INDICATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL ISOTOPES IN IDENTIFYING THE GROUNDWATER RECHARGE SOURCES IN ILI RIVER VALLEY
-
摘要:
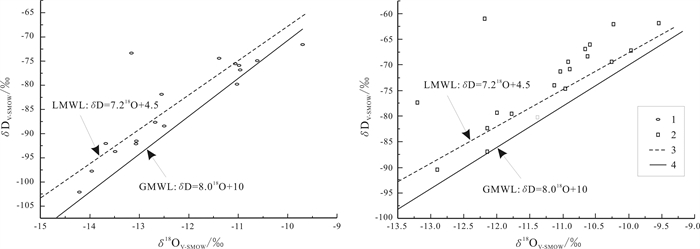
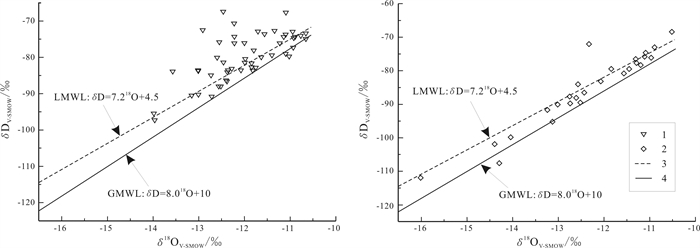
重点分析了研究区潜水、浅层承压水、泉水及地表水δD、δ18O的分布特征, 并对5组水文钻探井地下水样品进行分析. 潜水δD变化范围为-97.32‰~-67.51‰, 平均值为-80.34‰; δ18O为-15.85‰~-10.66‰, 平均值为-12.08‰. 浅层承压水δD为-111.93‰~-68.38‰, 平均值为-84.79‰; δ18O为-16.01‰~-10.52‰, 平均值为-12.30‰. 泉水δD为-102.06‰~-71.63‰, 平均值为-84.10‰; δ18O为-14.21‰~-9.70‰, 平均值为-12.24‰. 地表水δD为-90.53‰~-60.99‰, 平均值为-72.58‰; δ18O在-13.20‰~-9.54‰, 平均值为-11.21‰. 地下水δ13C为-9.4‰~-5.6‰, 平均值为-8.3‰, 极差为3.8‰. 结果表明: 地下水与地表水均起源于当地大气降水. 潜水与浅层承压水水力联系较强, 潜水与浅层承压水属于同一含水系统. 与浅层承压水相比, 深层承压水年龄较大, 在20 ka左右, 属于沉积埋藏水. 深层承压水与浅层承压水的水力联系较弱. 潜水与浅层承压水的δ13C值较为接近, 且接近大气CO2的δ13C值-7‰. 研究区地下水中碳的主要来源为大气CO2.
Abstract:This study analyzes the distribution characteristics of δD and δ18O in phreatic water, shallow confined water, spring water and surface water, as well as the δ13C of five groups of groundwater samples from hydrologic drilling wells. The results show that both groundwater and surface water originate from the local meteoric water. The phreatic water and shallow confined water, belonging to the same aquifer system, have a strong hydraulic connection. The age of deep confined water is about 20 ka, older than the shallow confined water, belonging to sedimentary buried water, with weak hydraulic relation between the two. The δ13C values of phreatic water and shallow confined water are close to each other, approximating that of atmospheric CO2(-7‰) which serves as the main source of carbon in groundwater of the study area.
-
Key words:
- environmental isotope /
- aquifer system /
- δD-δ18O relation /
- δ13C /
- Ili River Valley /
- Xinjiang
-

-
表 1 氢氧稳定同位素参数统计特征值表
Table 1. Statistical eigenvalues of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope parameters
特征值 潜水 浅层承压水 泉水 地表水 δD δ18O δD δ18O δD δ18O δD δ18O 最大值 -67.51 -10.66 -68.38 -10.52 -71.63 -9.70 -60.99 -9.54 最小值 -97.32 -15.85 -111.93 -16.01 -102.06 -14.21 -90.53 -13.20 极差值 29.81 5.19 43.55 5.49 30.43 4.51 29.54 3.66 平均值 -80.34 -12.08 -84.79 -12.30 -84.10 -12.24 -72.58 -11.21 含量单位:‰. 表 2 13C稳定同位素分析测试结果表
Table 2. Stable isotopic analysis and testing results of 13C
样品编号 取样深度/m δ13C/‰ ZK1 175.0 -5.6 ZK3 198.0 -9.0 ZK4 10.7 -8.0 ZK8 1.9 -9.4 ZK14 121.6 -9.4 表 3 承压水14C测试结果
Table 3. 14C radioactive isotope test results of confined water
样品编号 取样深度/m 现代碳占比/% 校正年龄/ka ZK4 240.0 5.55±1.60 23.90±2.38 ZK3-2 236.0 6.01±0.65 23.24±0.89 ZK3-1 198.0 9.48±0.62 19.48±0.54 -
[1] 李健, 王辉, 魏丽琼. 格尔木河流域平原区地下水同位素及水化学特征[J]. 西北地质, 2007, 40(4): 94-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2007.04.013
Li J, Wang H, Wei L Q. Isotopic and hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in the Golmud River Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2007, 40(4): 94-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2007.04.013
[2] 刘芬, 王水献, 蓝永超, 等. 黑河流域张掖盆地地表水-地下水系统同位素特征及转化关系[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2014, 12(2): 92-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201402022.htm
Liu F, Wang S X, Lan S C, et al. Environmental isotopes features and exchanges of surfacewater-groundwater system in the Zhangye Basin of Heihe River watershed[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2014, 12(2): 92-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201402022.htm
[3] 王文祥, 安永会, 李文鹏, 等. 基于环境同位素技术的张掖盆地地下水流动系统分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2016, 43(2): 25-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201602006.htm
Wang W X, An Y H, Li W P, et al. Groundwater flow system analysis of the Zhangye Basin based on environmental isotope techniques[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(2): 25-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201602006.htm
[4] 徐树媛. 李雅庄矿区地下水水化学及环境同位素特征研究[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2013, 11(2): 67-70, 120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201302019.htm
Xu S Y. Research on groundwater chemistry and environmental isotope in Liyazhuang mining area[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2013, 11(2): 67-70, 120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201302019.htm
[5] 孙金凤, 高宗军, 冯建国, 等. 泰莱盆地水环境同位素分布特征及其意义[J]. 水电能源科学, 2019, 37(12): 30-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY201912008.htm
Sun J F, Gao Z J, Feng J G, et al. Distribution characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in water environment and its significance in Tailai Basin[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2019, 37(12): 30- 32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY201912008.htm
[6] 王文科, 王雁林, 段磊, 等. 关中盆地地下水环境演化与可再生维持途径[M]. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 2006: 53-65.
Wang W K, Wang Y L, Duan L, et al. Groundwater environment evolution and renewable maintenance in Guanzhong Basin[M]. Zhengzhou: Yellow River Water Conservancy Press, 2006: 53-65. (in Chinese)
[7] 陈宗宇, 张光辉, 聂振龙, 等. 中国北方第四系地下水同位素分层及其指示意义[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2002, 27(1): 97-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200201020.htm
Chen Z Y, Zhang G H, Nie Z L, et al. Groundwater isotopic stratification and its implications in northern China[J]. Earth Science -Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2002, 27(1): 97- 104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200201020.htm
[8] 侯光才, 张茂省, 刘方, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地地下水勘查研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008: 67-72.
Hou G C, Zhang M S, Liu F, et al. Groundwater exploration in Ordos Basin[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2008: 67-72. (in Chinese)
[9] Li J, Liu J, Pang Z, et al. Characteristics of chemistry and stable isotopes in groundwater of the Chaobai River catchment, Beijing[J]. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 2013, 7: 487-490. doi: 10.1016/j.proeps.2013.03.092
[10] Ma J Z, He J H, Qi S, et al. Groundwater recharge and evolution in the Dunhuang Basin, northwestern China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2013, 28: 19-31. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.10.007
[11] 邵杰. 新疆伊犁-巩乃斯河谷地下水循环演化规律研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2015: 16-18.
Shao J. Groundwater circulation and evolution pattern in Yili-Gongnaisi Valley of Xinjiang Autonomous Region[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2015: 16-18.
[12] 邵杰, 李瑛, 王文科, 等. 水化学在新疆伊犁河谷地下水循环中的指示作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2016, 43(4): 30-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201604007.htm
Shao J, Li Y, Wang W K, et al. Indicative effects of hydrochemistry on groundwater circulation in the Yili River Valley of Xinjiang[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(4): 30-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201604007.htm
[13] 叶人源. 新疆伊犁-巩乃斯河谷地表水与地下水转化关系研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2015: 9-13.
Ye R Y. Interaction of surface water and groundwater in Yili-Gongnaisi River Valley[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2015: 9-13.
[14] 邵杰, 李瑛, 井晶晶, 等. 新疆霍城县水环境同位素特征及其指示作用[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(1): 167-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201701028.htm
Shao J, Li Y, Jing J J, et al. Feature of isotopes of water environment and their indication in Huocheng County of Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(1): 167-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201701028.htm
[15] 中国科学院新疆地理研究所. 天山山体演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986: 126-129.
Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Science. Evolution of Tianshan Mountains[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1986: 126-129. (in Chinese)
[16] 王恒纯. 同位素水文地质概论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1900: 66- 68.
Wang H C. Introduction to isotope hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1900: 66-68. (in Chinese)
[17] 刘宗鑫, 董新光, 吴彬, 等. 新疆鄯善县水环境氢氧同位素特征及其指示作用[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2014, 25(2): 162-165, 171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201402034.htm
Liu Z X, Dong X G, Wu B, et al. Feature of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of water environment and their indication in Shanshan County of Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 2014, 25(2): 162-165, 171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201402034.htm
[18] 李捷, 庞忠和, 古丽波斯坦·吐逊江, 等. 北疆大气降水水汽源识别及其对地下水补给的指示意义[J]. 科技导报, 2016, 34(18): 118-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJDB201618024.htm
Li J, Pang Z H, Tursun G, et al. Identification of moisture sources in Junggar Basin and its implication for groundwater recharge[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2016, 34(18): 118-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJDB201618024.htm
[19] 王骞迎, 张艺武, 苏小四, 等. 伊犁河谷西部平原多级次地下水循环模式[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文), 2020, 18(4): 167-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD202004017.htm
Wang Q Y, Zhang Y W, Su X S, et al. Study on multi-level groundwater cycle pattern in the western plain of Yili River Valley [J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2020, 18(4): 167-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD202004017.htm
[20] 马致远, 钱会. 环境同位素地下水文学[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 2004: 19-20.
Ma Z Y, Qian H. Environmental isotope groundwater hydrology[M]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press, 2004: 19-20. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: