Effects of the Hydrology-Water Chemistry Factors of the Xijiang River Basin on the Carbon Sink Flux in the Karst System
-
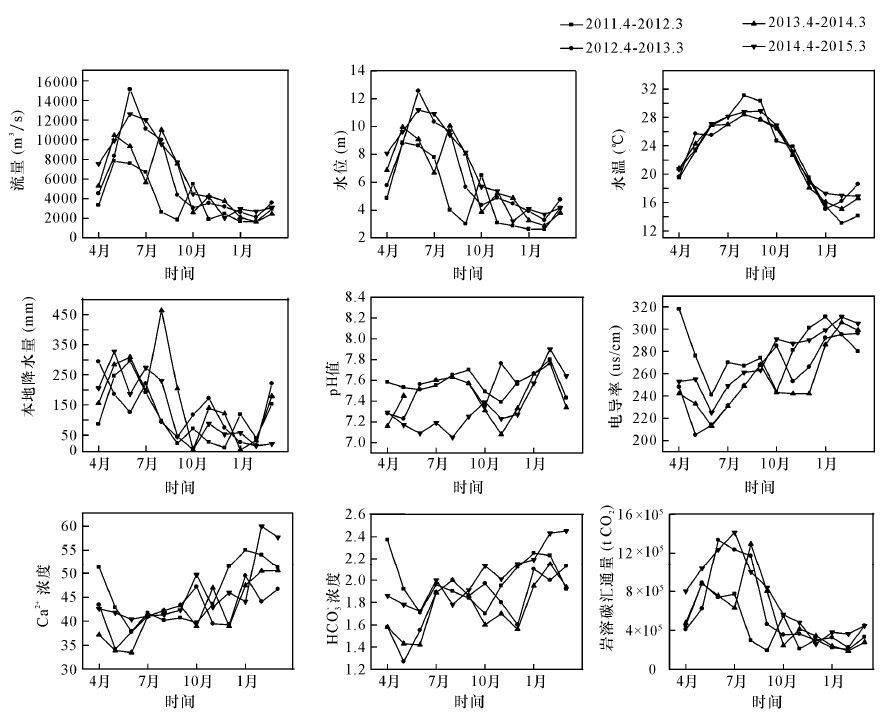
摘要: 河流岩溶碳汇通量的研究对于掌握全球碳循环机制、寻找“遗漏碳汇”具有重要意义。水文地质特征是岩溶动力系统的重要单元,为了分析河流岩溶碳汇在通量、长时间尺度的变化,本文选取受湿润季风气候影响显著的西江梧州断面为研究对象,探讨了2011~2015年西江流域流量、水位、本地降水量、水温、pH值、电导率、Ca2+和HCO3-浓度等水文水化学因子对岩溶碳汇通量的影响。结果表明:①岩溶碳汇通量与流量、水位的相关系数均在0.95以上,岩溶碳汇通量与流量达到了同步变化,岩溶碳汇通量与水位良好的相关关系则是通过水位对流量响应表现出来;降水通过不同方式进入河流直接改变地表径流状况,进而影响岩溶碳汇通量。②水温对岩溶碳汇通量的影响与西江流域雨季与夏季在同一时间段的气候特点有关,属于次要因子。③监测点水体常年呈弱碱性,pH值对岩溶碳汇通量的影响较弱;电导率、Ca2+和HCO3-浓度主要受流量影响,对岩溶碳汇通量变化的影响甚微。由此推断,流量是岩溶碳汇通量的主控因素。Abstract: The river carbon sink flux is important for the global carbon cycle and finding the missing carbon sink. Hydrogeological features are important parts of the karst dynamic system. In order to analyze the long-term trend and flux changes of river carbon sink, the Wuzhou section of Xijiang that was significantly affected by the wet monsoon climate was selected as the study object. In this paper, the effects of the hydrology and chemistry factors such as flow, water level, rainfall, water temperature, pH, EC, Ca2+, HCO-3 of Xijiang river basin from 2011 to 2015 on the river carbon sink flux are discussed. Results show that ① there is a good correlation of river carbon sink flux with the flow and water? level?(correlation coefficients>0.95). The carbon sink flux varies with flow and the good correlation between the carbon sink flux and water level was reflected by the effect of water level on the flow. The rainfall enters a river by different ways, which directly changes the run off in surface and further affects the river carbon sink flux.②The effect of water temperature on the river carbon sink flux was secondary and related to the climate of summer and monsoon of the Xijiang river basin during the same period. ③The pH has no obvious effect on the river carbon sink flux because the monitor point water is weakly alkaline. The EC, Ca2+ or HCO3- were mainly affected by flow and have little effect on the carbon sink flux. Therefore, the flow is the most important factor for the carbon sink flux.
-
Key words:
- Xijiang River Basin /
- carbon sinks /
- hydrology-water chemistry factors /
- flow
-

-
表 1 2011~2015梧州水文站岩溶碳汇通量与水文水化学因子之间的相关性
Table 1. Correlation of carbon sinks and physicochemical factors in the water of the Wuzhou hydrological station (2011—2015)
4个水文年 流量 (m3/s) 水位 (m) 本地降水量 (mm) 水温 (℃) pH值 电导率 (μs/cm) Ca2+浓度 (mg/L) HCO3-浓度 (mmol/L) 2011.4~2012.3 每月岩溶碳汇通量 (tCO2 ) 0.985** 0.981** 0.817** 0.316 -0.169 -0.469 -0.489 -0.377 2012.4~2013.3 每月岩溶碳汇通量 (tCO2 ) 0.963** 0.958** 0.214 0.639* 0.249 -0.674* -0.400 -0.156 2013.4~2014.3 每月岩溶碳汇通量 (tCO2 ) 0.955** 0.938** 0.931** 0.734** 0.205 -0.468 -0.456 -0.114 2014.4~2015.3 每月岩溶碳汇通量 (tCO2 ) 0.988** 0.983** 0.810** 0.749** -0.670* -0.896** -0.622* -0.731** 注:*表示在0.05水平上显著相关,**表示在0.01水平上显著相关。 -
[1] Stocker T F,Qin D,Plattner G K,et al.Climate Change 2013:The Physical Science Basis[M]//Contribution of Working Group Ⅰ to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.New York:Cambridge University Press,2013:465-570.
[2] Jiang Z,Yuan D.CO2 Source-Sink in Karst Processes in Karst Areas of China[J].Episodes,1999,22(1):33-35.
[3] Gombert P.Role of Karstic Dissolution in Global Carbon Cycle[J].Global and Planetary Change,2002,32(1-2):177-184. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2049773644&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[4] Liu Z,Zhao J.Contribution of Carbonate Rock Weathering to the Atmospheric CO2 Sink[J].Environmental Geology,2000,39(9):1053-1058. doi: 10.1007/s002549900072
[5] Yong J J,Yi J H,Schirmer M.Biogeochemical Controls on Daily Cycling of Hydrochemistry and δ13C of Dissolved Inorganic Carbon in a Karst Spring-Fed Pool[J].Journal of Hydrology,2013,478:157-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.12.001
[6] Liu Z H,Dreybrodt W.Significance of the Carbon Sink Produced by H2O-Carbonate-CO2-Aquatic Prototroph Interaction on Land[J].Science Bulletin,2015,60(2):182-191. doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0682-y
[7] White W B.Carbon Fluxes in Karst Aquifers:Sources,Sinks,and the Effect of Storm Flow[J].Acta Carsologica,2013,42(2-3):177-186. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2011138802&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[8] Meybeck M.Global Chemical Weathering of Sacrificial Rocks Estimated from River Dissolved Loads[J].American Journal of Science,1987,287(5):401-428. doi: 10.2475/ajs.287.5.401
[9] 吴卫华,郑洪波,杨杰东,等.硅酸盐风化与全球碳循环研究回顾及新进展[J].高校地质学报,2012,18(2):215-224. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201202005.htm
Wu W H,Zheng H B,Yang J D,et al.Review and Advancements of Studies on Silicate Weathering and the Global Carbon Cycle[J].Geological Journal of China University,2012,18(2):215-224. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201202005.htm
[10] Curl R L.Carbon Shifted But Not Sequestered[J].Science,2012,335(6069):655.
[11] 刘再华.岩石风化碳汇研究的最新进展和展望[J].科学通报,2012,57(2-3):95-102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2012Z1002.htm
Liu Z H.New Progress and Prospects in Study of Rock-Weathering-related Carbon Sinks[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2012,57(2-3):95-102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2012Z1002.htm
[12] 刘再华,Dreybrodt W,刘恒.大气CO2汇:硅酸盐风化还是碳酸盐风化的贡献?[J].第四纪研究,2011,31(3):426-430. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201103005.htm
Liu Z H,Dreybrodt W,Liu H.Atmosphere CO2 Sink:Silicate Weathering or Carbonate Weathering[J].Quaternary Sciences,2011,31(3):426-430. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201103005.htm
[13] Liu Z H,Dreybrodt W,Wang H.A New Direction in Effective Accounting for the Atmospheric CO2 Budget:Considering the Combined Action of Aarbonate Dissolution,the Global Water Cycle and Photosynthetic Uptake of DIC by Aquatic Organisms[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2010,99(3-4):162-172. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.03.001
[14] 刘再华,Dreybrodt W.碳酸盐风化碳汇与森林碳汇的对比[J].中国岩溶,2012,31(4):345-348. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201204002.htm
Liu Z H,Dreybrodt W.Comparison of Carbon Sequestration Capacity between Carbonate Weathering and Forests:The Necessity to Change Traditional Ideas and Methods of Study of Carbon Sinks[J].Carsologica Sinica,2012,31(4):345-348. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201204002.htm
[15] 蒋忠诚,袁道先,曹建华,等.中国岩溶碳汇潜力研究[J].地球学报,2012,33(2):129-134. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201202001.htm
Jiang Z C,Yuan D X,Cao J H,et al.A Study of Carbon Sink Capacity of Karst Processes in China[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2012,33(2):129-134. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201202001.htm
[16] 陈静生,何大伟.珠江水系河水主要离子化学特征及成因[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),1999,35(6):786-793. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ199906008.htm
Chen J S,He D W.Chemical Characteristics and Genesis of Major Ions in the Pearl River Basin[J].Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis,1999,35(6):786-793. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ199906008.htm
[17] 高全洲,沈承德,孙彦敏,等.珠江流域的化学侵蚀[J].地球化学,2001,30(3):223-230. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200103003.htm
Gao Q Z,Shen C D,Sun Y M,et al.Chemical Weathering in Zhujiang River Drainage[J].Geochemica,2001,30(3):223-230. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200103003.htm
[18] 张连凯,秦小群,杨慧,等.珠江流域河流碳输出通量及变化特征[J].环境科学,2013,34(8):3025-3034. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201308014.htm
Zhang L K,Qin X Q,Yang H,et al.Transported Fluxes of the Riverine Carbon and Seasonal Variations in Pearl River Basin[J].Environmental Science,2013,34(8):3025-3034. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201308014.htm
[19] Yu S,He S Y,Sun P,et al.Impacts of Anthropogenic Activities on Weathering and Carbon Fluxes:A Case Study in the Xijiang River Basin,Southwest China[J].Environment Earth Science,2016,75:589. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-5226-5
[20] Sun H G,Han J T,Zhang S R,et al.Carbon Isotopic Evidence for Transformation of DIC to POC in the Lower Xijiang River,SE China[J].Quaternary International,2015,380-381:288-296. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.01.018
[21] 黄婕,于奭.梧州水文站和昭平水文站岩溶碳汇特点研究[J].水文地质工程地质,2014,41(4):136-141. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201404029.htm
Huang J,Yu S.Studies of the Characteristic Carbon Sink in the Water of the Wu Zhou Hydrological Station and the ZhaoPing Hydrological Station[J].Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,2014,41(4):136-141. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201404029.htm
[22] 于奭,孙平安,杜文越,等.人类活动影响下水化学特征的影响:以西江中上游流域为例[J].环境科学,2015,36(1):72-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201501010.htm
Yu S,Sun P A,Du W Y,et al.Effect of Hydrochemistry Characteristics under Impact of Human Activity:A Case Study in the Upper Reaches of Xijiang River Basin[J].Environmental Science,2015,36(1):72-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201501010.htm
[23] 裴建国,章程,张强,等.典型岩溶水岩溶碳汇通量估算[J].岩矿测试,2012,31(5):884-888. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120524&flag=1
Pei J G,Zhang C,Zhang Q,et al.Flux Estimation of Carbon Sink in Typical Karst Water Systems[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis,2012,31(5):884-888. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120524&flag=1
[24] 曹建华,杨慧,康志强.区域碳酸盐岩溶蚀作用岩溶碳汇通量估算初探:以珠江流域为例[J].科学通报,2011,56(26):2181-2187. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201126007.htm
Cao J H,Yang H,Kang Z Q.Preliminary Regional Estimation of Carbon Sink Flux by Carbonate Rock Corrosion:A Case Study of the Pearl River Basin[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2011,56(26):2181-2187. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201126007.htm
[25] 康志强,梁礼革,何师意,等.广西弄拉表层岩溶动力系统水循环碳汇效应研究[J].地球学报,2014,35(4):481-486. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201404013.htm
Kang Z Q,Liang L G,He S Y,et al.The Carbon Sink during Karst Water Cycle in the Epikarst Dynamical System of Nongla,Guangxi[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2014,35(4):481-486. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201404013.htm
[26] 莫雪,蒲俊兵,袁道先,等.亚热带典型岩溶区地表溪流溶解无机碳昼夜变化特征及其影响因素[J].第四纪研究,2014,34(4):873-880. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201404020.htm
Mo X,Pu J B,Yuan D X,et al.Diel Variation and Influence Factors of Dissolved Inorganic Carbon in a Surface Creek Fed by a Karst Subterranean Stream in Subtropical Area SW China[J].Quaternary Sciences,2014,34(4):873-880. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201404020.htm
[27] 李亮,曹建华,黄芬,等.桂林潮田河Ca2+,Mg2+与HCO3-关系模型及岩溶碳汇影响因素分析[J].水文地质工程地质,2013,40(4):106-111. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201304020.htm
Li L,Cao J H,Huang F,et al.Relation Models of Ca2+,Mg2+ and HCO- 3and Analyses of Carbon Sinks Influencing Factors in the Chaotian River,Guilin[J].Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,2013,40(4):106-111. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201304020.htm
[28] 闫志为,刘辉利,陶宗涛.温度对水中碳酸平衡的影响浅析[J].中国岩溶,2011,30(2):128-131. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201102003.htm
Yan Z W,Liu H L,Tao Z T.Temperature Effect on Carbonic Acid Balance in Water[J].Carsologica Sinica,2011,30(2):128-131. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201102003.htm
[29] 康志强,袁道先,常勇,等.岩溶碳汇的主控因子——水循环[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2011,41(5):1542-1547. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201105031.htm
Kang Z Q,Yuan D X,Chang Y,et al.The Main Controlling Factor of Karst Carbon Sequestration:About Water Cycle[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2011,41(5):1542-1547. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201105031.htm
[30] 陶贞,高全州,刘昆.流域化学风化过程的碳汇能力[J].第四纪研究,2011,31(3):408-415. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201103003.htm
Tao Z,Gao Q Z,Liu K.Carbon Sequestration Capacity of the Chemical Weathering Process within Drainage Basins[J].Quaternary Sciences,2011,31(3):408-415. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201103003.htm
-



 下载:
下载: