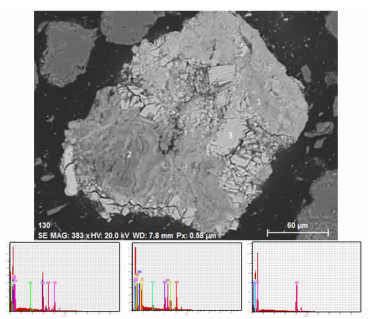
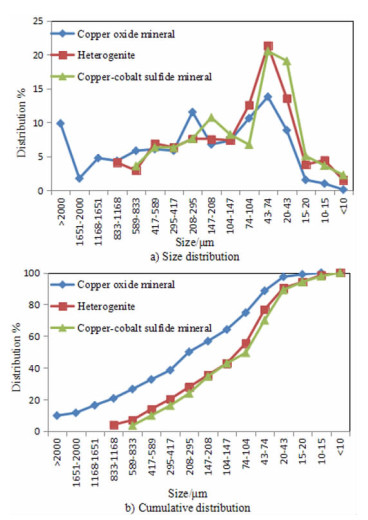
Process Mineralogy and Its Influence on Metallurgy Technology of a Copper-cobalt Oxidized Ore in Congo (DRC)
-
摘要:
为合理开发利用刚果(金)某氧化铜钴矿提供理论依据,利用先进仪器—矿物参数自动定量分析系统(AMICS)、扫描电子显微镜等综合手段对该矿进行了工艺矿物学研究,指出影响铜钴浸出的矿物学因素。结果表明,铜的氧化率为92.22%,氧化铜矿物主要为孔雀石和蓝磷铜矿;钴的氧化率为85.84%,氧化钴矿物主要为水钴矿。矿石中铜钴矿物粒度分布不均,其中,铜矿物以中粗粒为主,钴矿物以中细粒为主,并且黏土矿物较多,铜钴矿物在粗磨条件下易与脉石裸露连生,因此建议在适当粗磨条件下采用酸法搅拌浸出工艺回收铜钴。矿石中分别有3.69%的铜和9.46%的钴以吸附态分布在褐铁矿和铁锰水合氧化物中,这部分铜、钴较难浸出,是影响浸出率提高的主要因素。
Abstract:Process mineralogy of copper-cobalt oxidized ore in Congo has been studied by multiple methods such as advanced instrμment—AMICS (Advanced Mineral Identification and Characterization System) and scanning electron microscope, which points out the mineralogical factors affecting the acid leaching of copper and cobalt. The results show that the oxidation ratio of copper is 92.22%, mainly in malachite and cornetite; the oxidation ratio of cobalt is 85.84%, mainly in heterogenite. The size distribution of copper and cobalt minerals in the ore is uneven, among which copper minerals are mainly mediμm-coarse, cobalt minerals are mainly mediμm-fine, and there are many clay minerals. The copper and cobalt minerals are easy to be exposed under the condition of coarse grinding, it is suggested that acid agitation leaching should be adopted for copper and cobalt recovery under proper coarse grinding conditions. 3.69% copper and 9.46% cobalt are distributed in limonite and Fe-Mn hydrated oxide in the adsorption state, and this part of copper and cobalt is difficult to leach, which mainly affects the improvement of leaching rate.
-

-
表 1 矿石的化学分析结果
Table 1. Multi-element analysis results of the ore
/% Composition Cu Co Pb Zn Mo Fe S SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O C Content 2.00 0.356 0.014 0.017 0.002 2.88 0.078 70.63 6.46 0.99 4.34 1.42 0.19 0.48 表 2 矿石中铜的化学物相分析结果
Table 2. Chemical Phase analysis result of Cu in the ore
/% Phase Oxidized copper native copper Secondary copper sulfide Primary copper sulfide Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides Total Cu Content 1.85 0.01 0.042 0.03 0.077 2.009 Distribution 92.09 0.50 2.09 1.49 3.83 100.00 表 3 矿石中钴的化学物相分析结果
Table 3. Chemical Phase analysis result of Co in the ore
/% Phase Oxidized cobalt Cobalt sulfide Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides Total Co Content 0.31 0.017 0.023 0.35 Distribution 88.57 4.86 6.57 100.00 表 4 矿石的矿物组成及相对含量
Table 4. Mineral composition and relative content of the ore
/% Mineral Content Mineral Content malachite 1.74 quartz 61.91 cornetite 1.40 dolomite 2.78 tenorite※ 0.01 calcite 0.26 native copper 0.01 chlorite 14.54 chalcocite※ 0.04 muscovite 7.42 chalcopyrite 0.09 potash feldspar 4.01 heterogenite 0.57 albite 1.61 carrolite 0.04 kaolinite 0.33 pyrite 0.04 rutile 0.14 limonite 2.18 others 0.73 Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides 0.15 Note:chalcocite includes chalcocite, digenite, covellite and bornite;tenorite includes tenorite and cuprite. 表 5 铜在各矿物中的平衡计算
Table 5. Equilibriμm calculation of copper in each mineral
/% Mineral Content Copper in minerals The metal amount of Copper Copper distribution Malachite 1.74 57.44 1.00 49.86 Cornetite 1.40 56.63 0.80 39.64 Tenorite 0.01 79.85 0.01 0.52 Chalcocite 0.04 79.85 0.03 1.63 Chalcopyrite 0.09 34.63 0.03 1.50 Native copper 0.01 100.00 0.01 0.50 Carrollite 0.04 20.52 0.01 0.46 Heterogenite 0.57 7.81 0.044 2.21 Limonite 2.18 1.94 0.04 2.11 Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides 0.15 21.40 0.03 1.58 Total 2.006 100.00 表 6 钴在各矿物中的平衡计算
Table 6. Equilibriμm calculation of cobalt in each mineral
/% Mineral Content Copper in minerals The metal amount of Cobalt Cobalt distribution Heterogenite 0.57 54.53 0.31 85.84 Carrollite 0.04 38.00 0.02 4.70 Limonite 2.18 0.19 0.004 1.15 Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides 0.15 20.27 0.03 8.31 Total 0.361 100.00 表 7 水钴矿的X-射线能谱分析结果
Table 7. SEM energy spectrum analysis of heterogenite
/% No. Element O Al Si P Ca Mn Fe Co Cu 1 33.89 0.00 0.87 0.00 0.00 0.00 4.24 51.18 9.83 2 38.56 0.00 4.47 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 50.89 6.09 3 31.19 0.00 0.00 0.76 0.00 0.00 0.00 57.82 10.22 4 30.22 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 59.64 10.15 5 34.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 65.98 0.00 6 35.68 4.74 0.00 1.66 0.57 2.43 0.00 49.67 5.25 7 36.70 4.29 0.00 1.35 0.00 1.74 2.18 49.20 4.53 8 36.58 4.75 0.00 1.45 0.00 2.35 2.51 47.07 5.28 9 35.07 5.35 0.00 1.57 0.56 2.00 2.32 48.42 4.71 10 34.65 3.27 0.00 0.95 0.00 1.98 2.42 51.98 4.76 11 36.04 3.86 0.00 1.12 0.00 0.00 0.00 55.38 3.61 12 30.81 3.92 0.00 1.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 60.09 4.17 13 31.80 0.00 0.00 0.75 0.00 0.00 0.00 56.02 11.43 14 32.23 0.00 0.68 0.70 0.91 6.78 0.00 41.83 16.87 15 32.11 0.00 0.00 0.66 0.00 0.00 0.00 57.32 9.90 16 31.32 0.00 0.00 0.60 0.00 0.00 0.00 58.29 9.79 17 29.59 0.00 0.68 0.71 0.00 1.74 1.73 52.21 13.34 18 30.15 0.00 0.00 0.71 0.00 0.00 0.00 58.37 10.77 19 31.67 0.00 0.00 0.62 0.00 0.00 0.00 57.83 9.88 20 33.21 3.98 0.00 1.09 0.00 0.00 0.00 57.56 4.16 21 26.83 0.00 0.00 0.71 0.00 0.00 0.00 59.97 12.48 22 34.13 3.64 0.00 1.27 0.00 1.50 1.74 53.03 4.69 -
[1] 江少卿.全球铜矿资源分布[J].世界色金属, 2018(2):1-3. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjysjs201802001
[2] 李成伟, 王家义.全球钴资源供应现状简析[J].中国资源综合利用, 2018(7):102-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2018.07.036
[3] 肖仪武, 方明山, 付强, 等.工艺矿物学研究的新技术与新理念[J].矿产保护与利用, 2018(3):49-54. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=45914c74-828a-41f1-b1bc-517f0ead33b3
[4] 商宗占.浅谈刚果(金)铜钴资源项目[J].低碳世界, 2017(32):281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2066.2017.32.191
[5] 刘媛媛, 杨洪英, 陈国宝, 等.赞比亚某复杂氧化铜钴矿石的工艺扩物学研究[J].有色冶金节能, 2016(3):13-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YJJN201603005.htm
[6] 《矿产资源工业要求手册》编委会.矿产资源工业要求手册[M].北京:地质出版社, 2012:330-338.
[7] 王濮, 潘兆橹, 翁玲宝.系统矿物学(上、中、下册)[M].北京:地质出版社, 1982.
[8] 蒋太国, 方建军, 张铁民, 等.氧化铜矿选矿技术研究进展[J].矿产保护与利用, 2014(2):49-53. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=a1ac81aa-08a1-4611-8d5f-f763fcfadb2f
[9] 欧乐明, 胡本福, 段景文.刚果(金)某难选氧化铜钴矿选矿工艺研究[J].金属矿山, 2011(9):76-81. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsks201109020
[10] 刘俊, 李林艳, 徐盛明, 等.还原酸浸法从低品位水钴矿中提取铜和钴[J].中国有色金属学报, 2014, 22(1):304-309. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgysjsxb201201040
[11] 谢添, 廖春发, 吴免利, 等.刚果(金)铜钴氧化矿回收铜钴研究[J].中国资源利用, 2013, 31(5):23-26. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kygc201303016
[12] 商宗占.浅谈刚果(金)铜钴资源项目[J].低碳世界, 2017(32):281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2066.2017.32.191
-



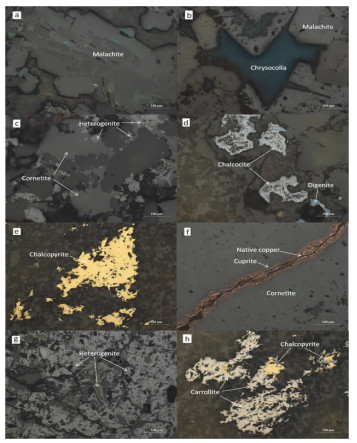
 下载:
下载: