Study on the Total Iodine and Iodine Speciation Characteristics in Xilingol League, Inner Mongolia and Tacheng, Xinjiang High Iodine Area by HPLC-ICP-MS
-
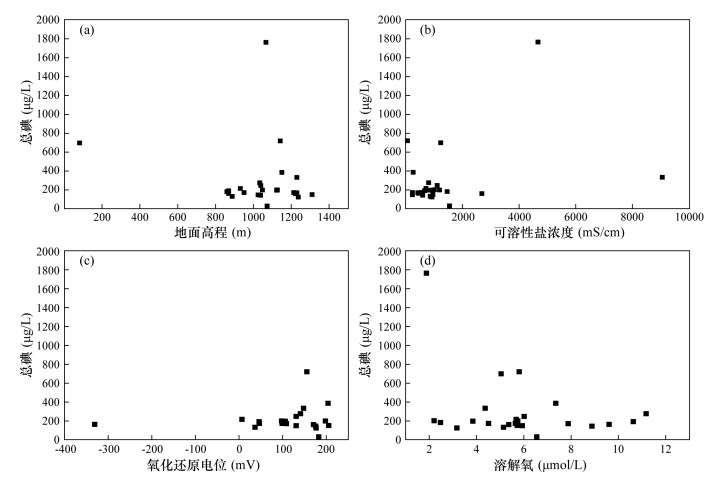
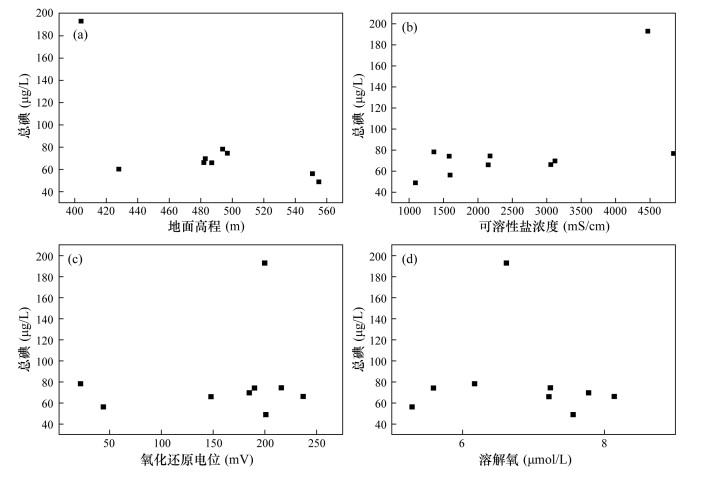
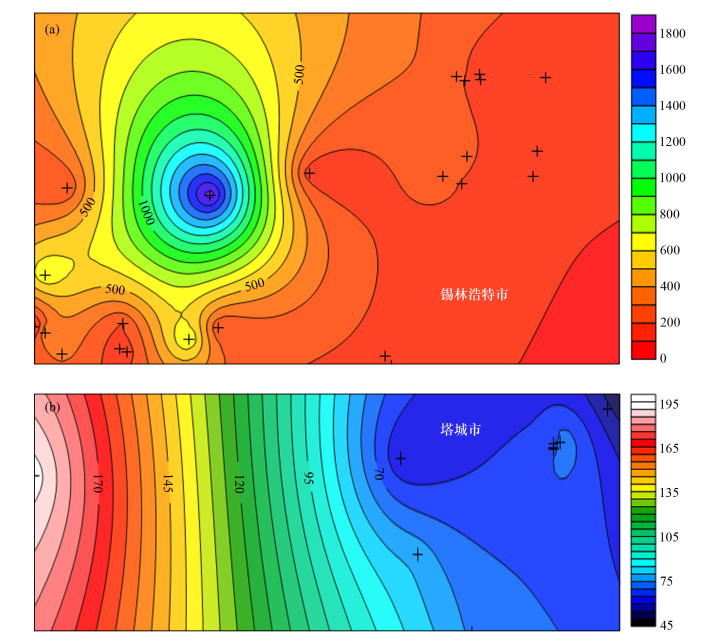
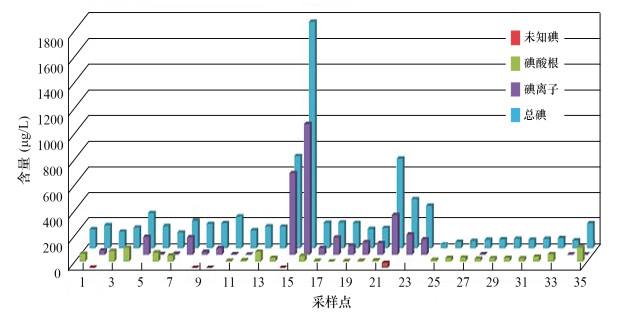
摘要: 长期饮用高碘水将对人体造成危害,地下水总碘及碘形态分析对于高碘地区碘环境地球化学研究具有重要价值。本文采用高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱联用技术对内蒙古锡盟与新疆塔城高碘地区地下水总碘及碘形态进行测定。研究表明:锡盟地区地下水中碘以I-形态为主,总碘量维持在200 μg/L,个别点位达到600 μg/L甚至1700 μg/L,呈环状分布,从东北至西南呈现“低-高-低”的分布规律;塔城地区地下水中的碘以IO3-形态为主,总碘量不足100 μg/L,个别点位接近200 μg/L,呈层状分布,自东向西逐渐升高。分析认为,氧化性的条件利于不同碘形态之间的转化;溶解氧过高或过低都不利于碘的储存;碘会随着可溶性盐的流失而流失;沿河流的流向,下游地势较低,总碘得到积累。本研究结果对于锡盟和塔城地区科学预防甲状腺肿、制定法律法规具有指导作用。
-
关键词:
- 地下水 /
- 总碘 /
- 碘形态 /
- 高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱
Abstract: Long-term drinking of high-content iodine water will cause harm to human health. The analysis of total iodine and iodine speciation in high iodine groundwater is of great value for iodine environmental geochemistry in high iodine regions. In this study, High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-ICP-MS) was used to analyze the total iodine and iodine speciation of groundwater in Xilingol League, Inner Mongolia and Tacheng, Xinjiang high iodine area. Results show that I- is dominant in Xilingol League groundwater and the total iodine is maintained at 200 μg/L, with individual points reaching 600 μg/L or even 1700 μg/L. The content of iodine in Xilingol League groundwater is distributed in a circular pattern, showing a 'low-high-low' distribution pattern from northeast to southwest. IO3- is dominant in Tacheng groundwater, with the total iodine content of less than 100 μg/L and the individual points are close to 200 μg/L. Moreover, the total iodine content increases gradually from east to west, showing a layered distribution. Oxidation condition is beneficial to the transformation between different iodine speciations. It is not conducive to the iodine enrichment when dissolved oxygen is too high or too low. Iodine will decrease with soluble salt loss. The downstream total iodine content is higher than the upstream content along the flow direction. This study is of significance to the scientific prevention of goiter and the establishment of laws and regulations in Xilingol League and Tacheng. -

-
[1] Cui S L, Liu P, Su X H, et al.Surveys in areas of high risk of iodine deficiency and iodine excess in China, 2012-2014:Current status and examination of the relationship between urinary iodine concentration and goiter prevalence in Children aged 8-10 years[J].Biomedical and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 30(2):88-96. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0895398817300375
[2] Andersen S, Iversen F, Terpling S, et al.Iodine deficiency influences thyroid autoimmunity in old age-A comparative population-based study[J].Maturitas, 2012, 71:39-43. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2011.10.001
[3] Chao H, Zhang Y F, Liu P, et al.Relationship between iodine content in household iodized salt and thyroid volume distribution in children[J].Biomedical and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 29(6):391-397. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/309259063_Relationship_between_Iodine_Content_in_Household_Iodized_Salt_and_Thyroid_Volume_Distribution_in_Children
[4] Weng H X, Hong C L, Yan A L, et al.Biogeochemical transport of iodine and its quantitative model[J].Science China:Earth Sciences, 2013, 56:1599-1606. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4594-5
[5] Aslami A A, Ansari M A, Khalique N, et al.Iodine deficiency in school children in Aligarh district, India[J]. Indian Pediatrics, 2016, 53(8):742-743. https://www.indianpediatrics.net/Epub01062016/RL-00009.pdf
[6] 吴飞, 王曾祺, 童秀娟, 等.我国典型地区浅层高碘地下水分布特征及其赋存环境[J].水资源与水工程学报, 2017, 28(2):99-104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404021.htm
Wu F, Wang Z Q, Tong X J, et al.The distribution characteristics and storage environments of rich iodine in shallow groundwater of typical areas in China[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 2017, 28(2):99-104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404021.htm
[7] Togo Y S, Takahashi Y, Amano Y, et al.Age and spe-ciation of iodine in groundwater and mudstones of the horonobe area, Hokkaido, Japan:Implications for the origin and migration of iodine during basin evolution[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 191:165-186. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.07.012
[8] Schwehr K A, Santschi P H.Sensitive determination of iodine species, including organo-iodine, for fresh water and seawater samples using high performance liquid chromatography and spectrophoto metric detection[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2003, 482:59-71. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00197-1
[9] Zhang S J, Chen X, Creeley D, et al.Iodine-129 and iodine-127 speciation in groundwater at the Hanford Site, U.S.:Iodate incorporation into calcite[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47:9635-9642. http://www.academia.edu/14345031/Response_to_Comment_on_Iodine-129_and_Iodine-127_Speciation_in_Groundwater_at_Hanford_Site_U.S._Iodate_Incorporation_into_Calcite_
[10] Li J X, Wang Y X, Guo W, et al.Iodine mobilization in groundwater system at Datong Basin, China:Evidence from hydrochemistry and fluorescence characteristics[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 468-469:738-745. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.092
[11] Romarís-Hortas V, Bianga J, Moreda-Piñeiro A, et al.Speciation of iodine-containing proteins in Nori seaweed by gel electrophoresis laser ablation ICP-MS[J].Talanta, 2014, 127:175-180. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2014.04.003
[12] 刘列钧, 王海燕, 李秀维, 等.我国水源型高碘地区水碘形态的研究[J].疾病监测, 2012, 27(11):891-893. doi: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2012.11.015
Liu L J, Wang H Y, Li X W, et al.Research on forms of iodine in water in areas with rich iodine in water in China[J].Disease Surveillance, 2012, 27(11):891-893. doi: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2012.11.015
[13] Zhang E Y, Wang Y Y, Qian Y, et al.Iodine in ground-water of the North China Plain:Spatial patterns and hydrogeochemical processes of enrichment[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 135:40-53. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.11.016
[14] Li J X, Wang Y X, Xie X J, et al.Effects of water-sediment interaction and irrigation practices on iodine enrichment in shallow groundwater[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 543:293-304. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.10.002
[15] 谭俊, 朱霞萍, 刘苗苗, 等.紫外光谱法同时测定卤水海产品中I-和IO3-[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(6):1628-1632. http://doi.wanfangdata.com.cn/10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)06-1628-05
Tan J, Zhu X P, Liu M M, et al.Determination of iodine and iodate in brine and seafood simultaneously by ultraviolet absorption spectrometry[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(6):1628-1632. http://doi.wanfangdata.com.cn/10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)06-1628-05
[16] 刘崴, 杨红霞, 李冰, 等.乙醇增强-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定植物样品中的痕量碘[J].分析试验室, 2010, 29(6):31-33. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxsys201006008
Liu W, Yang H X, Li B, et al.Determination of iodine concentration in plant samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with ethanol as a signal enhancer[J].Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2010, 29(6):31-33. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fxsys201006008
[17] Liu L J, Li X W, Wang H Y, et al.Reduction of iodate in iodated salt to iodide during cooking with iodine as measured by an improved HPLC/ICP-MS Method[J].Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 2017, 42:95-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.12.009
[18] Yang H X, Liu W, Li B, et al.Speciation analysis for iodine in groundwater using high performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (HPLC-ICP-MS)[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2007, 31(4):345-351. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2007.31.issue-4
[19] 刘崴, 杨红霞, 李冰, 等.高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱测定地下水中碘形态稳定[J].分析化学, 2007, 35(4):571-574. http://online.analchem.cn:8080/fxhx/CN/abstract/abstract6439.htm
Liu W, Yang H X, Li B, et al.Study on speciation stabilities of iodine in underground water by high performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 35(4):571-574. http://online.analchem.cn:8080/fxhx/CN/abstract/abstract6439.htm
[20] 李冰, 杨红霞, 刘崴, 等.溴、碘、砷、镉等有益有害元素元素形态分析技术及生态环境地球化学应用[J].地球学报, 2013, 34(4):395-400. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2013.04.02
Li B, Yang H X, Liu W, et al.The speciation analysis of such elements as bromine, iodine, arsenic and cadmium and their application in environmental geochemistry[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2013, 34(4):395-400. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2013.04.02
[21] 杨红霞, 陈俊良, 高津旭, 等.利用傅立叶变换离子回旋共振质谱测定不同季节水源水中天然有机质分子结构[J].生态学杂志, 2017, 36(4):1053-1059. http://www.cje.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8040.shtml
Yang H X, Chen J L, Gao J X, et al.Characterization of molecular composition and seasonal variation of NOM in source water using Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(4):1053-1059. http://www.cje.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8040.shtml
[22] 刘崴, 杨红霞, 李冰.电感耦合等离子体质谱在高碘区碘含量分布特征中的应用[J].内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学汉文版), 2014, 43(6):703-707. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95820X/201406/663323062.html
Liu W, Yang H X, Li B.Application of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in the study of iodine distribution in a high iodine content area[J].Journal of Inner Mongolia Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 43(6):703-707. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95820X/201406/663323062.html
[23] 徐芬, 马腾, 石柳, 等.内蒙古河套平原高碘地下水的水文地球化学特征[J].水文地质工程地质, 2012, 39(5):8-15. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swdzgcdz201205002
Xu F, Ma T, Shi L, et al.Hydrogeochemical characteristics of high iodine groundwater in the Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia[J].Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2012, 39(5):8-15. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swdzgcdz201205002
[24] Li J X, Zhou H l, Qian K, et al.Fluoride and iodine enrichment in groundwater of North China Plain:Evidences from speciation analysis and geochemical modeling[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 598:239-248. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.158
[25] 王妍妍, 马腾, 董一慧, 等.内陆盆地区高碘地下水的成因分析:以内蒙古河套平原杭锦后旗为例[J].地学前缘, 2014, 21(4):66-73. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98600X/201404/49830511.html
Wang Y Y, Ma T, Dong Y H, et al.The formation of inland-high-iodine groundwater:A case study in Hangjinhouqi, Hetao Plain[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(4):66-73. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98600X/201404/49830511.html
[26] Duan L, Wang W K, Sun Y B, et al.Iodine in ground-water of the Guanzhong Basin, China:Sources and hydrogeo chemical controls on its distribution[J].Environment Earth Science, 2016, 75(11):1-11.
[27] Li J X, Wang Y X, Xie X J, et al.Effects of water-sediment interaction and irrigation practices on iodine enrichment in shallow groundwater[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 543:293-304. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.10.002
[28] 钱永, 张兆吉, 费宇红, 等.华北平原饮用地下水碘分布及碘盐分区供应探讨[J].生态与农村环境学报, 2014, 30(1):9-14. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ncsthj201401002
Qian Y, Zhang Z J, Fei Y H, et al.Spatial distribution of iodine in underground drinking water and discussion on region-specific supply of iodized salt in the North China Plain[J].Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2014, 30(1):9-14. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ncsthj201401002
[29] Li J X, Wang Y X, Guo W, et al.Factors controlling spatial variation of iodine species in groundwater of the Datong Basin, Northern China[J].Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 2013, 7:483-486. doi: 10.1016/j.proeps.2013.03.054
[30] 李洪伟, 刘晓端, 李保山.地下水和土壤中不同形态碘的分离测定[J].岩矿测试, 2009, 28(4):337-341. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20090407
Li H W, Liu X D, Li B S.Separation and determination of different iodine species in ground water and soil samples[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2009, 28(4):337-341. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20090407
-




 下载:
下载: