Effect of Nano Iron Powder-ammonium Persulfate Oxidation Pretreatment on Non-Cyanide Leaching of a Fine Disseminated Gold Ore and Quantum Chemical Calculation
-
摘要:
以微细浸染型原生金矿石为研究对象,采用纳米铁粉(nZVI)-/过硫酸铵(APS)体系氧化预处理载金黄铁矿后加入非氰浸金剂,并运用量子化学计算nZVI-APS体系产生的中间体
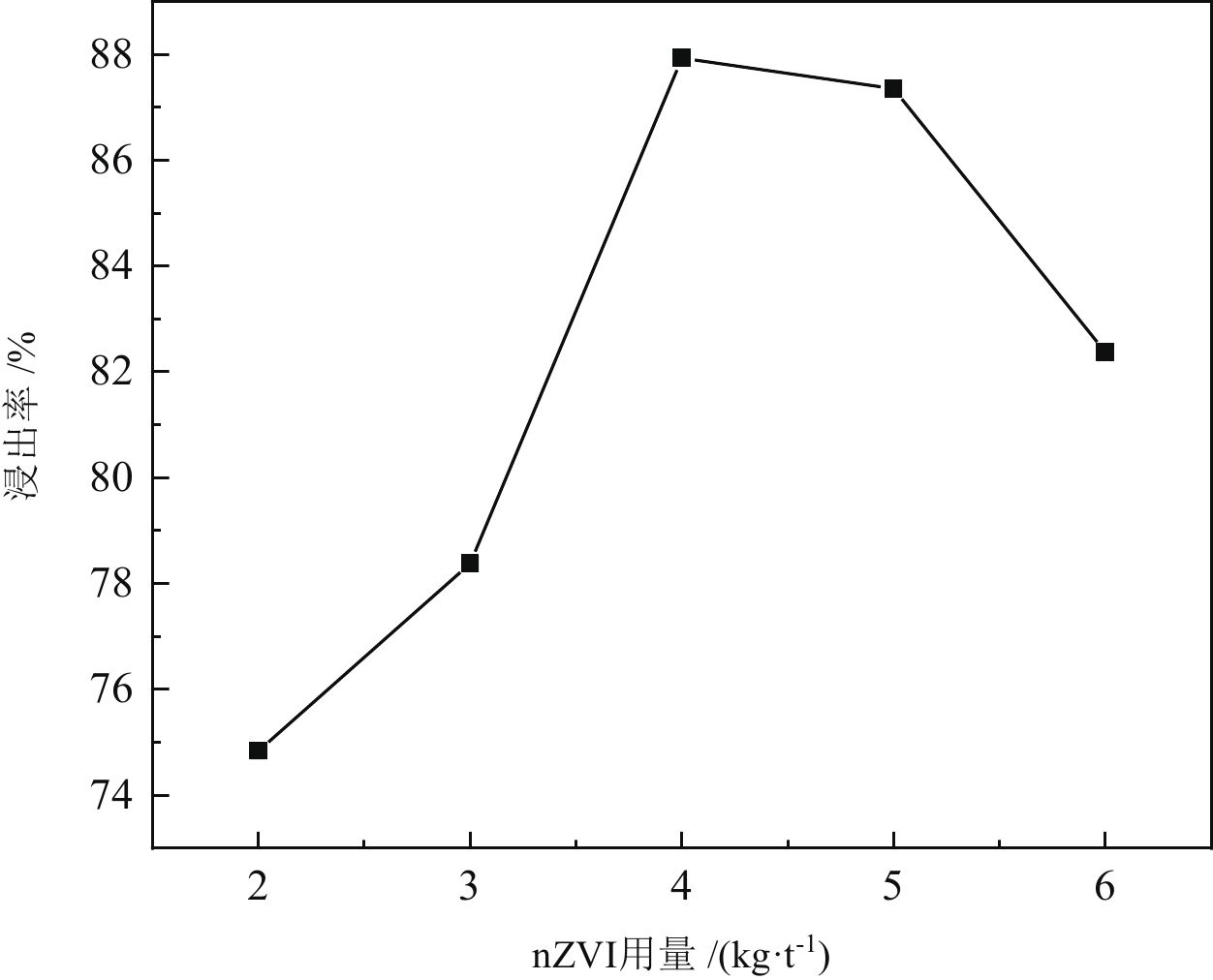
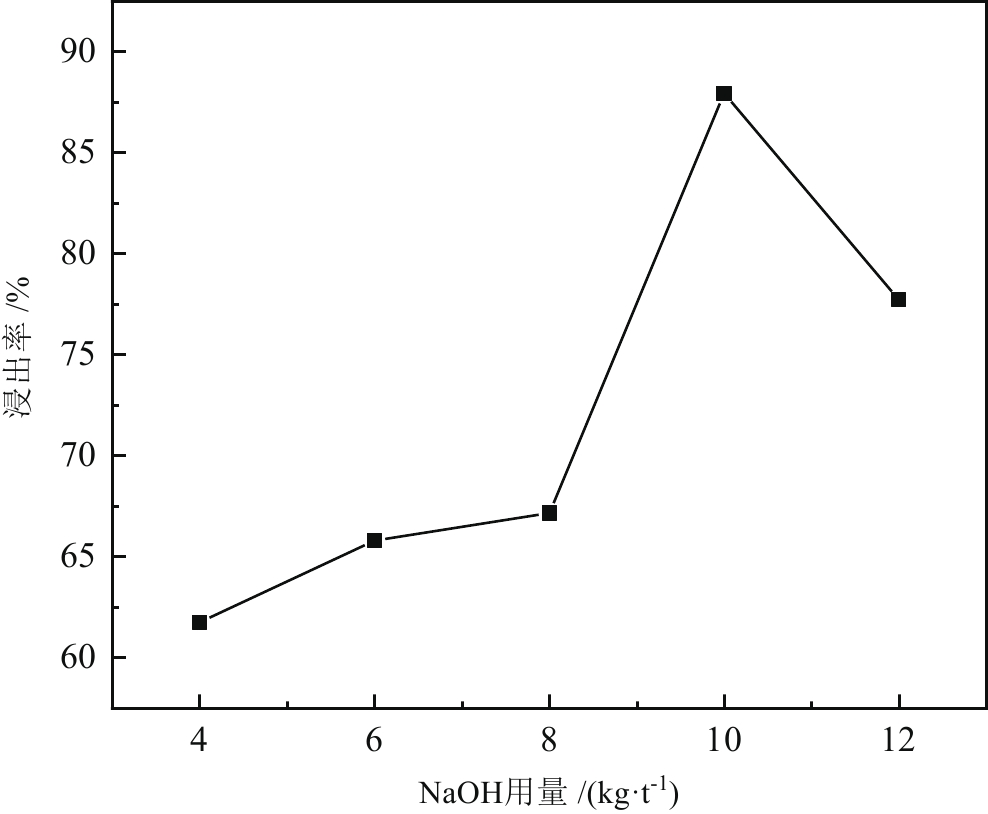
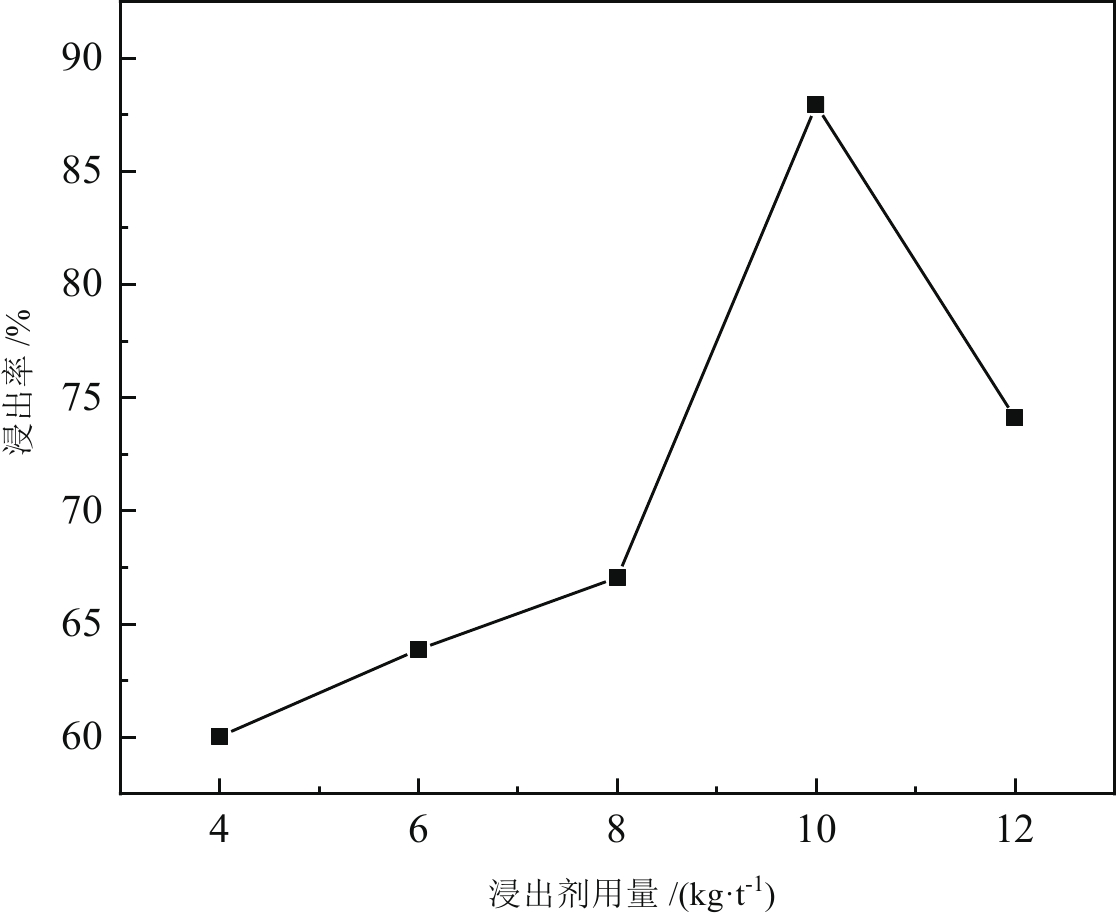
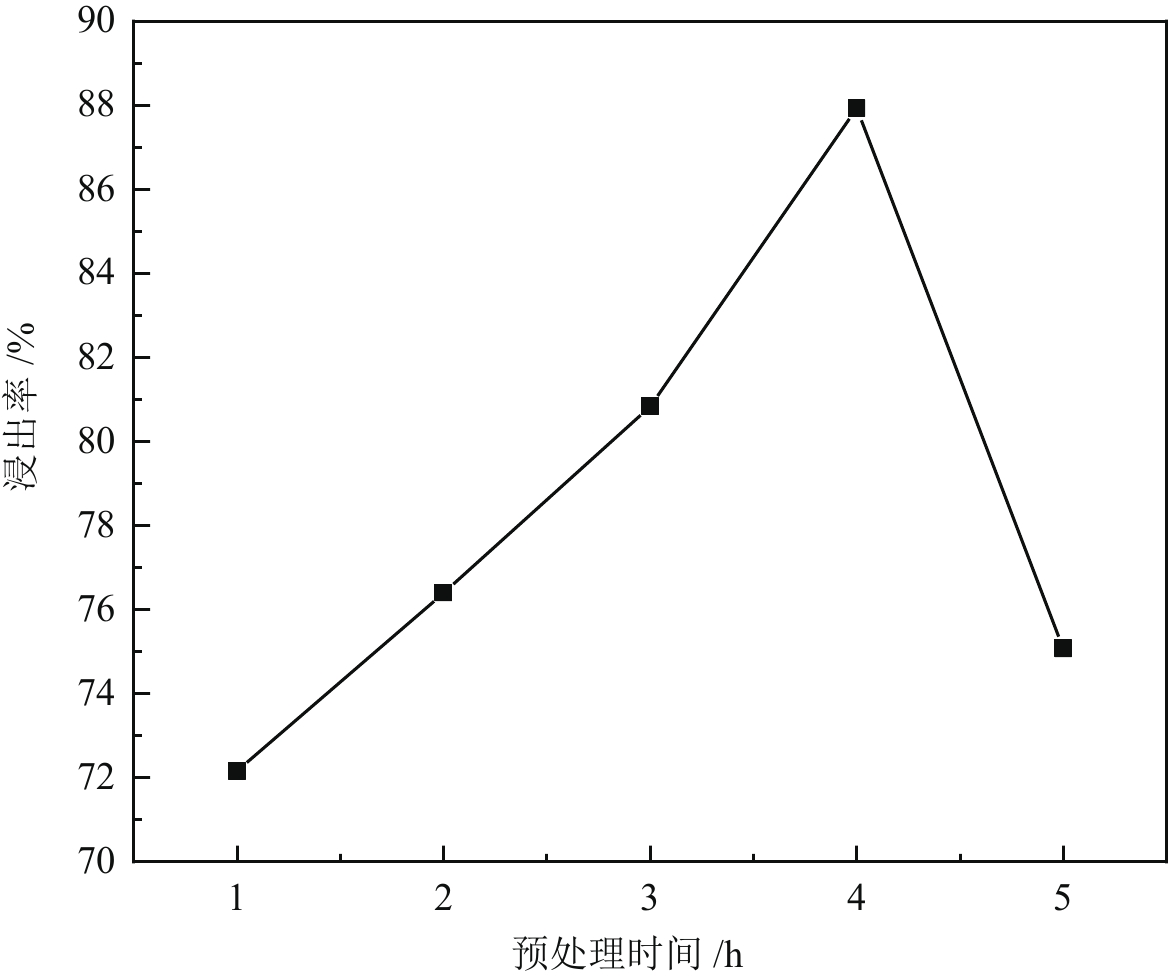
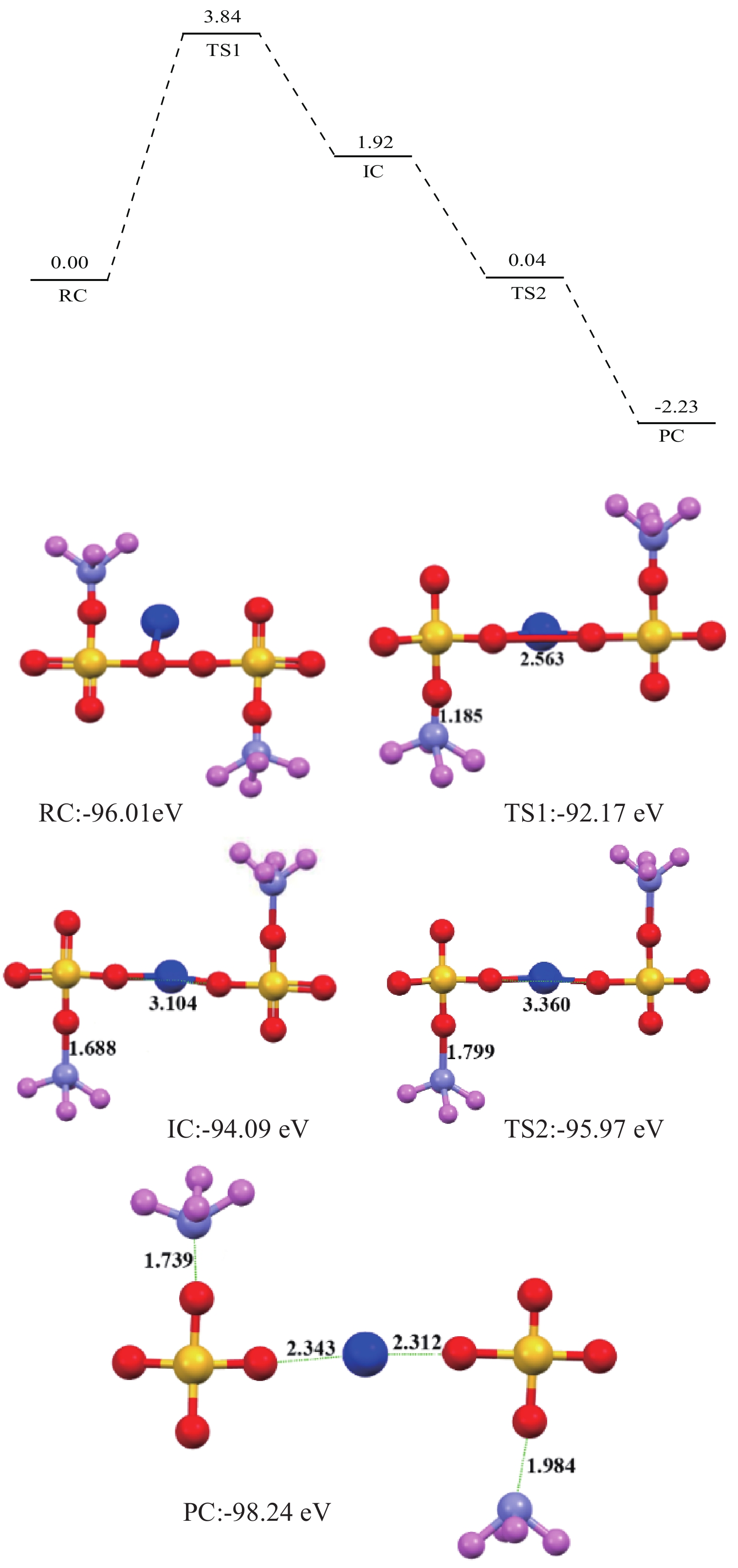
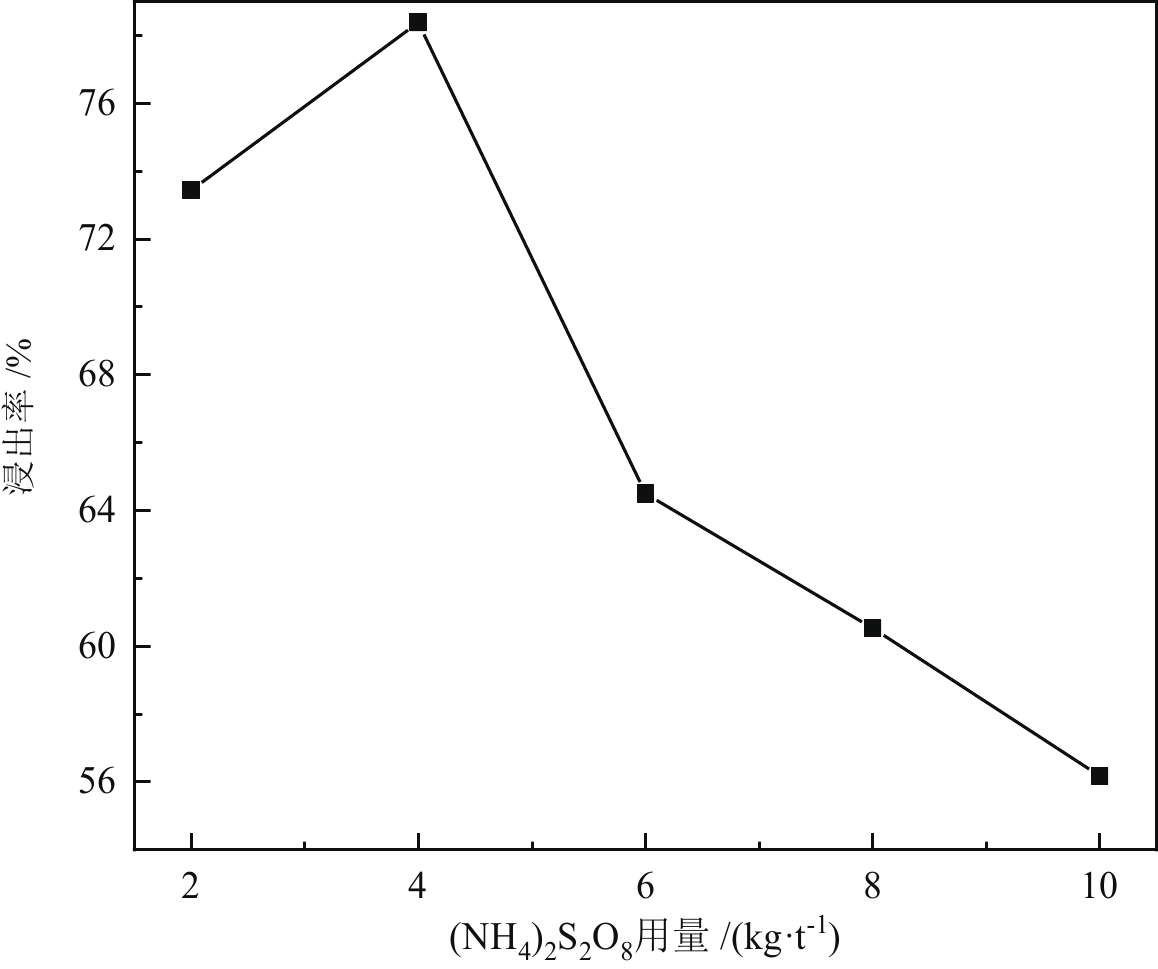
< span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > ${\rm{SO}}_{4}^-\cdot $ < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='2022-08-0016_Z-20230331175138.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='2022-08-0016_Z-20230331175134.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='2022-08-0016_Z-20230331175128.png'/ > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > ${\rm{SO}}_{4}^-\cdot $ < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='2022-08-0016_Z-20230331175138.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='2022-08-0016_Z-20230331175134.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='2022-08-0016_Z-20230331175128.png'/ > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > < span class="inline-formula-span" > ${\rm{SO}}_{4}^-\cdot $ < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='2022-08-0016_Z-20230331175138.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='2022-08-0016_Z-20230331175134.png'/ > < /span > < img text_id='' class='formula-img' style='display:none;' src='2022-08-0016_Z-20230331175128.png'/ > Abstract:A micro-disseminated primary gold ore was taken as the research object and the gold-bearing pyrite was pretreated with the nano iron powder (nZVI)-ammonium persulfate (APS) system before treated with a non-cyanide leaching agent. The reaction path of oxidized pyrite enhanced by the intermediate SO4−∙ produced by nZVI-APS system, was calculated by quantum chemical calculation. The results showed that the leaching rate of gold reached 87.93% under the conditions of APS dosage of 4 kg/t, nZVI dosage of 4 kg/t, pretreatment time of 4 h, NaOH dosage of 10 kg/t, leaching agent of gold cicada dosage of 10 kg/t, and leaching time of 2 h. Notably, quantum chemical calculations revealed that the reaction path of oxidation pretreatment of pyrite in the nZVI-APS system was the first transition state (TS1) → intermediate (IC) → second transition state (TS2), where TS1 was the rate-controlling step for the production of SO4−∙ in the system. Specifically, Fe2+ adsorbed with the S atom, O atom, and O bridge bond in APS, with the adsorption bond on the O bridge bond exhibiting the most stability. Additionally, the SO4−∙ could oxidize Fe and S in pyrite, with Fe serving as the main active site.
-

-
表 1 不同吸附点位吸附能计算结果
Table 1. Calculation results of adsorption energy at different adsorption sites
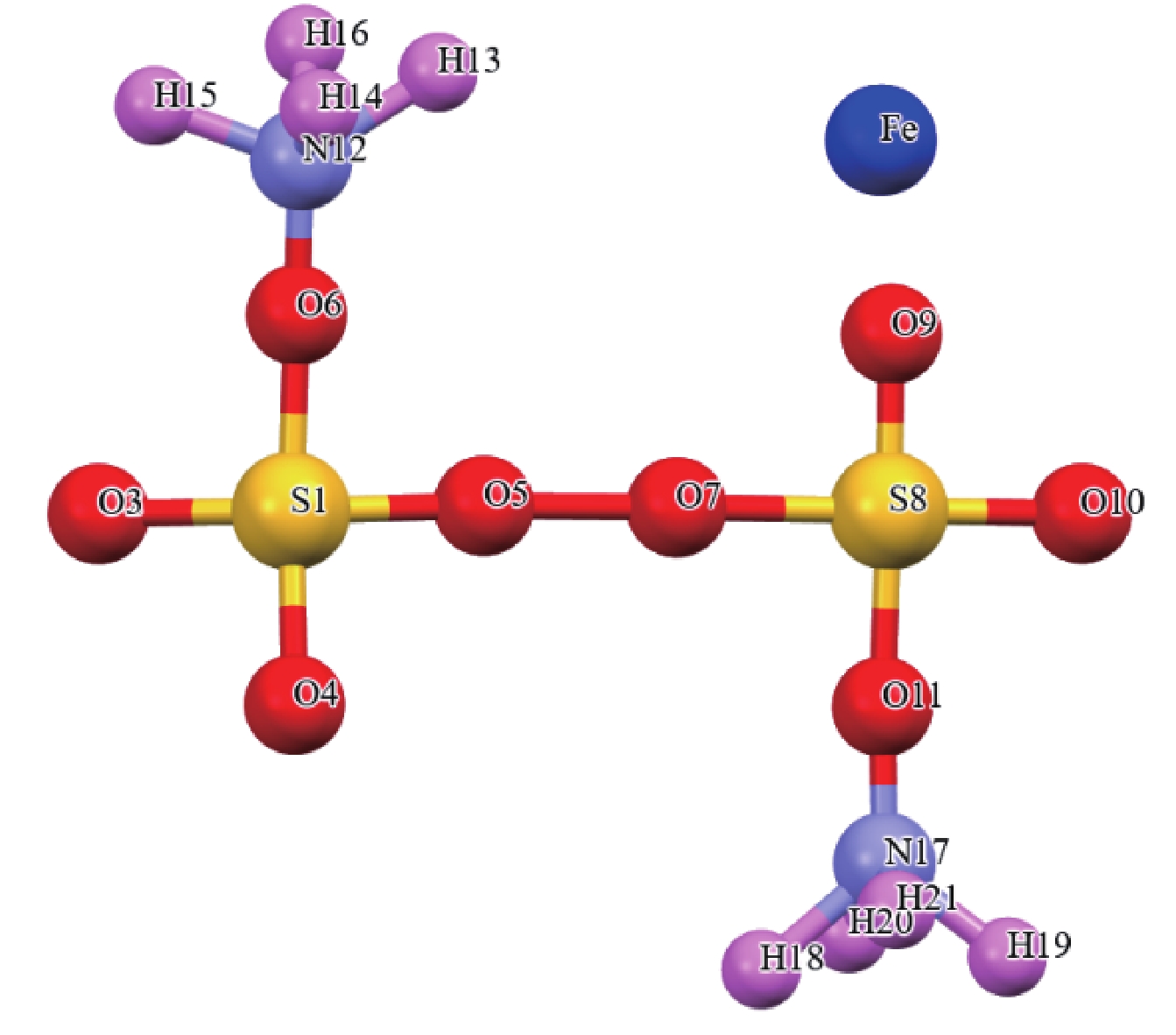
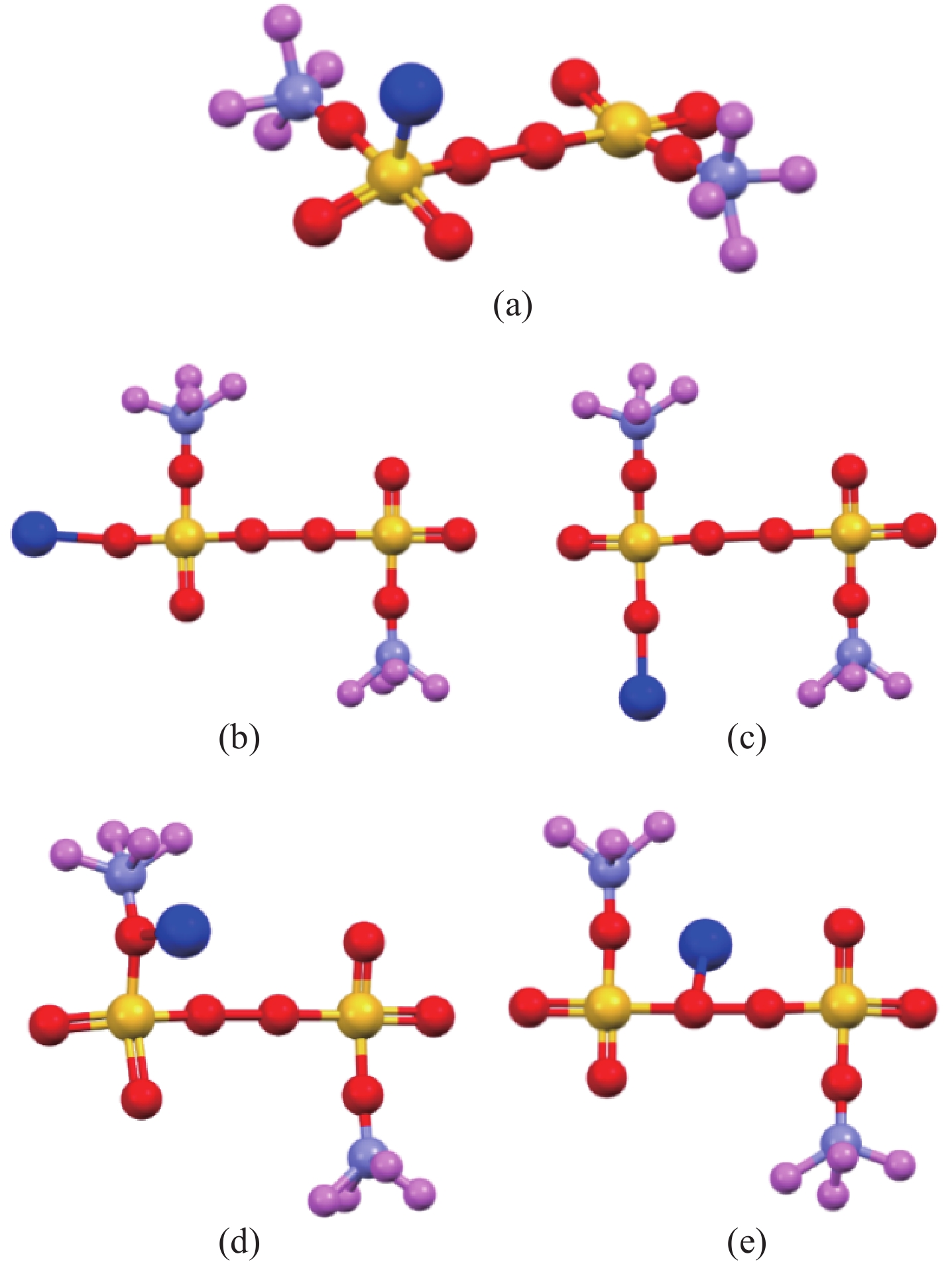
/eV 能量 S点位 O1点位 O2点位 O3点位 O桥键点位 EAPS-Fe2+ −87.37 −92.14 −91.72 −89.26 −95.41 Eads 0.59 −4.18 −3.76 −1.29 −7.45 表 2 不同吸附点位APS构型的键长
Table 2. Bond lengths (Å) of APS configurations at different adsorption sites
/Å 键 S点位 O1点位 O2点位 O3点位 O桥键点位 S1-O2 1.488 1.508 1.508 1.508 1.508 S1-O4 1.575 1.492 1.616 1.616 1.492 S8-O9 1.373 1.334 1.334 1.373 1.334 O5-O7 1.480 1.480 1.480 1.480 1.345 O6-N12 1.246 1.185 1.185 1.213 1.185 N12-H13 1.228 1.228 1.228 1.228 1.228 Fe2+-吸附点位 1.683 1.876 1.752 1.993 2.082 表 3 黄铁矿晶格参数
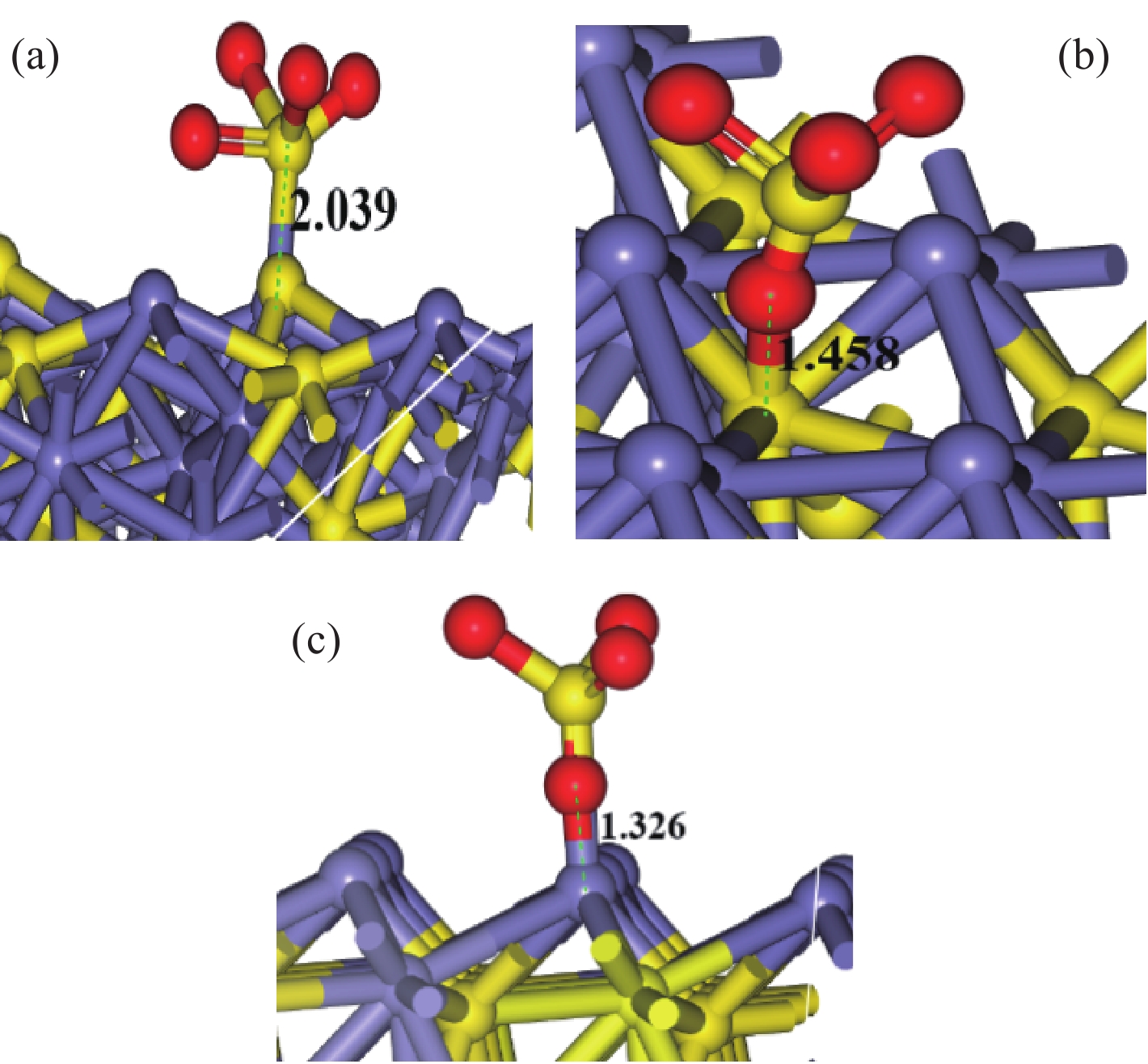
Table 3. Pyrite lattice parameters
a=b=c α=β=γ 5.4281 Å 90° 表 4 黄铁矿原子位置
Table 4. Pyrite atomic positions
Atom X Y Z Fe 0 0 1 S 0.38504 0.38504 0.38504 -
[1] 中国黄金年鉴: 我国黄金资源量连续15年增长[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2021, 29(4): 611.
China Gold Yearbook: China's gold resources have increased for 15 consecutive years[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2021, 29(4): 611.
[2] 李夕兵, 周健, 黄麟淇, 等. 中国黄金矿山开采技术回顾与展望[J]. 黄金, 2020, 41(9): 41−50.
LI X B, ZHOU J, HUANG L Q, et al. Review and prospect of gold mining technology in China[J]. Gold, 2020, 41(9): 41−50.
[3] 牛翠祎, 刘烊, 张岱. 中国金矿成矿地质特征、预测模型及资源潜力[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(3): 1−12.
NIU C W, LIU Y, ZHANG D. Metallogenic geological features, prediction models and resources potential of gold deposits in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(3): 1−12.
[4] 牛会群, 佟琳琳, 衷水平, 等. 卡林型金矿碳质物特征及其去碳方法研究现状[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2019(6): 33−39.
NIU H Q, TONG L L, ZHONG S P, et al. Research status on carbonaceous matter characteristic and decarbonization of carlin-type gold ore[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2019(6): 33−39.
[5] 崔毅琦, 陈海亮, 董鹏, 等. 卡林型金矿预处理技术研究现状[J]. 黄金, 2014, 35(10): 61−63. doi: 10.11792/hj20141014
CUI Y Q, CHEN H L, DONG P, et al. Research on the status of pretreatment techniques for carlin-type gold deposits[J]. Gold, 2014, 35(10): 61−63. doi: 10.11792/hj20141014
[6] 张博, 李诺, 陈衍景. 热液矿床金的赋存状态及研究方法[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(5): 251−265.
ZHANG B, LI N, CHEN Y J. Occurrence state of gold in hydrothermal deposits and related research methods[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(5): 251−265.
[7] 刘一浩, 薛春纪, 赵云, 等. 我国热液金矿中黄铁矿的载金性研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(1): 1−12.
LIU Y H, XUE C J, ZHAO Y, et al. Research on auriferous pyrite in hydrothermal gold deposits, China[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(1): 1−12.
[8] 董再蒸, 韩跃新, 高鹏. 卡林型金矿化学氧化预处理技术研究现状[J]. 金属矿山, 2015(12): 92−97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2015.12.021
DONG Z Z, HAN Y X, GAO P. Research status on chemical pre-oxidation for carlin-type gold ore[J]. Metal Mine, 2015(12): 92−97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2015.12.021
[9] 吴冰. 复杂难处理金矿石预处理工艺研究现状及进展[J]. 黄金, 2020, 41(5): 65−72. doi: 10.11792/hj20200513
WU B. Current status and progress of the research on complex refractory gold ore pretreatment technology[J]. Gold, 2020, 41(5): 65−72. doi: 10.11792/hj20200513
[10] KOOHESTANI B, DARBAN A K, MOKHTARI P, et al. Influence of hydrofluoric acid leaching and roasting on mineralogical phase transformation of pyrite in sulfidic mine tailings[J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(6): 10060513.
[11] 殷书岩, 赵鹏飞, 陆业大, 等. 加压氧化技术在难处理金矿上的应用[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2018, 47(1): 28−30.
YIN S Y, ZHAO P F, LU Y D, et al. Application of POX technology on refractory gold ores[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2018, 47(1): 28−30.
[12] YIN L, YANG H Y, LI X, et al. Changes of microbial diversity during pyrite bioleaching[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(5): 1477−1483. doi: 10.1007/s11771-020-4383-1
[13] CHAN T, COLLINS M, DENNETT J, et al. Pilot plant pressure oxidation of refractory gold-silver concentrate from Eldorado Gold Corporation's Certej Project in Romania[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2015, 54(3): 252−260. doi: 10.1179/1879139515Y.0000000018
[14] AMANKWAH R K, OFORI-SARPONG G. Microwave roasting of flash flotation concentrate containing pyrite, arsenopyrite and carbonaceous matter[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 151: 106312. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106312
[15] MARCHEVSKY N, BARROSO QUIROGA M M, GIAVENO A, et al. Microbial oxidation of refractory gold sulfide concentrate by a native consortium[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(5): 1143−1149. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60133-X
[16] 马方通, 高利坤, 董方, 等. 难处理金矿预处理及强化氰化技术研究现状及进展[J]. 黄金, 2016, 37(4): 51−55. doi: 10.11792/hj20160412
MA F T, GAO L K, DONG F, et al. Pretreatment of refractory gold ores and current research status and progress of intensified cyanidation process[J]. Gold, 2016, 37(4): 51−55. doi: 10.11792/hj20160412
[17] MA J, TANG Y, YANG D Q, et al. Kinetics of advanced oxidative leaching of pyrite in a potassium peroxy-disulphate solution[J]. Journal of the Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2020, 120(2): 165−172.
[18] TANG Y, LI G H, YANG Y, et al. Oxidation of gold-bearing pyrite by ammonium persulfate[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2021, 7(3): 1280−1292. doi: 10.1007/s40831-021-00416-5
[19] SILVA J C M, DOS SANTOS E C, HEINE T, et al. Oxidation mechanism of arsenopyrite in the presence of water[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(48): 26887−26894. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b09706
[20] JIN J Q, MILLER J D, DANG L X, et al. Effect of surface oxidation on interfacial water structure at a pyrite (100) surface as studied by molecular dynamics simulation[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2015, 139: 64−76. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2015.04.006
[21] XIAN H Y, ZHU J X, TAN W, et al. The mechanism of defect induced hydroxylation on pyrite surfaces and implications for hydroxyl radical generation in prebiotic chemistry, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2019, 244: 163- 172.
[22] 胡静文, 王艳红, 顾帼华, 等. 选矿废水的净化处理技术及机理研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(4): 35−42.
HU J W, WANG Y H, GU J H, et al. Research progress on purification technology and mechanism of mineral processing wastewater[J]. Conservation and utilization of mineral resources, 2021, 41(4): 35−42.
[23] 占鹏, 孙微, 廖小龙, 等. Fe0活化氧化体系处理垃圾渗滤液实验研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2019, 45(12): 37−41.
ZHAN P, SUN W, LIAO X L, et al. Experimental study on landfill leachate treatment by Fe0 activated oxidation system[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2019, 45(12): 37−41.
[24] 吕超飞, 党晓娥, 贠亚新等. 环保型“金蝉”浸出剂处理金精矿的试验研究[J]. 黄金, 2014, 35(5): 60−64. doi: 10.11792/hj20140515
LV C F, DANG X E, YUN Y X, et al. Experimental research on the extraction of gold from the concentrates by environment-friendly Jinchan leaching agents[J]. Gold, 2014, 35(5): 60−64. doi: 10.11792/hj20140515
[25] 唐云, 杨典奇, 唐立靖, 等. 微细浸染型难选金矿两段预处理-非氰化浸出研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2017, 37(1): 60−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2017.01.017
TANG Y, YANG D Q, TANG L J, et al. Experimental research on non-cyanide leaching of micro-disseminated gold ore with two-stage pretreatment[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2017, 37(1): 60−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2017.01.017
-




 下载:
下载: