Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution of Soil in a Copper Mining Area in the Alpine Desert
-
摘要:
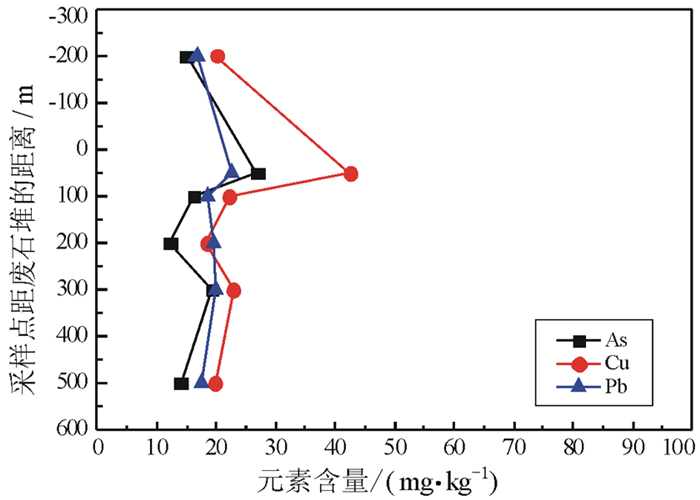
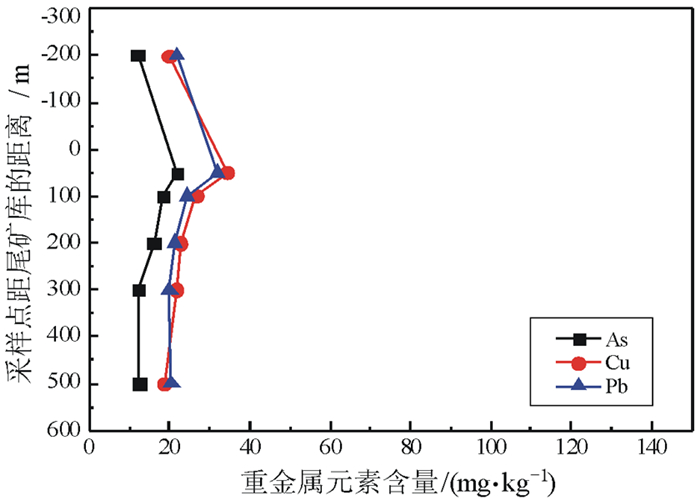
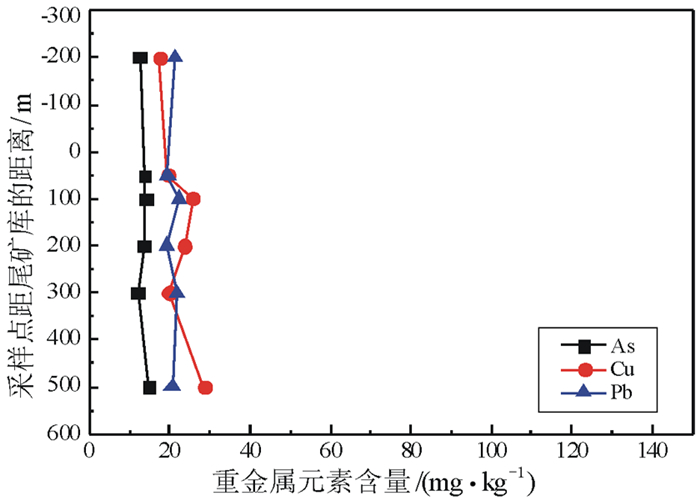
分析检测了高寒荒漠区某铜矿周边土壤重金属元素(As、Cd、Hg、Pb、Cu、Zn、Cr、Ni)含量,并进行了简要评价,结合主导风向和河流方向,对矿业活动剧烈区一定范围内加密采样,研究重金属元素污染分布范围。结果表明:(1)铜矿区土壤环境质量总体良好,仅围岩、废石堆场周边区域个别的样品As、Pb、Cu元素超标;(2)围岩、废石堆场重金属元素污染范围小,集中在其周边200 m区域内,土壤污染深度小于40 cm;(3)尾矿库主导风向下风向200 m内,重金属元素出现一定程度富集;(4)高寒荒漠区,气候寒冷、干旱、少雨、常年多风、蒸发强烈,土壤中重金属扩散主要影响因素是风力和水流作用,垂向传播作用较弱。
Abstract:The contents of soil heavy metals (As, Cd, Hg, Pb, Cu and Zn, Cr, Ni) in a copper mine in the alpine desert were analyzed, and a brief evaluation was given. The pollution scope of heavy metals was studied based on a certain range of encrypted sampling in the active mining area, which was collected in combination with predominant wind direction and the direction of river. The results showed that:(1) The overall soil environmental quality in the copper mining area was generally good except that the contents of As, Pb and Cu elements in a small amount of samples distributed in the area around the rock waste dump were higher than the standard(GB15618-2018); (2) The heavy metal pollution around the rock waste dump was small, which was concentrated within 200 m, and the contaminated soil was less than 40 cm in depth; (3) Within 200 m from the dominant wind direction of tailings pond, there was a certain degree of enrichment of heavy metal elements; (4) In the alpine desert area, the climate was cold, dry, less rain, windy all year round, and evaporation was strong. The main influencing factors for the diffusion of heavy metals in the soil were wind and water, and the vertical transmission was weak.
-
Key words:
- alpine desert /
- copper mining area /
- heavy metal pollution /
- copper /
- cadmium /
- arsenic
-

-
表 1 矿石、尾矿、岩石样品中重金属含量 /(mg·kg-1)
Table 1. Content of heavy metals in the ore, tails and rock samples
样品 Hg As Cu Pb Zn Cr Ni Cd 原矿 <0.001 11 700 4 600 470 8 000 13 0.71 230 尾矿砂 0.119 >500 241 1 375 >2 500 22.3 13.8 89 围岩、废石1# 0.359 284 13.3 121 1 050 13.8 6.60 4.6 围岩、废石2# 0.005 10.9 54.0 24.5 90.6 21.6 12.8 0.95 全国土壤背景值[22] 0.065 11.2 22.6 26.0 74.2 61.0 26.9 0.097 注:围岩、废石1#由铜铅锌多金属矿采坑周边最大的围岩、废石堆场采集;围岩、废石2#由铜钼矿采坑附近围岩、废石堆场采集。 表 2 土壤重金属检测结果统计
Table 2. Statistic results of heavy metals in soil
元素 最大值 最小值 平均值 (GB 15618—2018)风险筛选值 超标个数 样品总数 超标率/% Hg 0.089 0.014 0.026 3.4 0 150 0 As 64.5 9.82 14.36 25 2 1.33 Cu 950 12.60 22.58 100 2 1.33 Pb 378 8.31 19.38 170 1 0.67 Zn 123 30.3 51.83 300 0 0 Cd 0.31 0.06 0.1 0.6 0 0 Cr 69.4 20.5 42.04 250 0 0 Ni 36.8 12.7 20.06 190 0 0 pH 8.36 7.52 7.90 - - - 注:各元素实测含量和标准限值单位均为mg·kg-1。 -
[1] 毛香菊, 马亚梦, 邹安华, 等.内蒙古草原某铜钼矿区土壤重金属污染特征研究[J].环境科学与技术, 2016, 39(6):156-161. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjkxyjs201606029
[2] 江涛, 刘小波, 韦秋莲, 等.长湖水库沉积物重金属污染特征及释放机制[J].生态环境学报, 2017, 26(7):1193-1200. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201707015
[3] 张昱, 胡君利, 白建峰, 等.电子废弃物拆解区周边农田土壤重金属污染评价及成因解析[J].生态环境学报, 2017, 26(7):1228-1234. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201707020
[4] 郭鸿, 高斌, 陈茜.重金属污染物在土壤中的扩散规律及埋置策略研究[J].水资源与水工程学报, 2016, 27(2):237-240. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbszyysgc201602044
[5] 张文静, 何川, 魏威.大脚岭铅锌矿尾矿库重金属污染迁移的无损探测与评价[J].有色金属工程, 2015, 5(5):79-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2015.05.019
[6] 周科平, 林允, 胡建华, 等.大脚岭铅锌尾矿库重金属迁移规律与污染评价[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 46(5):1953-1958. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zngydxxb201505051
[7] 李致春, 桂和荣, 孙林华, 等.沱河芦岭矿塌陷区段沉积物重金属污染及迁移能力评价[J].环境科学与技术, 2013, 36(7):13-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2013.07.003
[8] 乔鹏炜, 周小勇, 杨军, 等.土壤重金属元素迁移模拟方法在矿集区适用性比较[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(8):1121-1131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.08.005
[9] 朱昌宇, 黄道友, 朱奇宏, 等.模拟降雨条件下污染土壤中重金属元素径流迁移特征[J].水土保持学报, 2012, 26(4):49-53. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqsystbcxb201204010
[10] 毛香菊, 邹安华, 马亚梦, 等.南京某铁尾矿库复垦土壤重金属污染评价[J].矿产保护与利用, 2015(1):54-58. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=1628bc63-09c1-42cb-ac2b-9f280f290a44
[11] 谢志宜, 张雅静, 陈丹青, 等.土壤重金属污染评价方法研究:以广州市为例[J].农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(7):1329-1337. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ncsthj200601011
[12] 张金婷, 孙华.内梅罗指数法和模糊综合评价法在土壤重金属污染评价应用中的差异分析[J].环境监测管理与技术, 2016, 28(4):27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2016.04.007
[13] 张东明, 吕新, 王海江, 等.工业区周边农田重金属污染评价及来源分析[J].土壤通报, 2017, 48(3):715-722. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trtb201703029
[14] 王兵.铬渣堆场周边土壤中重金属污染及风险评估[J].有色金属(冶炼部分), 2018(4):81-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2018.04.018
[15] 陈志良, 袁志辉, 黄玲, 等.生物炭来源、性质及其在重金属污染土壤修复中的研究进展[J].生态环境学报, 2016, 25(11):1879-1884. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201611021
[16] 孙鑫, 娄燕宏, 王会, 等.重金属污染土壤的植物强化修复研究进展[J].土壤通报, 2017, 48(4):1008-1013. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201301024
[17] 张乃明.重金属污染土壤修复理论与实践[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2017:97-190.
[18] 张爱奎, 莫宣学, 李云平, 等.青海西部祁漫塔格成矿带找矿新进展及其意义[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(7):1062-1074. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.07.013
[19] 时超, 李荣社, 何世平, 等.东昆仑祁漫塔格虎头崖铅锌多金属矿成矿时代及其地质意义-黑云二长花岗岩地球化学特征和锆石U-Pb年龄证据[J].地质通报, 2017, 36(6):977-986. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.06.010
[20] 张永康, 曹耀华, 冯乃琦, 等.青海某铁多金属矿区土壤重金属污染评价[J].矿产保护与利用, 2017(3):94-99. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=9b7acd65-9673-4010-a12b-e97b6ea4b8b4
[21] 张永康, 曹耀华, 高照国, 等.某铜矿区土壤重金属污染评价[J].有色金属(冶炼部分), 2018(8):78-82. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysjs-yl201808018
[22] 中国国家环境保护局.中国土壤元素背景值[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社, 1990:87-91.
-




 下载:
下载: