Study on Flotation Behaviors of the Frothers with Similar Formation in the Flotation of Sulfide Ores
-
摘要:
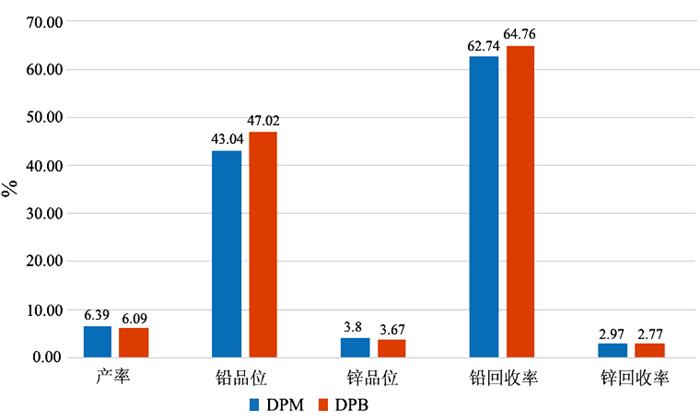
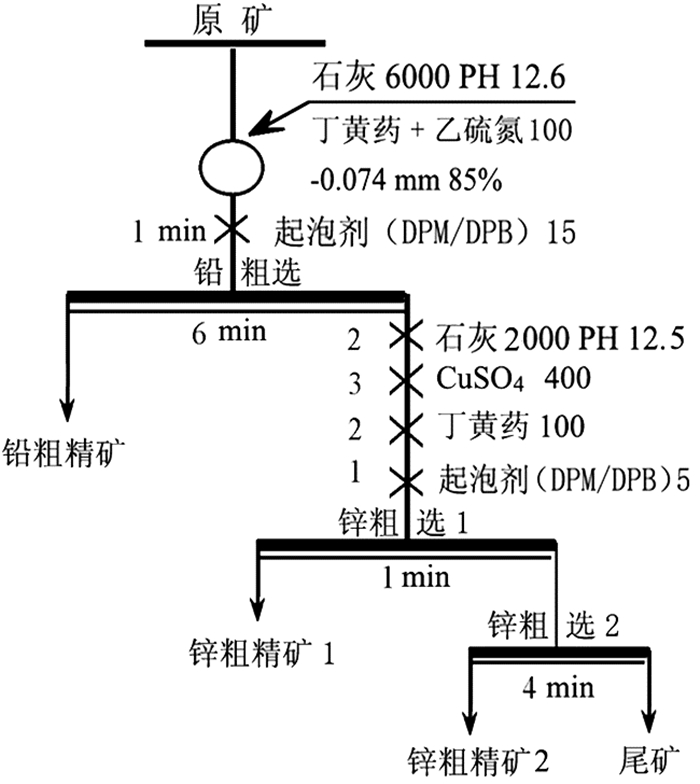
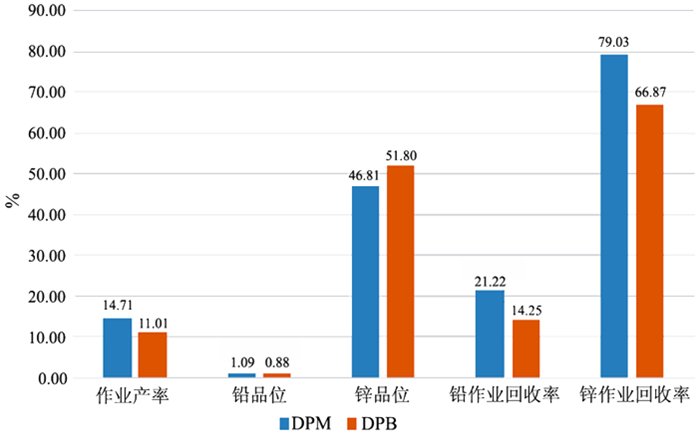
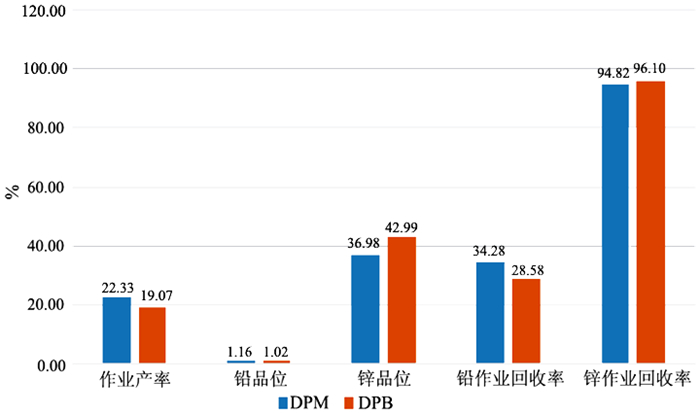
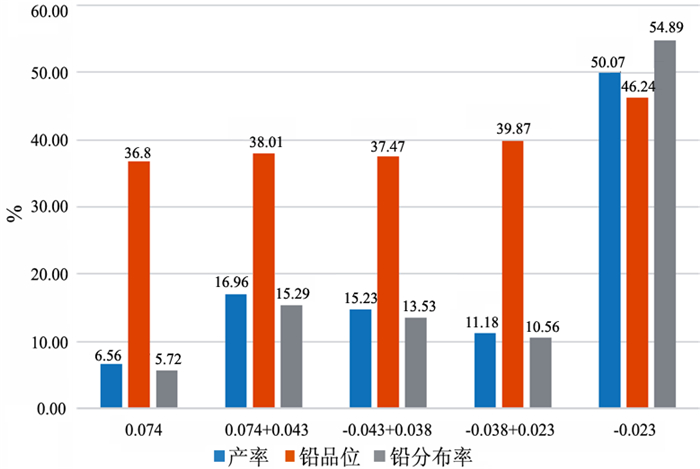
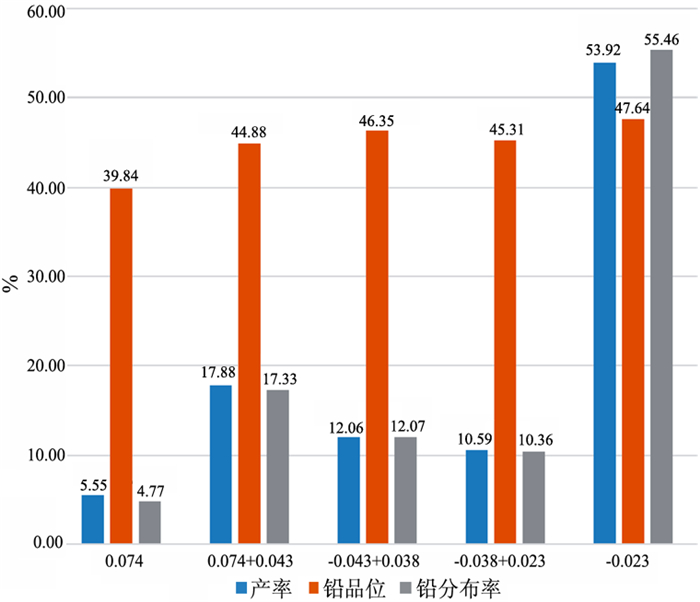
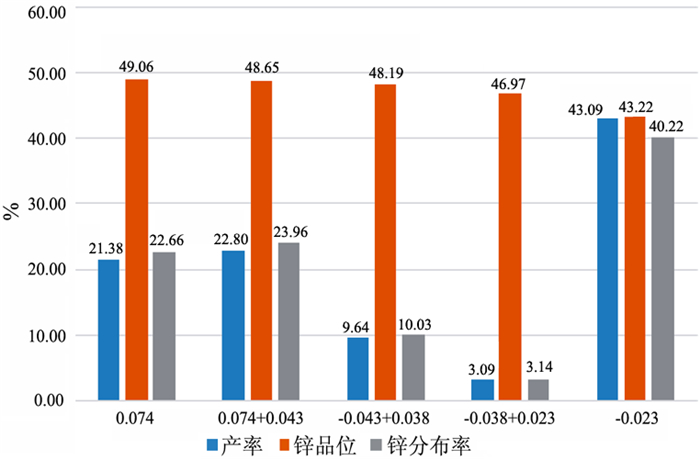
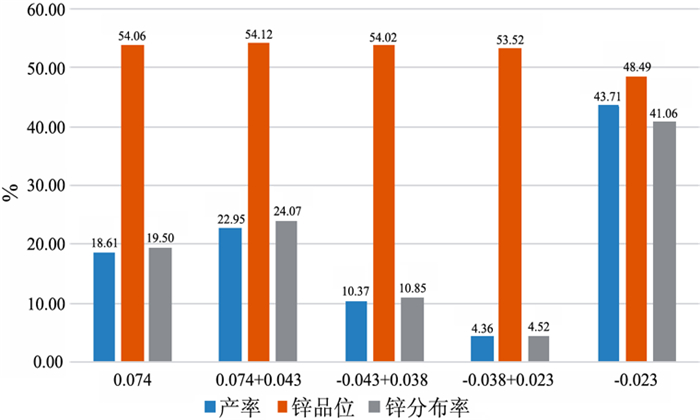
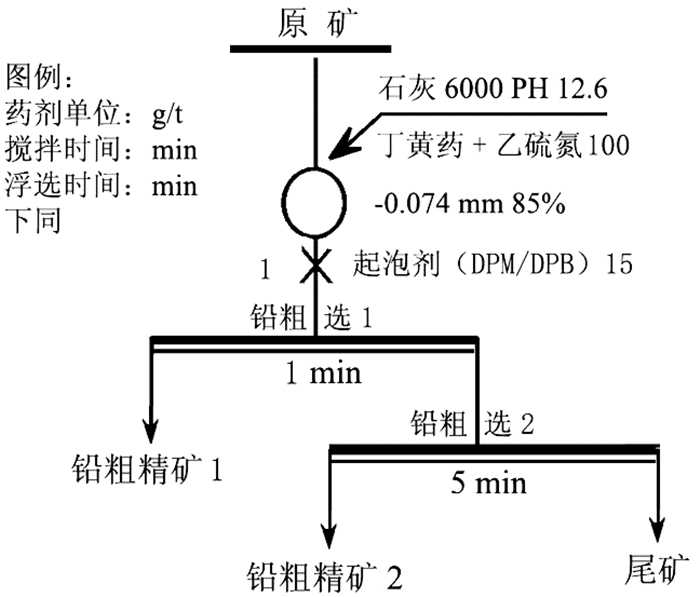
在浮选工艺条件及其它药剂条件相同的情况下,从铅锌矿物的硫化矿浮选回收的变化角度出发,考察两种相似化学结构的起泡剂聚丙二醇单甲基醚(DPM)和聚丙二醇单丁基醚(DPB)的浮选特性。通过分析在铅锌硫化矿的浮选试验结果中所表现的浮选速率的差异以及粗精矿各粒级的分布差异和有价金属量的分布差异,研究了起泡剂DPM和DPB浮选特性的差异。研究结果表明:起泡剂DPB的浮选效率优于DPM。起泡剂DPB对回收较细粒级的铅矿物更有利,而起泡剂DPM对回收较粗粒级的锌矿物更有利。起泡剂DPB比DPM更有利于提高铅锌精矿的品位。
Abstract:Under the same flotation process conditions and reagent regime, the flotation characteristics of two frothers (DPM and DPB) with similar chemical structure were investigated from the perspective of the flotation recovery change of lead-zinc minerals. The differences between these two frothers were estimated by analyzing the differences of flotation rates, size distribution of rough concentrates, and the amount of valuable metals. The results showed that the flotation efficiency of the frother DPB was higher than that of DPM. The frother DPB is more favorable for recovering the fine size lead mineral, while the frother DPM is more favorable for recovering the coarse size zinc mineral. Compared with DPM, DPB can improve the grade of lead-zinc concentrate.
-
Key words:
- frothers /
- flotation behavior /
- rapid flotation /
- size distribution /
- lead-zinc sulfide ore
-

-
[1] 张泾生, 阙宣兰.矿用药剂[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 2008:545-621
[2] 周高云, 陈旭波, 胡志强.高效起泡剂的浮选特性及可生物降解性研究[J].矿产保护与利用, 2018(1):72-75. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=c45df3ea-0e62-4c5a-9cb1-2f87649bf1d4
[3] Klimpel R. The interaction of grind size, collector dosage, and frother type in industrial chalcopyrite rougher flotation[J]. Society for mining, metallurgy&exploration, 1993:80-93.
[4] Hassas B·V, Caliskan H, Guven O, et al. Effect of roughness and shape factor on flotation characteristics of glass beads[J]. Colloids and surfaces A:physicochemical engineering aspects, 2016:492:88-99. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5fde998c3ded66f8c20a535ba9e5283e
[5] Ralston J, Dukhin SS. The interaction of particles and bubbles[J]. Colloids and surfaces A:physicochemical engineering aspects, 1999, 151:3-14. doi: 10.1016/S0927-7757(98)00642-6
[6] Karakas F, Hassas BV. Effect of roughness on interaction of particles in flotation[J]. Physicochemical problem of mineral processing, 2016, 52(1):19-35. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a0bf276b0c1a11133501c9fed5831318
[7] Trahar WJ. A rational interpretation of the role of particle size in flotation[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 1981, 8(4):289-327. doi: 10.1016/0301-7516(81)90019-3
[8] Rahman RM. Ara S, Jameson GJ. The effect of flotation variables on the recovery of different particle size fractions in the froth and pulp[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 2012, 106:70-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a926dec25bb8f6b7319594487031e27b
[9] Ahmed N, Jameson GJ. The effect of bubble size on the rate of flotation of fine particles[J]. International journal of mineral processing. 1985, 14(3):195-215. doi: 10.1016/0301-7516(85)90003-1
[10] Aldrich C, Feng D. The effect of frothers on bubble size distributions in flotation pulp phases and surface froths[J]. Minerals engineering, 2000, 13(10-11):1049-1057. doi: 10.1016/S0892-6875(00)00089-3
[11] Gomez C O, Finch J A. Gas dispersion measurements in flotation cells[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 2007, 84(1-4):51-58. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2007.03.009
[12] Finch J A, Xiao J, Hardie C, et al. Gas dispersion properties:bubble surface area flux and gas holdup[J]. Minerals engineering, 2000, 13(4):365-372. doi: 10.1016/S0892-6875(00)00019-4
[13] Tavera F J, Escudero R, Finch J A. Gas holdup in flotation columns:laboratory measurements[J]. International journal of mineral processing, 2001, 61(1):23-40. doi: 10.1016/S0301-7516(00)00026-0
[14] 陈典助, 肖晋开.凡口铅锌矿选矿工艺流程更新浅析[J].湖南有色金属, 2001(1):12-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5540.2001.01.004
-



 下载:
下载: