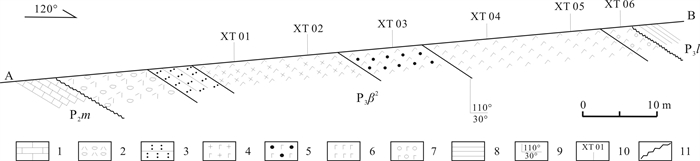
GEOLOGY AND GENESIS OF XITIAN SUPER-LARGE BASALT DEPOSIT IN HUAYINGSHAN FOLD BELT, EASTERN SICHUAN
-
摘要:
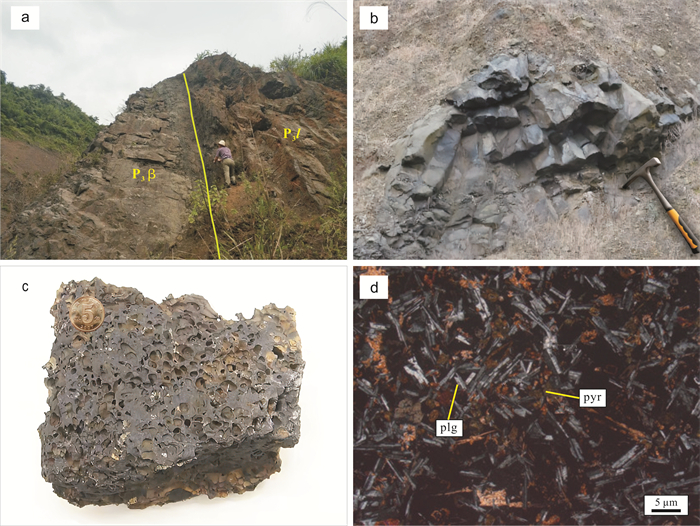
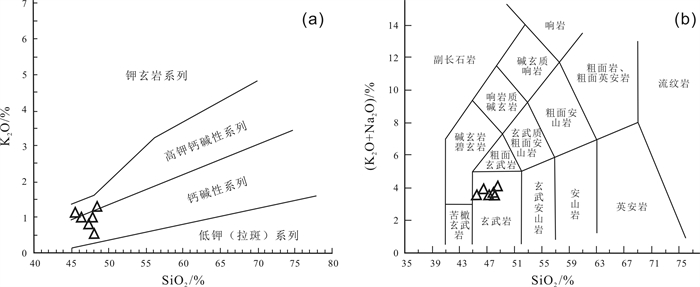
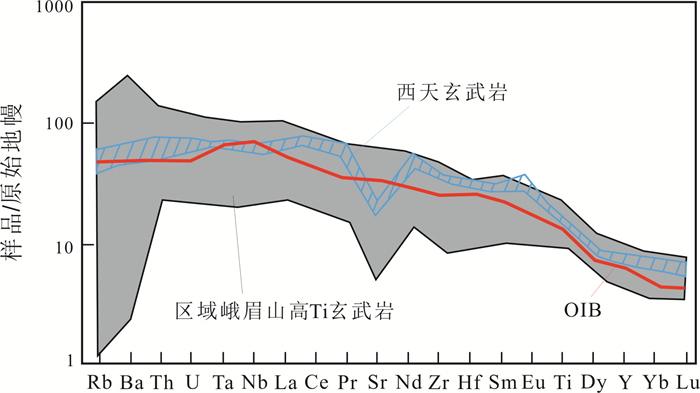
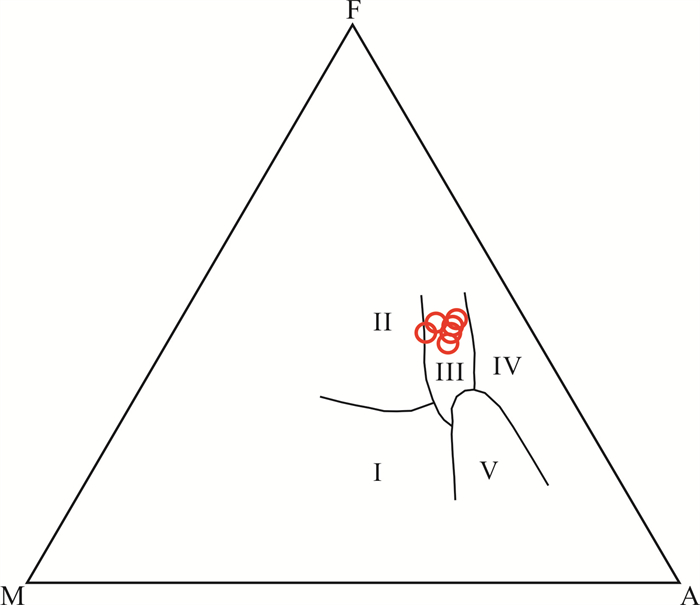
通过野外和镜下岩相学观察,结合主、微量元素地球化学方法,研究了四川省广安市邻水县西天超大型纤维用玄武岩矿床的地质特征,分析了矿石工业指标和矿床成因. 结果表明:矿床位于川东褶皱带华蓥山背斜东翼,矿体呈似层状赋存于上二叠统峨眉山玄武岩组(P3β)地层中,矿石储量约1 594×104 t,达超大型规模;主量元素地球化学特征表明,西天玄武岩岩浆属高钛、高钾钙碱性-钙碱性系列;稀土元素、微量元素地球化学特征与区域内高钛峨眉山玄武岩及OIB型玄武岩特征相似;西天玄武岩为峨眉山大火成岩省的外带组成部分,形成于板内构造环境,岩浆演化来源于OIB型源区且基本未受地壳物质混染,为地幔热柱成因的产物;矿床中的柱状节理玄武岩、块状玄武和气孔状玄武岩可用于纤维拉丝生产.
Abstract:Through field survey and petrographic observation under microscope, combined with geochemical analysis for major and trace elements, the paper studies the geological characteristics of Xitian super-large fiber-used basalt deposit in Linshui County of Sichuan Province, and analyzes the industry indexes of ores and deposit genesis. The results show that the deposit is located in the east wing of Huayingshan anticline of eastern Sichuan fold belt, and the orebody is occurred in stratoid in the Upper Permian Emeishan basalt formation, with the ore reserves about 15.94 Mt, reaching the super-large size. The geochemistry of major elements indicate that the Xitian basaltic magma belongs to high Ti, high K calc alkaline-calc alkaline series. The geochemical characteristics of trace and rare earth elements are similar to those of the regional high Ti Emeishan basalt and OIB-type basalt. The Xitian basalt is the outer zone component of the Emeishan large igneous province, formed in the intraplate tectonic environment, with the magmatic evolution from OIB source area and basically no hybridization of crustal materials, which is of mantle plume origin. The columnar jointed, massive and vesicular basalts in the deposit can be used for fiber drawing production.
-
Key words:
- Huayingshan fold belt /
- basalt deposit /
- fiber material /
- magmatite /
- Sichuan Province
-

-
图 7 西天玄武岩AMF构造环境判别图解(底图据文献[18])
Figure 7.
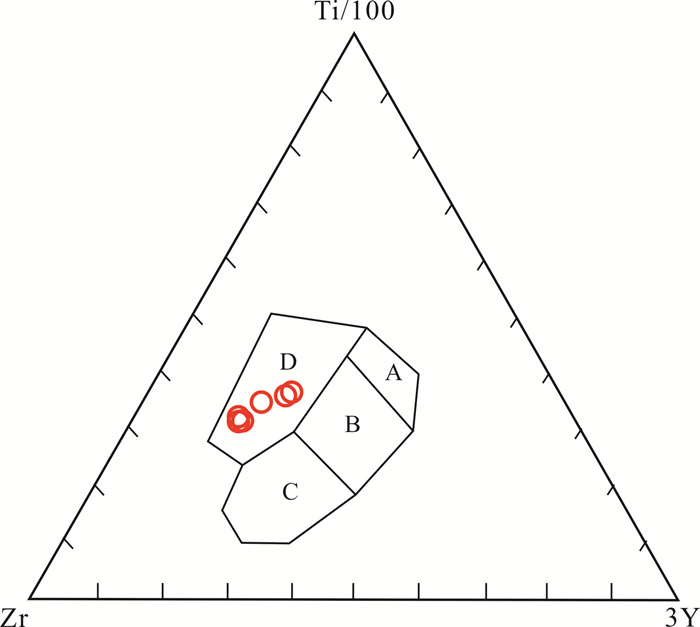
图 8 西天玄武岩Ti-Zr-Y构造环境判别图解(底图据文献[18])
Figure 8.
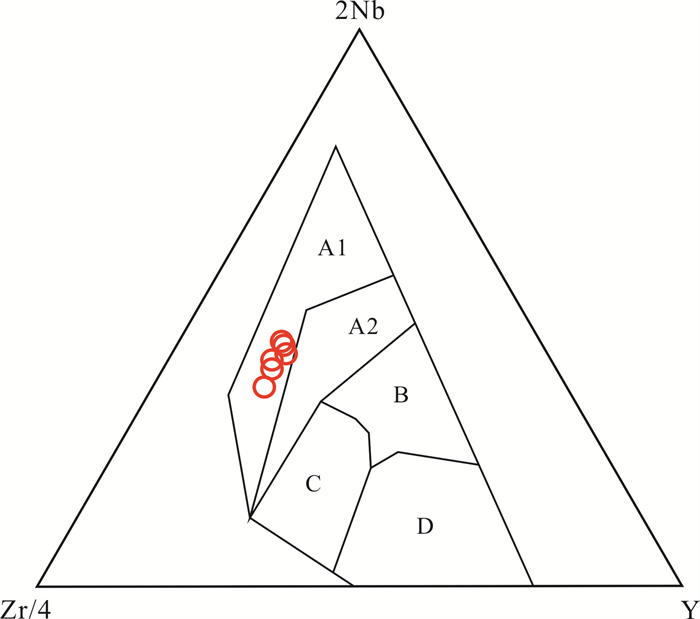
图 9 西天玄武岩Nb-Zr-Y构造环境判别图解(底图据文献[19])
Figure 9.
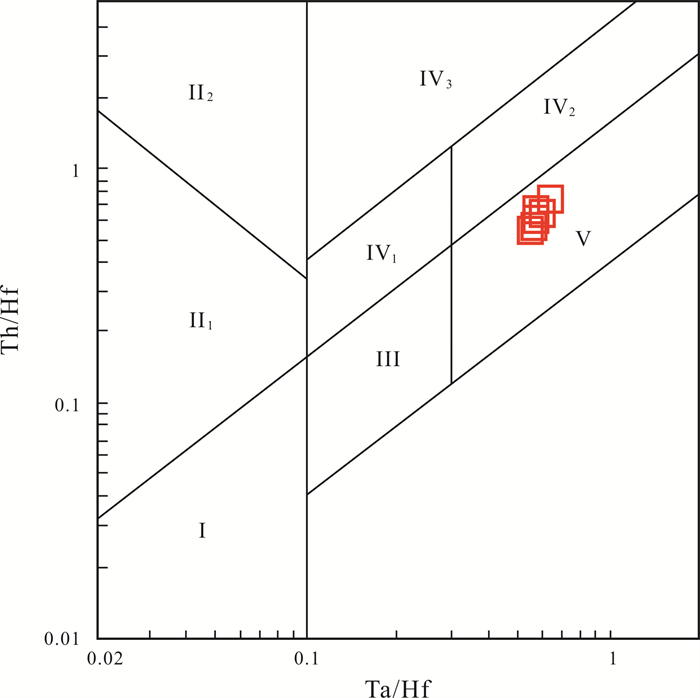
图 10 西天玄武岩Th/Hf-Ta/Hf判别图解(底图据文献[20])
Figure 10.
图 11 西天玄武岩原始地幔Th/Nb-La/Nb图解(底图据文献[11])
Figure 11.
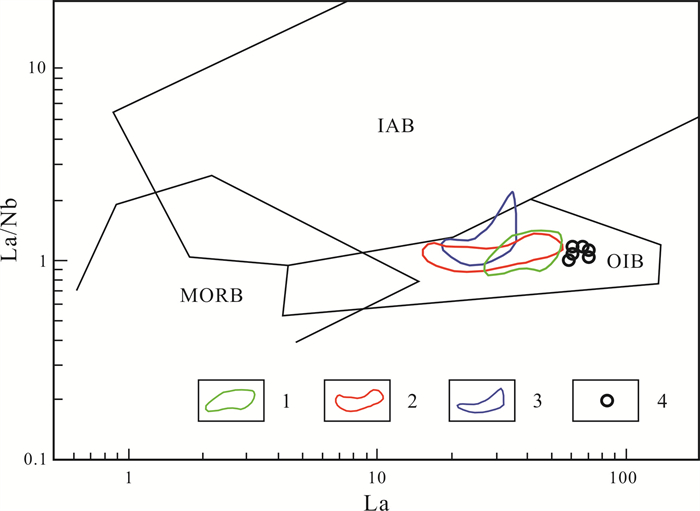
图 12 西天玄武岩矿石La/Nb-La源区判别图解(底图据文献[22])
Figure 12.
表 1 西天玄武岩矿床矿石主量、稀土、微量元素组成
Table 1. Contents of major, rare earth and trace elements of ores from Xitian basalt deposit
样品号 XT01 XT02 XT03 XT04 XT05 XT06 SiO2 48.46 47.29 49.86 48.46 45.54 47.88 Al2O3 13.51 13.19 13.67 13.23 13.21 13.63 Fe2O3 5 6.37 5.64 5.89 7.17 7.48 FeO 8.51 8.37 8.82 8.72 8.59 8.77 MgO 4.28 5.55 4.33 4.78 5.51 5.66 CaO 7.82 8.83 6.93 7.84 7.6 7.34 Na2O 2.93 2.68 2.7 2.97 2.39 2.79 K2O 1 0.84 0.98 1.29 1.14 0.56 TiO2 3.07 2.95 2.99 3.07 2.97 3.58 烧失量 5.26 3.87 3.84 3.62 5.81 2.08 总量 99.84 99.94 99.76 99.87 99.93 99.77 La 53.46 54.63 51.74 43.64 45.38 45.52 Ce 119.73 124.65 109.51 96.25 98.16 97.67 Pr 17.38 18.42 16.56 13.47 13.47 14.52 Nd 74.21 78.04 72.46 57.97 60.19 64.12 Sm 16.53 17.08 15.63 12.63 12.55 13.31 Eu 4.38 4.58 4.31 3.67 3.49 3.57 Gd 12.57 12.73 12.07 10.53 10.69 10.38 Tb 1.76 1.81 1.64 1.61 1.67 1.72 Dy 8.27 8.65 9.07 8.22 8.46 8.85 Ho 1.58 1.65 1.58 1.49 1.54 1.63 Er 4.15 4.28 4.39 3.59 3.81 4.12 Tm 0.53 0.52 0.56 0.57 0.63 0.61 Yb 3.25 3.41 3.52 3.33 3.65 3.61 Lu 0.44 0.46 0.48 0.49 0.51 0.53 ∑REE 318.24 330.91 303.52 257.46 264.2 270.16 LREE 285.69 297.4 270.21 227.63 233.24 238.71 HREE 32.55 33.51 33.31 29.83 30.96 31.45 δEu 0.93 0.95 0.96 0.97 0.92 0.93 δCe 0.96 0.96 0.92 0.97 0.97 0.93 Rb 29.18 37.43 35.26 30.25 31.48 30.93 Ba 567.83 519.47 538.72 415.62 347.37 437.71 Th 5.74 6.61 5.76 5.19 4.96 5.69 U 1.34 1.25 1.46 1.43 1.52 1.29 Nb 48.25 51.65 44.77 42.08 40.51 39.38 Ta 5.32 5.88 5.03 4.92 5.12 5.75 Zr 358.73 378.39 346.37 359.43 367.62 413.24 Hf 8.89 9.13 8.74 8.75 9.24 10.07 Sr 444.63 436.72 447.48 438.19 455.31 369.48 Y 36.58 39.72 37.92 34.43 36.11 38.63 含量单位:主要元素%,稀土、微量元素10-6. 表 2 西天玄武岩矿床矿石主量元素含量与企业纤维用玄武岩工业指标对比
Table 2. Comparison between major element contents of ores from Xitian basalt deposit and industrial indexes of fiber-used basalt
样品号 矿石构造 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO MgO CaO Na2O K2O TiO2 是否满足 XT01 含斑柱状节理玄武岩 48.46 13.51 5.00 8.51 4.28 7.82 2.93 1.00 3.07 否 XT02 柱状节理玄武岩 47.29 13.19 6.37 8.37 5.55 8.83 2.68 0.84 2.95 是 XT03 杏仁状玄武岩 49.86 13.67 5.64 8.82 4.33 6.93 2.70 0.98 2.99 否 XT04 含斑块状玄武岩 48.46 13.23 5.89 8.72 4.78 7.84 2.97 1.29 3.07 否 XT05 块状玄武岩 45.54 13.21 7.17 8.59 5.51 7.60 2.39 1.14 2.97 是 XT06 气孔状玄武岩 47.88 13.63 7.48 8.77 5.66 7.34 2.79 0.56 3.58 是 矿物纤维制品工业指标 44~49 10~14 6~15 — 5.5~10 7~12 — — 1.5~3.0 — 含量单位:%. -
[1] 王跃忠. 四川省纤维用玄武岩找矿远景分析[J]. 矿物学报, 2019, 39(6): 664-672. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201906006.htm
Wang Y Z. A prospective appraisal for the exploration of fiber-applied basalts in Sichuan province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2019, 39(6): 664-672. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201906006.htm
[2] 张剑, 徐小明, 刘作磊. 四川省峨眉山玄武岩组连续纤维用玄武岩矿特征分析[J]. 高科技纤维与应用, 2019, 44(3): 52-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GKJQ201903007.htm
Zhang J, Xu X M, Liu Z L. Feature analysis of continuous fibre used basalt deposits in Emeishan basalt formation, Sichuan Province[J]. Hi-Tech Fiber and Application, 2019, 44(3): 52-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GKJQ201903007.htm
[3] 申桂英. 世界首条玄武岩纤维2400孔漏板拉丝智能化池窑生产线在广安点火[J]. 精细与专用化学品, 2020, 28(7): 29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXHX202007012.htm
Shen G Y. The world's first basalt fiber 2400-hole bushing wire drawing intelligent pool kiln production line starts in Guang'an City [J]. Fine and Specialty Chemicals, 2020, 28(7): 29. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXHX202007012.htm
[4] Ali J R, Thompson G M, Zhou M F, et al. Emeishan large igneous province, SW China[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79(3/4): 475-489.
[5] He B, Xu Y G, Huang X L, et al. Age and duration of the Emeishan flood volcanism, SW China: Geochemistry and SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of silicic ignimbrites, post-volcanic Xuanwei Formation and clay tuff at the Chaotian section[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 255(3/4): 306-323.
[6] Xu J F, Suzuki K, Xu Y G, et al. Os, Pb, and Nd isotope geochemistry of the Permian Emeishan continental flood basalts: Insights into the source of a large igneous province[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(8): 2104-2119. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.01.027
[7] Xu Y G, Chung S L, Jahn B M, et al. Petrologic and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Permian-Triassic Emeishan flood basalts in southwestern China[J]. Lithos, 2001, 58(3/4): 145-168.
[8] Xu Y G, He B, Chung S L, et al. Geologic, geochemical, and geophysical consequences of plume involvement in the Emeishan flood- basalt province[J]. Geology, 2004, 32(10): 917-920. doi: 10.1130/G20602.1
[9] Xu Y G, Luo Z Y, Huang X L, et al. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints on crustal melting associated with the Emeishan mantle plume[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72(13): 3084- 3104. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.04.019
[10] 张招崇, 王福生, 郝艳丽, 等. 峨眉山大火成岩省中苦橄岩与其共生岩石的地球化学特征及其对源区的约束[J]. 地质学报, 2004, 78(2): 171-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200402004.htm
Zhang Z C, Wang F S, Hao Y L, et al. Geochemistry of the picrites and associated basalts from the Emeishan large igneous basalt province and constraints on their source region[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2004, 78(2): 171-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200402004.htm
[11] 程文斌, 董树义, 金灿海, 等. 四川省沐川地区峨眉山玄武岩元素地球化学特征与成因探讨[J]. 矿物岩石, 2019, 39(4): 49-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201904007.htm
Cheng W B, Dong S Y, Jin C H, et al. Characteristics of elemental geochemistry and petrogenesis discussion of the Emeishan basalts in Muchuan area, Sichuan Province[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2019, 39(4): 49-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201904007.htm
[12] 宋谢炎, 侯增谦, 汪云亮, 等. 峨眉山玄武岩的地幔热柱成因[J]. 矿物岩石, 2002, 22(4): 27-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200204005.htm
Song X Y, Hou Z Q, Wang Y L, et al. The mantle plume features of Emeishan basalts[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 22 (4): 27-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200204005.htm
[13] Lai S C, Qin J F, Li Y F, et al. Permian high Ti/Y basalts from the eastern part of the Emeishan large igneous province, southwestern China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 47: 216-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.07.010
[14] 万渝生, 伍家善, 耿元生. 碱性玄武岩形成的时限及其地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 1995(4): 365-374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB504.002.htm
Wan Y S, Wu J S, Geng Y S. The time limit of the formation of alkaline basalts and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 1995(4): 365-374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB504.002.htm
[15] 孙贤初. 安山岩连续纤维成型工艺的研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2008: 1-65.
Sun X C. Research on the continuous andesite fiber forming technics [D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2008: 1-65.
[16] 陈兴芬. 连续玄武岩纤维的高强度化研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018: 1-124.
Chen X F. Study on the high strength and performance of continuous basalt fiber[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2018: 1-124.
[17] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes [C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society Publication, 1989: 313-345.
[18] Pearce T H, Gorman B E, Birkett T C. The relationship between major element chemistry and tectonic environment of basic and intermediate volcanic rocks[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1977, 36(1): 121-132. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(77)90193-5
[19] Meschede M. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 56(3/4): 207-218.
[20] 汪云亮, 张成江, 修淑芝. 玄武岩类形成的大地构造环境的Th/ Hf-Ta/Hf图解判别[J]. 岩石学报, 2001, 17(3): 413-421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200103008.htm
Wang Y L, Zhang C J, Xiu S Z. Th/Hf-Ta/Hf identification of tectonic setting of basalts[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2001, 17(3): 413-421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200103008.htm
[21] Rudnick R L, Cao S. Composition of the continental crust[C]// Holland H D, Turekian K K. The Crust: Treatise on Geochemistry. Oxford: Elsevier, 2003: 1-64.
[22] 魏菊英, 王关玉. 同位素地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988: 1-166.
Wei J Y, Wang G Y. Isotopic geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1988: 1-166. (in Chinese)
[23] 李曙光. 蛇绿岩生成构造环境的Ba-Th-Nb-La判别图[J]. 岩石学报, 1993, 9(2): 146-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199302004.htm
Li S G. Ba-Nb-Th-La diagrams used to identify tectonic environments of ophiolite[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1993, 9(2): 146-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199302004.htm
[24] 朱弟成, 莫宣学, 王立全, 等. 新特提斯演化的热点与洋脊相互作用: 西藏南部晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆作用推论[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(2): 225-237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200802006.htm
Zhu D C, Mo X X, Wang L Q, et al. Hotspot-ridge interaction for the evolution of Neo-Tethys: Insights from the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous magmatism in southern Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(2): 255-237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200802006.htm
[25] Li J, Zhong H, Zhu W G, et al. Elemental and Sr-Nd isotopic geochemistry of Permian Emeishan flood basalts in Zhaotong, Yunnan Province, SW China[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2017, 106(2): 617-630.
[26] Qi L, Zhou M F. Platinum-group elemental and Sr-Nd-Os isotopic geochemistry of Permian Emeishan flood basalts in Guizhou Province, SW China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 248(1/2): 83-103.
[27] Fan W M, Zhang C H, Wang Y J, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Permian basalts in western Guangxi Province, Southwest China: Evidence for plume-lithosphere interaction[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102(1/2): 218-236.
[28] 肖龙, 徐义刚, 梅厚钧, 等. 云南金平晚二叠纪玄武岩特征及其与峨眉地幔柱关系——地球化学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 19(1): 38-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200301004.htm
Xiao L, Xu Y G, Mei H J, et al. Late Permian flood basalts at Jinping area and its relation to Emei mantle plume: Geochemical evidences[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2003, 19(1): 38-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200301004.htm
[29] 肖龙, 徐义刚, 何斌. 峨眉地幔柱-岩石圈的相互作用: 来自低钛和高钛玄武岩的Sr-Nd和O同位素证据[J]. 高校地质学报, 2003, 9(2): 207-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200302005.htm
Xiao L, Xu Y G, He B. Emei mantle plume-subcontinental lithosphere interaction: Sr-Nd and O isotopic evidences from low-Ti and high-Ti basalts[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2003, 9(2): 207-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200302005.htm
[30] 鄢圣武, 白宪洲, 秦宇龙, 等. 四川昭觉-美姑地区峨眉山玄武岩古火山机构的发现及其喷发旋回的确定[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48 (2): 536-548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202102014.htm
Yan S W, Bai X Z, Qin Y L, et al. Discovery of paleo-volcanic edifice and determination of its eruptive circles of Emeishan basalt in Zhaojue-Meigu area, Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(2): 536-548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202102014.htm
-




 下载:
下载: