Determination of Ultra-trace Potassium in High Purity Quartz by Low RF Power-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
-
摘要:
碱金属元素钾作为高纯石英产品中重要的杂质元素,其含量的准确测定对科学评价、开发高纯石英产品意义重大。采用常压混酸浸取—高温挥发除酸的方式进行高纯石英样品的化学前处理,基于电感耦合等离子体质谱仪,在低射频功率下,以50 ng/mL铷为内标元素,大幅消除了钾元素测定中背景产生的质谱干扰,实现了高纯石英样品中痕量钾元素的测定。对测试过程中的样品称样量、质谱测定中的射频功率、采样深度、载气流速等进行了条件优化。最终在称样量1.000 0 g、射频功率800 W、采样深度5.6 mm、载气流速1.06 L/min的最优条件下,经测定钾质量浓度在0.100~50 ng/mL范围内与其质谱强度呈线性相关,相关系数为0.999 6。以1.000 0 g称样量计,方法对高纯石英中钾的检出限为0.057 μg/g,定量限为0.191 μg/g。选择典型商品化高纯石英样品进行本方法的应用试验,每个样品平行测定9次,并进行加标回收率试验和方法比对试验,测定值与石墨炉原子吸收光谱法的测定结果基本一致,相对标准偏差(RSD)在2.9%~5.1%之间,加标回收率在96.4%~105.4%之间。
-
关键词:
- 高纯石英 /
- 钾 /
- 痕量分析 /
- 低射频功率 /
- 电感耦合等离子体质谱法
Abstract:Potassium (K) is an important impurity element in high-purity quartz and accurate determination of its content is of great significance for the evaluation of the quality of high-purity quartz products. Via ultra-trace K in high-purity quartz samples were dissolved by atmospheric acid dissolution method, an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) determination method for K was established and the interference of multi-atomic molecular ions was eliminated by cold plasma with low RF power in ICP-MS and 50 ng/mL rubidium was used as the internal standard elements in this process. Background interference in mass spectrometry for the determination of potassium was greatly eliminates. And the sample weight, RF power, sampling depth and atomized gas flow were optimized in this work. Finally, under the optimal conditions of 1.000 0 g of weight sample, 800 W of RF power, 5.6 mm of sampling depth and 1.06 L/min of atomized gas flow rate, K element standard series solutions were determined and the mass spectrometry intensity of K showed good linear relationship with ρ(K) in the range of 0.100~50 ng/mL with the correlation coefficients of calibration curve was 0.999 6. The detection limit and quantification limit of K in high-purity quartz were 0.057 μg/g and 0.191 μg/g, respectively. Typical commercial high-purity quartz samples were selected for the application experiment of this method, and the relative standard deviations (RSD) for 9 parallel measurements were between 2.9%~5.1% and the recoveries of K were between 96.4%~105.4%.
-

-
表 1 ICP-MS仪器工作参数
Table 1. The operation paramenters of ICP-MS instrument
仪器参数
Instrument paramenters数值
Value仪器参数
Instrument paramenters数值
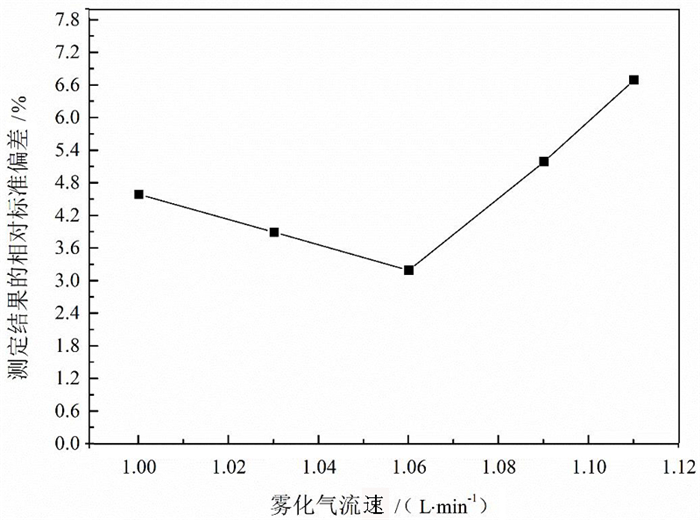
Value功率/W 800 数据采集方式 跳峰 采样深度/mm 5.6 扫描次数 30 冷却气流量/(L·min-1) 14 读数通道 1 辅助气流量/(L·min-1) 0.80 测量时间/ms 10 雾化气流量/(L·min-1) 1.06 表 2 样品化学前处理中酸试剂用量优化
Table 2. Dosage optimization of reagent in sample chemical pretreatment
试剂组合 1# 2# 3# 4# 5# 溶解试剂 HF+HNO3
(6+1)mLHF+ HNO3
(7+1)mLHF+HNO3
(8+1)mLHF+ HNO3
(9+1)mLHF+ HNO3
(10+1)mL样品溶解
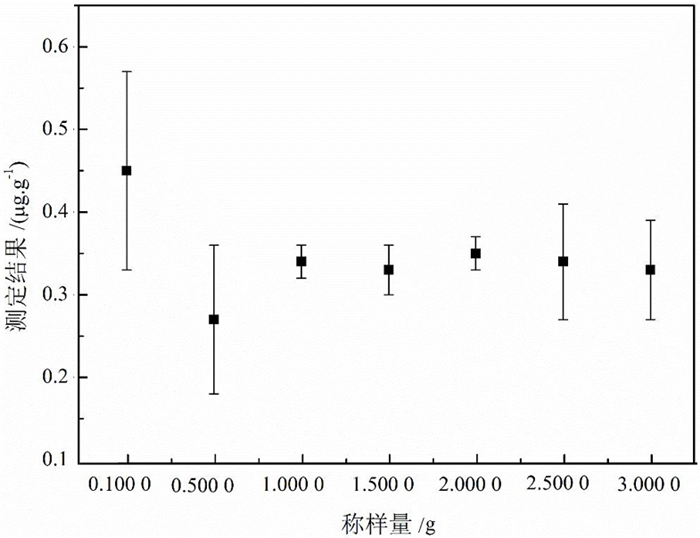
完全程度不完全 不完全 完全 完全 完全 K测定结果
/(μg·g-1)-- -- 0.34 0.33 0.34 RSD/% -- -- 4.04 3.77 3.97 表 3 钾元素同位素丰度及可能存在的质谱干扰
Table 3. Potassium isotopic abundance and possible mass spectrum interference
同位素 丰度/% 质谱干扰 39K 93.26 38Ar+1H,16O+23Na,12C+27Al,14N+25Mg,16O+1H+22Ne,15N+24Mg,16O+3H+20Ne,13C+26Mg 40K 0.01 40Ar,40Ca,16O+1H+23Na,1H+39K,12C+28Si,16O+24Mg,14N+26Mg,13C+27Al, 36Ar+4He 41K 6.73 40Ar+1H,14N+27Al,1H+40Ca,16O+1H+24Mg,16O+25Mg,12C+29Si,18O+23Na 表 4 质谱采样深度优化
Table 4. Optimization of sampling depths in ICP-MS
采样深度Sampling depth/mm 5.0 5.2 5.4 5.6 5.8 测定结果的相对标准偏差RSD(n=5)/% 4.9 4.6 3.6 3.2 5.3 表 5 高纯石英样品中钾的测定结果
Table 5. Determination results of Potassium in high purity quartz samples
样品
编号试验方法 GF-AAS
测定结果/
(μg·g-1)测定值/
(μg·g-1)相对标
准偏差
(n=9)/%加入量/
(μg·g-1)测得总量/
(μg·g-1)回收率/% 样品1 0.33 3.2 5 5.19 97.2 0.29 样品2 0.62 5.1 5 5.44 96.4 0.64 样品3 0.33 3.7 5 5.45 102.4 0.35 样品4 0.08 2.9 5 5.17 101.8 0.11 样品5 1.39 3.3 5 6.33 98.8 1.42 样品6 2.19 3.6 5 7.46 105.4 2.17 样品7 0.80 4.8 5 5.62 96.4 0.77 -
[1] 李光惠, 王超峰, 詹建华, 等. 高纯石英原料作为战略性矿产的分析及建议[J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2020(5): 20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2020.05.006
LI G H, WANG C F, ZHAN J H, et al. Analysis and suggestions on high purity quartz raw material as strategic minerals[J]. China Non-metallic Minerals Industry, 2020(5): 20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2020.05.006
[2] 贾德龙, 张万益, 陈丛林, 等. 高纯石英全球资源现状与我国发展建议[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2019, 39(5): 111-117. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=e759486c-8f66-4a5b-b137-23322ead3cfb
JIA D L, ZHANG W Y, CHEN C L, et al. Global resource status and China's development suggestions of high purity quartz[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019, 39(5): 111-117. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=e759486c-8f66-4a5b-b137-23322ead3cfb
[3] 汪灵, 党陈萍, 李彩侠, 等. 中国高纯石英技术现状与发展前景[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(5): 267-273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201405026.htm
WANG L, DANG C P, LI C X, et al. Technology of high-purity quartz in China: status quo and prospect[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(5): 267-273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201405026.htm
[4] 颜玲亚, 刘艳飞, 于海军, 等. 中国高纯石英资源开发利用现状及供需形势[J]. 国土资源情报, 2020(10): 98-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTZQ202010017.htm
YAN L Y, LIU Y F, YU H J, et al. Development and utilization status and supply and demand situation of high purity quartz resources[J]. Land and Resources Information, 2020(10): 98-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTZQ202010017.htm
[5] GÖTZE J. Chemistry, textures and physical properties of quartz-geological interpretation and technical application[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2009, 73(4): 645-671.
[6] 廊坊市市场监督管理局. 电子专用材料单晶硅生长用石英坩埚工艺技术规范: DB 1310/T 227-2020[S]. 2020.
Langfang Market Supervision Administration. Technical specification for quartz crucible process for growth of monocrystalline silicon for special electronic materials: DB1310/T 227-2020[S]. 2020.
[7] 湖南省经信委. 高纯(SiO2 ≥ 99.997%)石英砂: DB43/T 1167-2016[S]. 2016.
Hunan Provincial Economic and Information Commission. High purity (SiO2 ≥ 99.997%) quartz sand: DB43/T 1167-2016[S]. 2016.
[8] 全国半导体设备和材料标准化技术委员会. 光伏用高纯石英砂: GB/T 32649-2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
Semiconductor Equipment and Materials. High purity arenaceous quartz used in photovoltaic applications: GB/T 32649-2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[9] 全国半导体设备和材料标准化技术委员会. 电感耦合等离子质谱法检测石英砂中痕量元素: GB/T 32650-2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
Semiconductor Equipment and Materials. Determining the content of trace elements in arenaceous quartz by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS): GB/T 32650-2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[10] 全国工业陶瓷标准化技术委员会功能陶瓷分技术委员会. 高纯石英中杂质含量的测定方法会电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法: JC/T 2027-2010[S]. 2010.
Functional Ceramics, Determination of impurities in high purity quartz-Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry: JC/T 2027-2010[S]. 2010.
[11] 全国工业玻璃和特种玻璃标准化技术委员会. 石英玻璃中羟基含量检验方法: GB/T 12442-2019[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2019.
Industrial Glass and Special Glass. Test method for the hydroxyl groups content of silica glass: GB/T 12442-2019[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2019.
[12] 张金明, 胡艳巧, 魏利, 等. 聚氧化乙烯絮凝-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱(ICP-AES)法测定土壤中水溶性钾、钠、钙、镁、硫酸根[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2022, 12(2): 40-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX202202006.htm
ZHANG J M, HU Y Q, WEI L, et al, Polyethylene oxide flocculation-simultaneous determination of water-soluble potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium and sulfate in soil by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 12(2): 40-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX202202006.htm
[13] 樊颖果, 徐国津. 原子吸收光谱和原子发射光谱法测定酸雨中钾、钠、钙、镁方法比较[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2013, 3(2): 28-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX201302014.htm
FAN Y G, XUE G J, Comparison of atomic absorption spectrometry and atomic emission spectrometry for determination of potassium, sodium, calcium and magnesium in acid rain[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 3(2): 28-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX201302014.htm
[14] 郭红巧, 胡净宇, 侯艳霞, 等. 电感耦合等离子体串联质谱法测定高温合金中痕量磷和硫[J]. 冶金分析, 2021, 41(11): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202111001.htm
GUO H Q, HU J Y, HOU Y Z, et al, Determination of trace phosphorus and sulfur in superalloys by inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2021, 41(11): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202111001.htm
[15] 张宏丽, 倪文山, 刘磊, 等. 冷焰模式-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定高纯石英中痕量铁[J]. 冶金分析, 2021, 41(7): 28-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202107007.htm
ZHANG H L, NI W S, LIU L, et al. Determination of ultra-trace iron in high-purity quartz by cool flame mode-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2021, 41(7): 28-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202107007.htm
[16] 高小红. ICP-MS测定地球化学样品中多原子分子离子干扰消除技术的研究及方法应用[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2016.
GAO X H. Study on the elimination of polyatomic molecule ion interferences by ICP-MS for geochemical samples[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2016.
[17] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0130-2006地质矿产实验室测试质量管理规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006.
Ministry of Land and Resources, PRC. DZ/T 0130-2006 The specification of testing quality management for geological laboratories[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006.
-



 下载:
下载: