Study on Process Mineralogy of Duocaima Lead-zinc Ore in Tibet
-
摘要:
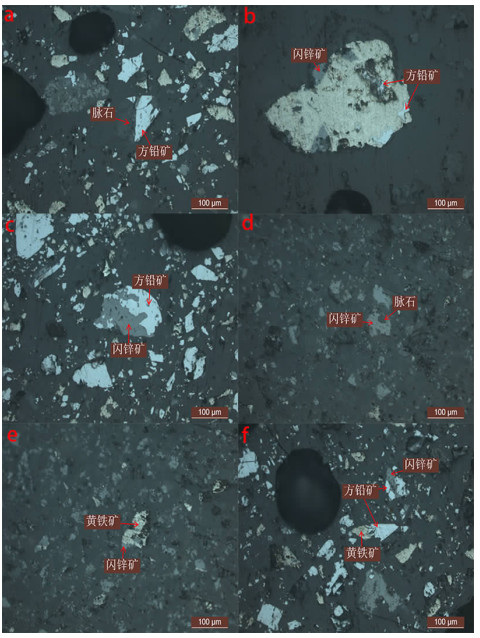
为给西藏多才玛铅锌矿详查阶段矿产评价提供依据,对其进行了详细工艺矿物学研究。研究结果表明:该矿石含Pb为4.21%、Zn为2.81%,银、镉、硒、碲和铊分别为27 g/t、0.017%、0.002%、0.03%、0.023%,可进行综合回收利用。铅主要以方铅矿的形式存在,锌主要以闪锌矿的形式存在。方铅矿、闪锌矿为主要回收目的矿物。铅、锌矿物嵌布关系复杂,与其他矿物紧密接触,分离较困难。方铅矿嵌布粒度相对较粗,有利于选矿回收,而闪锌矿嵌布粒度较细,-0.02 mm粒级以下含量高达22.07%,选矿难度大,需要进行细磨工作,才能提高回收率。此外,脉石矿物主要为方解石、石英,具有易磨碎、易泥化等特点,将给铅、锌矿物分选带来不利影响。
Abstract:In order to provide the basis for the mineral evaluation in the detailed investigation stage of the Tibet-Taicangma lead-zinc mine, a detailed process mineralogy study was conducted. The results show that the ore contains 4.2% Pb and 2.81% Zn. The silver, cadmium, selenium, tellurium and strontium are 27 g/t, 0.017%, 0.002%, 0.03% and 0.023%, respectively, which can be comprehensively recycled. Lead exists mainly in the form of galena, and zinc mainly exists in the form of sphalerite. Galena, sphalerite for the comprehensive recovery of minerals. The relationship between lead and zinc minerals is complex and it is in close contact with other minerals. Separation is difficult. The galena inlay grain size is relatively coarse, which is conducive to beneficiation and recovery. The grain size of the sphalerite inlay is fine, and the content below -0.02 mm is as high as 22.07%. It is difficult to be ore dressing and fine grinding work is needed to increase the recovery rate. In addition, gangue minerals are mostly mud-crystal-gray minerals, which are characterized by easy grinding and easy argillization, which will adversely affect the separation of lead and zinc minerals.
-
Key words:
- galena /
- sphalerite /
- disseminated grain size /
- process mineralogy
-

-
表 1 化学多元素分析结果
Table 1. Chemical multi-element analysis results of raw ore
/% 成分 Pb Zn S As Ba Mn Ni TFe SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO CaF2 Tl Se Cd Te U Au Ag Hg 含量 4.21 2.81 2.64 0.091 0.022 0.18 0.027 3.29 16.43 0.45 44.56 1.34 2.20 0.023 0.002 0.017 0.03 6.2 0.05 27 0.07 注:U、Au、Ag、Hg含量单位为g/t。 表 2 铅锌物相分析结果
Table 2. Phase analysis results of lead and zinc
/% 名称 铅矾 白铅矿 方铅矿 磷(砷、钒)氯铅矿
及其他形态铅矿合计 硫酸锌 氧化锌 硫化锌 其他锌 合计 含量 0.038 0.24 3.91 0.039 4.22 0.000 25 0.096 2.69 0.009 8 2.80 分布 0.91 5.63 92.81 0.65 100.00 0.01 3.42 96.22 0.35 100.00 表 3 矿石中主要矿物的相对含量
Table 3. Relative content of major minerals in ore
/% 矿物名称 方铅矿 闪锌矿 黄铁矿 白铅矿 方解石 石英 含量 4.7 2.9 2.8 0.5 89.1 微 表 4 矿石结构、构造
Table 4. Structure and construction of ore
结构与构造 矿石中的描述 包含结构 矿石中可见方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿相互包裹,构成包含结构 胶状结构 矿石中可见部分黄铁矿具有胶状结构 海绵陨铁结构 矿石中可见部分黄铁矿沿脉石矿物边缘分布,构成海绵陨铁结构 自形半自形结构 矿石中部分方铅矿结晶较好,晶形完整,构成自形半自形结构 他形粒状结构 闪锌矿等矿物晶形较差,呈他形粒状结构 块状构造 矿石中生物碎屑灰岩层理很厚,具有块状构造 脉状构造 部分矿石中方铅矿、部分方解石呈脉状分布,构成脉状构造 团窝状构造 部分矿石中部分方铅矿和闪锌矿呈团窝状分布,构成团窝状构造 浸染状构造 部分矿石中闪锌矿、方铅矿等呈浸染状分布,构成浸染状构造 表 5 主要有用矿物原生粒度统计结果
Table 5. Statistical results of primary grain size of valuable minerals
粒度/mm 方铅矿 闪锌矿 分布率/% 累计/% 分布率/% 累计/% +0.1 38.16 39.66 4.14 4.14 -0.1+0.075 23.88 62.04 11.03 15.17 -0.075+0.048 20.41 82.45 33.79 48.96 -0.048+0.02 11.43 93.88 28.97 77.93 -0.02 6.12 100.00 22.07 100.00 点分析 Pb S Fe Point1 85.684 12.112 0.047 Point2 84.566 13.470 0.037 Point3 86.065 13.602 0.039 Point4 86.504 13.560 0.025 Point5 87.518 13.584 0.071 平均 86.067 13.266 0.044 点分析 Zn S Se Point1 64.334 31.955 0.002 Point2 65.018 32.103 0.012 Point3 65.543 32.169 0.005 Point4 66.118 31.979 0.000 Point5 65.575 32.001 0.024 平均 65.318 32.041 0.009 -
[1] 李领贵, 郭海明.青海省沱沱河地区多才玛铅锌矿床成矿规律及找矿标志[J].有色金属(矿山部分).2016, 68(1):40-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4172.2016.01.009
[2] 刘长征, 苗国文, 张勤山, 等.三江北段成矿带区域化探工作进展及主要成果[J].现代矿业, 2016(7):150-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2016.07.050
[3] 周满赓.工艺矿物学在矿产资源找矿和综合利用中的应用[J].矿产综合利用, 2012(3):7-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2012.03.002
[4] 李琳清, 应永朋, 熊馨, 等.青海榴辉岩型金红石矿工艺矿物学研究[J].矿产综合利用, 2017(4):87-89, 97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2017.04.019
[5] 孙晓华.多才玛铅锌矿选矿流程试验报告[R].西宁: 青海省地质矿产测试应用中心, 2014.
[6] 杨晓文, 孙晓华, 贾宗勇, 等.青海某低品位铅锌矿工艺矿物学研究[J].矿产保护与利用, 2014(5):39-42. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=08ada505-2e10-4da4-97be-5ba1f4ad58e9
-



 下载:
下载: