Kinetics and Mechanism of Carbon Tetrachloride Rapid Reduction by Nanoscale Ni-Fe Using Scanning Electron Microscope
-
摘要:
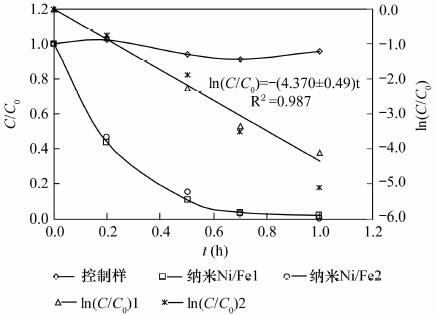
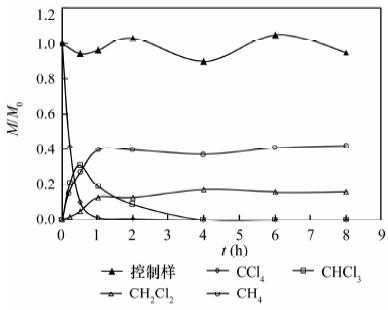
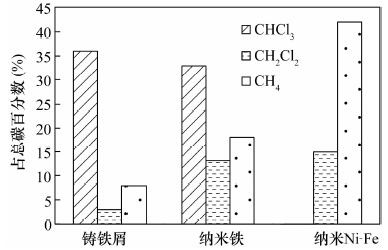
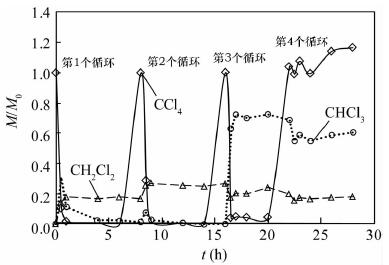
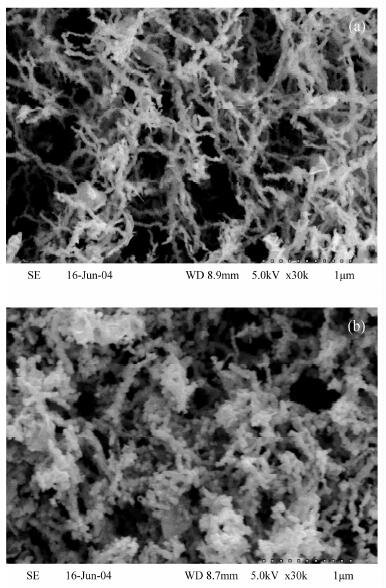
纳米铁具有高的比表面积和高反应活性, 能快速将氯代烯烃还原成无毒氯离子、乙烯和乙烷, 但对于氯代烷烃的脱氯仍能产生大量的氯代中间或最终产物, 可以通过合成制得纳米双金属提高脱氯速率和减少氯代中间产物。本文利用扫描电镜测得实验室制备的纳米Ni-Fe(2%, 质量分数)颗粒直径为20~60 nm, 通过批实验方式对纳米Ni-Fe降解四氯化碳的反应动力学性质、产物、持久性能和反应机理进行了探讨。结果表明, 纳米Ni-Fe体系主要最终产物为42% CH4和17% CH2Cl2。与铸铁屑和纳米铁相比, 纳米Ni-Fe由于催化脱氯加氢, 显著提高了氯代烃脱氯速率, 同时降低了有毒氯代产物的产量, 且Ni作为催化剂不会进入水体引起二次污染。纳米Ni-Fe颗粒在空气中具有很好的稳定性, 虽然降解四氯化碳的最终产物CH4与纳米Pd-Fe相比少13%, 但由于价格便宜, 有望在工程上应用于氯代有机化合物水土污染治理。
Abstract:The nanoscale iron particles have high specific surface area and high reactivity, can be used to rapidly reduce chlorinated alkene to the non-toxic chloride ions, chlorine-free end products ethene and ethane. But nanoscale iron particle degrades chlorinated alkanes with much toxic intermediate or end products. A small amount of a second metal deposited on the iron surface has proved to enhance the reactivity of metal particles. In this paper, laboratory-synthesized nanoscale Ni-Fe (2% by weight) particles have diameters on the order of 20-60 nm using Scanning Electron Microscope. In batch experiments, the kinetics, products, stability of performance, and mechanism of carbon tetrachloride (CT) by Ni-Fe nanoparticles were investigated. CH4 (~42%) and CH2Cl2 (~17%) in nanoscale Ni-Fe system were the major end products. Compared to nanoscale iron and the cast iron scarp, a major benefit of the nanoscale Ni-Fe particles for treatment of CT is the low yield of chlorinated by-product. Due to the presence of catalyst (Ni) on the surface, dechlorination rate was significantly increased and production of chlorinated byproducts was notably reduced. Catalytic metal Ni from the nanoscale Ni-Fe particles would not dissolve into water so that it would not form a secondary contamination of water body. The laboratory-synthesized nanoscale particles are quite stable under ambient conditions. For nano-scale Ni-Fe particles system, the end-product CH4 were reduced by 13% compared with nanoscale Pd-Fe particles. Although tnano-scale Pd-Fe particles are effective in dechlorination of chlorinated organic compounds, nano-scale Ni-Fe particles are more economically viable which made it possible for the large scale remediation of water and soil contaminated by chlorinated organic compounds.
-

-
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] doi: 10.1021/es034877k
[8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] doi: 10.1021/jp7097262
[14] doi: 10.1021/jp9041759
[15] [16] [17] doi: 10.1021/es048262e
[18] doi: 10.1289/ehp.0900793
[19] doi: 10.1021/cm020737i
[20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] doi: 10.1021/es9907358
[27] [28] [29] [30] [31] -



 下载:
下载: