STORAGE STRUCTURE AND SUPPLY CAPACITY OF KARST WATER IN NORTHERN XINGLONG COUNTY, HEBEI PROVINCE
-
摘要:
河北省承德市兴隆县北部地区赋存丰富的岩溶水资源, 该岩熔水为当地居民生产生活用水的主要来源. 在1:5万水文地质调查研究中, 以岩溶水为主要研究对象, 查明了区内基础水文地质条件; 对岩溶含水岩组进行了划分, 查明了区域岩溶储水结构特征, 将研究区划分为滦河流域下游柳河流域主要储水结构及滦河流域下游柴白河流域主要储水结构. 在研究区实施探采结合孔3眼, 施工配套观测孔3眼, 对探采结合孔供水服务能力进行分析评估, 可为该地区岩溶地下水资源的合理开发利用提供科学依据.
Abstract:The abundant karst water resources in the northern Xinglong County of Chengde City, Hebei Province, serve as the major water supplies for production and daily life of local residents. The basic hydrogeological conditions in the area are identified with karst water as the main study object in the 1: 50 000 hydrogeological survey. Through the classification of water-bearing rock formations and analysis of the storage structure characteristics of regional karst water, the study area is divided into the main water storage structures of Liuhe river basin and Qaibai river basin in the lower reaches of Luanhe River Basin. Three exploration-mining combination boreholes and three construction matching observation wells are applied for the analysis and evaluation of water supply capacity of boreholes, to provide scientific basis for rational development and utilization of karst groundwater resources in the area.
-
Key words:
- karst water /
- water storage structure /
- water supply capacity /
- water resource /
- Luanhe River Basin /
- Hebei Province
-

-
表 1 含水岩组划分
Table 1. Classification of water-bearing rock formations
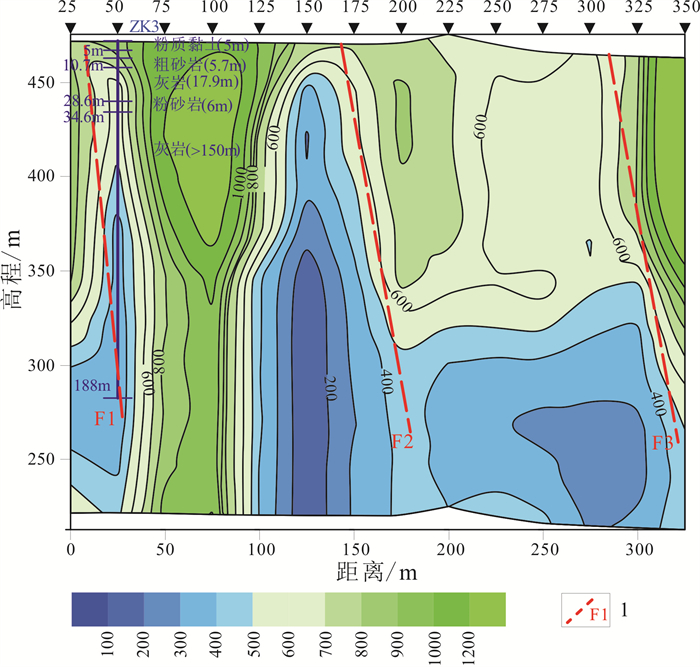
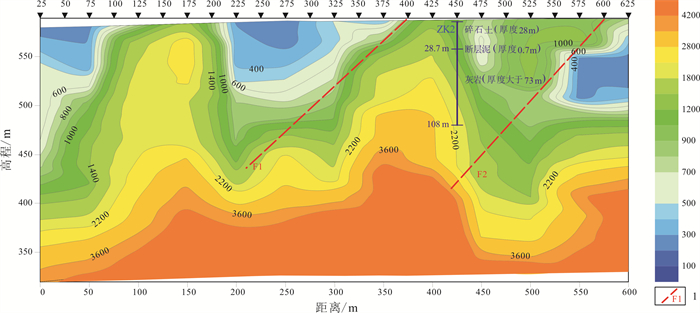
大类 亚类 次亚类 主要含水岩层 主要含水岩层岩性 碳酸盐岩裂隙溶洞含水岩组 1)奥陶系碳酸盐岩裂隙溶洞含水岩组(碳酸盐岩含量大于70%) —— 中下奥陶系统 灰岩、白云质灰岩、豹皮状灰岩、泥质条带灰岩等 2)寒武系碳酸盐岩裂隙溶洞含水岩组(碳酸盐岩含量大于70%) —— 炒米店组、崮山组、张夏组、馒头组、昌平组 灰岩、泥质条带灰岩、白云质灰岩等 3)蓟县系碳酸盐岩裂隙溶洞含水岩组 1)雾迷山组-高于庄组碳酸盐岩裂隙溶洞含水岩组(碳酸盐岩含量大于70%) 雾迷山组、杨庄组一段至二段、高于庄组一段至四段 中层及厚层状白云岩、砂质白云岩、泥质白云岩、硅质白云岩、白云质灰岩等 2)铁岭组碳酸盐岩裂隙溶洞含水岩组(碳酸盐岩含量50%~70%) 铁岭组 白云岩、含锰白云岩夹页岩、泥质白云岩等 4)长城系大红峪组碳酸盐岩裂隙溶洞含水岩组(碳酸盐岩含量50%~70%) —— 大红峪组 厚层石英砂岩夹硅质条带白云岩、页岩等 表 2 探采结合孔供水能力及服务对象一览表
Table 2. Water supply capacity and service objects of exploration-mining combination boreholes
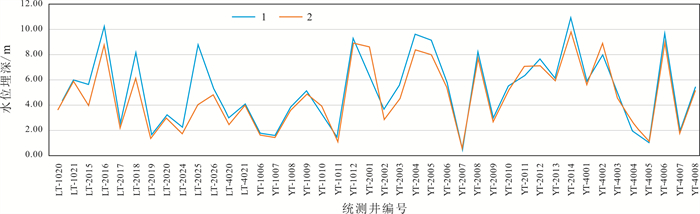
井号 地点 服务方向 单井出水量/(m3/d) 主要灌溉对象 灌溉面积/hm2 饮水户数 ZK1 南大洼村 革命老区扶贫攻坚 400 蘑菇、蔬菜大棚及果园等 20 200 ZK2 拨东村 饮用水源地 2 200 农田 13 500 ZK3 跳沟村 灌溉水源地 1 900 山楂果园、葡萄园等 20 150 合计 4 500 53 850 -
[1] 杨平恒, 张宇, 田萍, 等. 川东平行岭谷典型岩溶含水介质特征的识别方法探讨——以重庆青木关地下水系统为例[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 38(2): 90-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNND201602015.htm
Yang P H, Zhang Y, Tian P, et al. A methodological research on the identification of a typical karst aquifer media in the paralleled ridge- valley of east Sichuan: A case study of Qingmuguan karst groundwater system, Chongqing[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 38(2): 90-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNND201602015.htm
[2] 王晓红, 刘久荣, 辛宝东, 等. 北京岩溶水系统划分及特征分析[J]. 城市地质, 2016, 11(3): 8-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2016.03.002
Wang X H, Liu J R, Xin B D, et al. Division and characterization analysis of karst groundwater system in Beijing[J]. Urban Geology, 2016, 11(3): 8-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2016.03.002
[3] 袁建飞, 邓国仕, 徐芬, 等. 毕节市北部岩溶地下水水文地球化学特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2016, 43(1): 12-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201601004.htm
Yuan J F, Deng G S, Xu F, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of karst groundwater in the northern part of the city of Bijie[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(1): 12-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201601004.htm
[4] 张彦林, 李生永, 付东林, 等. 陇东盆地西部岩溶地下水形成机制研究[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(6): 1393-1399. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.06.024
Zhang Y L, Li S Y, Fu D L, et al. Formation mechanism of karst groundwater in the western Longdong basin, northwestern China[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(6): 1393-1399. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.06.024
[5] Noorishad J, Ayatollahi M S, Witherspoon P A. A finite-element method for coupled stress and fluid flow analysis in fractured rock masses[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1982, 19(4): 185-193.
[6] 刘建明, 张玉修, 曾璐, 等. 北京张坊地区中上元古界中岩溶发育与构造作用[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2019, 36(2): 208-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB201902005.htm
Liu J M, Zhang Y X, Zeng L, et al. Structure-controlled karst development in Middle-Upper Proterozoic strata in the Zhangfang area in Beijing[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019, 36(2): 208-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB201902005.htm
[7] 刘崇军, 刘全国, 于洋, 等. 北京西山岩溶水系统渗透系数计算及富水性分析[J]. 城市地质, 2017, 12(2): 73-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2017.02.014
Liu C J, Liu Q G, Yu Y, et al. Permeability coefficient calculation and aquiferous property analysis on karst water system in the west hill of Beijing[J]. Urban Geology, 2017, 12(2): 73-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2017.02.014
[8] 李向全, 张发旺, 毕二平, 等. 宁夏南部"南北古脊梁"岩溶裂隙水流系统分析[J]. 地球学报, 2004, 25(5): 571-574. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2004.05.014
Li X Q, Zhang F W, Bi E P, et al. The deep karst groundwater system in arid regions of northwestern China: A case study of karst fissure groundwater in southern Ningxia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2004, 25(5): 571-574. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2004.05.014
[9] 梁永平, 王维泰. 中国北方岩溶水系统划分与系统特征[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(6): 860-868.
Liang Y P, Wang W T. The division and characteristics of karst water systems in northern China[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2010, 31(6): 860-868.
[10] 甘伏平, 喻立平, 卢呈杰, 等. 不同岩溶储水结构分析与地球物理勘察[J]. 地质与勘探, 2011, 47(4): 663-672. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201104015.htm
Gan F P, Yu L P, Lu C J, et al. Geophysical prospecting and analyzing on different karst water-bearing structures[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2011, 47(4): 663-672. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201104015.htm
[11] 武选民, 文冬光, 张福存, 等. 我国西北人畜饮用缺水地区储水构造特征与工程范例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2010, 37(1): 22-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.01.005
Wu X M, Wen D G, Zhang F C, et al. Groundwater-bearing structures in northwestern China and their application to water-taking works for water-shortage towns[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(1): 22-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.01.005
[12] 武选民, 文冬光, 张福存, 等. 辽西山地缺水地区储水构造的特征和供水示范工程的建立[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(1): 142-146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.01.016
Wu X M, Wen D G, Zhang F C, et al. Groundwater-bearing structures in water deficient mountainous area, western Liaoning, China and set-up of civil water supply demonstration project[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(1): 142-146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.01.016
[13] 乔小娟, 侯泉林, 琚宜文, 等. 北京张坊地区岩溶地下水运移富集的构造控制分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2014, 33(2): 184-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201402009.htm
Qiao X J, Hou Q L, Ju Y W, et al. Research about the control of geological structure on karst groundwater system in Zhangfang, Beijing[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2014, 33(2): 184-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201402009.htm
[14] 高阳, 熊华山, 彭明涛, 等. 渝东南岩溶储水构造高密度电阻率法异常特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(6): 1108-1115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201606009.htm
Gao Y, Xiong H S, Peng M T, et al. High density electrical prospecting anomaly analysis of water-bearing structure in karst area of southeast Chongqing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(6): 1108-1115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201606009.htm
[15] 郑丹, 崔鹏飞, 陈永, 等. 2011-2017年我国城镇供水状况宏观数据分析总结[J]. 给水排水, 2020, 56(S1): 400-407. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZJS2020S1103.htm
Zheng D, Cui P F, Chen Y, et al. Summary of macro data analysis of urban water supply in China from 2011 to 2017[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2020, 56(S1): 400-407. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZJS2020S1103.htm
[16] 叶晓华, 白平. 川北地区岩溶发育特征及水资源利用前景浅析——以曾家山地区为例[J]. 四川地质学报, 2019, 39(4): 642-647. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2019.04.022
Ye X H, Bai P. A brief analysis of karstification development and prospects of water resources utilization in North Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2019, 39(4): 642-647. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2019.04.022
[17] 隋少强, 汪新伟, 周总瑛, 等. 天津岩溶地热田热储特征研究[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(6): 590-594, 569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.06.011 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract9535.shtml
Sui S Q, Wang X W, Zhou Z Y, et al. Study on the thermal reservoir characteristics of karst geothermal fields in Tianjin City[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(6): 590-594, 569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.06.011 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract9535.shtml
[18] 邓启军, 李伟, 朱庆俊, 等. 河北坝上张北县玄武岩区蓄水构造特征与找水实践[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(12): 1899-1907. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.12.004
Deng Q J, Li W, Zhu Q J, et al. An analysis of the characteristics of water storage structure and the practice of groundwater exploration in the basalt area of Zhangbei County, Bashang, Hebei Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020, 39(12): 1899-1907. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.12.004
[19] 李涛, 邓铭江, 王于宝, 等. 台兰河山前地下储水构造及地下水库可行性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2011, 38(1): 30-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201101009.htm
Li T, Deng M J, Wang Y B, et al. A study of the feasibility of the groundwater storage structure and groundwater reservoir in the piedmont of the Tailan River[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2011, 38(1): 30-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201101009.htm
[20] 刘声凯, 刘海飞, 黄超, 等. 水文地质调查与综合物探在赣南花岗岩地区找水中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2021, 57(3): 584-592. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT202103011.htm
Liu S K, Liu H F, Huang C, et al. Groundwater prospecting by combined hydrogeological and integrated geophysical surveys in granite areas, southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2021, 57(3): 584-592. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT202103011.htm
[21] 马超, 孙箐彬, 邵光宇, 等. 淄河源区含水层介质特征及富水规律研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(12): 173-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202012026.htm
Ma C, Sun Q B, Shao G Y, et al. Study on the characteristics of aquifers medium and the law of water abundance in Zihe River source area[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2020, 34 (12): 173-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202012026.htm
-



 下载:
下载: