Behaviour and Mechanism of Arsenic Removal From High-arsenic Waste Acid Using Ca/Fe-enriched Coal Slag
-
摘要:
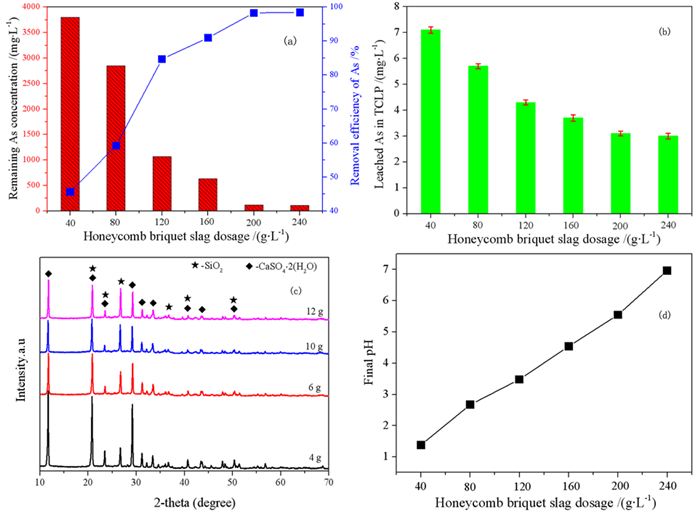
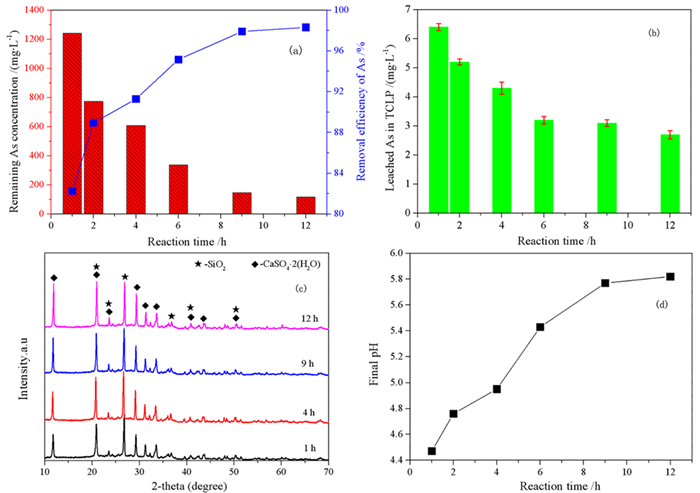
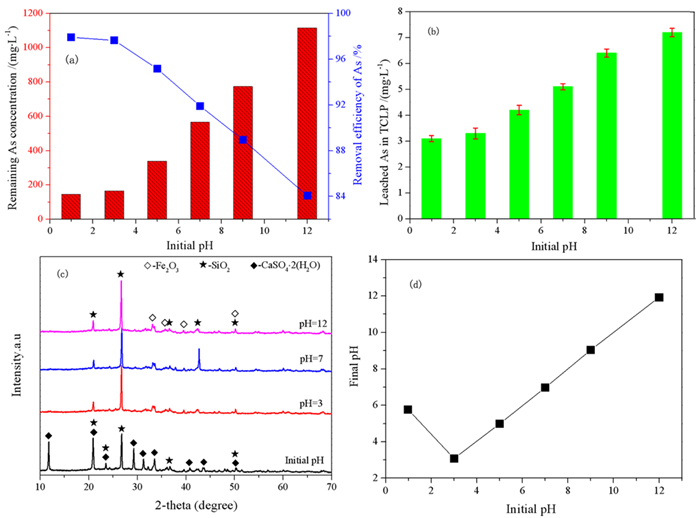
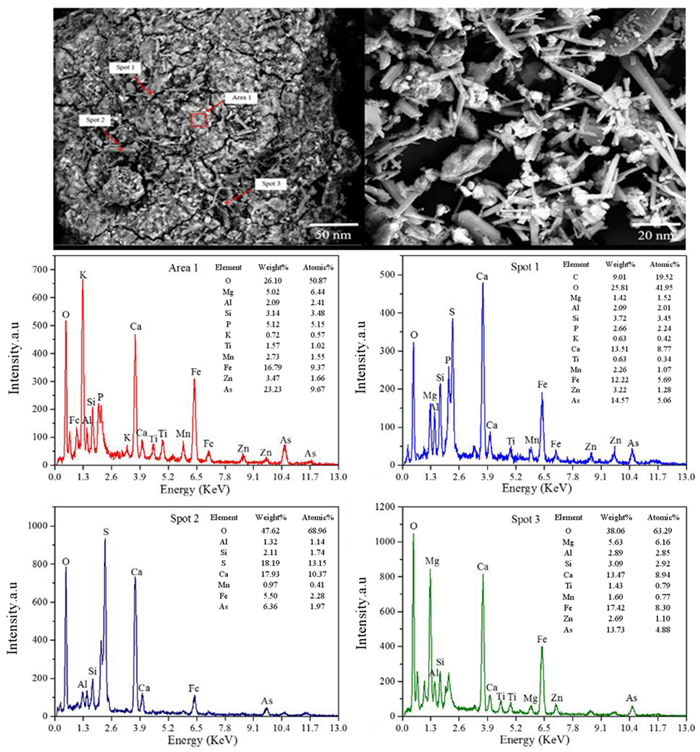
针对重有色冶炼过程中的污酸处置长期存在危废产量大、环境成本高等难题,本文提出一种绿色工艺,结合高铁高钙煤渣特征,提出了高铁高钙煤渣无害化处置含砷污酸的新思路,达到去除污酸中砷离子且生成稳定含砷化合物的目的。研究了污酸与高铁高钙煤渣的在不同条件(加入量、反应时间、初始pH)的反应行为,并借助材料分析手段揭示了除砷机理。结果表明燃煤渣富含钙和铁氧化物,煤渣与污酸具有良好的反应效果和除砷作用。燃煤渣用于污酸除砷,最高除砷率可达98.31%,除砷能力最高可达82.52 mg/g,随着反应时间增加除砷效率和沉淀物稳定性明显提高。初始pH=0.98时,除砷效果最好,并且随着pH升高显著下降。煤渣中氧化铁溶于污酸,释放Fe3+,在氧化条件下沉淀砷酸根离子生成无定形砷酸铁,而后在Si、Al和Ca氧化物保护下,达到除砷固砷目的,形成浸出毒性低于5 mg/L的富砷沉淀渣。
Abstract:The smelting industries of nonferrous metals are suffering from the emission of large number of hazardous wastes and high cost of environmental protection during the disposal of waste acid. We proposed to remove arsenic from waste acid using Ca/Fe-enriched coal slag to produce arsenic-stabilized precipitates. In combination with materials' characterization, the reaction behaviors (dosage of coal slag, reaction time and initial pH) between coal slag and waste acid have been investigated, and the reaction mechanism was also explored. The results shows that coal slag mainly composes of Ca and Fe oxides and exhibits high activity for arsenic removal from waste acid. At a coal slag-to-waste acid ratio of 100 g/L, the arsenic concentration decreases from 7 g/L to 118.2 mg/L and its arsenic removal capacity reaches 68.82 mg/g. The stability of arsenic-enriched precipitates increases with the increasing reaction time. Highest arsenic removal efficiency was obtained at an initial pH of 0.98 and it deceases with the increasing pHs. It is found that Fe oxides in coal slag dissolve in waste acid and then Fe3+ precipitates arsenate to form ferric arsenate. Under the protection of Si, Al and Ca oxides, the ferric arsenate is fixed in precipitates and results a lower arsenic leaching concentration in leaching testes.
-
Key words:
- coal slag /
- waste acid /
- ferric arsenate /
- leaching test
-

-
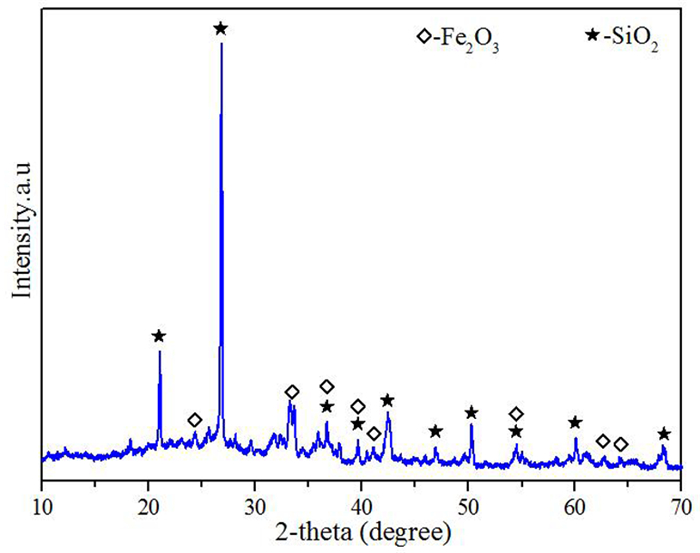
表 1 污酸成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of waste acid
/(mg·L-1) Element As Zn Sb Fe Cu Mg Pb Cr H2SO4 Content 7 000.0 21.2 9.3 17.5 24.6 11.3 4.5 0.7 64 000.0 表 2 煤渣的成分含量
Table 2. Composition of honeycomb cinde
/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 MnO SO3 K2O CaO TiO2 其他 40.59 15.57 16.09 0.98 1.05 1.78 14.96 2.33 4.32 -
[1] ADAMCZUK A, KOLODYNSKA D. Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies on removal of chromium, copper, zinc and arsenic from aqueous solutions onto fly ash coated by chitosan [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 274: 200-212. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.088
[2] WAN P, YUAN M, YU X, et al. Arsenate removal by reactive mixed matrix PVDF hollow fiber membranes with UIO-66 metal organic frameworks [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 382: 122921. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122921
[3] CUONG D V, WU P-C, CHEN L-I, et al. Active MnO2/biochar composite for efficient As(Ⅲ) removal: Insight into the mechanisms of redox transformation and adsorption [J]. Water Research, 2020, 188: 116495.
[4] MANI P, KIM Y, LAKHERA S K, et al. Complete arsenite removal from groundwater by UV activated potassium persulfate and iron oxide impregnated granular activated carbon [J]. ChemospHere, 2021, 277: 130225. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130225
[5] ZENG Q, ZHONG H, HE Z, et al. Efficient removal of arsenite by a composite of amino modified silica supported MnO2/Fe-Al hydroxide (SNMFA) prepared from biotite [J]. Journal of environmental management, 2021, 291: 112678. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112678
[6] GOSWAMI A, RAUL P K, PURKAIT M K. Arsenic adsorption using copper (Ⅱ) oxide nanoparticles [J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2012, 90(9): 1387-1396. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2011.12.006
[7] HASSAN A F, ABDEL-MOHSEN A M, ELHADIDY H. Adsorption of arsenic by activated carbon, calcium alginate and their composite beads [J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2014, 68: 125-130. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.04.006
[8] LI Y, QI X, LI G, et al. Double-pathway arsenic removal and immobilization from high arsenic-bearing wastewater by using nature pyrite as in situ Fe and S donator [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 410: 128303. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.128303
[9] DE KLERK R J, FELDMANN T, DAENZER R, et al. Continuous circuit coprecipitation of arsenic(Ⅴ) with ferric iron by lime neutralization: The effect of circuit staging, co-ions and equilibration pH on long-term arsenic retention [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2015, 151: 42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.11.003
[10] ZHANG S-L, JIA S-Y, YU B, et al. Sulfidization of As(Ⅴ)-containing schwertmannite and its impact on arsenic mobilization [J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 420: 270-279. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.11.020
[11] GIERE R, SIDENKO N V, LAZAREVA E V. The role of secondary minerals in controlling the migration of arsenic and metals from high-sulfide wastes (Berikul gold mine, Siberia) [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2003, 18(9): 1347-1359. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(03)00055-6
[12] KEMPAHANUMAKKAGARI S, DEEP A, KIM K-H, et al. Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors for arsenic- A review [J]. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2017, 95: 106-116.
[13] MALEKPOUR A, KHODADADI M. Albumin-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as an efficient sorbent for removal of Pb(Ⅱ), Cd(Ⅱ), Cu(Ⅱ) and Cr(Ⅵ) ions from aqueous solutions [J]. Rsc Advances, 2016, 6(18): 14705-14711. doi: 10.1039/C5RA22600G
[14] SALDANA ROBLES A, SALDANA ROBLES N, SALDANA ROBLES A L, et al. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions and the impact of humic and fulvic acids [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 159: 425-431. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.074
[15] SANCHEZ J, BUTTER B, CHAVEZ S, et al. Quaternized hydroxyethyl cellulose ethoxylate and membrane separation techniques for arsenic removal [J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2016, 57(52): 251619.
[16] ZHANG L, CHEN S, WANG L, et al. Application of Membrane Separation Technology in Wastewater Treatment of Iron and Steel Enterprise [M]//IKHMAYIES S, LI B, CARPENTER J S, et al. Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials, 2017. 2017: 545-551.
[17] ZHOU J, XU H, TONG Z, et al. Photo/pH-controlled host-guest interaction between an azobenzene-containing block copolymer and water-soluble pillar [6] arene as a strategy to construct the "compound vesicles" for controlled drug delivery [J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2018, 89: 237-244. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.04.010
[18] XI Y, ZOU J, LUO Y, et al. Performance and mechanism of arsenic removal in waste acid by combination of CuSO4 and zero-valent iron [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 375: 121928. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.121928
[19] XI Y, ZOU J, LUO Y, et al. Performance and mechanism of arsenic removal in waste acid by combination of CuSO4 and zero-valent iron [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 375: 121928. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.121928
[20] 易求实. 三段石灰-铁盐法处理高砷洗气污酸废水[J]. 湖北第二师范学院学报, 2011, 28(8): 24-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-344X.2011.08.009
[21] OCINSKI D, JACUKOWICZ-SOBALA I, MAZUR P, et al. Water treatment residuals containing iron and manganese oxides for arsenic removal from water-Characterization of physicochemical properties and adsorption studies [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 294: 210-221. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.111
[22] 邓凡政, 何家红. 煤渣除砷性能研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 1995(3): 22-23, 17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS503.005.htm
[23] 李娟, 刘新春, 余志晟, 等. 煤渣吸附水中氟和砷的研究[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2014, 31(4): 471-479. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB201404005.htm
[24] SARKAR C, BASU J K, SAMANTA A N. Removal of Ni2+ ion from waste water by Geopolymeric Adsorbent derived from LD Slag [J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2017, 17: 237-244. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2017.04.012
[25] JIN Z, ALI B S, TIANTIAN S, et al. Fe3O4 and MnO2 assembled on honeycomb briquette cinders (HBC) for arsenic removal from aqueous solutions [J]. Journal of hazardous materials, 2015, 286: 220-228. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.01.004
[26] 中国环境科学研究院固体废物污染控制技术研究所, 环境标准研究所. 危险废物鉴别标准浸出毒性鉴别[Z]. 中华人民共和国国家标准. 2007: 180p: A4
[27] GUO Z, PAN J, ZHU D, et al. Mechanism of composite additive in promoting reduction of copper slag to produce direct reduction iron for weathering resistant steel [J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 329: 55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.01.063
[28] XIAO HONG G, TINGZHI S, JIANMIN W. Quantifying effects of pH and surface loading on arsenic adsorption on NanoActive alumina using a speciation-based model [J]. Journal of hazardous materials, 2009, 166(1): 39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.10.121
[29] CHUANYONG J, SUQIN L, XIAOGUANG M. Arsenic leachability and speciation in cement immobilized water treatment sludge [J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 59(9): 1241-1247. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.039
[30] WANG S, ZHANG D, LI X, et al. Arsenic associated with gypsum produced from Fe(Ⅲ)-As(Ⅴ) coprecipitation: Implications for the stability of industrial As-bearing waste [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 360: 311-318. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.017
[31] CHAI L, YANG J, ZHANG N, et al. Structure and spectroscopic study of aqueous Fe(Ⅲ)-As(Ⅴ) complexes using UV-Vis, XAS and DFT-TDDFT[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 182: 595-604. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.018
[32] YANG J, CHAI L, YUE M, et al. Complexation of arsenate with ferric ion in aqueous solutions [J]. Rsc Advances, 2015, 5(126): 103936-103942. doi: 10.1039/C5RA21836E
[33] MARINKOV N, MARKOVA-VELICHKOVA M, GYUROV S, et al. Preparation and characterization of silicagel from silicate solution obtained by autoclave treatment of copper slag [J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2018, 87(2): 331-339. doi: 10.1007/s10971-018-4741-8
-



 下载:
下载: