Dynamic Study on Adsorption of Phosphate Ion in Water by Red Mud Particle Adsorbent
-
摘要:
采用拜耳法赤泥为原料,针对传统烧结法耗能大、成本高的问题,采用非烧结的方法制备颗粒吸附剂,考察以及吸附剂投加量、初始磷酸根浓度、pH值和温度因素对吸附除磷的赤泥颗粒吸附剂对磷酸根的吸附性能影响,吸附实验结果显示对磷酸根的吸附量达到了67.68 mg/g,优于其他文献报道的吸附剂。基于试验结果,对赤泥颗粒吸附剂对磷酸根的吸附行为进行等温吸附、动力学的数学拟合,伪二级动力学和Langmuir-Freundlich吸附等温式能较好描述赤泥颗粒吸附剂对磷酸根的吸附行为,其相关系数R2均大于0.98,赤泥颗粒吸附剂对磷酸根的吸附过程既存在多层吸附,也存在单层吸附且符合化学吸附的特点。
Abstract:Using Bayer's red mud as raw material, in view of the problem of high energy consumption and high cost of traditional sintering method, the particle adsorbent is prepared by non-sintering method, and the effect of the adsorption performance of the aerosol sorbent agent, the initial phosphate root concentration, pH value and temperature factors on the adsorption performance of the red mud particle adsorbent adsorption absorbent to phosphorus, The adsorption experiments showed that the adsorption capacity of phosphate was 67.68 mg/g, which was better than that reported in other literatures. Based on the experimental results, the adsorption behavior of red mud particle adsorbent for phosphate was isothermally adsorbed. The mathematical fitting of kinetics, pseudo-second-order kinetics and Langmuir-Freundlich adsorption isotherm equation can better describe the phosphorus adsorption of red mud particle adsorbent. The adsorption behavior of acid roots is higher than 0.98, and the adsorption process of red mud particle adsorbent for phosphate is not only multi-layer adsorption, but also monolayer adsorption, which accords with the characteristics of chemical adsorption.
-
Key words:
- red mud /
- phosphate radical /
- dynamic adsorption
-

-
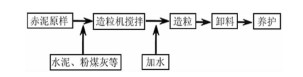
表 1 赤泥颗粒吸附剂药剂配比
Table 1. Mixture ratio of red mud particle adsorbent
序号/药剂 1号 2号 3号 4号 5号 6号 水泥/g 30 15 15 22 20 22 粉煤灰/g 15 15 30 30 30 20 赤泥/g 210 225 225 230 225 230 抑碱剂/g - - 9 9 9 9 硫铝酸钙/g 18 18 18 6 6 6 硅酸钠/g 6 6 6 6 6 6 硫酸铝/g 3 3 3 6 6 6 三乙醇胺/g 0.18 0.18 0.18 0.18 0.18 0.18 偶联剂/g 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.15 水/g 101.09 116.42 95.93 126.11 115.16 110.41 强度(7 d)/MPa 1.43 1.52 1.79 1.63 1.54 1.32 表 2 赤泥颗粒吸附剂X射线荧光光谱(XRF)单元素检测
Table 2. X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF) single element detection of red mud granules
Element Fe Ca Al Si Na Ti K Mg 原始赤泥/% 28.83 21.15 15.74 13.46 9.05 6.25 1.78 1.34 赤泥颗粒吸附剂/% 28.13 21.35 16.74 13.76 8.85 5.65 1.78 1.34 表 3 吸附剂比表面积(BET)分析
Table 3. Analysis of specific Surface area(BET) of adsorbents
项目 比表面积/
(m2·g-1)孔体积/
(mL·g-1)平均孔径/nm 赤泥颗粒吸附剂 54.78 0.34 224.00 表 4 赤泥吸附剂吸附脱除磷酸根试验结果
Table 4. Experimental results of adsorption of phosphate by red mud adsorbents
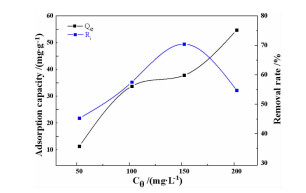
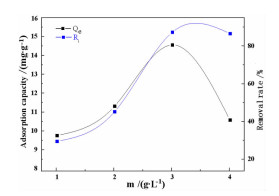
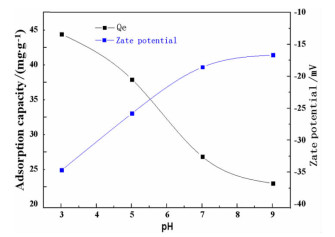
序号 C0/
(mg·L-1)m/
(g·L-1)T/℃ pH te
minqe/
(mg·g-1)Ri/% 1 50 1 50 5.0 1410 9.76 29.52 2 50 2 50 5.0 1290 11.32 45.28 3 50 3 50 5.0 1170 14.56 87.36 4 50 4 50 5.0 1050 10.58 86.64 5 100 2 30 5.0 1200 17.69 25.38 6 100 2 40 5.0 1140 25.79 31.58 7 100 2 50 5.0 1050 33.78 47.56 8 100 2 60 5.0 990 27.96 55.92 9 150 2 50 3.0 960 44.37 59.16 10 150 2 50 5.0 1020 37.86 50.48 11 150 2 50 7.0 1050 26.79 35.72 12 150 2 50 9.0 1140 22.98 30.64 13 200 2 50 3.0 930 67.68 67.68 14 200 2 50 5.0 960 54.78 54.78 表 5 动力学模型拟合计算结果
Table 5. Dynamic model fitting calculation results
数学模型 参数1 参数2 参数3 R2 伪一级动力学 k1=0.0056 qe=44.37 0.9134 伪二级动力学 k2=2.309×10-4 qe=67.68 - 0.9886 颗粒内扩散模型 ki=9.3133 - - 0.9858 液膜扩散模型 kl=0.00793 - - 0.95705 表 6 吸附等温式模型拟合结果(323K)
Table 6. Adsorption equidistant model fitting results(323K)
数学模型 参数1 参数2 参数3 R2 Langmuir吸附等温式 Qe=76.89 b=0.0256 - 0.9267 Freundlich吸附等温式 Kf=96.35 n=2.7854 - 0.9435 Langmuir-Freundlich吸附等温式 Klf=0.0031 qmax=83.23 n=1.439 0.9817 -
[1] 刘少名.赤泥的综合利用[D].沈阳: 东北大学, 2011.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10145-1013109238.htm [2] 吴文思.赤泥吸附除磷的性能及机制研究[D].北京: 华北电力大学, 2011.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-11412-1011107677.htm [3] 曹守坤.粉煤灰改性及处理含磷废水研究[D].泉州: 华侨大学, 2012.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10385-1013001119.htm [4] 赵雅琴.新型赤泥颗粒吸附材料的制备、表征及其对水体中磷的去除性能研究[D].济南: 山东大学, 2013.
http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y2327898 [5] 王黎.活性赤泥对水中磷酸盐吸附特性的研究[D].西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2010.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10703-2010134602.htm [6] 陈伟.改性赤泥多孔材料制备及污水处理探索研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学, 2010.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-2010085239.htm [7] 吕娜.膨润土与粉煤灰处理污水二级出水中磷的试验研究[D].阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2012.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10147-1013138455.htm [8] 周光红.几种固体废弃物吸附除磷性能及其机理探讨[D].大连: 大连理工大学, 2011.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10141-1011108739.htm [9] 任贵宁.赤泥吸附剂的制备及对溶液中磷和铬(Ⅵ)的吸附研究[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2016.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-1016091441.htm [10] 魏婧婧.赤泥质多孔陶瓷材料的制备及对重金属Cr(Ⅵ)吸附的研究[D].南宁: 广西大学, 2014.
http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D524326 [11] CHEN Wei, LIU Hai-cheng, Adsorption of sulfate in aqueous solutions by organo-nano-clay:Adsorption equilibrium and kinetic studies[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(5):1974-1981. doi: 10.1007/s11771-014-2145-7
[12] Nazanin Deihimi, Mehdi Irannajad, Bahram Rezai. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of ferricyanide adsorption from aqueous solution by activated red mud[J].Journal of environmental management. 2018(227):277-285. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=55c714884e2037068c7424f444779018
[13] P.Brea, J.A.Delgado, V.I.águeda, et al. Modeling of breakthrough curves of N2, CH4, CO, CO2 and a SMR type off-gas mixture on a fixed bed of BPL activated carbon[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017(179):61-71. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8764406996ca45cbec82ae56ebf23602
[14] 陈思辰.铁改性赤泥颗粒滤料的制备及其去除水中溴酸盐[D].哈尔滨: 黑龙江大学, 2016.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10212-1016185701.htm [15] LI Xin, WANG Guang-zhi, LI Wei-guang, et al. Adsorption of acid and basic dyes by sludge-based activated carbon:Isotherm and kinetic studies[J]. Journal of central south university, 2015, 22(1):103-113. doi: 10.1007/s11771-015-2500-3
[16] 张玉洁, 王文彬.赤泥颗粒吸附除磷性能研究[J].市政技术, 2017, 35(3):139-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7767.2017.03.043
[17] LI Xianbo, YE Junjian, LIU Zhihong, et al. Microwave digestion and alkali fusion assisted hydrothermal synthesisof zeolite from coal fly ash for enhanced adsorption of Cd(Ⅱ) in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of central south university. 2018(25):9-20 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZNGY201801002.htm
[18] Wentao Liang, Sara J. Couperthwaite, Gurkiran Kaur. Effect of strong acids on red mud structural and fluoride adsorption properties[J]. Journal of colloid and interface science. 2014(423):158-165. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=39e2862ce0d4d3aa8a5dd484bfe30d99
[19] Ren J, Li N, Li L, et al. Granulation and ferric oxides loading enable biochar derived from cotton stalk to remove phosphate from water[J]. Bioresource technology, 2015(178):119-125. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=98abfb5af931894a8bb67299d4ce9cb4
[20] Chen N, Feng C P, Zhang Z Y, et al. Preparation and characterization of lanthanum(Ⅲ) loaded granular ceramic for phosphorus adsorption from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of the Taiwan institute of chemical engineers, 2012, 451(5):783-789. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876107012000661
[21] 赵东.粉煤灰赤泥玻璃陶瓷制备与性能研究[D].济南: 山东建筑大学, 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10430-1013205843.htm -



 下载:
下载: