾, 等. 区域地球化学与农业和健康[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2000: 77-86.
Li J X, Wu G J, Huang H Z, et al. Regional geochemistry with agriculture and human health[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2000: 77-86.
[8] 宋运红, 刘凯, 戴慧敏, 等. 松辽平原典型黑土-古土壤剖面AMS 14C年龄首次报道[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1926-1927. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006027.htm
Song Y H, Liu K, Dai H M, et al. The first report of the AMS 14C age of mollisol-paleosol profile of Songliao Plain[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1926-1927. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006027.htm
[9] 翟富荣, 梁帅, 戴慧敏. 东北黑土地地球化学调查研究进展与展望[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 503-509, 532. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10238.shtml
Zhai F R, Liang S, Dai H M. Geochemical survey of black land in Northeast China: Progress and prospect[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 503-509, 532. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10238.shtml
[10] 房娜娜, 刘凯, 刘国栋, 等. 黑土肥力质量评价的生物指标研究进展[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 518-524, 542. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10240.shtml
Fang N N, Liu K, Liu G D, et al. Research progress on biological indicators of black soil fertility quality evaluation[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 518-524, 542. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10240.shtml
[11] 宋运红, 张哲寰, 杨凤超, 等. 黑龙江海伦地区垦殖前后典型黑土剖面主要养分元素垂直分布特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 543-549. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10243.shtml
Song Y H, Zhang Z H, Yang F C, et al. Vertical distribution of major nutrient elements in typical black soil sections in Hailun, Heilongjiang Province: Before and after reclamation[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 543-549. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10243.shtml
[12] 韩晓萌, 戴慧敏, 梁帅, 等. 黑龙江省拜泉地区典型黑土剖面元素地球化学特征及其环境指示意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 556-563. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10245.shtml
Han X M, Dai H M, Liang S, et al. Element geochemistry of the typical black soil sections in Baiquan area, Heilongjiang Province: Environmental implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29 (6): 556-563. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10245.shtml
[13] 国土资源部中国地质调查局. 中华人民共和国多目标区域地球化学图集——松辽平原中南部地区[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013: 1-308.
China Geological Survey, Ministry of Land and Resources. Multi- objective regional geochemical atlas: Central and southern Songliao Plain[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2013: 1-308. (in Chinese)
[14] 商翎, 提福魁, 王淑华, 等. 元素生态地球化学及其应用[M]. 沈阳: 辽宁大学出版社, 1997: 9-11.
Shang L, Ti F K, Wang S H, et al. Element ecological geochemistry and its application[M]. Shenyang: Liaoning University Press, 1997: 9-11. (in Chinese)
[15] 陈怀满. 环境土壤学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 55-64.
Chen H M. Environmental soil science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005: 55-64. (in Chinese)
[16] 刘驰, 刘希瑶, 刘澎. 松辽平原典型黑土区有机质的变化及影响因素分析[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 550-555. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10244.shtml
Liu C, Liu X Y, Liu P. Analysis on the changes of organic matters and their influencing factors of typical black soil areas in Songliao plain[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 550-555. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10244.shtml
[17] 蒋辉. 环境地质学[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008: 50-52.
Jiang H. Environmental geology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008: 50-52. (in Chinese)
[18] 张凤荣. 土壤地理学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2002: 76-77.
Zhang F R. Soil geography[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2002: 76-77. (in Chinese)
[19] 伍光和, 田连恕, 胡双熙, 等. 自然地理学[M]. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000: 256-264.
Wu G H, Tian L S, Hu S X, et al. Physical geography[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000: 256-264. (in Chinese)
[20] 刘景双, 于君宝, 王金达, 等. 松辽平原黑土有机碳含量时空分异规律[J]. 地理科学, 2003, 23(6): 668-673. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2003.06.005
Liu J S, Yu J B, Wang J D, et al. Temporal-spatial variation law of organic carbon content in typical black soil on Songliao Plain[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2003, 23(6): 668-673. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2003.06.005
[21] 王金达, 刘景双, 刘淑霞, 等. 松嫩平原黑土土壤有机碳库的估算及其影响因素[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2004, 23(4): 687-690. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2004.04.015
Wang J D, Liu J S, Liu S X, et al. Evaluation on soil organic carbon pool and affecting factors in phaeozem region in Songnen Plain[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2004, 23(4): 687-690. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2004.04.015
[22] 张素荣, 张燕, 杨俊泉, 等. 海河流域平原区土壤碳密度分布特征和碳储量估算[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2015, 38(4): 305-310. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2015.04.010
Zhang S R, Zhang Y, Yang J Q, et al. Distribution characteristics of soil carbon density and carbon reserve estimation in the plain areas of Haihe River Basin[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2015, 38 (4): 305-310. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2015.04.010
[23] 辛刚, 颜丽, 汪景宽, 等. 不同开垦年限黑土有机质变化的研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2002, 33(5): 332-335. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2002.05.004
Xin G, Yan L, Wang J K, et al. Changes of organic carbon in black soils with the different reclamation years[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2002, 33(5): 332-335. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2002.05.004
[24] 汪景宽, 王铁宇, 张旭东, 等. 黑土土壤质量演变初探Ⅰ——不同开垦年限黑土主要质量指标演变规律[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2002, 33(1): 43-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYNY200201012.htm
Wang J K, Wang T Y, Zhang X D, et al. An approach to the changes of black soil quality (I): Changes of the indices of black soil with the year(s) of reclamation[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2002, 33(1): 43-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYNY200201012.htm
[25] 汪景宽, 李双异, 张旭东, 等. 20年来东北典型黑土地区土壤肥力质量变化[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2007, 15(1): 19-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN200701005.htm
Wang J K, Li S Y, Zhang X D, et al. Spatial and temporal variability of soil quality in typical black soil area in Northeast China in 20 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2007, 15(1): 19-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN200701005.htm
[26] 汪景宽, 张旭东, 王铁宇, 等. 黑土土壤质量演变初探Ⅱ——不同地区黑土中有机质、氮、硫和磷现状及变化规律[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2002, 33(4): 270-273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYNY200204008.htm
Wang J K, Zhang X D, Wang T Y, et al. An approach to the changes of black soil quality (Ⅱ): The status and changes of organic matter, total N, total S and total P in black soils (isohumosols) in different areas[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2002, 33(4): 270-273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYNY200204008.htm
[27] 迟凤琴, 汪景宽, 张玉龙. 东北地区黑土硫的分布特征及其与土壤性质的关系[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2005, 11(1): 40-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWYF200501008.htm
Chi F Q, Wang J K, Zhang Y L. The sulphur distribution in relation to properties of black soil in northeastern China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2005, 11(1): 40-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWYF200501008.htm
[28] 王云, 魏复盛. 土壤环境元素化学[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1995: 367-370.
Wang Y, Wei F S. Chemistry of soil environmental elements[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1995: 367-370. (in Chinese)
[29] Thornton I. Geochemical aspects of the distribution and forms of heavy metals in soils[C]//Leep N W. Effect of heavy metal pollution on plants. Pollution Monitoring Series, vol 2. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-8099-0_1
[30] 迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 87-88.
Chi Q H, Yan M C. Handbook of elemental abundance for applied geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007: 87-88.
-



 下载:
下载: