Effect of Sodium Sulfate on Surface Oxidation−dissolution Behavior of Fine−grained Molybdenite and Its Mechanism
-
摘要:
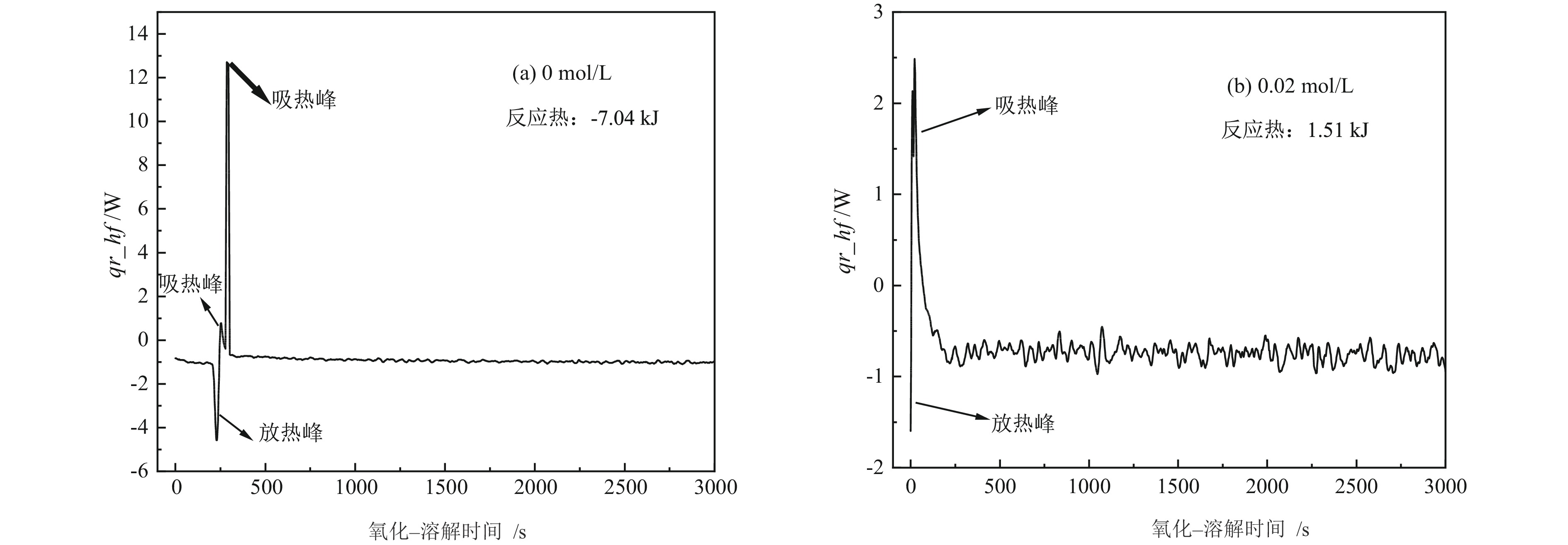
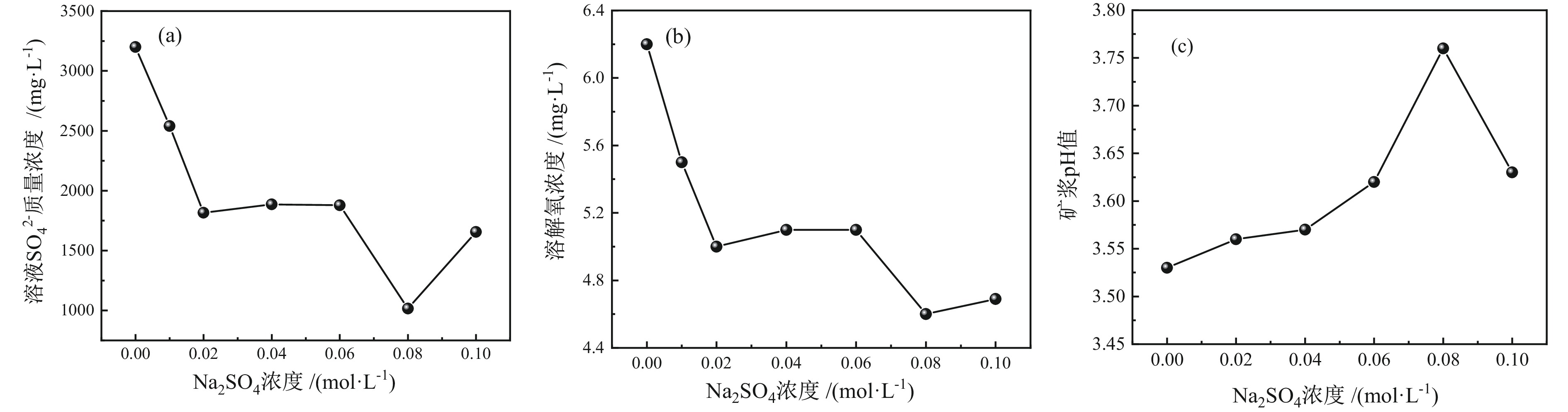
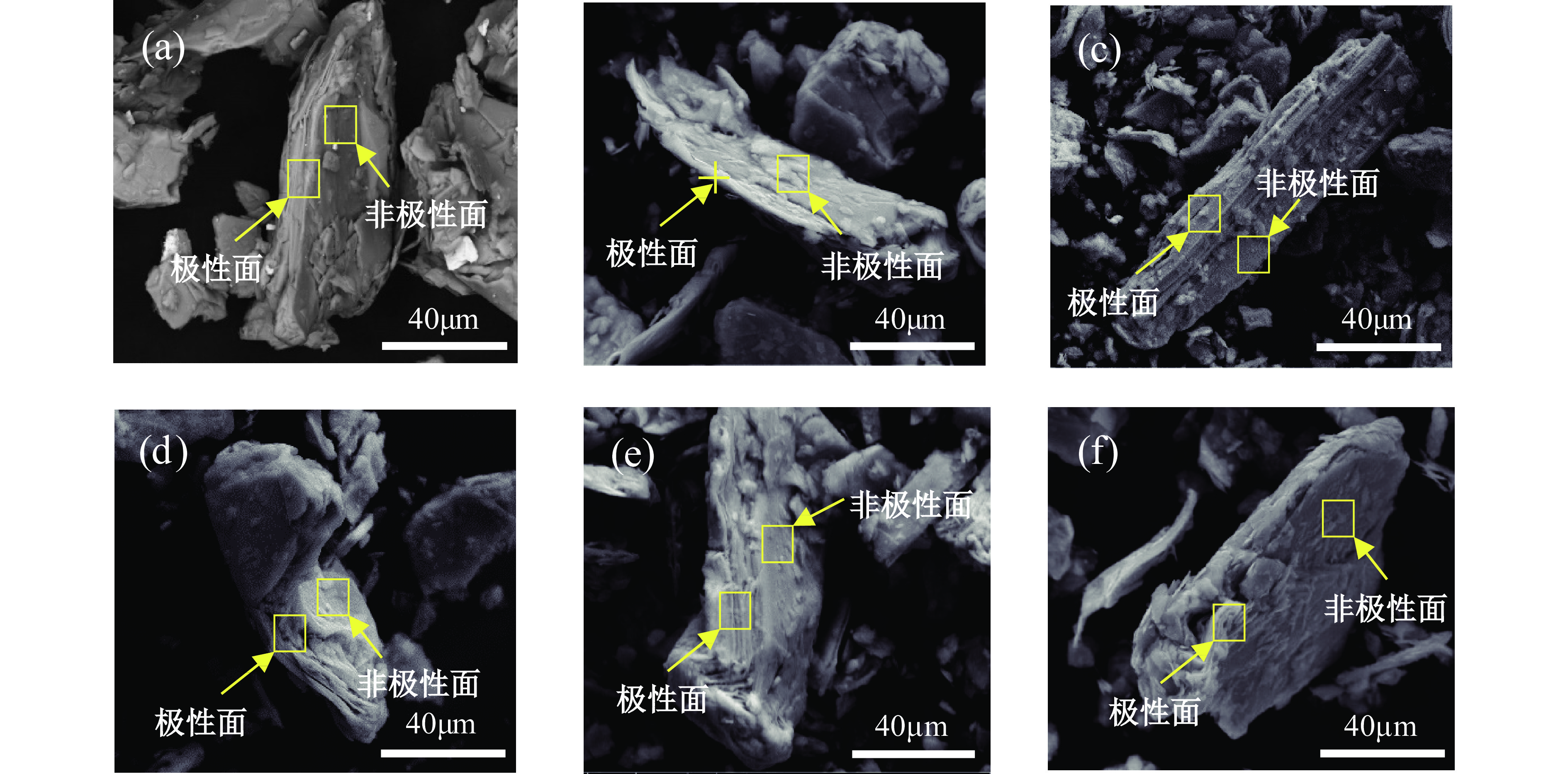
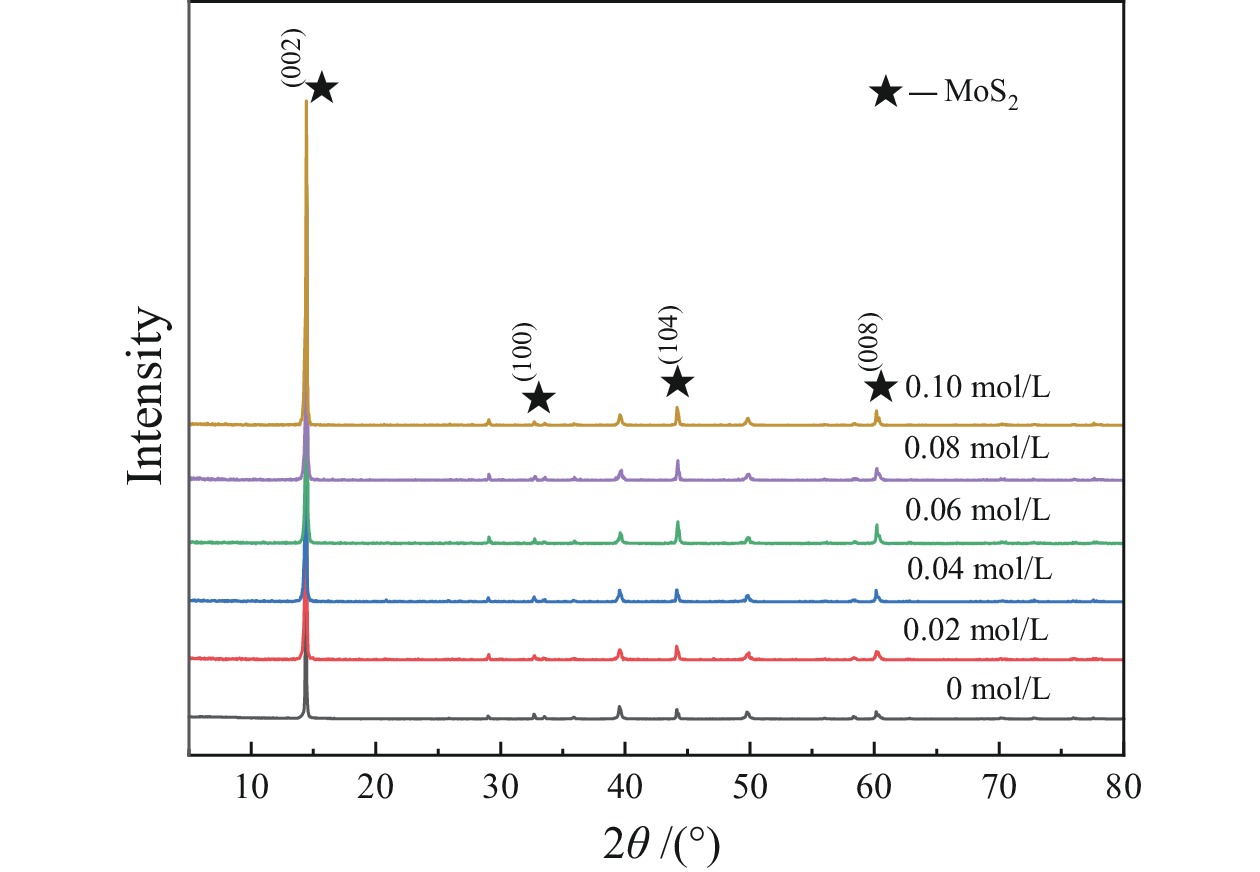
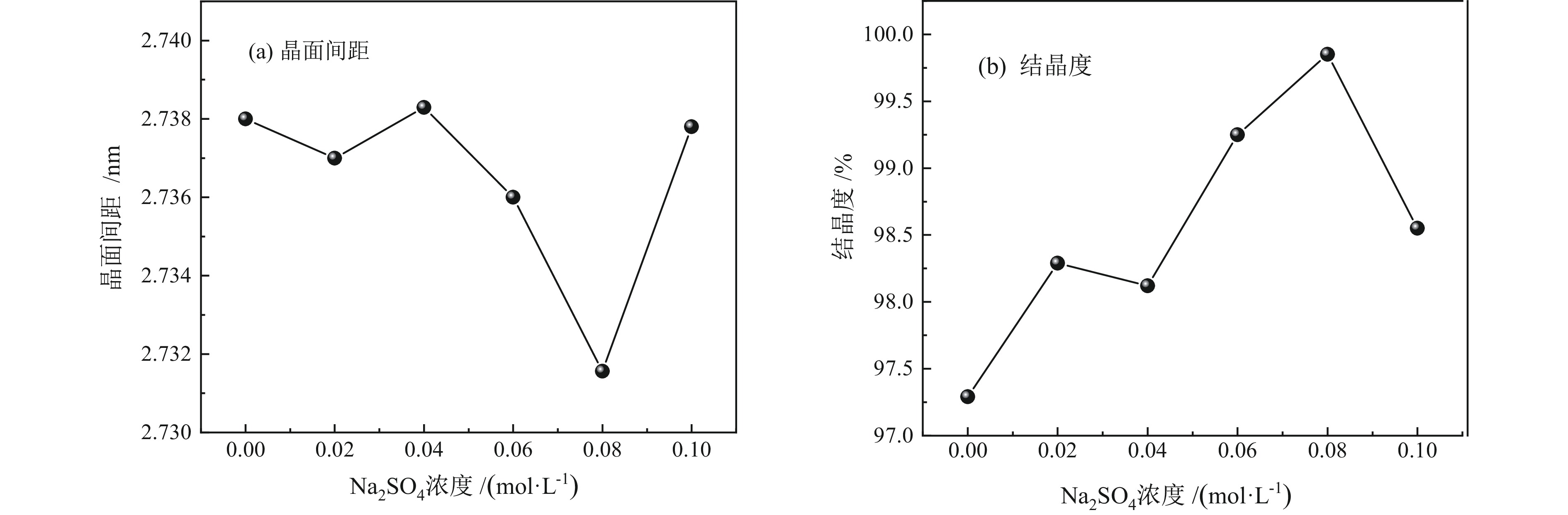
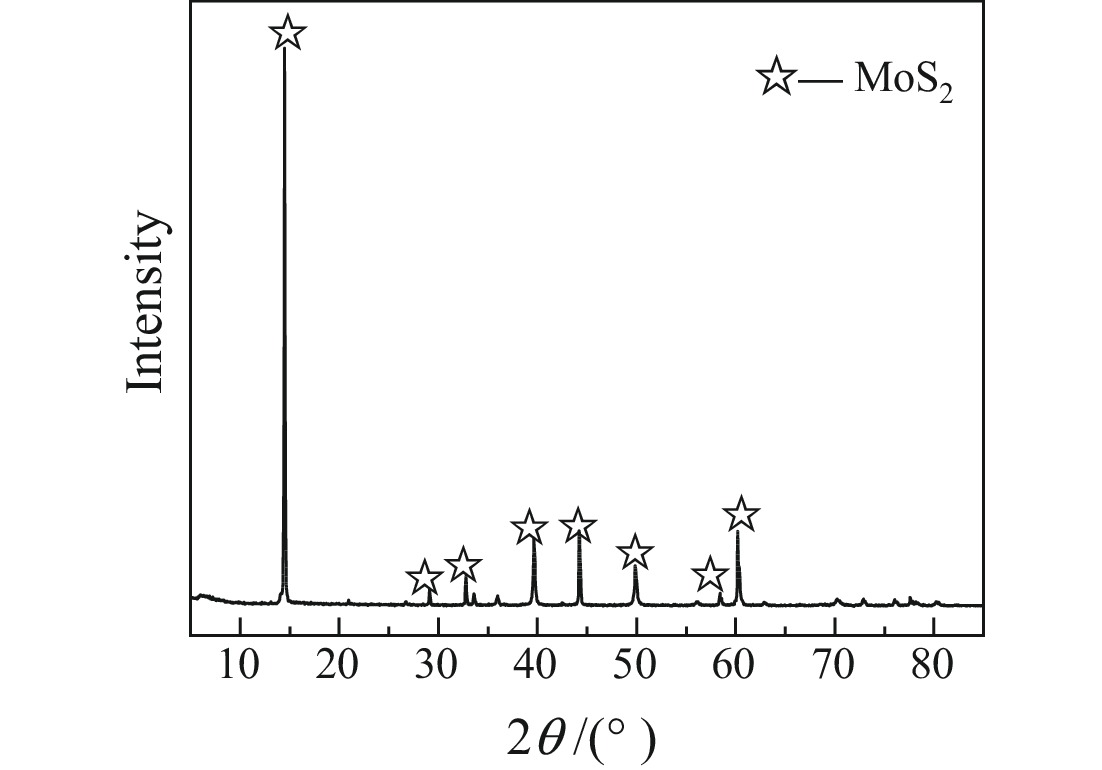
细粒辉钼矿表面的过度氧化以及表面氧化产物的溶解行为不利于辉钼矿浮选,为此,研究采用硫酸钠减小细粒辉钼矿表面氧化的程度以及抑制表面氧化产物的溶解以期改善辉钼矿的浮选效果。结果表明,适量的硫酸钠可减小细粒辉钼矿表面Mo−O键的相对含量,对细粒辉钼矿氧化反应及氧化产物的溶解过程具有一定的调控作用。0.08 mol/L的硫酸钠可使矿浆中矿物溶解的硫酸根离子质量浓度减小68.25%,溶解氧质量浓度减小25.81%,并使细粒辉钼矿(100)晶面的晶面间距减小,而结晶度增大。其次,硫酸钠在溶液中电离出的硫酸根离子对辉钼矿表面硫元素氧化产物的溶解反应产生同离子效应,使氧化产物溶解受阻,提高了细粒辉钼矿表面性质的均匀性和可浮性。研究对细粒辉钼矿氧化−溶解过程的调控及其浮选效果的提高具有一定的指导意义。
Abstract:The excessive oxidation on the surface of micro−fine molybdenite and the dissolution behavior of the surface oxidation products are not favorable for molybdenite flotation, for this reason, sodium sulfate was used to reduce the degree of surface oxidation of fine−grained molybdenite and inhibit the dissolution of surface oxidation products in order to improve the flotation efficiency of molybdenite. The results indicated that the appropriate amount of sodium sulfate could reduce relative content of Mo−O bonds on the surface of micro−fine molybdenite, which had a certain regulatory effect on the oxidation reaction of micro−fine molybdenite and the dissolution process of oxidation products. Sodium sulfate at 0.08 mol/L reduced the sulfate ion concentration in the slurry by 68.25% and the dissolved oxygen concentration by 25.81%, and reduced the crystalline spacing of the micro−fine molybdenite (100) crystal faces, while increasing the crystallinity. Secondly, the sulfate ions ionized by sodium sulfate in solution produce a common ion effect on the dissolution reaction of sulfur oxidation products on the surface of molybdenite, which hindered the dissolution of oxidation products and improved the uniformity and floatability of fine−grained molybdenite surface properties. The study has certain guiding significance for the regulation of the oxidation−dissolution process of micro−fine molybdenite and its flotation effects improvement.
-
Key words:
- oxidative /
- dissolution /
- common ion effect /
- crystal−plane distance /
- micro−fine molybdenite
-

-
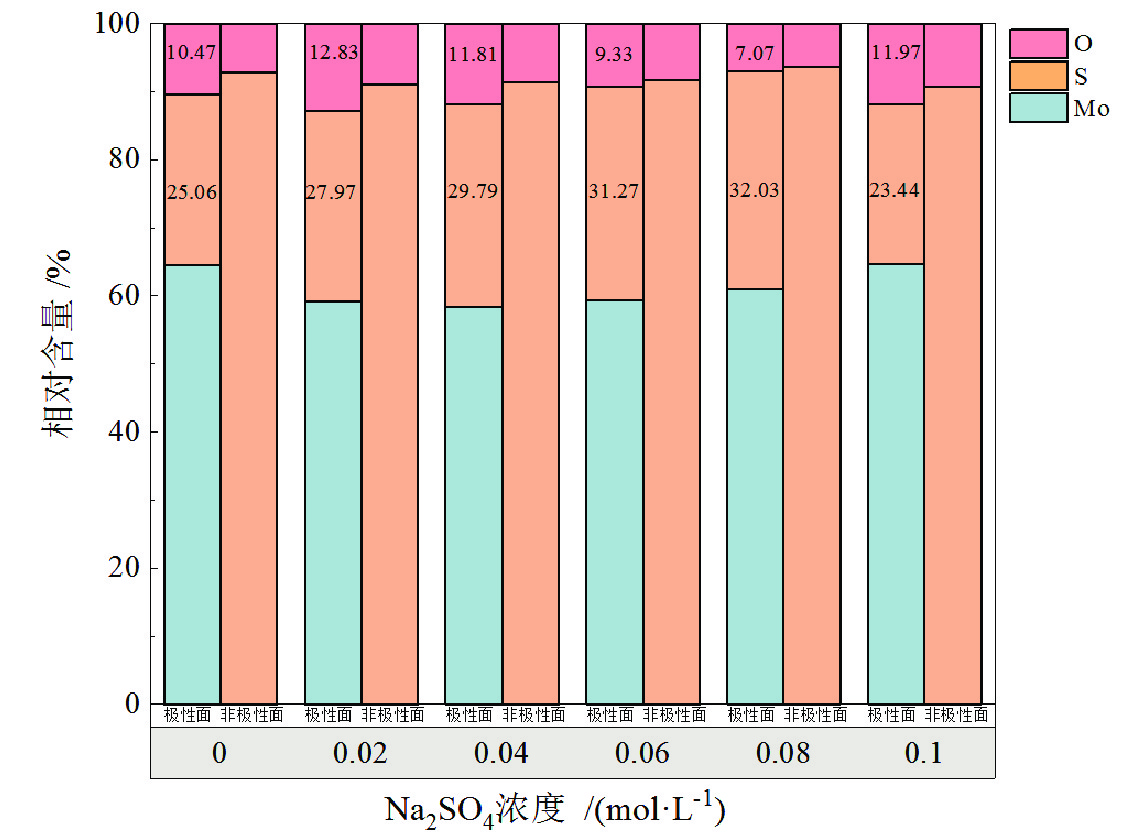
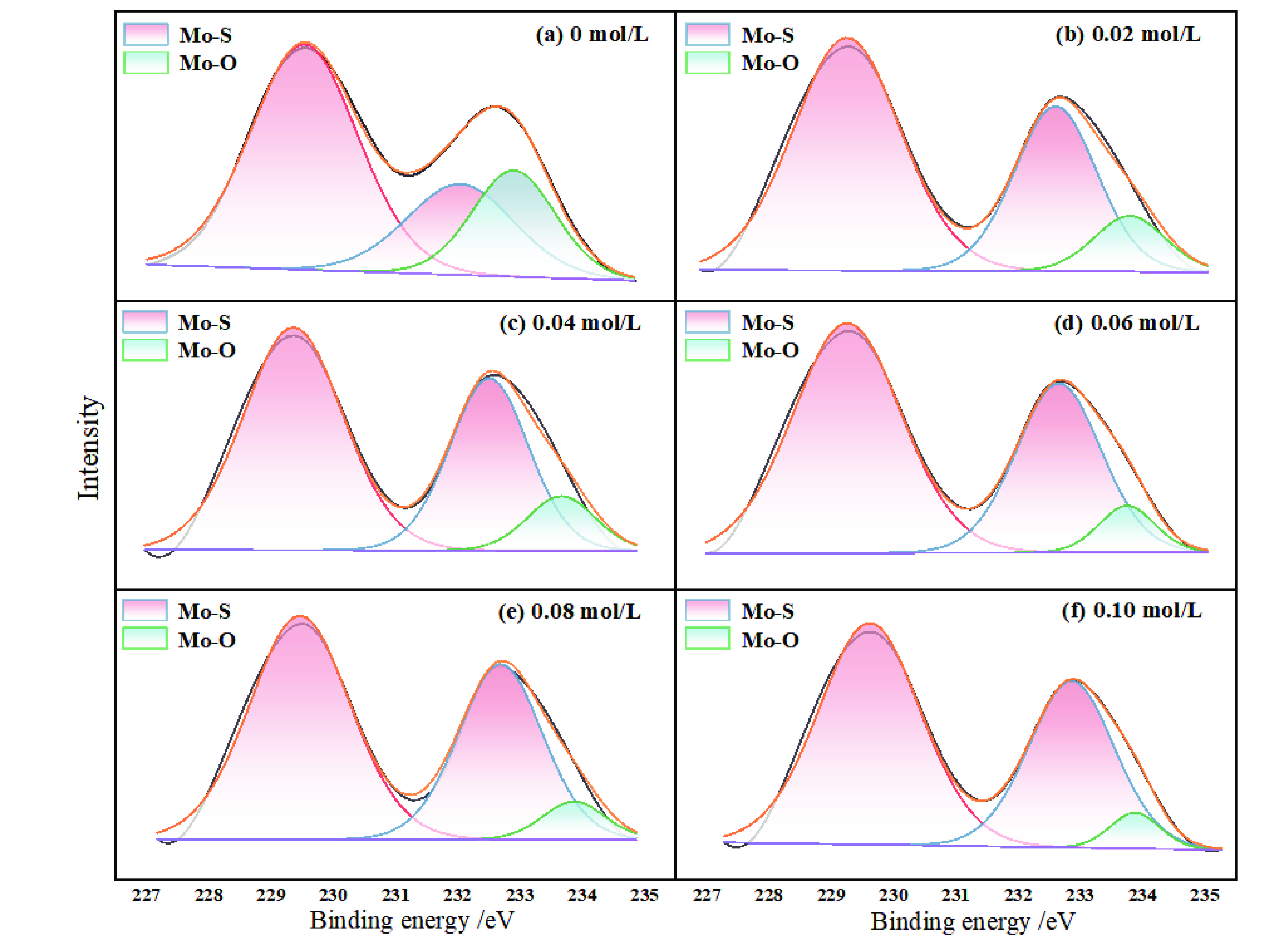
表 1 细粒辉钼矿表面Mo(3d3/2)的价健形态及分布
Table 1. Valence form and distribution of Mo (3d3/2) on fine molybdenite surface
Na2SO4浓度/(mol·L−1) 峰面积 峰面积比/% Mo−S (3d3/2) Mo−O (3d3/2) Mo−S (3d3/2) Mo−O (3d3/2) 0 5022.94 4862.13 50.81 49.19 0.02 55812.75 36676.12 60.35 39.65 0.04 23730.52 14496.75 62.08 37.92 0.06 57141.94 31079.40 64.77 35.23 0.08 39849.72 17225.21 59.82 30.18 0.10 16792.50 17423.97 79.34 20.66 -
[1] 林清泉, 吴启明, 戴智飞, 等. 微细粒辉钼矿浮选机理研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2021, 41(3): 37−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2021.03.009
LIN Q Q, WU Q M, DAI Z F, et al. Mechanism for hydrocarbon oil collectors in flotation of fine molybdenite ore[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2021, 41(3): 37−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2021.03.009
[2] 沈传刚, 肖庆飞, 宋念平, 等. 磨矿细度对辉钼矿浮选的影响[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2017(1): 51−54+68.
SHEN C G, XIAO Q F, SONG N P, et al. Effect of grinding fineness on molybdenite flotation[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2017(1): 51−54+68.
[3] 林清泉, 詹信顺, 张红华, 等. 辉钼矿和黄铁矿的晶体结构与表面性质研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2019, 39(3): 40−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2019.03.010
LIN Q Q, ZHAN X S, ZHANG H H, et al. Crystal structures and surface properties of molybdenite and pyrite[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2019, 39(3): 40−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2019.03.010
[4] 任强. 微细粒辉钼矿的浮选动力学研究[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2019, 37(2): 33−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2019.02.009
REN Q. Study on flotation kinetics of fine−grained molybdenite[J]. China Resource Comprehensive Utilization, 2019, 37(2): 33−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2019.02.009
[5] 杨丙桥, 黄鹏亮, 张汉泉, 等. 微细粒辉钼矿疏水聚团及聚团浮选研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2018(10): 86−91.
YANG B Q, HUANG P L, ZHANG H Q, et al. Study on the hydrophobic agglomeration and floc−flotation of molybdenite fines[J]. Metal Mine, 2018(10): 86−91.
[6] NOWAK P, LAAJALEHTO K. Oxidation of galena surface−an XPS study of the formation of sulfoxy species[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2000, 157(3): 101−111. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(99)00575-9
[7] HAMPTON M A, PLACKOWSKI C, NGUYEN A V. Physical and chemical analysis of elemental sulfur formation during galena surface oxidation[J]. Langmuir, 2011, 27(7): 4190−4201. doi: 10.1021/la104755a
[8] 荀婧雯, 王宇斌, 马晓晓, 等. 浮选过程中辉钼矿的氧化溶解特性[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(6): 95−101.
XUN J W, WANG Y B, MA X X, et al. Oxidation−dissolution characteristics of molybdenite during the flotation process[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020, 40(6): 95−101.
[9] 牛晓鹏. 方铅矿、黄铜矿和黄铁矿表面氧化与可浮性研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院过程工程研究所), 2019.
NIU X P. Correlation of surface oxidation of galena, chalcopyrite and pyrite with their floatability[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019.
[10] 陈志友, 苏小琼, 肖洪旭, 等. 云南某微细粒辉钼矿工艺矿物学与浮选回收技术研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2021, 41(3): 287−293.
CHEN Z Y, SU X Q, XIAO H X, et al. A study on process mineralogy and flotation recovery technology of a kind of fine molybdenite ore in Yunnan Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2021, 41(3): 287−293.
[11] 李慧. 不同粒级辉钼矿的可浮性及其影响因素和改善措施研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2019.
LI H. Study on floatability of molybdenite with different grain size and its influencing factors and improvement measures[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2019.
[12] 伊向艺, 叶金亮, 李沁, 等. 同离子效应对不同酸液与碳酸盐岩反应的影响[J]. 油田化学, 2014, 31(1): 25−28.
YI X Y, YE J L, LI Q, et al. Influence of common ion effect on the reaction between different acids and carbonate rock[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2014, 31(1): 25−28.
[13] 曲昌海, 汤韧, 刘宏, 等. 同离子效应对盐酸普萘洛尔渗透泵片释药速率的影响[J]. 中国药师, 2006, 9(2): 99−101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-049X.2006.02.001
QU C H, TANG R, LIU H, et al. Influence of homoion effect in drug release of propranolol hydrochloride osmotic pump tablets[J]. China Pharmacist, 2006, 9(2): 99−101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-049X.2006.02.001
[14] 王宇斌, 文堪, 王森, 等. 同离子效应对半水硫酸钙形貌的调控机理[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2018, 32(6): 1444−1449. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2018.06.027
WANG Y B, WEN K, WANG S, et al. Regulation mechanism of common ion effect on the morphology of calcium sulphate hemihydrate[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2018, 32(6): 1444−1449. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2018.06.027
[15] LUCAY F, CISTERNAS L A, GÀLVEZ E D, et al. Study of the natural floatability of molybdenite fines in saline solutions and effect of gypsum precipitation[J]. Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration, 2015, 32(4): 203−208.
[16] 荀婧雯, 王宇斌, 汪潇, 等. Cu2+对磁化蒸馏水改善辉钼矿浮选效果的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2020, 20(3): 332−337. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.219198
XUN J W, WANG Y B, WANG X, et al. Effect of Cu2+ on improvement of molybdenite floatability in magnetized distilled water[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2020, 20(3): 332−337. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.219198
[17] 宇文超, 刘秉国, 张利波, 等. 基于多重扫描速率法的辉钼矿氧化焙烧动力学参数分析[J]. 化学反应工程与工艺, 2018, 34(4): 359−364.
YU W C, LIU B G, ZHANG L B, et al. Analysis of kinetic parameters of molybdenite oxidation roasting based on the multiple scanning rate method[J]. Chemical Reaction Engineering and Technology, 2018, 34(4): 359−364.
[18] 马双忱, 范紫瑄, 万忠诚, 等. 高盐水条件下亚硫酸盐氧化特性实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(5): 1964−1972. doi: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20181237
MA S C, FAN Z X, WAN Z C, et al. Experimental study on oxidation characteristics of sulfite under high salt water condition[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(5): 1964−1972. doi: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20181237
[19] SINCHE−GONZALEZ M, FORNASIERO D. Understanding the effect of sulphate in mining−process water on sulphide flotation[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2021, 165: 106865. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2021.106865
[20] 林清泉, 顾帼华, 陈雄, 等. 微细粒辉钼矿的浮选动力学研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 49(7): 1573−1581.
LIN Q Q, GU G H, CHEN X, et al. Flotation kinetics of molybdenite fines[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2018, 49(7): 1573−1581.
[21] LI Y B, LARTEY C, SONG S X, et al. The fundamental roles of monovalent and divalent cations with sulfates on molybdenite flotation in the absence of flotation reagents[J]. Rsc Advances, 2018, 8(41): 23364−23371. doi: 10.1039/C8RA02690D
[22] WANG D Z. Flotation reagents: Applied surface chemistry on minerals flotation and energy resources beneficiation: Volume 1: Functional principle[M]. Metallurgical Industry Press, 2016.
[23] BERTRAND P A. Surface−phonon dispersion of MoS2[J]. Physical Review B, 1991, 44: 5745−5749. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.44.5745
[24] LEE C, YAN H, BRUS L E, et al. Anomalous lattice vibrations of single−and few−layer MoS2[J]. Acs Nano, 2010, 4(5): 2695−2700. doi: 10.1021/nn1003937
[25] 李慧, 何廷树, 王宇斌, 等. 不同粒级辉钼矿的XRD和SEM及其可浮性差异研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(11): 3588−3592.
LI H, HE T S, WANG Y B, et al. XRD and SEM analyses of molybdenite with different particle sizes and its floatability difference[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(11): 3588−3592.
[26] CASTRO S, LOPEZ−VALDIVIESO A, LASKOWSKI J S. Review of the flotation of molybdenite. Part I: Surface properties and floatability[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2016, 148: 48−58. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2016.01.003
-



 下载:
下载: