GEOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SANDSTONE FROM HOUSHIGOU FORMATION IN SOUTHERN SANJIANG BASIN: Geological Implication
-
摘要:
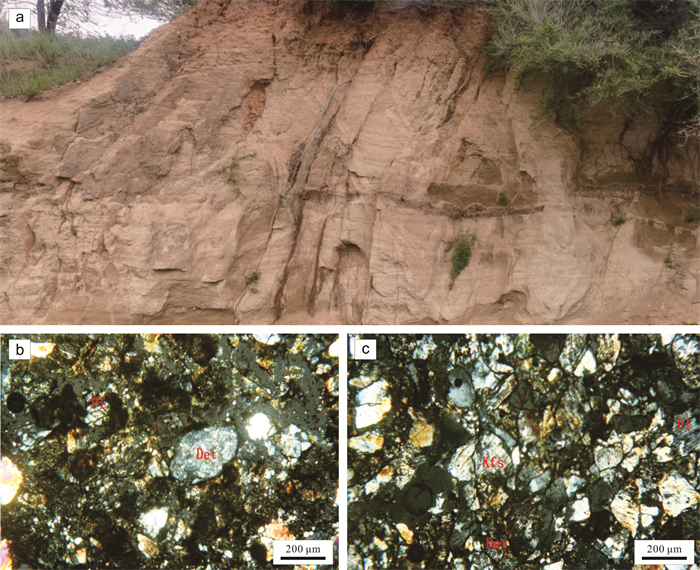
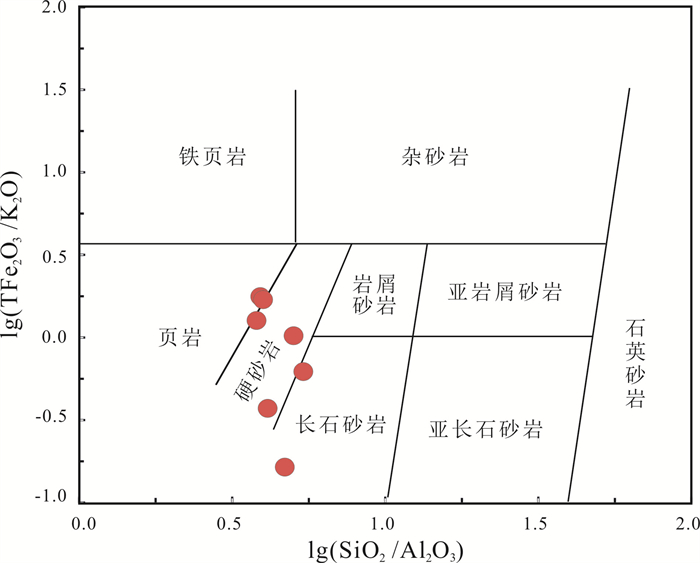
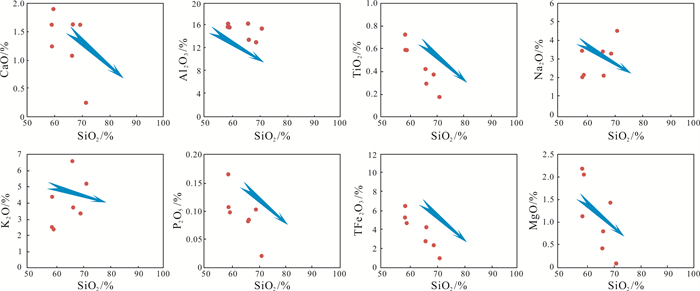
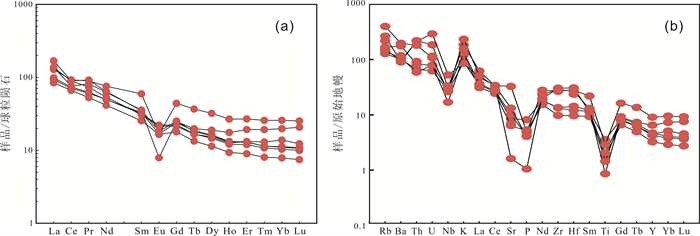
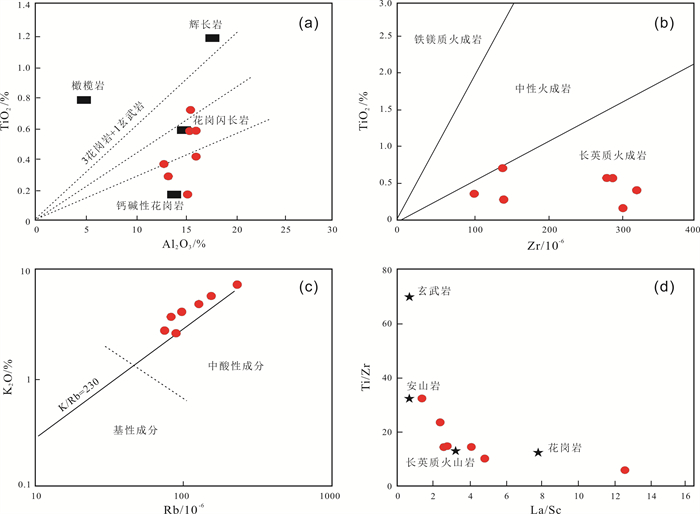
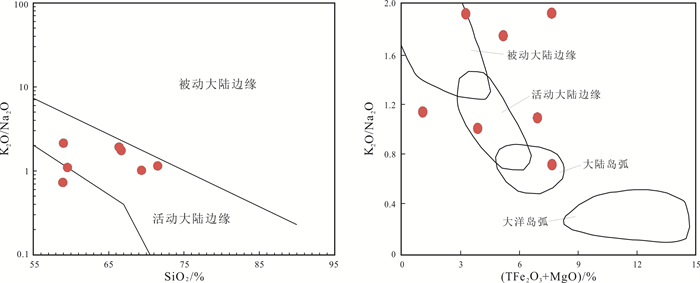
三江盆地白垩系猴石沟组是主要的铀矿含矿层,发育大面积灰色、浅黄色含砾中-细砂岩. 本文以松木河凹陷猴石沟组砂岩为研究对象,通过详细的岩石学、地球化学等特征探讨了猴石沟组的物源区成分、源区风化强度及构造背景. 结果表明,猴石沟组砂岩以长石和岩屑砂岩为主,主量元素SiO2含量在58.91%~71.51%之间,全碱含量4.59%~10.05%,铝含量12.87%~16.12%. 稀土元素总量100.72×10-6~171.34×10-6,平均为134.532×10-6,Eu负异常相对明显(δEu=0.27~0.84),说明岩石来源于上地壳. 元素地球化学特征表明,猴石沟组砂岩CIA=13.13~45.25,ICV=0.74~1.02,PIA=53.08~67.90,整体说明猴石沟组沉积时期为干旱-半干旱环境,源区经历了弱风化作用. Sr/Ba大多数小于1,相当B含量大多数亦小于200×10-6,SiO2/Al2O3平均为4.35,表明猴石沟组沉积时期为低盐度环境. 砂岩具有活动大陆边缘地球化学属性,结合区域演化史,认为其物源区应为佳木斯隆起地区发育的长英质岩石.
Abstract:The Cretaceous Houshigou Formation in Sanjiang Basin is the main ore-bearing layer of uranium deposit, developed with a large area of grey and light yellow gravel fine-medium sandstone. Taking the sandstone of Houshigou Formation in Songmuhe sag as the study object, the paper discusses the provenance composition, weathering intensity and tectonic setting of Houshigou Formation on the basis of detailed petrological and geochemical characteristics. The results show that the formation is mainly feldspar and lithic sandstone, with the major element SiO2 content of 58.91%-71.51%, total alkali content of 4.59%-10.05%, and Al content of 12.87%-16.12%. The total content of rare earth element (∑REE) is 100.72×10-6-171.34×10-6, averagely 134.532×10-6, with obvious negative Eu anomaly (δEu=0.27-0.84), indicating that the rock originates from the upper crust. The element geochemical characteristics reveal that CIA is 13.13-45.25, ICV 0.74-1.02 and PIA 53.08-67.90, indicating that the sedimentary period of Houshigou Formation was in arid-semi arid environment, and the source area experienced weak weathering. The Sr/Ba ratio is mostly less than 1, the equivalent B content mostly less than 200×10-6 and the SiO2/Al2O3 ratio averagely 4.35, indicating that the sedimentary period of Houshigou Formation was in low salinity environment. The sandstone has the geochemical properties of active continental margin. Combined with the regional evolution history, it is believed that the source area should be the felsic rock developed in Jiamusi uplift.
-
Key words:
- Houshigou Formation /
- uranium deposit /
- sandstone /
- geochemistry /
- Songmuhe sag /
- Sanjiang Basin
-

-
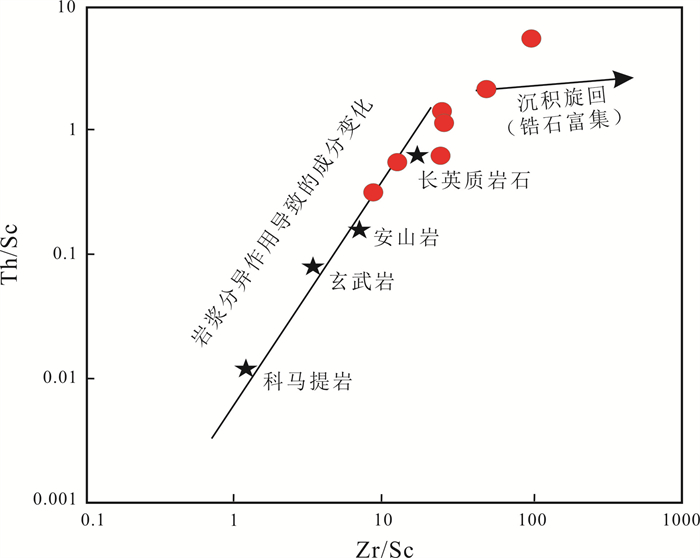
图 6 松木河凹陷猴石沟组砂岩Th/Sc-Zr/Sc图解(据文献[9])
Figure 6.
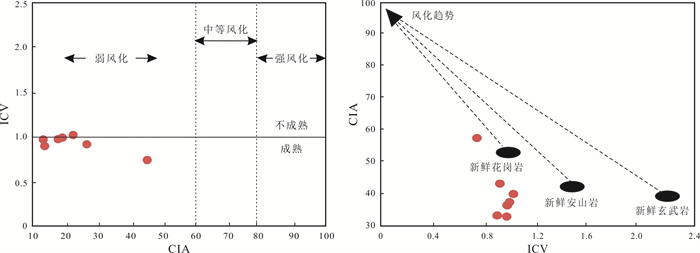
图 7 松木河凹陷猴石沟组砂岩CIA-ICV图解和ICV-CIA图解(据文献[12])
Figure 7.
-
[1] 高福红, 王枫, 曹花花, 等. 三江盆地绥滨断陷基底花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年代学及其构造意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2010, 40(4): 955-960. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201004029.htm
Gao F H, Wang F, Cao H H, et al. Zircon U-Pb age of the basement granite from Suibin depression in Sanjiang Basin and its tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2010, 40(4): 955-960. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201004029.htm
[2] 于介江, 张彦龙, 葛文春, 等. 三江盆地北缘晚白垩世花岗质岩石的年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(2): 369-385. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201302004.htm
Yu J J, Zhang Y L, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Late Cretaceous granitoids in the northern margin of the Sanjiang Basin, NE China and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(2): 369-385. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201302004.htm
[3] 冀华丽, 何中波, 卫三元, 等. 汤原断陷宝泉岭组微量元素地球化学特征及其对沉积环境的指示意义[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2022, 39(1): 27-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2022.01.003
Ji H L, He Z B, Wei S Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of trace elements and its sedimentary implication in Baoquanling Formation, Tangyuan fault depression[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2022, 39(1): 27-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2022.01.003
[4] 何中波, 冀华丽, 胡宝群, 等. 汤原断陷古近系宝泉岭组沉积特征及其对铀成矿作用的制约[J]. 矿产勘查, 2023, 14(3): 432-447. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS202303009.htm
He Z B, Ji H L, Hu B Q, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of Paleogene Baoquanling Formation in Tangyuan fault depression and its constraints on uranium mineralization[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2023, 14(3): 432-447. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS202303009.htm
[5] 何玉平, 刘招君, 董清水, 等. 依舒地堑汤原断陷古近系湖底扇沉积与层序特征[J]. 世界地质, 2006, 25(1): 23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2006.01.005
He Y P, Liu Z J, Dong Q S, et al. Sedimentary and sequence characteristics of Paleogene sublacustrine fan of Tangyuan fault depression in Yishu graben[J]. Global Geology, 2006, 25(1): 23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2006.01.005
[6] 何中波, 冀华丽, 卫三元, 等. 黑龙江省三江盆地砂岩型铀矿找矿方向探讨[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2021, 51(2): 367-379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202102006.htm
He Z B, Ji H L, Wei S Y, et al. Discussion on prospecting direction of sandstone-type uranium deposits in Sanjiang Basin, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2021, 51(2): 367-379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202102006.htm
[7] 杨君, 王善博, 刘飞. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘环县地区直罗组沉积相及其与铀矿化的关系[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(17): 64-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.17.008
Yang J, Wang S B, Liu F. Sedimentary facies of the Zhiluo Formation and its relationship with uranium mineralization in the Huanxian area, west of Ordos Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(17): 64-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.17.008
[8] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42: 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[9] McLennan S M, Hemming S, McDaniel D K, et al. Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics[C]//Johnson M J, Basu A. Processes Controlling the Composition of Clastic Sediments Boulder, Colorado: Geological Society of America, 1993, 284: 21-40.
[10] 陶瑞, 海连富, 王磊, 等. 宁夏灵武侏罗系直罗组碎屑岩地球化学特征及源区构造背景分析[J]. 中国地质, 2023, 50(6): 1817-1836. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202306016.htm
Tao R, Hai L F, Wang L, et al. Geochemical characteristics of clastic rocks from the Jurassic Zhiluo Formation in Lingwu, Ningxia and analysis of tectonic background of the source area[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(6): 1817-1836. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202306016.htm
[11] 付振柯, 王晓龙, 饶松, 等. 川西坳陷须三段致密砂岩优质储层特征及控制因素[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(1): 298-310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202201019.htm
Fu Z K, Wang X L, Rao S, et al. The characteristics and main controlling factors of high quality tight sandstone reservoir in the 3th member of Xujiahe Formation in West Sichuan Depression[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(1): 298-310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202201019.htm
[12] Cox R, Lowe D R, Cullers R L. The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(14): 2919-2940. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00185-9
[13] Schieber J. A combined petrographical-geochemical provenance study of the Newland Formation, Mid-Proterozoic of Montana[J]. Geological Magazine, 1992, 129(2): 223-237. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800008293
[14] Hayashi K I, Fujisawa H, Holland H D, et al. Geochemistry of~1.9 Ga sedimentary rocks from northeastern Labrador, Canada[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(19): 4115-4137. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00214-7
[15] Floyd P A, Leveridge B E. Tectonic environment of the Devonian Gramscatho Basin, South Cornwall: Framework mode and geochemical evidence from turbiditic sandstones[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1987, 144(4): 531-542. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.144.4.0531
[16] Bhatia M R, Crook K A W. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1986, 92(2): 181-193. doi: 10.1007/BF00375292
[17] 刘桂香, 赵广江, 李永胜. 佳木斯地块西缘太平沟地区蛇绿岩的发现及其构造意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2012, 21(1): 51-58. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract9012.shtml
Liu G X, Zhao G J, Li Y S. Discover of the ophiolite in Taipinggou area on the western margin of Jiamusi massif: Tectonic implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2012, 21(1): 51-58. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract9012.shtml
[18] 张兴洲, 马志红. 黑龙江东部中-新生代盆地演化[J]. 地质与资源, 2010, 19(3): 191-196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2010.03.001
Zhang X Z, Ma Z H. Evolution of Mesozoic-Cenozoic basins in the eastern Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China[J]. Geology and Resources, 2010, 19(3): 191-196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2010.03.001
[19] 赵立国, 王磊, 李娟娟, 等. 佳木斯地块中部兴东岩群大盘道岩组U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 地质与资源, 2015, 24(6): 532-538. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2015.06.004
Zhao L G, Wang L, Li J J, et al. Geochronological evidence of U-Pb for the Dapandao rock Formation of Xingdong Group in Jiamusi Block[J]. Geology and Resources, 2015, 24(6): 532-538. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2015.06.004
[20] 赵亮亮, 徐福忠, 张岩, 等. 牡丹江地区黑龙江杂岩锆石U-Pb年代学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(4): 405-413. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10310.shtml
Zhao L L, Xu F Z, Zhang Y, et al. Zircon U-Pb chronology of the Heilongjiang complex in Mudanjiang area: Geological implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(4): 405-413. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10310.shtml
[21] 赵立国, 王建民, 王磊, 等. 黑龙江省东部依兰地区金沟花岗岩的锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2016, 25(5): 436-442. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2016.05.003
Zhao L G, Wang J M, Wang L, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating and geological implication of the Jingou granite in Yilan area, eastern Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2016, 25(5): 436-442. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2016.05.003
[22] 王五力, 李永飞, 郭胜哲. 中国东北地块群及其构造演化[J]. 地质与资源, 2014, 23(1): 4-24. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8797.shtml
Wang W L, Li Y F, Guo S Z. The Northeast China block group and its tectonic evolution[J]. Geology and Resources, 2014, 23(1): 4-24. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8797.shtml
-



 下载:
下载: