Application of a Novel Inorganic Activator X-43 in Flotation of Germanium-bearing Sphalerite
-
摘要:
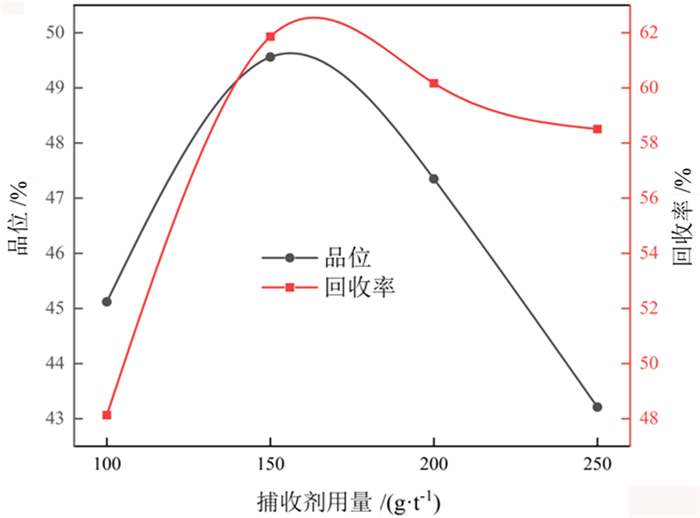
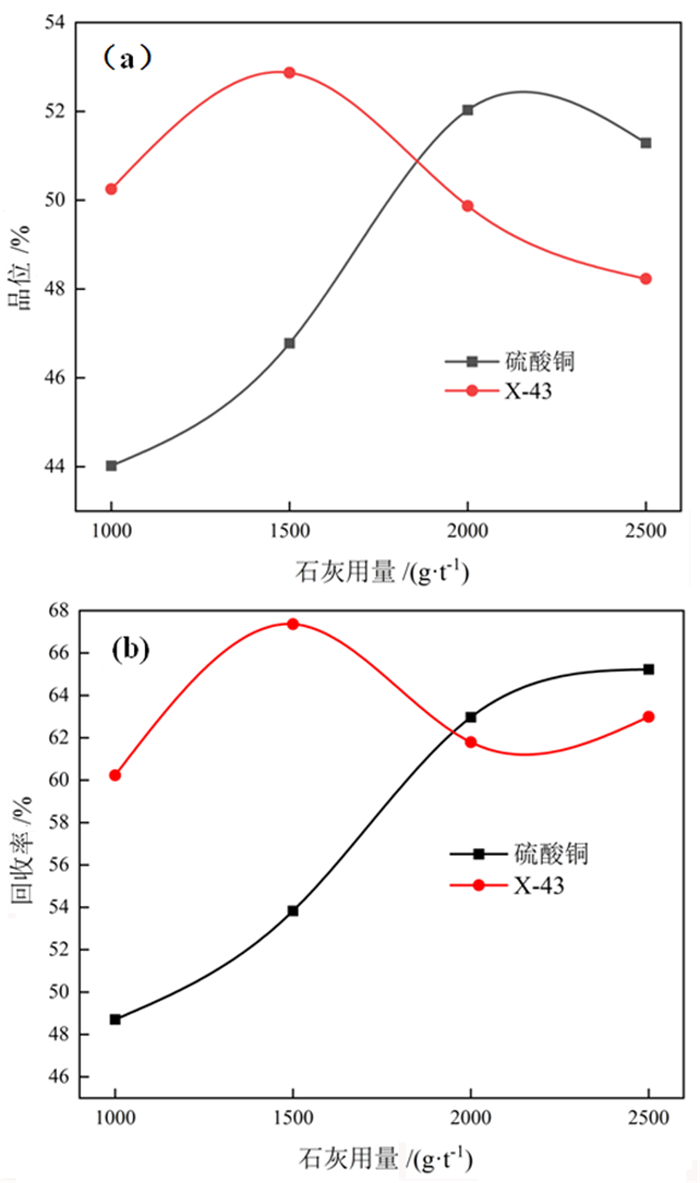
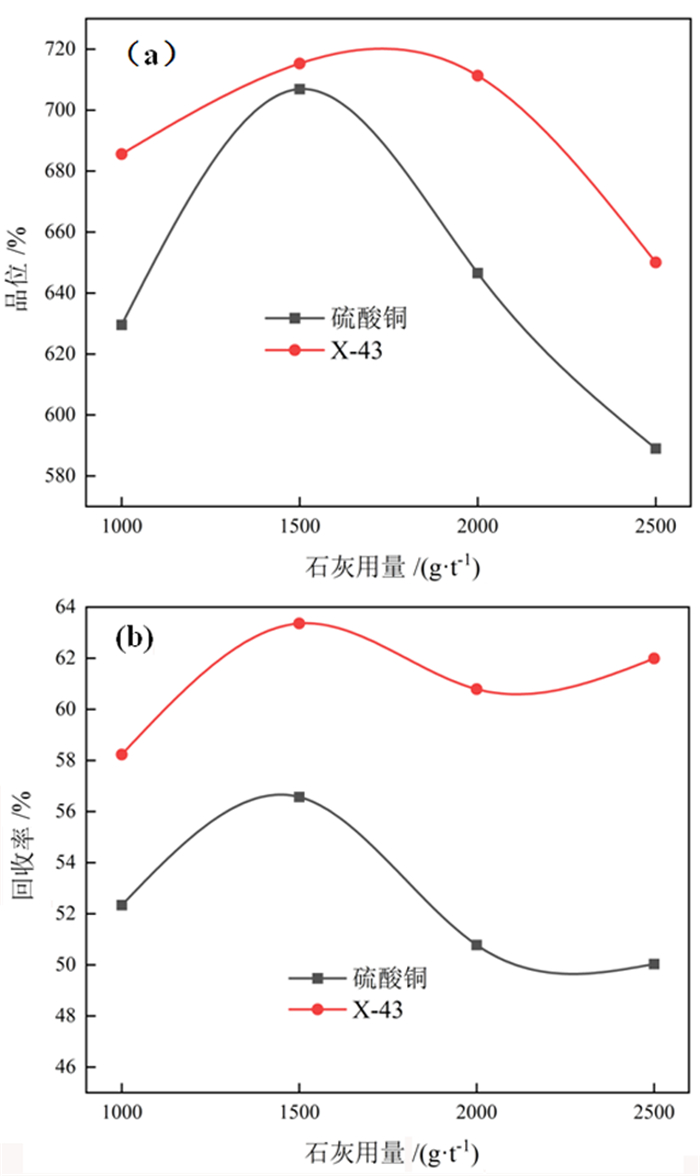
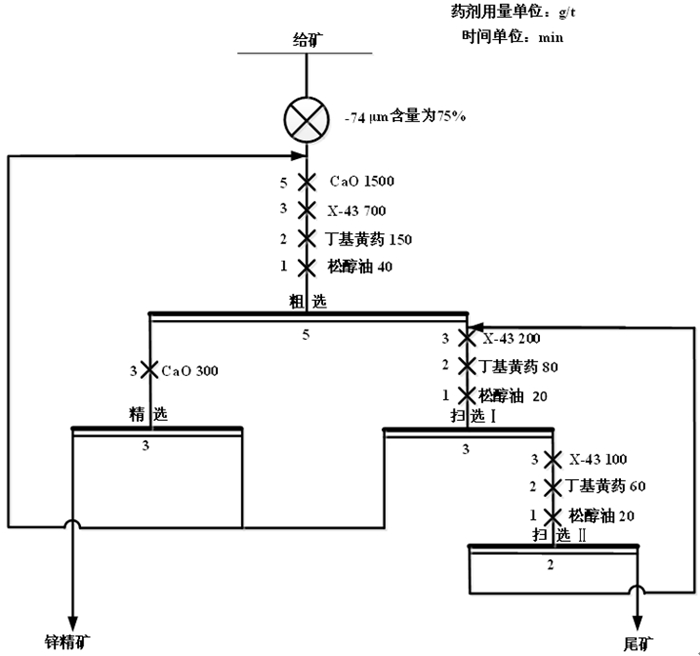
对贵州某载锗闪锌矿进行了锌活化剂优化试验研究, 用新型无机活化剂X-43与传统活化剂硫酸铜进行了对比。在石灰用量1 500 g/t、X-43活化剂用量700 g/t、捕收剂用量150 g/t的最佳条件下, 锌精矿中锌的品位和回收率分别为52.87%和67.24%, 锗的品位和回收率分别为715.30 g/t和63.36%。与使用硫酸铜相比, 使用X-43获得的锌精矿中锌品位高0.83百分点, 锌回收率高4.27百分点; 锗品位高8.4 g/t, 锗回收率高6.79百分点。试验结果表明, 相比传统的活化剂硫酸铜, 新型活化剂X-43的活化能力更强, 选择性更好。
Abstract:The optimization tests of zinc activator were carried out with a germanium-bearing sphalerite ore in Guizhou. The comparative tests were carried out with the novel inorganic activator X-43 and the traditional activator copper sulfate. Under the optimal conditions of lime dosage of 1 500 g/t, X-43 activator dosage of 700 g/t and collector dosage of 150 g/t, the grade and recovery of zinc in zinc concentrate were 52.87% and 67.24% respectively, and the grade and recovery of germanium were 715.30 g/t and 63.36% respectively. Compared with the use of copper sulfate, the zinc grade obtained by using X-43 increased 0.83 percent, and the zinc recovery increased 4.27 percent; the germanium grade increased 8.4 g/t, and the germanium recovery increased 6.79 percent. The results showed that compared with the traditional activator copper sulfate, the novel activator X-43 has stronger activation ability and better selectivity.
-
Key words:
- germanium /
- sphalerite /
- x-43 /
- copper sulfate /
- activator /
- flotation
-

-
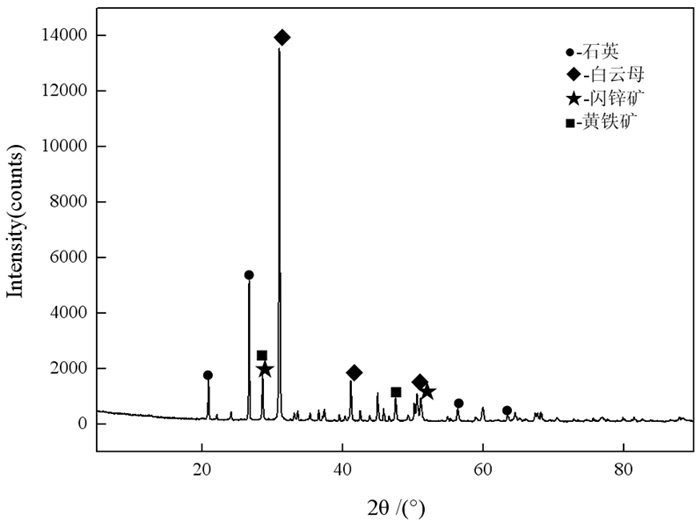
表 1 原矿化学多项分析(质量分数)结果
Table 1. Chemical multi-element analysis results (mass fraction) of the raw ore
/% 成分 MgO Al2O3 SiO2 S CaCO3 Fe Zn Ge 含量 12.04 6.98 35.66 2.44 34.79 1.98 6.01 91.00 注:Ge含量单位为g/t。 表 2 原矿锌物相分析结果
Table 2. Zinc phase analysis results of the raw ore
/% 物相 硫酸锌 氧化锌 硫化锌 锌铁尖晶石 总锌 含量 0.077 0.81 5.19 0.023 6.01 分布率 0.14 13.27 86.21 0.38 100.00 表 5 闭路试验结果
Table 5. Results of the closed-circuit tests
产品名称 产率/% 品位 回收率 Zn/% Ge/(g·t-1) Zn/% Ge/(g·t-1) 精矿 10.18 51.55 796.56 85.95 84.72 尾矿 89.82 0.98 13.73 14.05 15.28 给矿 100.00 6.07 93.00 100.00 100.00 -
[1] 刘建. 闪锌矿表面原子构型及铜吸附活化浮选理论研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2013.
LIU J. Theoretical study on surface atomic configuration and copper adsorption activation flotation of sphalerite[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Technology, 2013.
[2] 顾帼华, 王淀佐, 刘如意. 硫酸铜活化闪锌矿的电化学机理[J]. 长沙: 中南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 1999(4): 374-377. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD904.010.htm
GU J H, WANG D Z, LIU R Y. Electrochemical mechanism of copper sulfate activated sphalerite[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 1999(4): 374-377. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD904.010.htm
[3] 余润兰, 邱冠周, 胡岳华, 等. Cu2+活化铁闪锌矿的电化学[J]. 金属矿山, 2004(2): 35-37+40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS200402010.htm
YU R L, QIU G Z, Hu Y H, et al. Electrochemical activation of sphalerite by Cu2+[J]. Metal mines, 2004(2): 35-37+40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS200402010.htm
[4] 童雄, 何剑, 饶峰, 等. 云南都龙铁闪锌矿的活化试验研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2006(4): 19-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC200604005.htm
TONG X, HE J, RAO F, et al. Experimental study on activation of Yunnan Dulong iron sphalerite[J]. Mining and metallurgy engineering, 2006(4): 19-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC200604005.htm
[5] 王淀佐, 邱冠周, 胡岳华. 资源加工学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005.
WANG D Z, QIU G Z, HU Y H. Resource processing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005.
[6] 马原琳, 杨子轩, 谢贤, 等. X-45与硫酸铜的活化行为对比[J]. 有色金属工程, 2018(4): 90-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YOUS201804018.htm
MA Y L, YANG Z Y, XIE X, et al. Comparison of activation behavior between X-45 and copper sulfate[J]. Nonferrous metal engineering, 2018(4): 90-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YOUS201804018.htm
[7] 杨子轩. 新型高效活化剂X-45对铁闪锌矿浮选行为影响的研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2017.
YANG Z Y. Study on the effect of new efficient activator X-45 on the flotation behavior of marmatite[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Technology, 2017.
[8] 邓政斌. 载铟、载锗及普通闪锌矿表面的浮选药剂吸附特性与机理研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2015.
DENG Z B. Adsorption characteristics and mechanism of flotation reagents on the surface of indium, germanium and ordinary sphalerite[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2015.
-



 下载:
下载: