ISOTOPIC CHARACTERISTICS OF HOT SPRINGS AND GENESIS OF GEOTHERMAL FIELD IN LUSHAN COUNTY, HENAN PROVINCE
-
摘要:
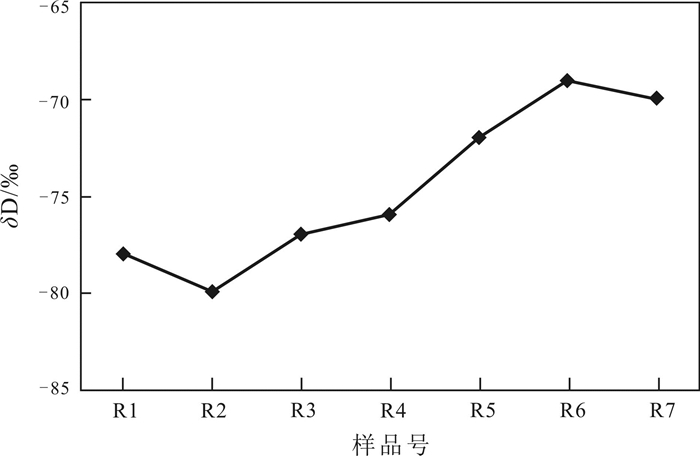
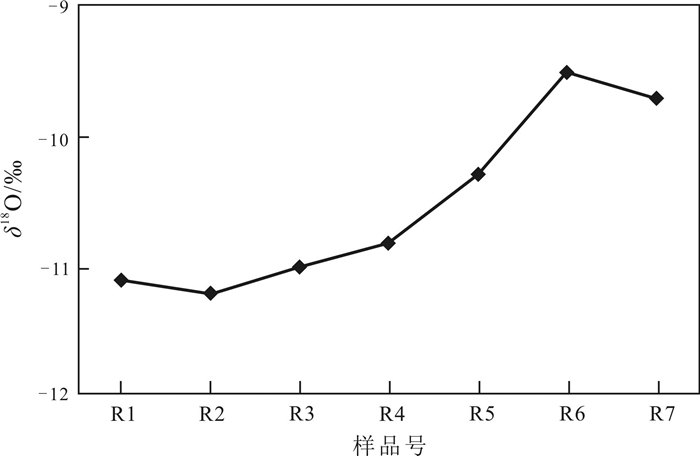
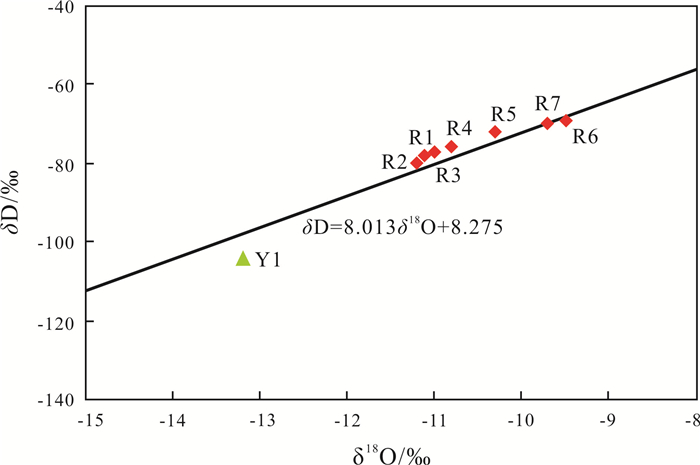
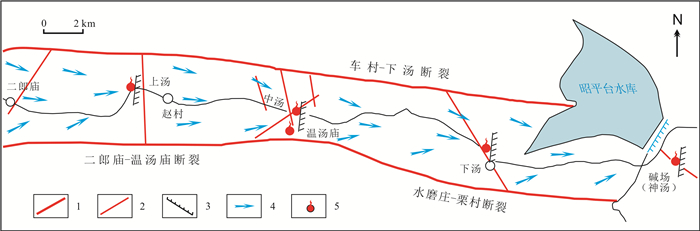
通过对河南省鲁山县五大温泉同位素测试结果的对比, 分析其基本特征, 研究地热田成因, 目的在于进一步查明地热资源条件, 合理开发利用. 从上游到下游, 地热流体氢氧稳定同位素δD、δ18O值总体上呈逐渐增大的趋势. 利用氢氧稳定同位素的组成变化判断地热流体的补给来源于大气降水, 利用其高程效应估算的补给高程为1 070~1 440 m, 补给源区为鲁山县西部至嵩县东南部的山区. 其中1个样品放射性同位素T为1.4±0.8 TU, 另外6个样品均小于1.0 TU, 表明地热流体是1952年以前“古水”成分占优势. 放射性同位素14C结果, 样品R3现代碳百分数为13.00±1.18%, 样品R7为29.68±0.97%, 表明R7混入了部分现代碳. 利用R3现代碳百分数计算地热流体的生成年龄为12.12~15.52 ka.
Abstract:Based on the comparison of isotope test results of five hot springs in Lushan County of Henan Province, the basic characteristics and genesis of geothermal field are analyzed for further identifying the conditions of geothermal resources, as well as rational development and utilization. The δD and δ18O values of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes of the geothermal fluid from upper to lower reaches are gradually increasing generally. Based on the composition change of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes, it is concluded that the recharge source of geothermal fluid comes from atmospheric precipitation, and the recharge elevation is 1 070-1 440 m estimated by elevation effect, with the recharge source area ranging from western Lushan County to the mountainous area of southeastern Songxian County. The value of radioisotope T in one of the samples is 1.4±0.8 TU, while that of other six samples are all less than 1.0 TU, indicating that the geothermal fluid is dominated by composition of fossil water before 1952. The radioisotope 14C age analysis results show that the modern carbon in sample R3 accounts for 13.00±1.18% and that in sample R7 29.68±0.97%, reflecting that sample R7 is mixed with partial modern carbon. The generation age of geothermal fluid is 12.12-15.52 ka calculated by the percentage of modern carbon in sample R3.
-
Key words:
- hot spring /
- geothermal field /
- hydrogen and oxygen isotope /
- Henan Province
-

-
表 1 地热流体及雨水样品同位素测试结果
Table 1. Isotopic test results of geothermal fluid and rainwater samples
样品号 采样地点 δDV-SMOW/‰ δ18OV-SMOW/‰ T/TU 现代碳百分数
(pmc)/%R1 上汤 -78 -11.1 <1.0 R2 赵村 -80 -11.2 <1.0 R3 中汤 -77 -11.0 <1.0 13.00±1.18 R4 温汤 -76 -10.8 <1.0 R5 下汤 -72 -10.3 <1.0 R6 碱场 -69 -9.5 1.4±0.8 R7 薛寨 -70 -9.7 <1.0 29.68±0.97 Y1 尧山镇铁匠炉村 -104 -13.2 8.1±0.8 表 2 补给高程计算结果
Table 2. Calculation results of recharge elevation
样品号 采样地点 样点高程/m δD计算补给高程/m δ18O计算补给高程/m R1 上汤 272 1139 1185 R2 赵村 270 1070 1139 R3 中汤 221 1121 1178 R4 温汤 220 1153 1263 R5 下汤 179 1246 1440 R6 碱场 149 1316 1671 R7 薛寨 135 1268 1570 表 3 14C校正年龄计算结果
Table 3. Calculation results of 14C correction age
样品号 采样地点 统计学校正 化学稀释模型校正 推荐年龄/ka AT/% 校正年龄/ka pH值 H+浓度/(mmol/L) HCO3-含量/(mg/L) b/(mmol/L) a/(mmol/L) AT/% 校正年龄/ka R3 中汤 85 15.52 7.24 5.75E-08 209.0 3.43 0.495 56.31 12.12 12.12~15.52 R7 薛寨 85 8.70 7.40 3.98E-08 190.1 3.12 0.312 54.55 5.03 5.03~8.70 -
[1] 刘虹, 张国平, 金志升, 等. 云南腾冲地区地热流体的地球化学特征[J]. 矿物学报, 2009, 29(4): 496-501. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2009.04.014
Liu H, Zhang G P, Jin Z S, et al. Geochemical characteristics of geothermal fluid in Tengchong area, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2009, 29(4): 496-501. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2009.04.014
[2] 信永水. 北京小汤山地热田成因的探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 1989, 13(8): 473-476.
Xin Y S. A preliminary discussion on the genesis of the Xiaotangshan geothermal field in Beijing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemicai Exploration, 1989, 13(8): 473-476. (in Chinese)
[3] 闫佰忠. 长白山玄武岩区地热水资源成因机制研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016.
Yan B Z. Study on the formation mechanism of geothermal water resources in Changbai Mountain basalt area[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016.
[4] 邹鹏飞, 邱杨, 王彩会. 南京汤山温泉区地热水成因模式分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2015, 21(1): 155-162.
Zou P F, Qiu Y, Wang C H. Analyses of the genesis of Tangshan hot spring area in Nanjing[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2015, 21(1): 155-162.
[5] 尚军. 黄山温泉地质、物探与激活[J]. 安徽地质, 2015, 25(3): 201-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6157.2015.03.010
Shang J. Geology, geophysical survey and reactivation of hot springs in the Huang Mountain[J]. Geology of Anhui, 2015, 25(3): 201-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6157.2015.03.010
[6] 温煜华, 王乃昂, 朱锡芬, 等. 甘肃武山地热田水化学与地热水起源[J]. 自然资源学报, 2010, 25(7): 1186-1193.
Wan Y H, Wang N A, Zhu X F, et al. Hydrochemistry and origin of the Wushan geothermal field, Gansu[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2010, 25(7): 1186-1193.
[7] 姜哲, 周训, 陈柄桦, 等. 四川康定市二道桥地区地下热水稳定同位素特征及热储温度计算[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(4): 1183-1192.
Jiang Z, Zhou X, Chen B H, et al. Stable isotope characteristics of geothermal water and calculation of geothermal reservoir temperature in the Erdaoqiao area of Kangding in Sichuan Province[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(4): 1183-1192.
[8] 吕志涛, 罗文金, 陈少茹, 等. 河南省五大温泉成因研究及综合开发利用规划[J]. 地下水, 2006, 28(4): 42-44, 51.
Lv Z T, Luo W J, Chen S R, et al. Study on formation causes and plan of comprehensive exploitation and utilization of five hot springs in Henan Province[J]. Ground Water, 2006, 28(4): 42-44, 51.
[9] 黄光寿, 郭丽丽, 黄凯. 河南省十大温泉地热地质特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(1): 91-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.01.012
Huang G S, Guo L L, Huang K. Geothermal geological characteristics of ten hot springs in Henan Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(1): 91-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.01.012
[10] 李秀丽. 鲁山县碱厂地热田地热资源特征及开发利用潜力研究[J]. 地下水, 2022, 44(3): 37-40.
Li X L. Study on geothermal resource characteristics and development and utilization potential of alkaline plant geothermal field in Lushan County[J]. Ground Water, 2022, 44(3): 37-40.
[11] 师刚强. 浅析地球化学理论及方法在地热水资源开发中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(S1): 401-404.
Shi G Q. Analysis of the application of geochemical theory and methods in the development of geothermal water resources[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2012, 27(S1): 401-404. (in Chinese)
[12] 卞跃跃, 赵丹. 四川康定地热田地下热水成因研究[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(4): 491-497.
Bian Y Y, Zhao D. Genesis of geothermal waters in the Kangding geothermal field, Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(4): 491-497.
[13] 张凌鹏, 丁宏伟, 张家峰, 等. 甘肃省地热流体化学及环境同位素特征和形成年龄分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(6): 1496-1504.
Zhang L P, Ding H W, Zhang J F, et al. Hydrochemistry and environmental isotopic characteristics and formation ages analysis of geothermal fluids in Gansu Province[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2020, 43(6): 1496-1504.
[14] 张天增, 刘运涛, 赵海军, 等. 驻马店市地热流体年龄研究[J]. 西部资源, 2013(3): 155-158.
Zhang T Z, Liu Y T, Zhao H J, et al. A study on the geothermal fluid age of Zhumadian City[J]. Western Resources, 2013(3): 155-158.
[15] 高正夏, 刘亚钦, 曹岩. 深圳抽水蓄能电站厂房区地下水环境同位素分析[J]. 勘察科学技术, 2009(3): 35-38.
Gao Z X, Liu Y Q, Cao Y. Analysis of groundwater environment isotopes in powerhouse area of Shenzhen pumped-storage power station[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology, 2009(3): 35-38.
[16] 王现国, 张慧, 张娟娟. 开封凹陷区地热水水化学特征及同位素分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2012, 19(6): 88-92.
Wang X G, Zhang H, Zhang J J. Analysis on the hydrochemical characteristics and isotope of geothermal water in Kaifeng depression[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2012, 19(6): 88-92.
[17] 赵振华. 某低、中放废物处置预选区地下水系统特征及水循环模式研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2017: 67-68.
Zhao Z H. The study of groundwater system characteristics and circulation model in a certain potential area for low-intermediate level radioactive waste disposal[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2017: 67-68.
[18] 王茜. 河南鲁山县五大温泉水文地球化学特征及成因模式[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2012: 42-43.
Wang X. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation mode of the five thermal springs in Lushan County, Henan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2012: 42-43.
[19] 刘存富. 地下水14C年龄校正方法——以河北平原为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1990, 17(5): 4-8.
Liu C F. Correction methods of 14C ages of groundwater: With the Hebei Plain as example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1990, 17(5): 4-8.
[20] 周称称, 杨博, 王丹. 河南省驻马店-遂平地热田地球化学特征及指示意义[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2021, 39(8): 69-72.
Zhou C C, Yang B, Wang D. Geochemical characteristics and indicative significance of Zhumadian-Suiping geothermal field in Henan Province[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2021, 39(8): 69-72.
[21] 曹自豪, 张建超. 鲁山县地热田地球化学特征及冷水混入研究[J]. 冶金管理, 2022(20): 109-112.
Cao Z H, Zhang J C. Study on the geochemical characteristics of geothermal fields and cold water mixing in Lushan County[J]. China Steel Focus, 2022(20): 109-112. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: