U-Pb Geochronology and Trace Element Compositions of Zircon in Biotite Granite from the Bagaladong Pb-Zn Deposit, Tibet and Their Geological Significance
-
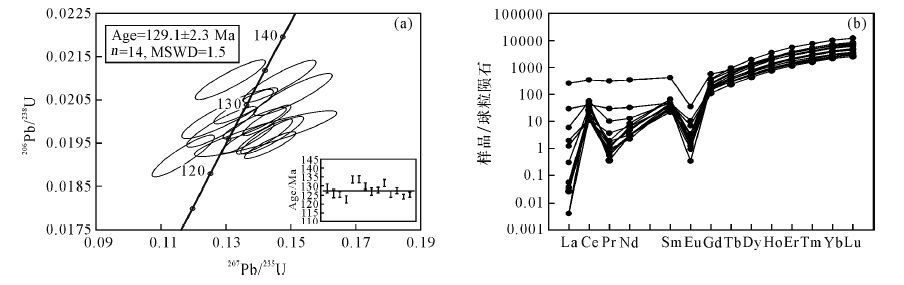
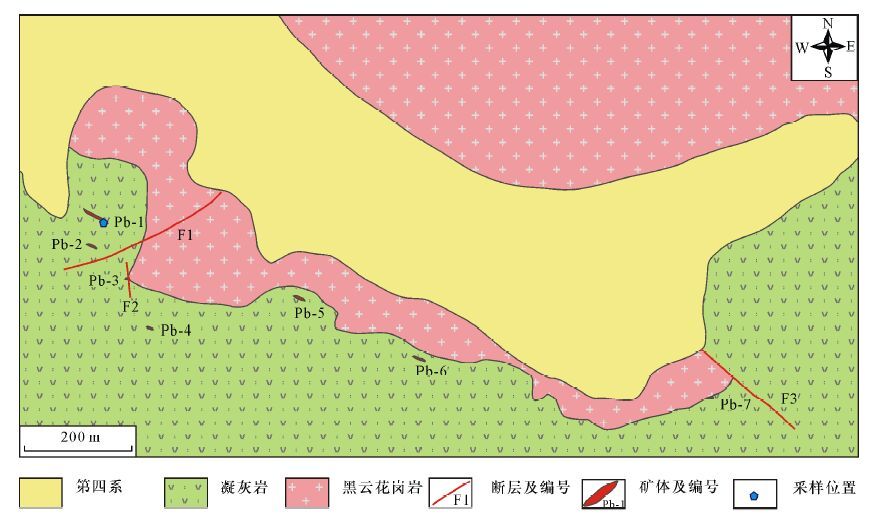
摘要: 巴嘎拉东铅锌矿床位于冈底斯弧背断隆带东段,研究程度较低,尚未开展成岩成矿年代学研究。本文选取该矿床黑云母花岗岩进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学和微量元素组成测试,并利用锆石Ti温度计方法获得锆石结晶温度。结果表明,黑云母花岗岩锆石均为典型岩浆成因锆石,14个测点得到的锆石206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为129.1±2.3 Ma(MSWD=1.5),岩体侵位于早白垩世中期,与前人获得的该期岩浆侵位年龄一致。锆石ΣLREEs=13.21~530.28 μg/g,平均值61.90 μg/g,ΣHREEs=849.16~3981.54 μg/g,平均值1826.91 μg/g,具有轻稀土亏损、重稀土富集的左倾配分模式;δCe=1.20~701.77,δEu=0.01~0.12,表现出明显的铈正异常和铕负异常特征。锆石Ti含量分布在0.60~7.40之间,结晶温度范围为593.9~795.3℃,平均温度724.3℃,一定程度反映了成岩温度。可以推断,巴嘎拉东黑云母花岗岩可能形成于班公湖-怒江洋闭合后的碰撞造山挤压阶段,黑云母花岗岩形成时代的厘定代表了成矿时代的上限,为区域上同时代铅锌矿找矿勘查提供了重要依据。Abstract: The Bagaladong Pb-Zn deposit is located in the eastern segment of the Gangdese back-arc uplift belt and lacks enough study with no available ages for ores and rocks. Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) zircon U-Pb dating and in situ trace elements were carried out for mineralization-related biotite granite in the Bagaladong Pb-Zn deposit and are reported in this paper. The crystallization temperatures of zircons in the biotite granite are obtained by using the zircon Ti thermometer. Trace element composition of zircons in the biotite granite indicates a magmatic origin. Fourteen zircons yield a weighted average 206Pb/238U ages of 129.1±2.3 Ma (MSWD=1.5), suggesting that the biotite granite was established in the middle of the Early Cretaceous, which is consistent with the age of magmatic intrusions obtained by previous studies. Zircon has ΣLREEs values of 13.21-530.28 μg/g with an average of 61.90 μg/g and ΣHREEs values of 849.16-3981.54 μg/g with an average of 1826.91 μg/g. Zircon has left-inclined REEs patterns with relative LREEs depletion and HREEs enrichment. These zircons have δCe and δEu values of 1.20-701.77 and 0.01-0.12, respectively, indicating obviously positive Ce anomalies and negative Eu anomalies. Zircons have Ti contents varying from 0.60 to 7.40 and crystallization temperatures of 593.9-795.3℃ with an average of 724.3℃, which partially reflect the diagenetic temperature. It can be concluded that the Bagaladong biotite granite was probably formed during the extrusion stage of collision after the closure of the Bangong Co-Nujiang ocean basin. The age of the biotite granite in the Bagaladong deposit represents the upper limit of the metallogenic epoch and provides important evidence for prospecting the Early Cretaceous Pb-Zn mineralization in the east section of the Gangdese back-arc fault uplift area.
-

-
表 1 巴嘎拉东铅锌矿床黑云母花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学测试结果
Table 1. Isotopic data of U-Pb age determinations on zircon of biotite granite form the Bagaladong Pb-Zn deposit
样品号(LQLZK6-828) 元素含量(μg/g) Th/U 同位素比值 年龄(Ma) Th U 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 01 287.80 384.40 0.70 0.02017 0.00038 0.13056 0.00932 0.04653 0.00344 129 2 125 8 33 161 02 226.10 424.20 0.50 0.01972 0.00035 0.14227 0.01447 0.05257 0.00572 126 2 135 13 309 248 03 686.50 1961.80 0.30 0.01965 0.00027 0.14187 0.00571 0.05198 0.00216 125 2 135 5 283 94 04 346.50 721.10 0.50 0.01920 0.0003 0.11689 0.00632 0.04373 0.00237 123 2 112 6 - - 05 325.90 806.00 0.40 0.02093 0.00032 0.14655 0.00741 0.05041 0.00261 134 2 139 7 213 116 06 605.30 640.90 0.90 0.02096 0.00030 0.13141 0.00713 0.04531 0.00261 134 2 125 6 - - 07 274.80 564.40 0.50 0.02036 0.00028 0.13611 0.00649 0.04823 0.00242 130 2 130 6 109 124 08 689.20 731.20 0.90 0.01987 0.00031 0.12872 0.00710 0.04670 0.00258 127 2. 123 6 35 126 09 1430.00 3073.80 0.50 0.02003 0.00023 0.14262 0.00489 0.05093 0.00172 128 2 135 4 239 78 10 384.10 779.20 0.50 0.02062 0.00032 0.15072 0.00798 0.05275 0.00288 132 2 143 7 317 126 11 427.60 1452.70 0.30 0.01968 0.00029 0.14429 0.00638 0.05263 0.00231 126 2 137 6 322 100 12 722.80 1301.20 0.60 0.01996 0.00024 0.13887 0.00646 0.04997 0.00231 127 2 132 6 195 107 13 835.20 3603.90 0.20 0.01945 0.00021 0.14361 0.00523 0.05315 0.00200 124 1 136 5 345 81 14 471.50 1534.00 0.30 0.01961 0.00023 0.13675 0.00535 0.05033 0.00201 125 2 130 5 209 88 注:“-”表示误差数据予以剔除。 表 2 巴嘎拉东铅锌矿床黑云母花岗岩锆石微量元素组成及锆石Ti温度计算结果
Table 2. Trace elements compositions and results of crystallization temperture of zircons from the biotite granite in Bagaladong Pb-Zn deposit
测定点号 含量(×10-6) 温度(℃) La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y Ti 01 <0.05 16.29 <0.05 1.45 3.47 0.19 22.70 8.60 110.87 43.40 190.88 40.65 367.17 64.80 1234.25 3.67 728.6 02 0.29 7.20 0.17 1.50 5.10 0.10 29.30 11.40 143.37 54.90 244.49 52.50 489.30 84.65 1583.56 3.45 723.1 03 0.07 20.40 0.10 2.19 6.96 0.19 52.39 24.10 330.88 133.74 618.50 135.65 1225.10 214.50 3889.87 0.60 593.9 04 <0.05 9.48 0.07 1.40 4.48 0.10 32.90 13.44 182.40 72.69 323.20 71.09 634.70 111.20 2077.46 - - 05 <0.05 7.69 0.07 1.38 4.20 0.06 29.76 13.50 179.69 72.79 331.60 71.50 639.10 115.80 2101.87 5.10 759.2 06 1.40 35.00 0.96 6.05 7.45 0.40 31.69 10.85 127.00 48.79 213.10 44.88 403.80 74.18 1419.66 5.90 773.3 07 7.00 25.50 2.88 15.40 7.37 0.60 33.20 10.97 132.18 51.85 226.35 46.98 429.90 78.30 1447.80 7.20 792.8 08 <0.05 28.50 0.10 2.95 5.49 0.20 36.90 13.50 168.40 63.80 281.10 58.40 512.96 91.47 1830.68 3.15 715.3 09 61.68 210.76 29.99 161.20 64.56 2.08 119.40 30.20 303.10 107.95 460.80 95.87 865.70 155.58 3099.90 107.89 1160.1 10 <0.05 7.85 0.10 2.45 5.90 0.07 37.59 15.57 200.47 79.10 355.55 76.20 687.59 124.96 2289.77 7.40 795.3 11 <0.05 7.10 0.05 1.47 6.35 0.09 49.30 21.67 296.10 120.78 560.29 121.30 1098.76 197.25 3508.10 0.90 619.1 12 <0.05 13.50 0.19 3.89 10.16 0.19 71.96 28.28 346.06 137.10 586.60 120.86 1049.20 189.35 3841.36 6.10 776.4 13 0.46 7.29 0.35 3.05 10.10 0.10 76.46 35.85 498.28 198.59 915.97 195.47 1748.37 312.50 5720.00 6.07 775.6 14 <0.05 6.57 0.09 1.00 5.48 <0.05 40.30 18.70 256.05 104.10 480.00 103.79 928.78 172.18 3029.50 1.20 639.1 注:球粒陨石标准化数据值据Sun等[17],“-”表示低于检出限数据。 -
[1] Ding L,Lai Q Z.New Geological Evidence of Crustal Thickening in the Gangdese Block Prior to the Indo-Asian Collision[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2003,48(15):1604-1610. doi: 10.1007/BF03183969
[2] 翟庆国,李才,王天武,等.西藏折无地区晚白垩世二云母花岗岩地球化学特征及构造环境[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2004,34(1):27-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200401005.htm
Zhai Q G,Li C,Wang T W,et al.The Geochemistry and Tectonic Settings of Two-Micagranite in Zhewu Area,Tibet[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2004,34(1):27-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200401005.htm
[3] 翟庆国,李才,李惠民,等.西藏冈底斯中部淡色花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报,2005,24(4):349-353. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200504008.htm
Zhai Q G,Li C,Li H M,et al.U-Pb Zircon Age of Leucogranite in the Central Ggangdise,Tibet,and Its Geological Significance[J].Geological Bulletin of China,2005,24(4):349-353. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200504008.htm
[4] 杨德明,黄映聪,戴琳娜,等.西藏嘉黎县措麦地区含石榴子石二云母花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其意义[J].地质通报,2005,24(3):235-238. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200503003.htm
Yang D M,Huang Y C,Dai L N.SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Age of Garnet-bearing Two-Mica Granite at Comai Township,Lhari County,Tibet,and Its Significance[J].Geological Bulletin of China,2005,24(3):235-238. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200503003.htm
[5] 和钟铧,杨德明,王天武.冈底斯带桑巴区早白垩世后碰撞花岗岩类的确定及构造意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志,2006,25(3):185-193. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200603002.htm
He Z H,Yang D M,Wang T W.The Determination of Carly Cretaceous Post-collision Granitoids in Sangba Area of Gangdese Tectonic Belt and Its Tectonic Significance[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2006,25(3):185-193. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200603002.htm
[6] 高一鸣,陈毓川,唐菊兴,等.西藏工布江达县亚贵拉铅锌钼多金属矿床石英斑岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其地质意义[J].地质学报,2009,83(10):1436-1444. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200910009.htm
Gao Y M,Chen Y C,Tang J X,et al.SHRIMP U-Pb Dating of Zircon from Quartz Porphyry in the Yaguila Pb-Zn-Mo Deposit,Gongbujiangda County,Tibet and Its Geological Implication[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2009,83(10):1436-1444. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200910009.htm
[7] 费光春,温春齐,王成松,等.西藏墨竹工卡县洞中拉铅锌矿床花岗斑岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年[J].中国地质,2010,37(2):470-476. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201002022.htm
Fei G C,Wen C Q,Wang C S,et al.Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Age of Porphyry Granite in the Dongzhongla Lead-Zinc Deposit,Maizhokunggar County,Tibet[J].Geology in China,2010,37(2):470-476. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201002022.htm
[8] 崔晓亮,唐菊兴,多吉,等.西藏洞中拉铅锌矿床石英斑岩锆石U-Pb年代学研究[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2011,38(5):557-562. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201105013.htm
Cui X L,Tang J X,Dorji,et al.Zircon U-Pb Age of the Quartz Porphyry from Dongzhongla Pb-Zn Deposit in Tibet,China[J].Journal of Chengdu University of Technology,2011,38(5):557-562. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201105013.htm
[9] 杜欣,刘俊涛,王亚平.西藏拉屋铅锌多金属矿床地质特征及成因分析[J].矿产与地质,2004,18(5):410-414. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200405002.htm
D Xin,Liu J T,Wang Y P.Geological Character and Ore Genesis of the Lawu Copper-Lead-Zinc Polymetallic Ore Deposit[J].Mineral Resources & Geology,2004,18(5):410-414. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200405002.htm
[10] 连永牢,曹新志,燕长海,等.西藏工布江达县亚贵拉铅锌矿床地质特征及成因分析[J].地质与勘探,2009,45(5):570-576. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200905012.htm
Lian Y L,Cao X Z,Yan C H,et al.Geological Characteristics and Genesis of Yaguila Lead-Zinc Deposit in the Gongbujiangda County of Tibet Province[J].Geology & Exploration,2009,45(5):570-576. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200905012.htm
[11] 连永牢,曹新志,燕长海,等.西藏当雄县拉屋铜铅锌多金属矿床喷流沉积成因[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2010,40(5):1041-1046. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201005011.htm
Lian Y L,Cao X Z,Yan C H,et al.Exhalative Sedimentary Genesis of Lawu Copper-Lead-Zinc Deposit in Dangxiong County of Tibet[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2010,40(5):1041-1046. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201005011.htm
[12] 连永牢,曹新志,燕长海,等.西藏念青唐古拉地区铅锌银矿床成矿系列及找矿前景[J].贵州大学学报(自然科学版),2011,28(2):31-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDI201102008.htm
Lian Y L,Cao X Z,Yan C H,et al.Metallogenic Series and Prospecting Potential of Lead-Zinc-Silver Ore District in Nyainqentanglha,Tibet[J].Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Science Edition),2011,28(2):31-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDI201102008.htm
[13] 唐菊兴,王立强,郑文宝,等.冈底斯成矿带东段矿床成矿规律及找矿预测[J].地质学报,2014,88(12):2545-2555. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201412027.htm
Tang J X,Wang L Q,Zheng W B,et al.Ore Deposits Metallogenic Regularity and Prospecting in the Eastern Section of the Gangdese Metallogenic Belt[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2014,88(12):2545-2555. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201412027.htm
[14] 顾枫华,章永梅,刘瑞萍,等.内蒙古沙德盖花岗岩岩浆混合作用:岩相学、矿物化学和年代学证据[J].岩石学报,2015,31(5):1374-1390. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201505014.htm
Gu F H,Zhang Y M,Liu R P,et al.Magma Mixing and Mingling of the Shadegai Granite in Inner Mongolia:Evidence from Petrography,Mineral Chemistry and Geochronology[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2015,31(5):1374-1390. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201505014.htm
[15] Liu Y S,Hu Z C,Zong K Q,et al.Reappraisement and Refinement of Zircon U-Pb Isotope and Trace Element Analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2010,55(15):1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
[16] 吴元保,郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报,2004,49(16):1589-1604. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200416001.htm
Wu Y B,Zheng Y F.Genesis of Zircon and Its Constraints on Interpretation of U-Pb Age[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2004,49(16):1589-1604. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200416001.htm
[17] Sun S S,McDonough W F.Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts:Implications for Mantle Composition and Process//Saundern A D,Norry M J(eds.).Magmatism in the Ocean Basins[J].Geological Society London Special Publication,1989,42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[18] Belousova E A,Griffin W L,O'Reilly S Y,et al.Igneous Zircon:Trace Element Composition as an Indicator of Source Rock Type[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2002,143:602-622. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7
[19] 钟玉芳,马昌前,佘振兵.锆石地球化学特征及地质应用研究综述[J].地质科技情报,2006,25(1):27-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200601004.htm
Zhong Y F,Ma C Q,She Z B.Geochemical Characteristics of Zircon and Its Applications in Geosciences[J].Geological Science & Technology Information,2006,25(1):27-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200601004.htm
[20] 赵振华.副矿物微量元素地球化学特征在成岩成矿作用研究中的应用[J].地学前缘,2010,17(1):267-286. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201001027.htm
Zhao Z H.Trace Element Geochemistry of Accessory Minerals and Its Applications in Petrogenesis and Metallogenesis[J].Earth Science Frontiers,2010,17(1):267-286. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201001027.htm
[21] Watson E B,Wark D A,Thomas J B.Crystallization Thermometers for Zircon and Rutile[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2006,151:413-433. doi: 10.1007/s00410-006-0068-5
[22] 高晓英,郑永飞.金红石Zr和锆石Ti含量地质温度计[J].岩石学报,2011,27(2):417-432. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201102006.htm
Gao X Y,Zheng Y F.On the Zr-in-Rutile and Ti-in-Zircon Geothermometers[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2011,27(2):417-432. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201102006.htm
[23] Ferry M,Watson E B.New Thermodynamic Models and Revised Calibrations for the Ti-in-Zircon and Zr-in-Rutile Thermometers[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2007,154(4):429-437. doi: 10.1007/s00410-007-0201-0
[24] Hayden L A,Watson E B.Rutile Saturation in Hydrous Siliceous Melts and Its Bearing on Ti-Thermometry of Quartz and Zircon[J].Earth Planetary Science Letters,2007,258(3-4):561-568. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.04.020
[25] Lee J,Williams I,Ellis D.Pb,U and Th Diffusion in Nature Zircon[J].Nature,1997,390:159-162. doi: 10.1038/36554
-



 下载:
下载: