SPATIAL VARIATION CHARACTERISTICS OF SOIL ORGANIC MATTER CONTENT IN TYPICAL BLACK SOIL: A Case Study of Beilin District in Suihua City, Heilongjiang Province
-
摘要:
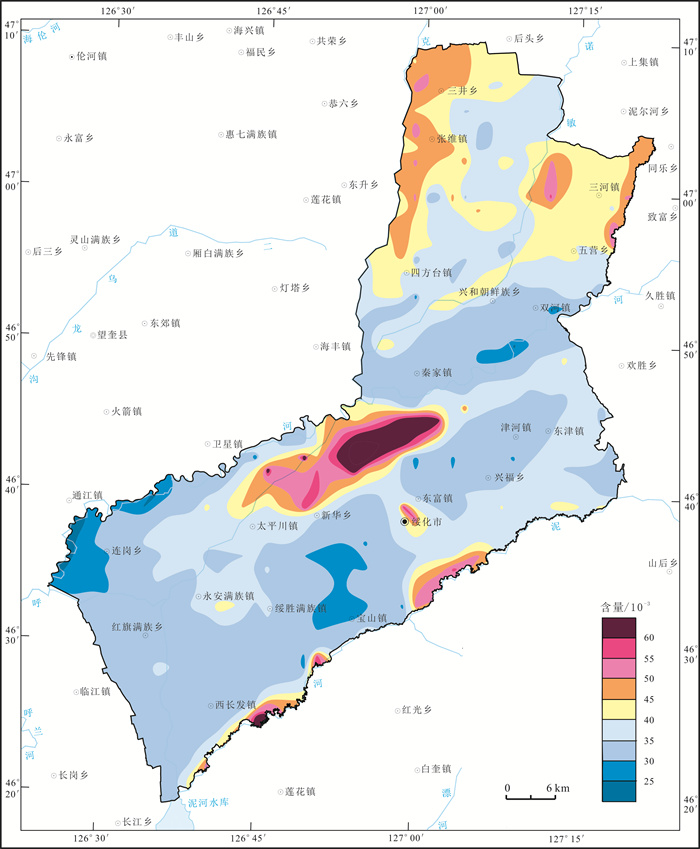
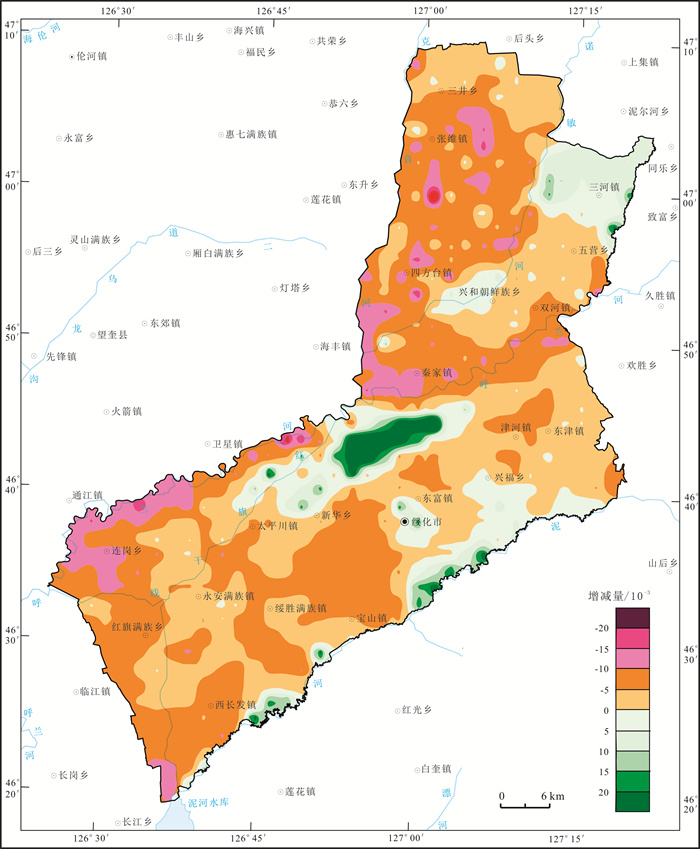
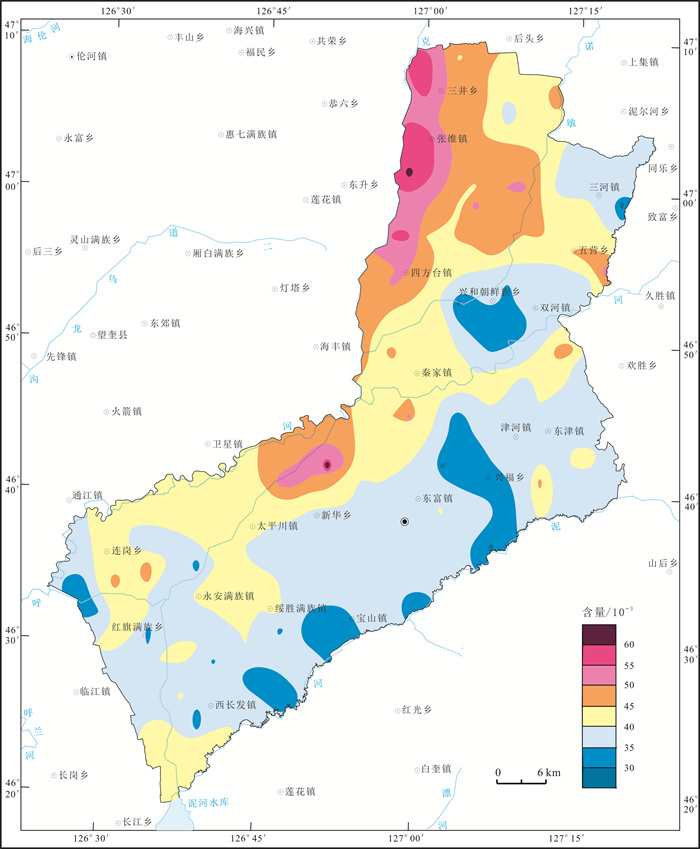
以20世纪80年代第二次土壤普查时期黑土有机质分析数据为基准, 以目前土地质量地球化学调查土壤有机质分析数据为研究对象, 利用MapGIS空间分析功能定量研究绥化市北林区黑土地土壤有机质含量的空间变化特征. 研究结果显示, 近30 a以来研究区土壤有机质含量由41.16×10-3下降到37.68×10-3, 土壤有机质流失率达8.45%; 20世纪80年代研究区土壤有机质含量在35×10-3~45×10-3的面积占研究区总面积的73.93%, 而目前研究区土壤有机质含量在30×10-3~40×10-3的面积占研究区总面积的70.24%;研究区82.1%的土地面积土壤中有机质呈现出不同程度的减少, 仅有17.9%的土地面积土壤中有机质呈现出增加的趋势; 研究区黑土地以轻度和轻微土壤有机质流失程度为主, 仅在张维镇和四方台镇中南部、秦家镇中西部以及连岗乡中北部等局部地段土壤有机质流失程度达中度和重度, 这为精准施策开展黑土地土壤有机质流失治理提供了科学依据.
Abstract:Based on the analysis data of organic matters in black soil during the second national soil survey in the 1980s and those in the current land quality geochemical survey, the MapGIS spatial analysis is used to quantitatively study the spatial variation of organic matter content in the black land core area of Northeast China. The results show that the content of soil organic matters decreases from 41.16×10-3 to 37.68×10-3 in recent 30 years, with the organic matter loss rate of 8.45%. In 1980s, the areas with soil organic matter content of 35×10-3-45×10-3 account for 73.93% of the total study area, while the areas with soil organic matter content of 30×10-3-40×10-3 make up 70.24% currently. Of the land area, 82.1% shows different degrees of reduction in organic matter, while only 17.9% shows an increasing trend. The black land is dominated by mild and slight loss of soil organic matter, except for local areas with moderate and severe loss degree, which provides scientific basis for soil organic matter loss control in black land region.
-
Key words:
- black land /
- organic matter /
- spatial variation /
- Beilin District of Suihua City /
- Heilongjiang Province
-

-
表 1 绥化市北林区土壤有机质地球化学参数特征表
Table 1. Characteristics of geochemical parameters of soil organic matter in Beilin District, Suihua City
时期 样本数 最大值 平均值 最小值 标准离差 变异系数 第二次土壤普查(1979-1990年) 1032 97.4 41.16 0.4 10.24 0.249 目前土地质量调查(2009-2019年) 726 119.6 37.68 4.0 10.84 0.288 含量单位:10-3. 表 2 绥化市北林区不同时期土壤有机质含量特征统计对比表
Table 2. Comparison of soil organic matter content characteristics between different periods in Beilin District, Suihua City
含量区间/10-3 第二次土壤普查 目前土地质量调查 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% >60 1.07 0.04 40.43 1.47 55~60 44.53 1.61 22.7 0.82 50~55 107.81 3.91 69.25 2.51 45~50 359.22 13.03 195.27 7.08 40~45 875.51 31.75 375.08 13.6 35~40 1163.15 42.18 844.25 30.61 30~35 205.2 7.44 1093.04 39.63 25~30 1.39 0.05 110.12 3.99 ≤25 0 0 7.73 0.28 表 3 绥化市北林区土壤有机质增减变化地球化学参数特征统计表
Table 3. Geochemical parameters of soil organic matter changes in Beilin District, Suihua City
最大值 平均值 中位数 众值 最小值 标准离差 变异系数 82.1 -3.35 -5.1 -6. 0 -48.5 10.28 -0.326 含量单位: 10-3. 表 4 绥化市北林区土壤有机质增减变化特征土地面积统计表
Table 4. Land areas and proportions of soil organic matter changes in Beilin District, Suihua City
增减量变化区间/10-3 面积/km2 占比/% <-20 1.84 0.07 -20~-15 7.42 0.27 -15~-10 185.44 6.72 -10~-5 1073.91 38.94 -5~0 995.48 36.10 0~5 268.70 9.74 5~10 127.15 4.61 10~15 42.01 1.52 15~20 21.46 0.78 ≥20 34.49 1.25 表 5 绥化市北林区土壤有机质流失程度评价表
Table 5. Evaluation of soil organic matter loss degree in Beilin District, Suihua City
评价 增加 轻微流失 轻度流失 中度流失 重度流失 等级 一级 二级 三级 四级 五级 增减量/10-3 >0 -5~0 -10~-5 -15~-10 ≤-15 面积/km2 493.81 995.48 1073.91 185.44 9.26 占比/% 17.90 36.10 38.94 6.72 0.34 -
[1] 董士伟, 李红, 孙丹峰, 等. 北京市大兴区土壤养分空间结构及影响因素分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 2015, 22(2): 32-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201502007.htm
Dong S W, Li H, Sun D F, et al. Analysis on spatial structure and influence factor of soil nutrients in Daxing District of Beijing[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 22(2): 32-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201502007.htm
[2] 熊杏, 熊清华, 郭熙, 等. 南方典型丘陵区耕地土壤全氮、有机碳和碳氮比空间变异特征及其影响因素[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(9): 1656-1668. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWYF202009009.htm
Xiong X, Xiong Q H, Guo X, et al. Spatial variation characteristics of total nitrogen, organic carbon and ratio of carbon to nitrogen of cultivated land in typical hilly areas in South China and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(9): 1656-1668. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWYF202009009.htm
[3] 刘希瑶. 辽宁南部地区土壤地球化学特征及评价[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(5): 470-476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.05.009 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8422.shtml
Liu X Y. Geochemistry and evaluation of the soil in southern Liaoning Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(5): 470-476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.05.009 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8422.shtml
[4] 翟富荣, 梁帅, 戴慧敏. 东北黑土地地球化学调查研究进展与展望[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 503-509, 532. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10238.shtml
Zhai F R, Liang S, Dai H M. Geochemical survey of black land in Northeast China: Progress and prospect[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 503-509, 532. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10238.shtml
[5] 宋运红, 刘凯, 戴慧敏, 等. 松辽平原典型黑土-古土壤剖面AMS14C年龄首次报道[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1926-1927. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006027.htm
Song Y H, Liu K Dai H M, et al. The first report of the AMS14C age of mollisol-paleosol profile of Songliao Plain[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1926-1927. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006027.htm
[6] 戴慧敏, 赵君, 刘国栋, 等. 东北黑土地质量调查成果[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(3): 299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.03.014 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10207.shtml
Dai H M, Zhao J, Liu G D, et al. Progress in the quality survey of black soil in Northeast China[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29 (3): 299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.03.014 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10207.shtml
[7] 杨贺平. 松嫩平原中南部黑土氮流失程度及分布特征研究[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(5): 577-582. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10335.shtml
Yang H P. Nitrogen loss degree and distribution characteristics of black soil area in south-central Songnen Plain[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(5): 577-582. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10335.shtml
[8] 刘国栋, 杨泽, 戴慧敏, 等. 黑龙江省海伦市长发镇土地质量地球化学评价及开发建议[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 533-542. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10242.shtml
Liu G D, Yang Z, Dai H M, et al. Geochemical evaluation of land quality and development suggestion of land in Hailun City, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 533-542. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10242.shtml
[9] 韩晓增, 邹文秀. 东北黑土地保护利用研究足迹与科技研发展望[J]. 土壤学报, 2021, 58(6): 1341-1358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB202106001.htm
Han X Z, Zou W X. Research perspectives and footprint of utilization and protection of black soil in Northeast China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021, 58(6): 1341-1358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB202106001.htm
[10] 张一鹤, 杨泽, 戴慧敏, 等. 穆棱河-兴凯湖平原土地质量地球化学评价[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(1): 62-70. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10266.shtml
Zhang Y H, Yang Z, Dai H M, et al. Geochemical evaluation of land quality in Muling River-Xingkai Lake Plain[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(1): 62-70. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10266.shtml
[11] 韩晓萌, 戴慧敏, 梁帅, 等. 黑龙江省拜泉地区典型黑土剖面元素地球化学特征及其环境指示意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 556-563. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10245.shtml
Han X M, Dai H M, Liang S, et al. Element geochemistry of the typical black soil sections in Baiquan area, Heilongjiang Province: Environmental implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 556-563. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10245.shtml
[12] 孙泽群. 秸秆腐熟还田及其对黑土肥力的影响研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2019.
Sun Z Q. Study on straw maturity returning to field and its effect on black soil fertility[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2019.
[13] 董芳辰, 刘晓光, 于杰, 等. 富锦市湿地不同开垦年限土壤养分时空分布特征研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(8): 167-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201708027.htm
Dong F C, Liu X G, Yu J, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of soil nutrient under different reclamation years for wetlands in Fujin City[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(8): 167-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201708027.htm
[14] 杨子, 刘晓光, 宁静, 等. 典型黑土垄作区耕地沟蚀对土壤养分的影响研究[J]. 土壤, 2017, 49(2): 379-385. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201702025.htm
Yang Z, Liu X G, Ning J, et al. Effects of gully erosion on soil nutrients in ridge area of typical black soil[J]. Soils, 2017, 49(2): 379-385. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201702025.htm
[15] 方洪宾. 松辽平原第四纪地质环境与黑土退化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 189-193.
Fang H B. Quaternary geological environment and black soil degradation in Songliao Plain[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009: 189-193. (in Chinese)
[16] 梁尧, 韩晓增, 丁雪丽. 东北黑土有机质组分与结构的研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2012, 44(6): 888-897. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9829.2012.06.002
Liang Y, Han X Z, Ding X L. Review of soil organic matter fractions and structure of black soil in Northeast China[J]. Soils, 2012, 44 (6): 888-897. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9829.2012.06.002
[17] 隋跃宇, 张兴义, 张少良, 等. 黑龙江典型县域农田黑土土壤有机质现状分析[J]. 土壤通报, 2008, 39(1): 186-188. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2008.01.035
Sui Y Y, Zhang X Y, Zhang S L, et al. Soil organic matter actuality of the black soil farmland in Heilongjiang counties[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2008, 39(1): 186-188. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2008.01.035
[18] 戴慧敏, 刘凯, 宋运红, 等. 东北地区黑土退化地球化学指示与退化强度[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 510-517. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10239.shtml
Dai H M, Liu K, Song Y H, et al. Black soil degradation and intensity in Northeast China: Geochemical indication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 510-517. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10239.shtml
[19] 张少良, 张兴义, 崔战利. 哈尔滨市辖区黑土有机质、全氮的空间异质性分析[J]. 农业系统科学与综合研究, 2007, 23(3): 333-337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0068.2007.03.018
Zhang S L, Zhang X Y, Cui Z L. The spatial variability of organic matter and total nitrogen contents in black soil region of Harbin[J]. System Sciences and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 2007, 23(3): 333-337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0068.2007.03.018
[20] 孟凯, 王德录, 张兴义, 等. 黑土有机质分解、积累及其变化规律[J]. 土壤与环境, 2002, 11(1): 42-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ200201010.htm
Meng K, Wang D L, Zhang X Y, et al. Decomposition, accumulation and their variant pattern of organic matter in black soil area[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 2002, 11(1): 42-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ200201010.htm
[21] 谢雅慧. 黑土区田块土壤养分空间分布预测研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2019.
Xie Y H. Prediction of soil nutrients spatial distribution in black soil area at the field scale[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2019.
[22] 宋运红, 刘凯, 戴慧敏, 等. 35年来东北松辽平原耕地土壤全氮时空变化[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(1): 332-333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202101024.htm
Song Y H, Liu K, Dai H M, et al. Spatio-temporal variation of total N content in farmland soil of Songliao Plain in Northeast China during the past 35 years[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(1): 332-333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202101024.htm
[23] 赵军, 葛翠萍, 商磊, 等. 农田黑土有机质和全量氮磷钾不同尺度空间变异分析[J]. 农业系统科学与综合研究, 2007, 23(3): 280-284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0068.2007.03.007
Zhao J, Ge C P, Shang L, et al. Analysis for spatial heterogeneity of soil organic content and total nutrients in black soil crop area with different scales[J]. System Sciences and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 2007, 23(3): 280-284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0068.2007.03.007
[24] 韩晓增, 李娜. 中国东北黑土地研究进展与展望[J]. 地理科学, 2018, 38(7): 1032-1041. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201807004.htm
Han X Z, Li N. Research progress of black soil in Northeast China [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2018, 38(7): 1032-1041. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201807004.htm
[25] 陈怀满. 环境土壤学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 15.
Chen H M. Environmental soil science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005: 15. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: