Accurate Measurement of High Copper in Copper Ores with Automatic Potentiometric Titration Technique
-
摘要:
铜矿石中百分含量铜的分析通常采用手动目视滴定法, 该方法借助化学指示剂判定终点, 存在终点判断和人为操作等误差, 精密度、可靠性相对较差。基于此, 本文建立了精确测定铜矿石中高含量铜的分析方法, 采用智能型自动电位滴定仪自动判定终点, 高分辨加液器精确控制硫代硫酸钠标准溶液加入量至0.001 mL, 并且通过加大碘化钾用量使得滴定中产生的碘化亚铜被高浓度的I-溶解, 消除对碘的吸附影响。本法应用于铜含量为24.2%~59.09%的铜精矿、黄铜矿、铅黄铜国家标准物质分析, 相对标准偏差(RSD, n=10) < 0.3%, 极差仅为0.13%、0.21%、0.29%, 优于手动目视滴定法。本法提高了铜矿石分析的自动化程度, 适用于精确测定铜含量大于0.5%尤其是10%以上的铜矿石。
Abstract:Copper in copper ores is commonly determined by a manual visual titration method. The method has large errors, poor precision and poor reliability due to the need to gauge the end of the chemical reaction by a chemical indicator. Based on these disadvantages, a high precision determination method for high Cu content in Cu ores has been developed. In this new method, the terminal point is determined by intelligent potentiometric titrator automatically and the amount of sodium thiosulfate standard solution is accurate to 0.001 mL by a high-resolution dosing device. Moreover, the amount of potassium iodide is increased to eliminate the absorption of iodine with copper iodide which was produced during titration, as the copper iodide can be dissolved by high concentrations of iodide. National standard materials such as copper concentrate, chalcopyrite and lead brass with copper content ranging from 24.2% to 59.09% are determined using this method. The relative standard deviation is lower than 0.3%(n=10). The extreme differences are 0.13%, 0.21% and 0.29%, better than manual visual titration. The proposed method improves the automation for accurate determination of ores with Cu content greater than 0.5%, especially for those with Cu content more than 10%.
-
Key words:
- copper ore /
- copper /
- sodium thiosulfate /
- automatic potentiometric titration
-

-
表 1 手动目视滴定和自动电位滴定标定结果
Table 1. Analytical results of calibration by manual visual titration and automatic potentiometric titration
滴定方式 实验员 铜含量
(mg)4次测定消耗
的标准溶液
(mL)4次测定的
滴定度
(mg/mL)单人极差
(%)双人极差
(%)手动
目视
滴定1 25.00 13.20 1.8939 0.38 0.61 13.18 1.8968 13.20 1.8939 13.15 1.9011 2 25.00 13.16 1.8997 0.30 13.12 1.9055 13.14 1.9026 13.13 1.904 自动
电位
滴定1 25.00 13.262 1.8851 0.10 0.10 13.265 1.8847 13.257 1.8858 13.270 1.8839 2 25.00 13.258 1.8857 0.08 13.269 1.8841 13.269 1.8841 13.264 1.8848 表 2 硫氰酸钾加入时间对标定结果的影响
Table 2. Effect of apotassium thiocyanate added time on calibration
铜含量
(mg)硫代硫酸钠
消耗量(mL)消耗标准溶液
(mL)铜的标定结果
(mg/mL)单人极差
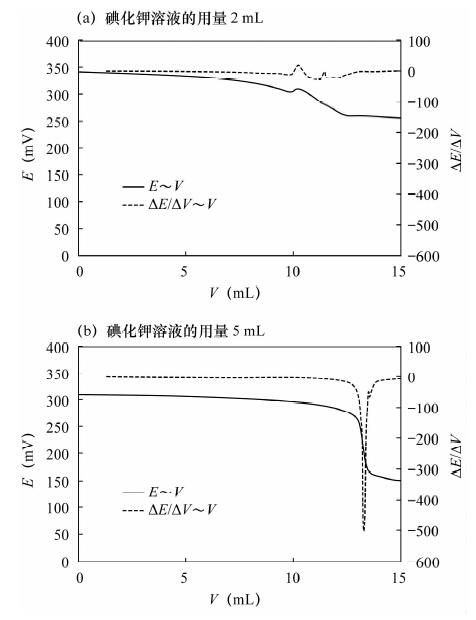
(%)25.00 0.00 12.685 1.9708 0.86 25.00 3.00 12.757 1.9597 25.00 5.00 12.795 1.9539 25.00 9.00 12.917 1.9354 表 3 加入5 mL碘化钾溶液时标准物质分析结果
Table 3. Analytical results of standard substances with 5 mL potassium iodide solution
标准物质
编号矿物
名称称样量
(g)滴定读数
(mL)铜含量(%) 标准值 测定值 GBW07233 铜矿石 0.4456 2.765 1.15 1.17 GBW07169 铜矿石 0.5229 15.504 5.49 5.59 GBW07170 铜矿石 0.4107 27.985 12.59 12.84 GBW07166 铜精矿 0.1642 21.376 24.2 24.54 GBW07268 黄铜矿 0.2121 37.676 33.30 33.48 GBW(E)020015 铅黄铜 0.07395 23.230 59.09 59.21 表 4 铜矿石国家标准物质测定结果
Table 4. Analytical results of Cu in copper ore national standard reference materials
标准物质
编号矿物名称 测定方式 铜含量(%) 相对误差
(%)RSD
(%)极差
(%)测定平均值 标准值 GBW07166 铜精矿 手动目视滴定 24.26 24.2 0.26 0.8 0.58 自动电位滴定 24.28 0.34 0.2 0.13 GBW07268 黄铜矿 手动目视滴定 33.33 33.30 0.09 0.6 0.52 自动电位滴定 33.29 -0.04 0.2 0.21 GBW(E)020015 铅黄铜 手动目视滴定 59.06 59.09 -0.05 0.4 0.78 自动电位滴定 59.06 -0.04 0.2 0.29 -
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] -



 下载:
下载: