RISK ANALYSIS OF WIND EROSION AND DESERTIFICATION IN BLACK LAND BASED ON ANALYTIC HIERARCHY PROCESS: A Case Study of Fuyu County, Heilongjiang Province
-
摘要:
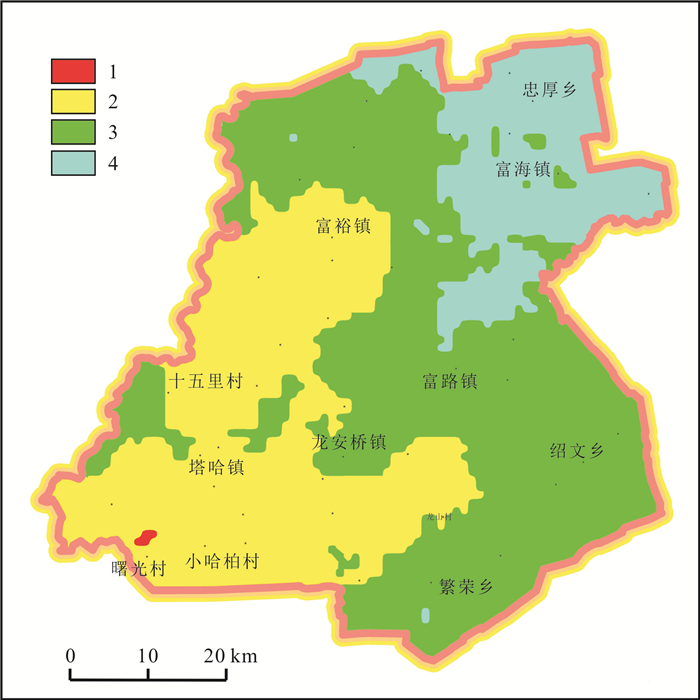
黑土地风蚀沙化危险性分析对黑土地沙化趋势具有一定预测意义, 可以服务下一步沙化灾害预防工作. 通过结合前人所作的风蚀危险性评价和土地沙化敏感性评价因子, 结合富裕县实际, 选出适合其风蚀沙化危险性评价的因子, 采用层次分析法计算各因子所占权重, 依托地表基质调查项目所得调查点位实验数据, 利用GIS平台计算功能, 得出富裕县风蚀沙化危险性的空间分布规律. 评价结果表明, 富裕县以危险型区和轻险型区为主, 总计占比达82.99%, 强险型区占比不到0.1%, 说明区内存在不同程度的风蚀沙化情况, 危险级别从东北向西南上升, 其治理紧迫性和难易程度从东北向西南升高. 本研究界定了风蚀沙化危险级别的界限, 可为土地沙化防治提供借鉴.
Abstract:The risk analysis of wind erosion and desertification in black land is significant for the prediction of desertification trend of black land and prevention of desertification disaster. Based on the previous wind erosion risk assessment and land desertification sensitivity assessment factors as well as the practice in Fuyu County, the study selects the factors suitable for the risk assessment and calculate the weights of each factor with analytic hierarchy process(AHP) method. Adopting the experimental data from the ground substrate survey project, the spatial distribution regularity of wind erosion and desertification risk in Fuyu County is obtained through the calculation function of GIS. The assessment results show that Fuyu County is dominated by risk area and light risk area, accounting for 82.99% of the total, and the high risk area less than 0.1%, indicating that there are varying degrees of wind erosion and desertification in the area, with the risk level rising from northeast to southwest, and the governance urgency and difficulty increasing from northeast to southwest. The study defines the risk level limits of wind erosion and desertification, which can provide references for desertification control and prevention.
-
Key words:
- black land /
- wind erosion /
- desertification /
- risk assessment /
- analytic hierarchy process(AHP) /
- Heilongjiang Province
-

-
表 1 风蚀沙化危险性影响因子权重判断矩阵
Table 1. Judgment matrix of impact factor weight for wind erosion and desertification risk
权重因子 黏粒含量 黑土层厚度 含水率 有机碳含量 NDVI 权重值 黏粒含量 1 1.5 2 3.56 2 0.3371 黑土层厚度 0.67 1 1.5 2.5 1.5 0.2382 含水率 0.5 0.67 1 1.75 1 0.1641 有机碳含量 0.28 0.4 0.57 1 0.5 0.092 NDVI 0.5 0.67 1 2 1 0.1687 表 2 富裕县风蚀沙化危险等级划分
Table 2. Degrees of wind erosion and desertification risk in Fuyu County
危险型 无险型 轻险型 危险型 强险型 危险性指数 R<0.5 0.5≤R<0.7 0.7≤R<0.9 R≥0.9 -
[1] 李丹丹, 陈明. "耕地中的大熊猫"——寒地黑土[N]. 中国矿业报, 2021-05-28(04).
Li D D, Chen M. Black soil in cold region[N]. China Mining News, 2021-05-28(04). (in Chinese)
[2] 马超. 黑龙江省黑土地保护性耕作实施基本情况及问题研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(17): 143-147. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0092
Ma C. Basic situation and problems of conservation tillage in black soil in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(17): 143-147. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0092
[3] 侯红星, 葛良胜, 孙肖, 等. 地表基质在中国黑土地资源调查评价中的应用探讨——基于黑龙江宝清地区地表基质调查[J]. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(9): 2264-2276.
Hou H X, Ge L S, Sun X, et al. A study on the application of ground substrate in the survey and evaluation of China's black soil resources: Based on ground substrate survey in Baoqing, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2022, 37(9): 2264-2276.
[4] 侯淑艳, 朱金兆, 刘建新, 等. 黑龙江省西部风蚀荒漠化特性与防治技术[J]. 水土保持研究, 2011, 18(2): 6-9.
Hou S Y, Zhu J Z, Liu X J, et al. The characteristics and control techniques of wind-induced desertification in the west of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 18(2): 6-9.
[5] 韩丽芳, 刘玲. 黑龙江省西部土地沙化的危害及防治措施[J]. 黑龙江科技信息, 2011(7): 70.
Han L F, Liu L. The harm and prevention measures of land desertification in the west of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Information, 2011(7): 70. (in Chinese)
[6] 李取生. 松嫩沙地历史演变的初步研究[J]. 科学通报, 1990, 35(11): 854-856.
Li Q S. A primary study on the historical change of Songnen sandy land[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1991, 36(6): 487-489.
[7] 李宜垠, 吕金福. 松嫩沙地晚更新世以来的孢粉记录及古植被古气候[J]. 中国沙漠, 1996, 16(4): 339-344.
Li Y G, Lv J F. The sporo-pollen records and vegetation and climate history in Songnen sandy land since Epipleistocene[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 1996, 16(4): 339-344.
[8] 李宝林. 松嫩沙地沙漠化的气候因素与沙地发育特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 1996, 16(3): 250-257.
Li B L. The climatic factors of desertification and the developed characteristic of Songnen sandy land[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 1996, 16(3): 250-257.
[9] 介冬梅, 吕金福. 松嫩沙地末次冰期以来降水量和干燥度的时空变化[J]. 地理科学, 1995, 15(4): 337-343.
Jie D M, Lv J F. The time-space change of precipitation and aridity degree of Songnen sand land since last glacial age[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 1995, 15(4): 337-343.
[10] 海春兴, 赵烨, 马礼. 中国北方农牧交错区夏季土壤风蚀研究——以河北丰宁县大滩乡二道河为例[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2002, 16(2): 6-9.
Hai C X, Zhao Y, Ma L. Studies on the wind erosion on farming-pastoral zone of northern China in summer[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2002, 16(2): 6-9.
[11] 何清, 杨兴华, 艾力·买买提明, 等. 塔中地区土壤风蚀的影响因子分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2010, 33(4): 502-508.
He Q, Yang X H, Ali M, et al. Impact factors of soil wind erosion in Tazhong area[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2010, 33(4): 502-508.
[12] 贾丹, 赵永军, 黄军荣, 等. 北京市大兴区风蚀危险度评价[J]. 水土保持通报, 2009, 29(6): 144-147.
Jia D, Zhao Y J, Huang J R, et al. Risk degree assessment of soil erosion by wind in Daxing District of Beijing City[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 29(6): 144-147.
[13] 于国茂, 刘越, 艳燕, 等. 2000~2008年内蒙古中部地区土壤风蚀危险度评价[J]. 地理科学, 2011, 31(12): 1493-1499.
Yu G M, Liu Y, Yan Y, et al. Soil wind erosion risk assessment in the middle part of Inner Mongolia Plateau during 2000 to 2008[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2011, 31(12): 1493-1499.
[14] 吴芳芳, 曹月娥, 卢刚, 等. 准东地区土壤风蚀影响因子分析与风蚀量估算[J]. 水土保持学报, 2016, 30(6): 56-60, 66.
Wu F F, Cao Y E, Lu G, et al. Impact factors of soil wind erosion and estimation of soil loss in Zhundong, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 30(6): 56-60, 66.
[15] 孙传龙, 张卓栋, 邱倩倩, 等. 基于层次分析法的锡林郭勒草地景观系统风蚀危险性分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2016, 39(05): 1036-1042.
Sun C L, Zhang Z D, Qiu Q Q, et al. AHP based wind erosion risk analysis of the Xilinguole grassland landscape system[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2016, 39(5): 1036-1042.
[16] 师华定, 梁海超, 齐永清, 等. 风蚀危险性评价研究综述[J]. 资源与产业, 2010, 12(5): 43-49.
Shi H D, Liang H C, Qi Y Q, et al. Study review of wind erosion hazard assessment[J]. Resources & Industries, 2010, 12(5): 43-49.
[17] 范建容, 刘淑珍, 钟祥浩, 等. 金沙江干热河谷土地荒漠化评价方法研究[J]. 地理科学, 2002, 22(2): 243-248.
Fan J R, Liu S Z, Zhong X H, et al. Evaluation method of land degradation/desertification[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2002, 22(2): 243-248.
[18] 刘光磊. 晋北地区土地沙化致灾孕育因子时空特征及危险性评价[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2014.
Liu G L. Spatio-temporal patterns and risk assessment of desertification disaster-pregnant factors in the northern Shanxi[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2014.
[19] 沈亚楠, 仇梦梦, 岳耀杰. 中国北方土地沙漠化灾害危险性评价[J]. 干旱区研究, 2017, 34(1): 174-184.
Shen Y N, Qiu M M, Yue Y J. Sandy desertification hazard assessment in North China[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2017, 34(1): 174-184.
[20] 王梅梅, 朱志玲, 吴咏梅. 宁夏中部干旱带土地沙漠化评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(2): 320-324.
Wang M M, Zhu Z L, Wu Y M. Assessment on the sensitivity to aeolian desertification and importance of controlling aeolian desertification in the middle arid region of Ningxia[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2013, 33(2): 320-324.
[21] 刘建宇, 聂洪峰, 宋保芳, 等. 内蒙古阴山北麓的风蚀沙化作用及其生态地质效应[J]. 中国地质, 2024, 51(3): 1020-1033.
Liu J Y, Nie H F, Song B F, et al. Wind erosion, land desertification and ecogeological effects in the northern piedmont of Yinshan Mountain in Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 2024, 51(3): 1020-1033.
[22] 周利军, 张淑花. 黑龙江省西南部土地沙漠化敏感性评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(21): 324-327.
Zhou L J, Zhang S H. Study on land desertification sensitivity evaluation in south-west Heilongjiang Provence[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 25(21): 324-327.
[23] 任利广, 马维伟, 李广, 等. 基于GIS的甘肃省农牧交错带土地沙化敏感性时空分布格局[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(6): 149-156.
Ren L G, Ma W W, Li G, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution pattern of land desertification sensitivity in agro pastoral ecotone of Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2022, 36(6): 149-156.
[24] 刘朝霞, 李钢铁, 李玉灵. 用聚类分析法进行毛乌素风蚀荒漠化强度分级──以乌审旗为例[J]. 内蒙古林学院学报(自然科学版), 1996, 18(1): 27-33.
Liu Z X, Li G T, Li Y L. Intensity grading of blow desertification with cluster analyse in the Mao Wu Shu: An example as Wu Sheng County[J]. Journal of Neimenggu Forestry College, 1996, 18(1): 27-33.
[25] 赵举. 阴山北麓农牧交错带风蚀荒漠化治理的保持耕作模式研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2002.
Zhao J. Study on conservative tillage models for controlling wind erosion at transition zone between agriculture and pasture areas in the north foot region of Yinshan Mountain[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2002.
[26] 王涛, 陈广庭, 钱正安, 等. 中国北方沙尘暴现状及对策[J]. 中国沙漠, 2001, 21(4): 322-327.
Wang T, Chen G T, Qian Z A, et al. Situation of sand-dust storms and countermeasures in North China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2001, 21(4): 322-327.
[27] 戴全厚, 喻理飞, 刘明义, 等. 吉林省西部沙地土壤风蚀机理分析[J]. 水土保持通报, 2008, 28(3): 81-84, 96.
Dai Q H, Yu L F, Liu M Y, et al. Mechanism of soil erosion by wind on sandy land in West Jilin Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 28(3): 81-84, 96.
[28] 田耀武, 黄志霖, 肖文发, 等. 三峡库区兰陵溪流域森林土壤有机碳、有机质与容重间的回归模型[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2016, 37(1): 89-95.
Tian Y W, Huang Z L, Xiao W F, et al. Organic carbon, organic matter and bulk density regression models for forest soils in Lanlingxi watershed, Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2016, 37(1): 89-95.
[29] 梁海超, 师华定, 白中科, 等. 中国北方典型农牧交错区的土壤风蚀危险度研究[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2010, 12(4): 510-516
Liang H C, Shi H D, Bai Z K, et al. Assessment of wind erosion hazard degree in typical farming-pastoral ecotone of northern China[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2010, 12(4): 510-516.
-



 下载:
下载: