Raman Spectra Characteristics of Fluid Inclusion in the Shaanxi Formation of the Dingbian Area in the Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
拉曼光谱技术是对流体包裹体进行无损分析的重要手段。本文应用激光拉曼技术对鄂尔多斯盆地定边地区山西组石英矿物颗粒中流体包裹体组分特征进行分析研究, 发现该区包裹体主要呈现2种拉曼光谱图:分别是代表芳烃存在的荧光型拉曼光谱图和代表饱和烃存在的饱和烃型拉曼光谱图。从所测得的2种谱图来看, 该地层包裹体捕获于煤系烃源岩的生烃演化阶段。经过进一步分析, 发现在石英颗粒的Ⅰ期、Ⅱ期次生加大边中的包裹体的拉曼谱图主要显现2250 cm-1±和2945 cm-1±拉曼谱峰, 而裂缝中的包裹体除了具有与其相同的峰值之外, 在600~1500 cm-1之间亦显示出多个拉曼谱峰, 说明存在于这2种构造中的包裹体处于不同的煤系烃源岩演化之中, 因此所测包裹体组分不完全相同。该研究测得的拉曼光谱图揭示了研究区山西组地层中流体包裹体的主要组分, 并且反映了包裹体被捕获时的成烃流体组分变化特征, 对最终确定当时地层的流体环境及其与煤系烃源岩生烃演化之间的关系有着重要意义。
-
关键词:
- 鄂尔多斯盆地流体包裹体 /
- 荧光型拉曼光谱图 /
- 饱和烃型拉曼光谱图 /
- 芳烃 /
- 饱和烃
Abstract:Raman Spectroscopy is an important means of non-destructive fluid inclusions analysis. Composition of fluid inclusions in quartz from the Shaanxi formation of the Dingbian area in the Ordos Basin was determined by the Raman technique. These inclusions show two kinds of Raman spectra, fluorescence-type Raman spectra which indicate aromatic hydrocarbon and saturated hydrocarbon-type Raman spectra which indicate saturated hydrocarbon. According to these two kinds of Raman spectra, the conclusion is that the fluid inclusions were possibly captured during the stage of hydrocarbon generation of coal hydrocarbon source rocks. Peaks of 2250 cm-1± and 2945 cm-1± are the main Raman peaks in the quartz overgrowths during stages Ⅰ and Ⅱ. The inclusions in cracks not only have the same peak with those in quartz overgrowths, but also show multiple Raman peaks between 600 and 1500 cm-1. This indicates that two kinds of fluid inclusions exist in different evolution stages of the coal source rocks with different compositions. The Raman spectra reveal the main composition of fluid inclusions in the Shaanxi Formation of the Dingbian area in the Ordos basin and reflect the composition changes during capture of fluid inclusions. It is of great significance to determine the relationship between the fluid formation environment at that time and the evolution of the coal hydrocarbon source rocks.
-

-
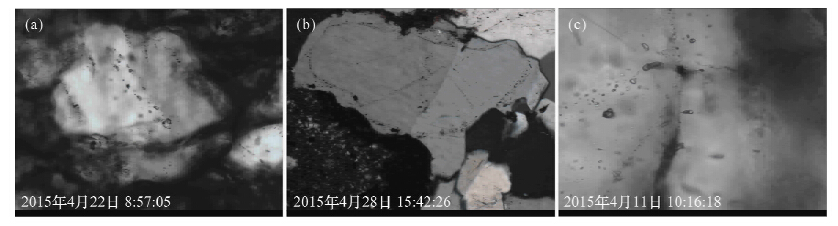
表 1 定边地区研究井段拉曼峰值特征
Table 1. The characteristics of Raman peaks in Dingbian well
井名 层位 样品深度
(m)包裹体所在位置
(石英)包裹体主要拉曼峰值
(cm-1±)Y409 山西组 3826.99 Ⅰ期加大边 2255,2939 Ⅰ期加大边 627,2247,2944 Ⅰ期加大边 2250,2945 Y575 山西组 3337.51 Ⅰ期加大边 2250,2946 Ⅰ期加大边 2248,2941 Ⅱ期加大边 2250,2943 Y442 山西组 3388.65 Ⅰ期加大边 1160,2250,2945 Ⅰ期加大边 1160,2250,2945 Y482 山西组 3837.45 裂缝 584,638,792,1057,1161 Ⅰ期加大边 2250,2946 Y482 山西组 3888.07 裂缝 627,862,2250,2944 裂缝 628,859,2250,2946 Y443 山西组 3667.1 裂缝 696,805,1160,2250,2962 裂缝 695,806,1160,2259,2962 -
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] doi: 10.1130/G23465A.1
[14] [15] 崔宏伟, 陈义才. 鄂尔多斯盆地定边地区延10储层特征及有利区带预测[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2011.
Cui H W, Chen Y C. The Reservoir Characteristics and Forcasting Perspective Plays of Yan 10 in Ding Bian Area, Ordos Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chendu University of Technology, 2011.
[16] [17] [18] [19] 曹青, 柳益群. 鄂尔多斯盆地东部上古生界致密储层成岩作用特征及其与天然气成藏摘合关系[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2013.
Cao Q, Liu Y Q. Characteristics of Diagenesis and Diagenesis-gas Accumulation for Upper Paleozoic Tight Reservoir in Eastern Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an: Xibei University, 2013.
-



 下载:
下载:

