MULTIPLE WATER QUALITY ASSESSMENT METHODS BASED ON PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS: A Case Study of Shallow Groundwater in the Middle Reaches of Yitong River
-
摘要:
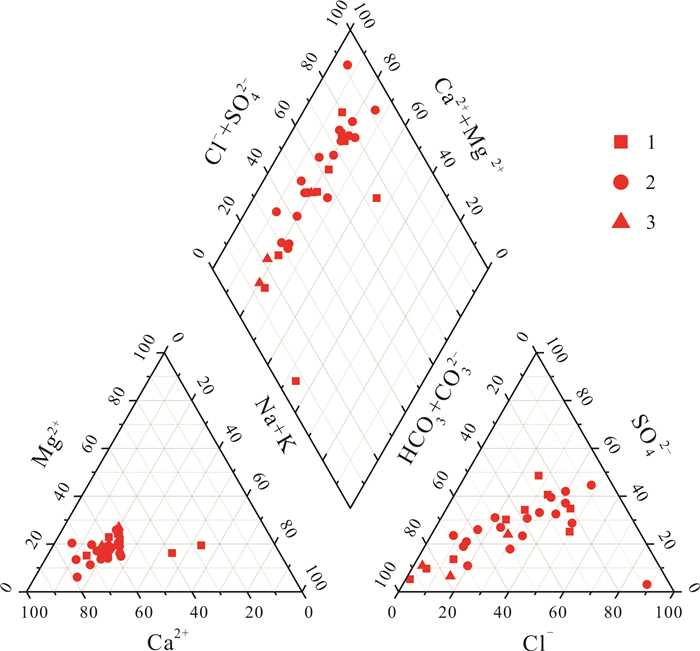
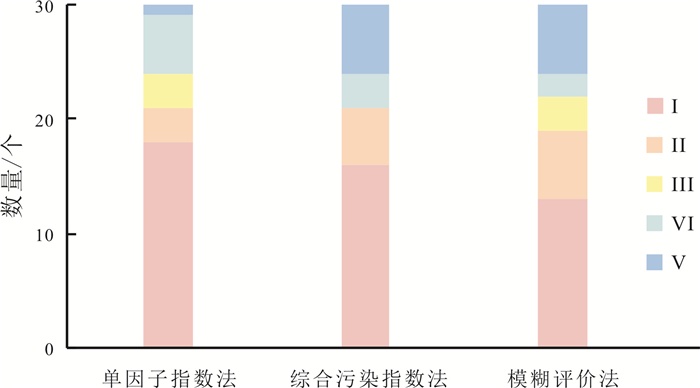
伊通河中游地区浅层地下水水质退化日趋严重, 开展水质现状调查对水资源保护及利用具有重要意义. 针对目前多种水质评价方法, 选择适当的水质评价模型是研究地下水质量现状的重中之重. 按地貌类型分别采集低山丘陵区、波状台地、阶地及河漫滩区水质样品共计30件, 运用舒卡列夫分类法、Piper三线图等相关统计分析法对地下水水化学特征进行了分析. 利用主成分分析法初选评价指标, 降低数据维度, 得出水质评价的主要成分, 随后运用模糊评价法对地下水质量进行评价, 并与单项指标法、内梅罗综合指数法进行对比分析. 结果显示, 研究区水质整体较差, 以Ⅴ类水为主, 仅低山丘陵区水质较好; 选取的多种评价方法中, 模糊综合评价考虑了评价因子之间的相互作用, 反映了水质的整体程度, 评价结果相对可靠, 可作为水质评价的首选评价方法.
Abstract:As the degradation of shallow groundwater quality in the middle reaches of Yitong River is becoming more and more serious, it is of great significance to investigate the current situation of water quality for protection and utilization of water resources. In view of the various water quality assessment methods at present, selecting an appropriate assessment model is of primary importance to study the status of groundwater quality. A total of 30 water quality samples are collected from low hilly area, undulating platform, terrace and flood plain in terms of geomorphologic types, and the hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater are analyzed by relevant statistical analysis such as Schukalev classification and Piper diagram. Principal component analysis(PCA) is used for the preliminary selection of assessment indexes, reducing the data dimension and getting the main components of water quality assessment. Then fuzzy evaluation method is used to assess groundwater quality, and compared with single index method and Nemerow comprehensive index method. The results show that the water quality in the study area is generally poor, dominated by Class V water quality, with good quality only in the low hilly areas. Among the various selected assessment methods, fuzzy comprehensive evaluation considers the interaction between evaluation factors and reflects the overall water quality, with relatively reliable evaluation results, which can be used as the first choice for water quality assessment.
-

-
表 1 指标初始统计表
Table 1. Initial statistics of indexes
水化学指标 最大值 最小值 标准差 平均值 pH 8.49 6.33 0.48 7.60 TH 1222.49 95.41 246.92 392.92 TDS 1722.00 163.00 353.68 629.00 SO42- 225.00 12.10 57.70 90.42 Cl- 360.00 3.28 71.06 79.87 CODMn 1.92 0.12 0.38 0.67 Na+ 88.46 12.30 21.48 43.16 NO3- 174.32 0.02 35.87 35.90 含量单位: mg/L. 表 2 皮尔逊相关关系表
Table 2. Pearson correlation coefficient table
相关性 PH TH TDS SO42- Cl- CODMn Na+ NO3- pH 1 TH -0.278 1 TDS -0.324 0.983 1 SO42- -0.377 0.450 0.534 1 Cl- -0.364 0.897 0.907 0.343 1 CODMn -0.195 -0.016 -0.044 0.028 -0.014 1 Na+ -0.292 0.511 0.612 0.790 0.488 -0.052 1 NO3- -0.251 0.858 0.865 0.137 0.853 -0.102 0.263 1 表 3 特征值及方差贡献率
Table 3. Eigenvalues and variance contribution rates
成分 初始特征值 提取特征值 总计 方差贡献率/% 累积/% 总计 方差贡献率/% 累积/% 1 4.431 55.392 55.392 4.431 55.39 55.40 2 1.393 17.417 72.809 1.393 17.42 72.81 3 1.093 13.668 86.477 1.093 13.67 86.48 4 0.687 8.585 95.062 5 0.216 2.695 97.757 6 0.107 1.336 99.093 7 0.070 0.872 99.966 8 0.003 0.034 100.000 表 4 主成分荷载值矩阵
Table 4. Principal component load value matrix
指标 主成分 1 2 3 pH -0.451 -0.417 -0.421 TH 0.946 -0.211 0.040 TDS 0.982 -0.129 -0.015 SO42- 0.610 0.679 -0.270 Cl- 0.918 -0.238 0.116 CODMn -0.025 0.346 0.831 Na+ 0.689 0.524 -0.347 NO3- 0.823 -0.497 0.129 表 5 地下水质量单因子评价结果
Table 5. Single factor evaluation results of groundwater quality
水化学指标 水质类别 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ TH 4 9 6 8 3 TDS 6 6 15 3 0 SO42- 9 17 4 0 0 Cl- 12 16 1 0 1 CODMn 26 4 0 0 0 Na+ 30 0 0 0 0 NO3- 4 3 3 3 17 表 6 模糊评价综合隶属度
Table 6. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation results of membership grade
样品编号 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ 样品编号 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ SY01 0.997 0.003 0.000 0.000 0.000 SY16 0.180 0.126 0.151 0.543 0.000 SY02 0.129 0.145 0.000 0.000 0.725 SY17 0.611 0.388 0.000 0.000 0.000 SY03 0.046 0.041 0.173 0.031 0.708 SY18 0.562 0.370 0.068 0.000 0.000 SY04 0.280 0.457 0.263 0.000 0.000 SY19 0.025 0.076 0.093 0.005 0.801 SY05 0.092 0.100 0.115 0.000 0.692 SY20 0.143 0.068 0.064 0.000 0.725 SY06 0.380 0.430 0.190 0.000 0.000 SY21 0.033 0.071 0.096 0.032 0.768 SY07 0.043 0.047 0.084 0.053 0.773 SY22 0.055 0.064 0.101 0.001 0.779 SY08 0.058 0.064 0.095 0.000 0.783 SY23 0.880 0.120 0.000 0.000 0.000 SY09 0.143 0.299 0.499 0.054 0.004 SY24 0.083 0.116 0.025 0.000 0.776 SY10 1.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 SY25 0.602 0.381 0.017 0.000 0.000 SY11 0.067 0.116 0.094 0.000 0.723 SY26 0.068 0.151 0.101 0.000 0.680 SY12 0.058 0.029 0.147 0.116 0.649 SY27 0.207 0.022 0.000 0.517 0.254 SY13 0.091 0.068 0.506 0.334 0.000 SY28 0.017 0.000 0.000 0.046 0.937 SY14 0.033 0.087 0.122 0.006 0.753 SY29 0.092 0.085 0.160 0.014 0.650 SY15 0.110 0.062 0.101 0.002 0.726 SY30 0.244 0.000 0.716 0.040 0.000 表 7 地下水质量评价结果
Table 7. Assessment results of groundwater quality
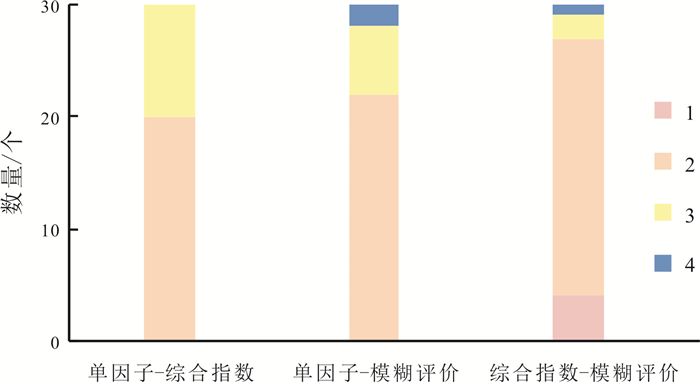
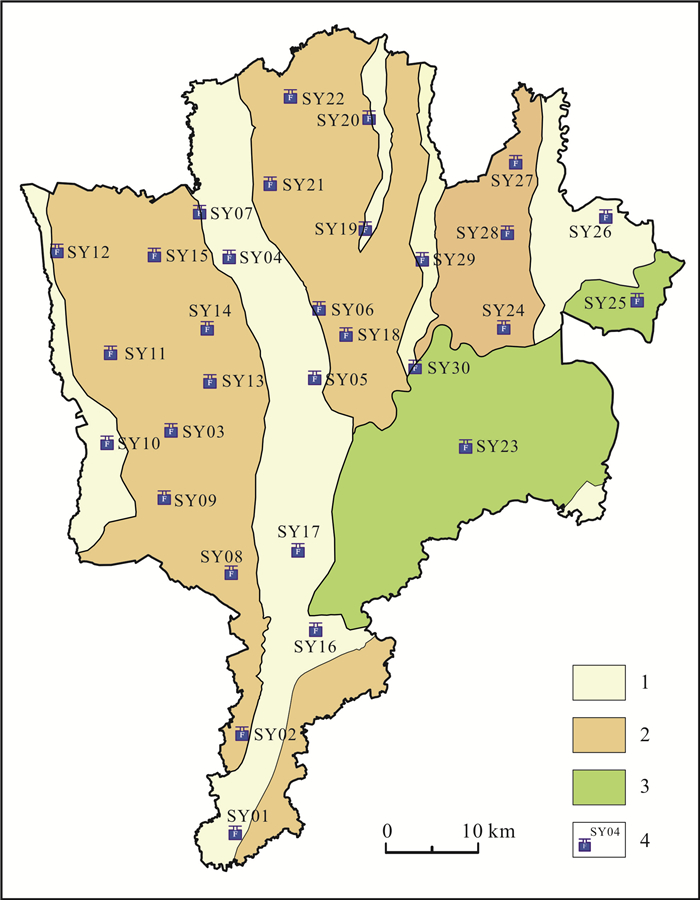
样品原号 类型 单因子等级 综合指数法 模糊评价法 F 评级 最大法等级 G 加权平均法等级 SY01 漫滩及阶地 II 0.713 Ⅰ Ⅰ 1.000 Ⅰ SY02 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.179 Ⅳ Ⅴ 4.769 Ⅴ SY03 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.463 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.861 Ⅴ SY04 漫滩及阶地 Ⅲ 2.236 Ⅱ Ⅱ 1.974 Ⅱ SY05 漫滩及阶地 Ⅴ 7.248 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.823 Ⅴ SY06 波状台地 Ⅱ 0.729 Ⅰ Ⅱ 1.703 Ⅱ SY07 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.492 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.949 Ⅴ SY08 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.248 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.930 Ⅴ SY09 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.289 Ⅴ Ⅲ 2.648 Ⅲ SY10 漫滩及阶地 Ⅰ 0.000 Ⅰ Ⅰ 1.000 Ⅰ SY11 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.248 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.861 Ⅴ SY12 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.616 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.841 Ⅴ SY13 波状台地 Ⅳ 4.472 Ⅳ Ⅲ 3.236 Ⅲ SY14 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.311 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.904 Ⅴ SY15 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.289 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.855 Ⅴ SY16 漫滩及阶地 Ⅳ 4.317 Ⅳ Ⅳ 3.584 Ⅳ SY17 漫滩及阶地 Ⅱ 0.791 Ⅰ Ⅰ 1.287 Ⅰ SY18 波状台地 Ⅲ 2.167 Ⅱ Ⅰ 1.320 Ⅰ SY19 漫滩及阶地 Ⅴ 7.311 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.944 Ⅴ SY20 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.248 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.812 Ⅴ SY21 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.408 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.936 Ⅴ SY22 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.311 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.928 Ⅴ SY23 低山丘陵 Ⅱ 0.755 Ⅰ Ⅰ 1.018 Ⅰ SY24 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.179 Ⅳ Ⅴ 4.888 Ⅴ SY25 低山丘陵 Ⅱ 0.713 Ⅰ Ⅰ 1.287 Ⅰ SY26 漫滩及阶地 Ⅴ 7.382 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.785 Ⅴ SY27 波状台地 Ⅳ 4.301 Ⅳ Ⅳ 3.827 Ⅳ SY28 波状台地 Ⅴ 7.754 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.996 Ⅴ SY29 漫滩及阶地 Ⅴ 7.311 Ⅴ Ⅴ 4.771 Ⅴ SY30 低山丘陵 Ⅲ 2.138 Ⅱ Ⅲ 2.795 Ⅲ -
[1] 王维, 纪枚, 苏亚楠. 水质评价研究进展及水质评价方法综述[J]. 科技情报开发与经济, 2012, 22(13): 129-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6033.2012.13.056
Wang W, Ji M, Su Y N. Reviews of the progress in the research of water quality evaluation and the methods for water quality evaluation[J]. Sci-Tech Information Development & Economy, 2012, 22(13): 129-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6033.2012.13.056
[2] 郭彤, 张永祥, 贾瑞涛. 多重水质评价方法在地下水水质评价中的对比研究——以北京市朝阳区为例[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2022, 12(6): 2020-2026.
Guo T, Zhang Y X, Jia R T. Comparative study of multiple water quality assessment methods in groundwater quality assessment: Taking Chaoyang District of Beijing as an example[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2022, 12(6): 2020-2026.
[3] Nemerow N L. Scientific stream pollution analysis[M]. New York: McGraw Hill, 1974.
[4] 郑志国, 张秀敏, 岳超, 等. 模糊数学法在水质评价中的应用[J]. 治淮, 2016(1): 88-89.
Zheng Z G, Zhang X M, Yue C, et al. Application of fuzzy mathematics in water quality evaluation[J]. Harnessing the Huaihe River, 2016 (1): 88-89. (in Chinese)
[5] 李霄, 柴璐, 王晓光, 等. 基于层次分析法的丹东地区地下水污染防治区划[J]. 地质与资源, 2018, 27(4): 396-405. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2018.04.012
Li X, Chai L, Wang X G, et al. Regionalization of groundwater pollution prevention in Dandong area based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Geology and Resources, 2018, 27(4): 396-405. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2018.04.012
[6] 孔庆轩, 董宏志, 王燕, 等. 哈尔滨地区浅层地下水质量与污染评价[J]. 地质与资源, 2015, 24(1): 70-74. http://www.dzyzy.cn/article/doi/10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2015.01.012
Kong Q X, Dong H Z, Wang Y, et al. Assessment for the quality and pollution of shallow groundwater in Harbin, Heilongjiang province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2015, 24(1): 70-74. http://www.dzyzy.cn/article/doi/10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2015.01.012
[7] 薛伟锋, 褚莹倩, 刘强, 等. 主成分分析和模糊综合评价法在大连市地下水水质评价中的应用研究[J]. 辽宁大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 47(3): 218-226.
Xue W F, Chu Y Q, Liu Q, et al. Groundwater quality assessment in Dalian based on principal component analysis and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Journal of Liaoning University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 47(3): 218-226.
[8] 郭新强. 基于主成分分析法的福建某滨海场地地下水水质评价[J]. 地下水, 2022, 44(6): 17-19.
Guo X Q. Evaluation on groundwater quality of a seashore field in Fujian Province based on principal component analysis[J]. Ground Water, 2022, 44(6): 17-19.
[9] 田福金, 马青山, 张明, 等. 基于主成分分析和熵权法的新安江流域水质评价[J]. 中国地质, 2023, 50(2): 495-505.
Tian F J, Ma Q S, Zhang M, et al. Evaluation of water quality in Xin'anjiang River Basin based on principal component analysis and entropy weight method[J]. Geology in China, 2023.50(2): 495-505.
[10] 张梅桂, 黄永明, 蔡贺. 松嫩平原地下水位动态影响因素分析[J]. 地质与资源, 2016, 25(6): 558-562. http://www.dzyzy.cn/article/doi/10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2016.06.008
Zhang M G, Huang Y M, Cai H. Analysis on the dynamic impacting factors for the groundwater table of Songnen Plain[J]. Geology and Resources, 2016, 25(6): 558-562. http://www.dzyzy.cn/article/doi/10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2016.06.008
[11] 杨威, 卢文喜, 卞玉梅, 等. 吉林西部地下水水质评价与分析[J]. 节水灌溉, 2008(2): 42-45.
Yang W, Lu W X, Bian Y M, et al. Groundwater quality evaluation and analyses in west Jilin Province[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2008 (2): 42-45.
[12] 王建伟, 高博, 佟智强, 等. 牡丹江市主城区第四系地下水主要离子特征与成因分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2023, 37(2): 399-405.
Wang J W, Gao B, Tong Z Q, et al. Characteristics and origin analysis of major ions in Quaternary groundwater at Mudanjiang City[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2023, 37(2): 399-405.
[13] 寇文杰. 基于EXCEL的地下水化学舒卡列夫分类方法[J]. 工程勘察, 2013, 41(5): 48-50, 96.
Kou W J. Groundwater chemical Shoka Lev classification method based on EXCEL[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2013, 41(5): 48-50, 96.
[14] 林卉, 李楠, 黄伯当, 等. 基于主成分分析的南流江水质评价[J]. 广东化工, 2020, 47(4): 144-146, 148.
Lin H, Li N, Huang B D, et al. Water quality evaluation of Nanliu River based on principal component analysis[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2020, 47(4): 144-146, 148.
[15] 张亚娟, 牛姗姗, 孙亚乔, 等. SPSS软件在渭河流域(陕西段)水质主成分分析评价中的运用[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(29): 14414-14416.
Zhang Y J, Niu S S, Sun Y Q, et al. Application of SPSS in the principal component analysis of water quality in Weihe River[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(29): 14414-14416.
[16] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 地下水质量标准: GB/T 14848—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration. Standard for groundwater quality: GB/T 14848-2017[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2017.
[17] 江峰, 刘汉武, 吉勤克补子, 等. 单因子水质标识指数法在贵州省洋水河流域地下水水质评价中的应用[J]. 四川地质学报, 2021, 41(1): 151-153, 176.
Jiang F, Liu H W, Ji Q, et al. The application of single factor water quality identification index method to the evaluation of groundwater quality in the Yangshuihe River basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2021, 41(1): 151-153, 176.
[18] 冯林娜. 基于内梅罗污染综合指数方法的克兰河水质评价研究[J]. 地下水, 2022, 44(1): 116-118.
Feng L N. Research on water quality evaluation of the Kelan River based on the Nemero pollution comprehensive index method[J]. Ground Water, 2022, 44(1): 116-118.
[19] 潘峰, 付强, 梁川. 模糊综合评价在水环境质量综合评价中的应用研究[J]. 环境工程, 2002, 20(2): 58-61.
Pan F, Fu Q, Liang C. Applying fuzzy synthesize judgement in the study of water environment quality evaluation[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2002, 20(2): 58-61.
[20] 杨志峰, 张玉先. 水源水质模糊评价中的综合赋权和折减系数赋权[J]. 给水排水, 2004, 30(4): 37-40.
Yang Z F, Zhang Y X. Indices combination and coefficient reduction in fuzzy assessment of raw water quality[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2004, 30(4): 37-40.
[21] 张进. 基于模糊综合指数法对丹江上游水质评价[J]. 陕西水利, 2022(7): 98-100, 106.
Zhang J. Evaluation of water quality in the upper reaches of Danjiang River based on fuzzy comprehensive index method[J]. Shaanxi Water Resources, 2022(7): 98-100, 106.
[22] 潘荦, 黄晓荣, 魏晓玥, 等. 三种常用水质评价方法的对比分析研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2019(6): 51-55.
Pan L, Huang X R, Wei X Y, et al. A comparative analysis of three common water quality evaluation methods[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2019(6): 51-55.
-



 下载:
下载: