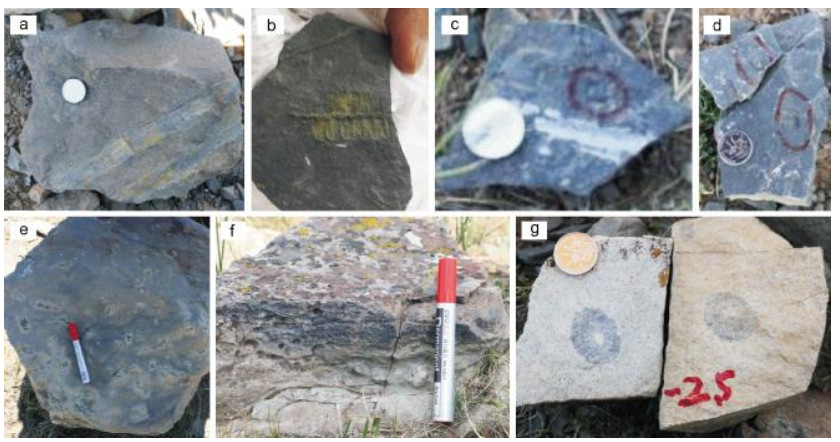
SEDIMENTARY CHARACTERISTICS OF ELITU FORMATION IN ZHENGXIANGBAI QI OF INNER MONGOLIA IDENTIFIED BY MARKOV CHAIN ANALYSIS
-
摘要:
通过野外地质剖面实测识别了额里图牧场额里图组各层岩性特征, 利用马尔可夫链分析方法分析该剖面下岩段地层的沉积旋回, 综合地质基础资料, 进一步分析了沉积环境. 结果识别出一个以砂岩-粉砂质泥岩-粉砂岩-泥岩为特征和一个以砂岩-灰岩-泥岩为特征的两个岩性旋回, 分别代表浅海陆棚-深水浊积岩相序和陆棚浅海礁滩相沉积. 结合剖面分别划分出陆棚、斜坡和盆地(海槽)3个相, 进一步识别出潮坪滩相、滩前斜坡相、浊积滩坝相、滩相、斜坡盆地相、缓坡相、深水海槽相和礁滩相等亚相. 整个剖面由两次海侵半旋回和一次完整的海侵海退旋回组成. 研究认为古亚洲洋的最终闭合时限应该在额里图组时期之后.
Abstract:The lithologic characteristics of each layer of Elitu Formation are identified by field survey of geological section. The sedimentary cycles of the strata are studied by Markov chain analysis, and the sedimentary environment is further analyzed with the basic geological data. Two lithologic cycles characterized separately by sandstone-silty mudstone-siltstone-mudstone and sandstone-limestone-mudstone are identified, which represent the facies sequence of shallow sea continental shelf-deepwater turbidite and continental shelf shallow sea reef beach sediments respectively. Combined with the section, three facies including continental shelf, slope and basin(trough) can be further identified as several subfacies such as tidal flat beach, beach front slope, turbidite beach bar, beach, slope basin, gentle slope, deepwater trough and reef beach. Two transgression semi-cycles and one complete transgression-regression cycle can be recognized in the section. It is concluded that the final closure time of Paleo-Asian Ocean should be after the period of Elitu Formation.
-
Key words:
- Elitu Formation /
- sedimentary environment /
- sedimentary cycle /
- Markov chain /
- Inner Mongolia
-

-
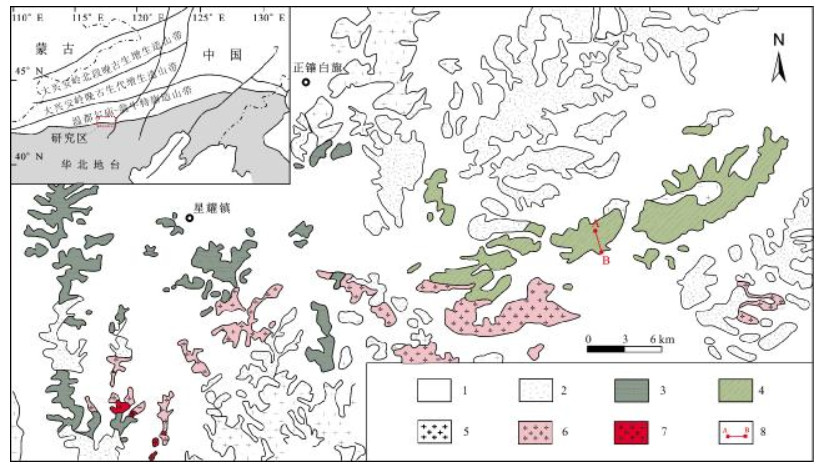
图 1 内蒙古正镶白旗地区地质简图(据文献[2]修改)
Figure 1.
表 1 岩相转移频数矩阵
Table 1. Lithofacies transfer frequency matrix
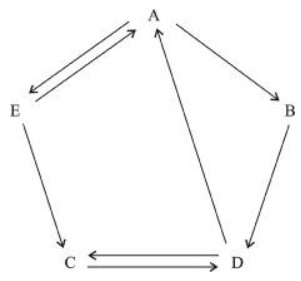
向上转移频数 A B C D E $N_{i \cdot} $ A 0 2 5 5 7 19 B 1 0 1 2 1 5 C 5 1 0 6 3 15 D 7 1 5 0 3 16 E 6 1 4 3 0 14 $N_{j \cdot} $ 19 5 15 16 14 69 表 2 岩相转移频数矩阵马氏检验
Table 2. Markov test of lithofacies transfer frequency matrix
χ2 A B C D E Σ A 5.23 0.28 0.18 0.08 2.57 8.34 B 0.10 0.36 0.01 0.61 0.00 1.08 C 0.18 0.01 3.26 1.83 0.00 5.28 D 1.53 0.02 0.67 3.71 0.02 5.94 E 1.19 0.00 0.30 0.02 2.84 4.35 Σ 8.24 0.67 4.42 6.25 5.43 25.00 表 3 岩相转移概率矩阵
Table 3. Lithofacies transfer probability matrix
向上转移概率 A B C D E A 0.00 0.11 0.26 0.26 0.37 B 0.20 0.00 0.20 0.40 0.20 C 0.33 0.07 0.00 0.40 0.20 D 0.44 0.06 0.31 0.00 0.19 E 0.43 0.07 0.29 0.21 0.00 表 4 岩相转移差值矩阵
Table 4. Lithofacies transfer difference matrix
岩相转移差值矩阵 A B C D E A -0.38 0.01 -0.04 -0.06 0.09 B -0.10 -0.08 -0.03 0.15 -0.02 C -0.02 -0.03 -0.28 0.10 -0.06 D 0.08 -0.03 0.03 -0.30 -0.08 E 0.08 -0.02 0.01 -0.08 -0.25 -
[1] 和政军, 刘淑文, 任纪舜, 等. 内蒙古林西地区晚二叠世-早三叠世沉积演化及构造背景[J]. 中国区域地质, 1997(4): 403-409, 427. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD704.008.htm
He Z J, Liu S W, Ren J S, et al. Late Permian-Early Triassic sedimentary evolution and tectonic setting of the Linxi region, Inner Mongolia[J]. Regional Geology of China, 1997(4): 403-409, 427. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD704.008.htm
[2] 朱俊宾, 和政军. 兴蒙造山带南缘早-中二叠世砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(2/3): 357-371. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2017Z1019.htm
Zhu J B, He Z J. Detrital zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of Early- Middle Permian sandstones from the south margin of Xing-Meng orogenic belt and their tectonic significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2017, 36(2/3): 357-371. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2017Z1019.htm
[3] 陈井胜, 邢德和, 刘淼, 等. 内蒙古元宝山小建昌营子地区三面井组沉积环境[J]. 世界地质, 2015, 34(4): 1013-1023. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2015.04.013
Chen J S, Xing D H, Liu M, et al. Depositional environment of Sanmianjing Formation in Xiaojianchangyingzi area of Yuanbaoshan, Inner Mongolia[J]. Global Geology, 2015, 34(4): 1013-1023. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2015.04.013
[4] 朱如凯, 许怀先, 邓胜徽, 等. 中国北方地区二叠纪岩相古地理[J]. 古地理学报, 2007, 9(2): 133-142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2007.02.002
Zhu R K, Xu H X, Deng S H, et al. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Permian in northern China[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2007, 9(2): 133-142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2007.02.002
[5] 梅杨. 内蒙古正镶白旗二叠系地层特征及对比[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄经济学院, 2013.
Mei Y. Characteristics and correlation of the Permian strata in Zhengxiangbaiqi, Inner Mongolia[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang University of Economics, 2013.
[6] 田树刚, 张永生, 王俊涛, 等. 兴安-内蒙古地区晚古生代生物礁及其构造和油气意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41(4): 493-503. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201104007.htm
Tian S G, Zhang Y S, Wang J T, et al. Late Paleozoic reefs and their significance for tectonics and oil-gas exploration in the Hinggan-Inner Mongolia area[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(2): 212-222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201104007.htm
[7] 王俊涛, 张永生, 宋天锐, 等. 内蒙古扎赉特旗中二叠统岩石地层、生物地层特征及沉积环境分析[J]. 地层学杂志, 2011, 35(4): 375-384. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201104007.htm
Wang J T, Zhang Y S, Song T R, et al. The Middle Permian lithostratigraphy, biostratigraphy and sedimentary environments of the Jlaid Qi, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2011, 35(4): 375-384. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201104007.htm
[8] 田树刚, 李子舜, 王峻涛, 等. 内蒙古东部及邻区石炭纪-二叠纪构造地层格架与形成环境[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(10): 1554-1564. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.10.002
Tian S G, Li Z S, Wang J T, et al. Carboniferous-Permian tectonic and stratigraphic framework of eastern Inner Mongolia as well as adjacent areas and its formation environment[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2012, 31(10): 1554-1564. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.10.002
[9] 翟大兴, 张永生, 田树刚, 等. 内蒙古林西地区上二叠统林西组沉积环境与演变[J]. 古地理学报, 2015, 17(3): 359-370. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201503008.htm
Zhai D X, Zhang Y S, Tian S G, et al. Sedimentary environment and evolution of the Upper Permian Linxi Formation in Linxi area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2015, 17(3): 359-370. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201503008.htm
[10] 翟大兴, 张永生, 田树刚, 等. 兴蒙地区晚二叠世林西组灰岩微量元素与碳、氧同位素特征及沉积环境讨论[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(3): 333-343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201503009.htm
Zhai D X, Zhang Y S, Tian S G, et al. The Late Permian sedimentary environments of Linxi Formation in Xingmeng area: Constraints from carbon and oxygen isotopes and trace elements[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2015, 36(3): 333-343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201503009.htm
[11] 翟大兴. 内蒙古东部及邻区晚二叠世古地理特征与油气远景[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
Zhai D X. Oil and gas prospect and palaeogeographic characteristics of Late Permian in east Inner Mongolia and its adjacent area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2015.
[12] 田树刚, 张永生, 宫月萱, 等. 内蒙古林西县及邻区晚二叠世生物礁和环境意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2016, 46(7): 963-975. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201607008.htm
Tian S G, Zhang Y S, Gong Y X, et al. Environmental and tectonic significance of Late Permian reefs in the Linxi and adjacent areas in Inner Mongolia of China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(7): 1463-1476. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201607008.htm
[13] 田树刚, 李子舜, 张永生, 等. 内蒙东部及邻区晚石炭世-二叠纪构造古地理环境及演变[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(4): 688-707. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201604007.htm
Tian S G, Li Z S, Zhang Y S, et al. Late Carboniferous-Permian tectono-geographical conditions and development in eastern Inner Mongolia and adjacent areas[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(4): 688-707. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201604007.htm
[14] 田树刚, 张永生, 翟大兴, 等. 内蒙古南部晚二叠世同生变形构造与陆缘裂陷[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(2): 144-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201802003.htm
Tian S G, Zhang Y S, Zhai D X, et al. Late Permian syngenetic deformation structures and epicontinental faulted depression in southern Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(2): 144-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201802003.htm
[15] Vistelius A B. On the question of the mechanism of formation of strata[J]. Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, 1949, 65(2): 191-194.
[16] 门桂珍, 史晓宏, 赵淑芝. 马尔科夫链-熵分析在环境分析中的应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 1989(1): 55-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB198901007.htm
Men G Z, Shi X H, Zhao S Z. Application of Markov chains-entropy to analysis of depositional environments[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 1989(1): 55-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB198901007.htm
[17] 武安斌, 张成君, 宋春晖. 马尔科夫链法在西成矿田中泥盆统沉积相分析中的应用[J]. 甘肃地质学报, 1995, 4(2): 80-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ502.009.htm
Wu A B, Zhang C J, Song C H. The application of Markov chain method to the sedimentary facies analysis of the Middle Devonian in Xicheng orefield[J]. Acta Geologica Gansu, 1995, 4(2): 80-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ502.009.htm
[18] 杨明慧, 牛雅莉. 德令哈盆地早侏罗世冲积扇-扇三角洲沉积体系及其马尔科夫链分析[J]. 中国煤田地质, 2000, 12(1): 13-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT200001005.htm
Yang M H, Niu Y L. Early Jurassic alluvial fan-fan delta depositional system of Delingha Basin and its Markov model[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2000, 12(1): 13-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT200001005.htm
[19] 吕红华, 夏正楷, 江波, 等. 数学地质方法在储层沉积相分析中的应用——以柴达木盆地花土沟油田新近系砂岩储层为例[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 42(4): 462-469. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ200604010.htm
Lü H H, Xia Z K, Jiang B, et al. Application of mathematical geology methods to analysis of the sedimentary facies of sandstone reservoir: An example of the reservoir of the Neogene in Huatugou oilfield, Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2006, 42(4): 462-469. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ200604010.htm
[20] 杨帅, 谢小平. 剑门关丹霞地貌晚侏罗-早白垩系沉积相的马尔科夫链特征[J]. 地质学刊, 2017, 41(2): 276-281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201702017.htm
Yang S, Xie X P. Markov chain characteristics of Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous sedimentary facies of the Danxia landform in Jianmenguan Pass[J]. Journal of Geology, 2017, 41(2): 276-281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201702017.htm
[21] 赵玉琛. 应用马尔科夫链对宁芜一些地层剖面的计算模拟和分析[J]. 江苏地质, 1991, 15(3): 169-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ199103011.htm
Zhao Y C. Simulation and analysis on some formation sections with Markov chain in Ning-Zheng area[J]. Jiangsu Geology, 1991, 15(3): 169-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ199103011.htm
[22] 郭光裕. 马尔科夫概型分析及其在地质研究中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 1992, 28(8): 29-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT199208007.htm
Guo G Y. Markov probability model analysis and its application in geological examination[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1992, 28(8): 29-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT199208007.htm
[23] 周斌, 汤军, 周金应, 等. 湖北刘家场地区奥陶系地层沉积相及马尔科夫链分析[J]. 地质学刊, 2013, 37(4): 621-625. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201304018.htm
Zhou B, Tang J, Zhou J Y, et al. The Ordovician sedimentary facies and Markov chain analysis in the region of Liujiachang in Hubei[J]. Journal of Geology, 2013, 37(4): 621-625. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201304018.htm
[24] 龚一鸣. 湖南宁远早-中泥盆世陆源碎屑岩地层剖面马尔科夫概型分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 1983(1): 35-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ198301009.htm
Gong Y M. Markov probability analysis of stratigraphic profile of continental clastic rocks from Ningyuan Early-Middle Devonian in Hunan[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 1983(1): 35-38. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ198301009.htm
[25] 朱筱敏, 信荃麟. 马尔柯夫链法在建立沉积相模式中的应用[J]. 沉积学报, 1987, 5(4): 96-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB198704009.htm
Zhu X M, Xin Q L. Application of Markov chain method to establishment sedimentary facies model[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1987, 5(4): 96-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB198704009.htm
[26] 张成凤. 马尔科夫链模拟在济阳坳陷中的应用[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学, 2010.
Zhang C F. Application of Markov chain simulation in the Jiyang depression[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum, 2010.
[27] 张成凤, 吕洪波, 夏邦栋, 等. 南盘江盆地中三叠统复理石韵律的马尔科夫链特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 2011, 57(5): 632-640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201105004.htm
Zhang C F, Lü H B, Xia B D, et al. Markov chain simulation on the rhythmic sequences of Middle Triassic flysch in Nanpanjing basin, SW China[J]. Geological Review, 2011, 57(5): 632-640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201105004.htm
[28] 景毅, 王世称, 苑清扬. 马尔柯夫过程在地质学中的应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1986: 32-50.
Jing Y, Wang S C, Yuan Q Y. Application of Markov process in geology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1986: 32-50.
[29] Wang Z Z, Huang X, Liang Y R. Oil-gas reservoir lithofacies stochastic modeling based on one- to three-dimensional Markov chains[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(6): 1399-1408.
[30] Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W J, et al. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164(1): 31-47.
[31] 内蒙古自治区地质矿产局. 内蒙古自治区区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991: 1-725.
Inner Mongolia Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Regional geology of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1991: 1-725. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: