-
摘要: 经过酸化改性后的天然磁铁矿,由于比表面积和内部结构发生变化,从而表现出很好的除砷性能,进一步研究其对水体中砷的吸附特征,为实际工程应用提供数据是十分必要的。本文对经0.5 mol/L盐酸浸泡、150℃温度下灼烧10 min的改性磁铁矿吸附砷的特征进行了表征,绘制吸附速率曲线图。吸附影响因素实验结果显示:当初始pH为6~9时,吸附性能强;Cl-、Ca2+、Mg2+、HCO3-、CO32-离子与As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ)不会产生竞争吸附,PO43-、NO3-、SO42-离子与As(Ⅲ)产生竞争性吸附,且PO43- > SO42- > NO3-;PO43-、NO3-离子与As(Ⅴ)产生竞争性吸附。结合X射线衍射、扫描电镜等研究结果,初步探讨了改性磁铁矿的除砷机理,认为改性后的磁铁矿比表面积明显增大,表面生成物含有Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)是其吸附砷能力提高的主要原因。实验结果证实,改性天然磁铁矿是一种值得进一步研究并实际应用的水体除砷材料。Abstract: Acid-modified natural magnetite shows excellent arsenic removal properties due to its change in specific surface area and internal structure. It is essential to study further its adsorption to arsenic in water, in order to provide data for practical engineering applications. The feature of arsenic adsorption by modified magnetite immersed in 0.5 mol/L hydrochloric acid and ignited for 10 minutes at 150℃, and the construction of its adsorption rate curve chart is described in this paper. Results of the experiment on adsorption influencing factors indicate that when initial pH value are 6-9, magnetite shows strong adsorption property. Ions such as Cl-, Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3-, CO32- do not have competitive adsorption with As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ), but PO43-, NO3-, and SO42- have competitive adsorption with As(Ⅲ), in the order of PO43->SO42- >NO3-. PO43- and NO3- have competitive adsorption with As(Ⅴ). In combination with XRD, SEM, and other research results, preliminarily studies show the arsenic removal mechanism of modified magnetite, and conclude that modified magnetite shows an obviously increased specific surface area and that Fe(Ⅱ) and Fe(Ⅲ) contained in its surface products are the main cause for improving arsenic adsorption ability. Experimental results demonstrate that modified natural magnetite is a de-arsenic material for water, which deserves further study and practical application.
-

-
表 1 Lagergren准一级和假二级吸附动力学模型拟合参数
Table 1. Kinetic parameters for As adsorption on the modified magnetite
As形态 温度
(℃)准一级动力学模型 假二级动力学模型 qe(exp)
(μg/g)R2 K1(h-1) qe(cal)(μg/g) R2 K2[(g/μg)h] q2(μg/g) As(Ⅲ) 15 0.9126 2.1017 54.97 0.9813 0.0108 92.59 91.53 25 0.9920 2.2845 43.77 0.9809 0.0118 84.75 91.12 35 0.9408 2.1667 18.92 0.9983 0.0106 94.34 94.10 45 0.9090 2.0934 18.92 0.9979 0.0108 92.59 98.29 As(Ⅴ) 15 0.9909 0.0507 1.12 0.9289 0.0068 147.06 97.49 25 0.9092 0.0654 1.16 0.9953 0.0103 97.08 98.00 35 0.9701 0.0209 1.05 0.9383 0.0093 107.53 94.20 45 0.9092 1.2271 16.87 0.9933 0.0088 113.64 97.89 -
[1] Mahanta R, Chowdhury J, Nath H K.Health costs of arsenic contamination of drinking water in Assam, India[J].Economic Analysis & Policy, 2016, 49:30-42. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0313592615300436
[2] Ouédraogo I W K, Pehlivan E, Tran H T, et al.Removal of arsenic(Ⅴ) from aqueous medium using manganese oxide coated lignocellulose/silica adsorbents[J].Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry, 2015:1-21. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233611863_Chrome_Waste_as_Sorbent_for_the_Removal_of_ArsenicV_from_Aqueous_Solution
[3] Taleb K, Markovski J, Milosavljević M, et al.Efficient arsenic removal by cross-linked macroporous polymer impregnated with hydrous iron oxide:Material performance[J].Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 279:66-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.147
[4] Michael H A.An arsenic forecast for China[J].Science, 2013, 341(6148):852-853. doi: 10.1126/science.1242212
[5] Rodríguez-Lado L, Sun G, Berg M, et al.Groundwater arsenic contamination throughout China[J].Science, 2013, 341(6148):866-868. doi: 10.1126/science.1237484
[6] Baig S A, Sheng T, Hu Y, et al.Arsenic removal from natural water using low cost granulated adsorbents:A review[J].CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water, 2015, 43(1):13-26. doi: 10.1002/clen.201200466
[7] Bora A J, Mohan R, Dutta R K.Simultaneous removal of arsenic, iron and manganese from groundwater by oxidation-coagulation-adsorption at optimized pH[J].Water Science & Technology Water Supply, 2017:ws2017092. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/es048991u
[8] Mohan D, Sharma R, Singh V K, et al.Fluoride removal from water using bio-char, a green waste, low-cost adsorbent:Equilibrium uptake and sorption dynamics modeling[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(2):900-914. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ie202189v
[9] Basu A, Saha D, Saha R, et al.A review on sources, toxicity and remediation technologies for removing arsenic from drinking water[J].Cheminform, 2014, 40(2):447-485. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s11164-012-1000-4.pdf
[10] 吴昆明, 郭华明, 魏朝俊.天然磁铁矿化学改性及其在水体除砷中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(1):32-39. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.005
Wu K M, Guo H M, Wei C J.Chemical modification of natural magnetite and its application in arsenic removal from water[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(1):32-39. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.005
[11] Wang Y, Shen F, Qi X.A corn stalk-derived porous carbonaceous adsorbent for adsorption of ionic liquids from aqueous solution[J].RSC Advances, 2016, 39:32505-32513. http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/RA/2016/C6RA06908H#!
[12] Yamani J S, Lounsbury A W, Zimmerman J B.Towards a selective adsorbent for arsenate and selenite in the presence of phosphate:Assessment of adsorption efficiency, mechanism, and binary separation factors of the chitosan-copper complex[J].Water Research, 2016, 88:889. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.017
[13] Zhu N, Yan T, Qiao J, et al.Adsorption of arsenic, ph-osphorus and chromium by bismuth impregnated biochar:Adsorption mechanism and depleted adsorbent utilization[J].Chemosphere, 2016, 164:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.036
[14] Lagergren S.About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances[J].Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar Band, 1989, 24(4):1-39. http://www.sciepub.com/reference/163936
[15] Ho Y S, Mckay G.Pseudo-second order model for sorp-tion processes[J].Process Biochemistry, 1999, 34(5):451-465. doi: 10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
[16] Lladó J, Lao-Luque C, Ruiz B, et al.Role of activated carbon properties in atrazine and paracetamol adsorption equilibrium and kinetics[J].Process Safety & Environmental Protection, 2015, 95:51-59. http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/Database/HAZ3507001554
[17] 赵凯, 郭华明, 李媛, 等.天然菱铁矿改性及强化除砷研究[J].环境科学, 2012, 33(2):459-468. http://www.oalib.com/references/17743116
Zhao K, Guo H M, Li Y, et al.Modification of natural siderite and enhanced adsorption of arsenic[J].Environmental Science, 2012, 33(2):459-468. http://www.oalib.com/references/17743116
[18] Qiao J, Jiang Z, Sun B, et al.Arsenate and arsenite re-moval by FeCl3:Effects of pH, As/Fe ratio, initial As concentration and co-existing solutes[J].Separation & Purification Technology, 2012, 92(1):106-114.
[19] Amstaetter K, Borch T, Laresecasanova P, et al.Redox transformation of arsenic by Fe(Ⅱ)-activated goethite (α-FeOOH)[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(1):102-108.
[20] Hcry M, Van Dongen B E, Gill F, et al.Arsenic release and attenuation in low organic carbon aquifer sediments from West Bengal[J].Geobiology, 2010, 8(2):155-168. doi: 10.1111/gbi.2010.8.issue-2
-

| 引用本文: | 吴昆明, 郭华明, 魏朝俊. 改性磁铁矿对水体中砷的吸附特性研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2017, 36(6): 624-632. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201709110147 |
| Citation: | Kun-ming WU, Hua-ming GUO, Chao-jun WEI. Adsorption Characteristics of Arsenic in Water by Modified Magnetite[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(6): 624-632. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201709110147 |
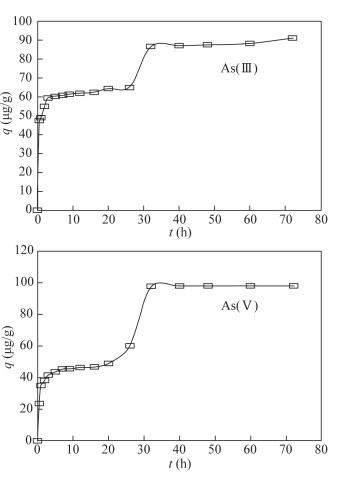
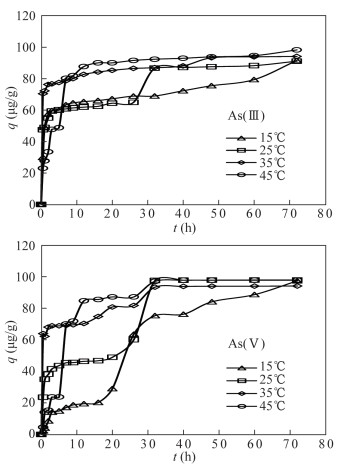
- Figure 1. Effect of contact time on arsenic adsorption from As(Ⅲ) solution and As(Ⅴ) solution by the modified magnetite
- Figure 2. Effect of the existing form of As on the adsorption reaction of modified magnetite
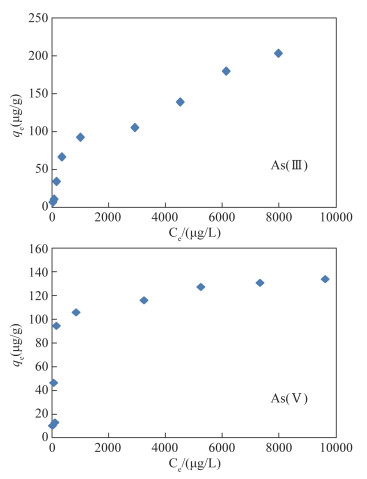
- Figure 3. Effect of the initial concentration of As on the adsorption of As by modified magnetite
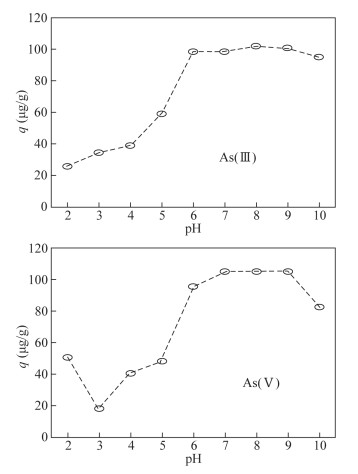
- Figure 4. Effect of initial pH of solution on adsorption of As by modified magnetite
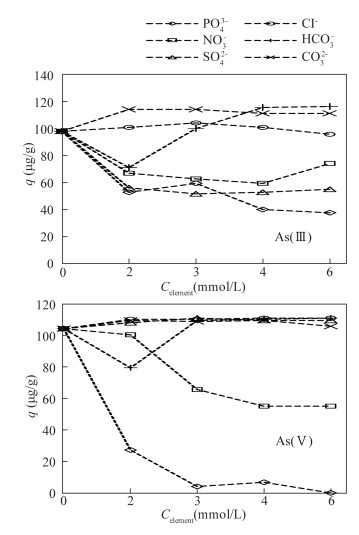
- Figure 5. Effect of coexisting anions on adsorption of As by modified magnetite
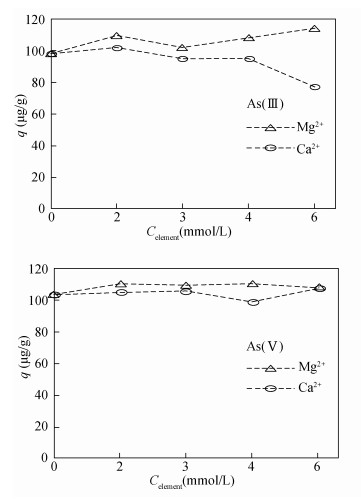
- Figure 6. Effects of coexisting cations on adsorption of As by modified magnetite
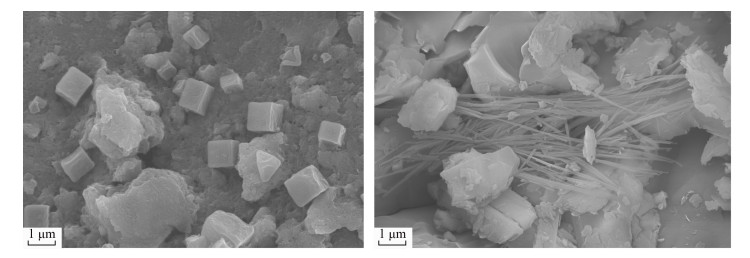
- Figure 7. SEM micrographs of natural magnetite (Left) and modified magnetite (Right)


 下载:
下载: