Study on Shale Organic Porosity in the Longmaxi Formation, AnYe-1 Well Using Field Emission-Scanning Electron Microscopy and PerGeos System
-
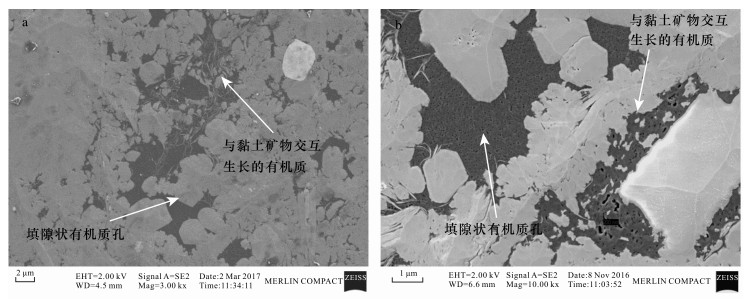
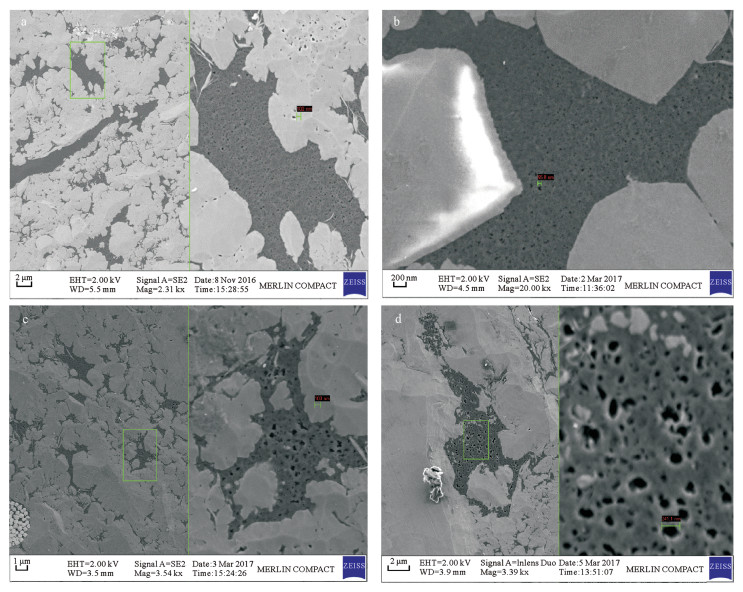
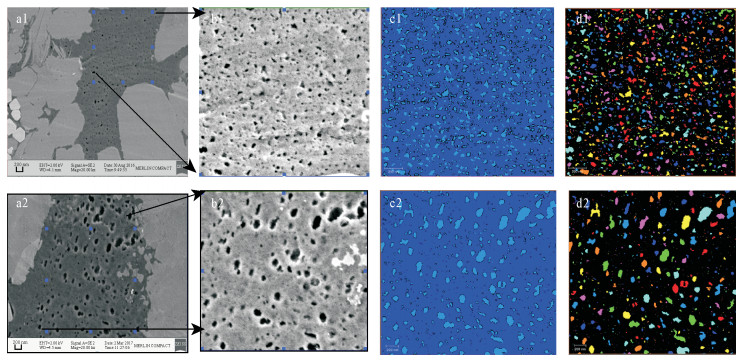
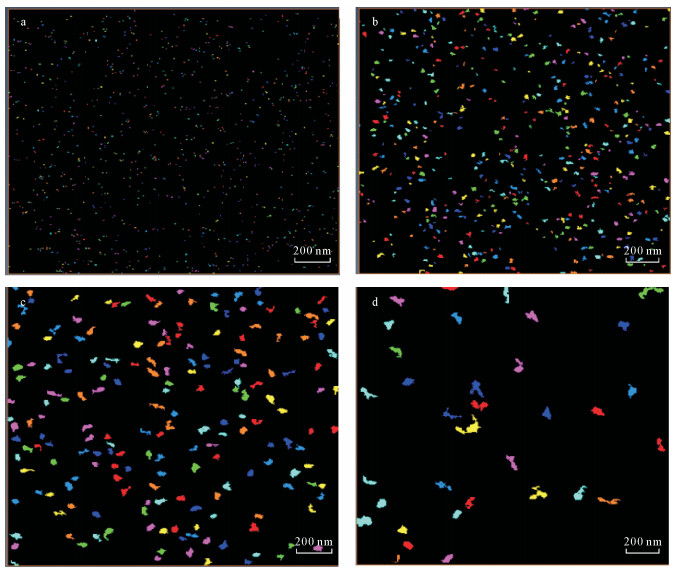
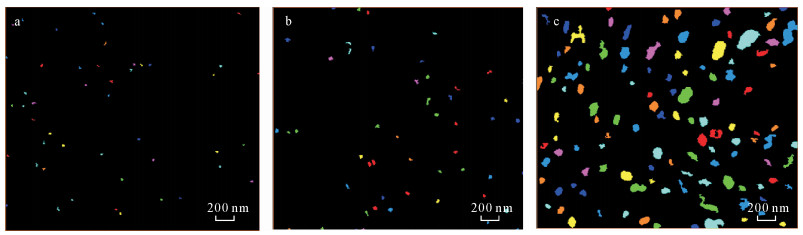
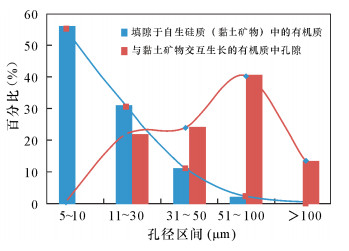
摘要: 安页1井是中国地质调查局在我国南方盆地外围武陵山复杂构造区实施并取得页岩气突破的一口地质调查参数井。本文以安页1井龙马溪组富有机质页岩为研究对象,利用场发射扫描电镜,研究了上扬子地区盆地外围龙马溪组富有机质页岩储集空间类型,并将PerGeos数字岩石处理系统引入有机质孔隙定量分析,定量刻画了有机质微纳米孔隙结构及发育特征。研究认为:有机质孔隙是安页1井龙马溪组富有机质页岩最主要的储集空间,形态上表现为填隙于自生硅质中的有机质发育着均匀海绵状孔隙结构,或与黏土矿物交互生长的有机质发育着气泡状孔隙结构,这两类不同赋存形态的有机质的孔隙均极为发育。通过PerGeos数字岩石系统处理,揭示了两类有机质孔隙孔径发育呈现双众数分布,其中海绵状结构的有机质孔隙孔径众数为5~10 nm,气泡状结构的有机质孔隙孔径众数为51~100 nm,有机质孔隙主要介于中孔~宏孔范畴。安页1井龙马溪组有机质孔隙的大量发育,指示了盆地外围的龙马溪组页岩经历了较强烈的生烃过程并具有较好的储集能力,具备良好的开发潜力。
-
关键词:
- 龙马溪组 /
- 页岩 /
- 场发射扫描电镜 /
- 有机质微纳米孔隙 /
- PerGeos数字岩石处理系统
Abstract:BACKGROUND AnYe-1 well is a geological survey parameter well implemented by China Geological Survey. It has achieved shale gas breakthrough in the Wuling complex structural area outside the southern basin of China. BAOBJECTIVES To quantitatively characterize micro-and nano-pore structure and development characteristics of organic matter, by researching organic matter pore on Longmaxi shale of AnYe-1 well. METHODS Field Emission-Scanning Electron Microscope was used to study the reservoir type of the organic-rich shale of the Longmaxi Formation at the periphery of the basin in the Upper Yangtze region, and the PerGeos digital rock treatment system was introduced into the organic pores quantitative analysis. RESULTS The organic pore is the most important reservoir space of the organic-rich shale of the Longmaxi Formation in Anye-1 well. It is characterized by organic matter interstitially forming in the authigenic siliceous organic matter with uniform sponge-like pore structure, or organic matter that interacts with clay minerals with a bubble-like pore structure. Pores in two different types of organic matter are extremely developed. The PerGeos digital rock system reveals that the pore sizes of the two organic pores show a bimodal distribution, in which the pore size of the organic pores with the sponge-like structure is 5 to 10 nm, and the pore size of the organic pores with the bubble-like structure is 51 to 100 nm. The organic pores are mainly in the mesopore to macropore category. CONCLUSIONS The abundant development of organic matter pores in the Longmaxi Formation in AnYe-1 well indicates that the Longmaxi Formation shale in the periphery of the basin has experienced a strong hydrocarbon generation process and has a good storage capacity, showing a potential for development in the future. -

-
表 1 两类有机质及其孔隙发育特征、参数对比
Table 1. A comparison of pores characteristics and parameters developed in two types of organic matters
统计参数(PerGeos系统统计及电镜观察) 填隙于自生硅质中的有机质 与黏土矿物交互生长的有机质 两类有机质占总有机质百分比(观察) 约55% 约40% 有机孔等效圆孔隙直径主体范围(观察) 10~50 nm 30~120 nm 数字岩石系统统计的单位面积内(μm2)孔隙个数范围 200~500 10~50 数字岩石系统统计的单个有机质面孔率范围(%) 15~30 5~40 数字岩石系统统计的孔径平均值 20 85 数字岩石系统统计的孔径D10/D50/D90值(或范围) 6/6/15~30 50/60/80~120 -
[1] Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al.Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometer-scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett shale[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2009, 79(9):848-861. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2009JSedR..79..848L
[2] Schieber J. Common themes in the formation and preserv-ation of intrinsic porosity in shales and mudstones-illuminated with examples across the phanerozoic[R]. 2010, SPE132370: 2-10.
[3] Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C.Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1071-1098. doi: 10.1306/08171111061
[4] Chalmers G R, Bustin R M, Power I M.Characterization of gas shale pore systems by porosimetry, pycnometry, surface area, and field emission scanning electron microscopy/transmission electron microscopy image analyses:Examples from the Barnett, Woodford, Haynesville, Marcellus, and Doigunits[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1099-1119. doi: 10.1306/10171111052
[5] Löhr S C, Baruch E T, Hall P A.Is organic pore development in gas shales influenced by the primary porosity and structure of thermally immature organic matter?[J].Organic Geochemistry, 2015, 87:119-132. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2015.07.010
[6] Loucks R G, Reed R M.Scanning electron microscope petrographic evidence for distinguishing organic matter pores associated with depositional organic matter versus migrated organic matter in mudrock[J].GCAGS Journal, 2014, 3:51-60. http://www.mendeley.com/catalog/scanningelectronmicroscope-petrographic-evidence-distinguishing-organicmatter-pores-associated-depos/
[7] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 白斌, 等.中国油气储层中纳米孔首次发现及其科学价值[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(6):1857-1864. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201106024.htm
Zou C N, Zhu R K, Bai B, et al.First discovery of nanopore throat in oil and gas reservoir in China and its scientific value[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(6):1857-1864. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201106024.htm
[8] 帅琴, 黄瑞成, 高强, 等.页岩气实验测试技术现状与研究进展[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(6):931-938. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120604
Shuai Q, Huang R C, Gao Q, et al.Research development of analytical techniques for shale gas[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(6):931-938. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120604
[9] 于炳松.页岩气储层孔隙分类与表征[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(4):211-220. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Conference?id=Conference_8681345
Yu B S.Classification and characterization of gas shale pore system[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4):211-220. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Conference?id=Conference_8681345
[10] 张盼盼, 刘小平, 王雅杰, 等.页岩纳米孔隙研究新进展[J].地球科学进展, 2014, 29(11):1242-1249. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.11.1242
Zhang P P, Liu X P, Wang Y J, et al.Research progress in shale nanopores[J].Advances in Earth Science, 2014, 29(11):1242-1249. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.11.1242
[11] 焦淑静, 张慧, 薛东川, 等.泥页岩孔隙类型、形态特征及成因研究[J].电子显微学报, 2015, 34(5):422-427. http://www.doc88.com/p-3397745325075.html
Jiao S J, Zhang H, Xue D C, et al.Study on morphological characteristics of micropores and microcracks in shale[J].Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2015, 34(5):422-427. http://www.doc88.com/p-3397745325075.html
[12] 伍岳, 樊太亮, 蒋恕, 等.海相页岩储层微观孔隙体系表征技术及分类方案[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(4):92-97. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/f5a970eaf46527d3240ce0e0-2.html
Wu Y, Fan T L, Jiang S, et al.Characterizing techniques and classification methods for microscope pore system in marine shale reservoir[J].Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(4):92-97. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/f5a970eaf46527d3240ce0e0-2.html
[13] Clarkson C R, Solano N, Bustin R M, et al.Pore structure characterization of North American shale gas reservoirs using USANS/SANS, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion[J].Fuel, 2013, 103:606-616. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.06.119
[14] 郭旭升, 李宇平, 刘若冰, 等.四川盆地焦石坝地区龙马溪组页岩微观孔隙结构特征及其控制因素[J].天然气工业, 2014, 34(6):9-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRQG201412003.htm
Guo X S, Li Y P, Liu R B, et al.Characteristics and controlling factors of micro-pore structures of Longmaxi shale play in the Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin[J].Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(6):9-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRQG201412003.htm
[15] 武景淑, 于炳松, 张金川, 等.渝东南渝页1井下志留统龙马溪组页岩孔隙特征及其主控因素[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(3):260-269. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201601012.htm
Wu J S, Yu B S, Zhang J C, et al.Pore characteristics and controlling factors in the organic-rich shale of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation revealed by samples from a well in Southeastern Chongqing[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(3):260-269. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201601012.htm
[16] 姜振学, 唐相路, 李卓, 等.川东南地区龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构全孔径表征及其对含气性的控制[J].地学前缘, 2016, 23(2):126-134. http://www.doc88.com/p-2724480335167.html
Jiang Z X, Tang X L, Li Z, et al.The whole-aperture pore structure characteristics and its effect on gas content of the Longmaxi Formation shale in the Southeast Sichuan Basin[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(2):126-134. http://www.doc88.com/p-2724480335167.html
[17] 杨文新, 李继庆, 赵江艳, 等.四川盆地涪陵地区龙马溪组页岩微观孔隙结构定性定量研究[J].石油实验地质, 2018, 40(1):98-102. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91405A/201305/47446178.html
Yang W X, Li J Q, Zhao J Y, et al.Qualitative and quantitative study of micro-pore structures of Longmaxi Formation shale in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(1):98-102. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91405A/201305/47446178.html
[18] 王玉满, 董大忠, 李建忠, 等.川南下志留统龙马溪组页岩气储层特征[J].石油学报, 2012, 33(4):551-561. doi: 10.7623/syxb201204003
Wang Y M, Dong D Z, Li J Z, et al.Reservoir characteristics of shale gas in Longmaxi Formation of the Lower Silurian, Southern Sichuan[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(4):551-561. doi: 10.7623/syxb201204003
[19] 蔡潇, 王亮, 靳雅夕, 等.渝东南地区页岩有机孔隙类型及特征[J].天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(3):513-519. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.03.0513
Cai X, Wang L, Jin Y X, et al.Types and characteristics of organic pore in shale gas reservoir of Southeastern Chongqing area[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(3):513-519. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.03.0513
[20] 耿一凯, 金振奎, 赵建华, 等.页岩储层孔隙类型控制因素研究——以川东焦石坝地区龙马溪组为例[J].石油实验地质, 2017, 39(1):72-78. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGKA201512019.htm
Geng Y K, Jin Z K, Zhao J H, et al.Controlling factors of pore types in shale reservoirs:A case study from the Longmaxi Formation in Jiaoshiba area, Eastern Sichuan Basin[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(1):72-78. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGKA201512019.htm
[21] 刘尧文, 王进, 张梦吟, 等.四川盆地涪陵地区五峰-龙马溪组页岩气层孔隙特征及对开发的启示[J]石油实验地质, 2018, 40(1):45-50. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRQG201406007.htm
Liu Y W, Wang J, Zhang M Y, et al.Pore features of shale gas layer in Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in Fuling area of Sichuan Basin and the application to development[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(1):45-50. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRQG201406007.htm
[22] 陈生蓉, 帅琴, 高强, 等.基于扫描电镜-氮气吸脱附和压汞法的页岩孔隙结构研究[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(6):636-642. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ykcs201506005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Chen S R, Shuai Q, Gao Q, et al.Analysis of the pore structure of shale in Ordos Basin by SEM with nitrogen gas adsorption-desorption[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(6):636-642. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ykcs201506005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[23] 王羽, 金婵, 汪丽华, 等.应用氩离子抛光-扫描电镜方法研究四川九老洞组页岩微观孔隙特征[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(3):278-285. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.03.003
Wang Y, Jin C, Wang L H, et al.Characterization of pore structures of Jiulaodong Formation Shale in the Sichuan Basin by SEM with Ar-ion milling[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(3):278-285. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.03.003
[24] 庞河清, 曾焱, 刘成川, 等.基于氮气吸附-核磁共振-氩离子抛光场发射扫描电镜研究川西须五段泥质岩储层孔隙结构[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(1):66-74. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.010
Pang H Q, Zeng Y, Liu C C, et al.Investigation of pore structure of an argillaceous rocks reservoir in the 5th member of Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan, using NAM, NMR and AIP-FESEM[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(1):66-74. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.010
-




 下载:
下载: