Three-dimension Characterization of Organic Matter Pore Structures of Shale Using Focused Ion Beam-Scanning Electron Microscope
-
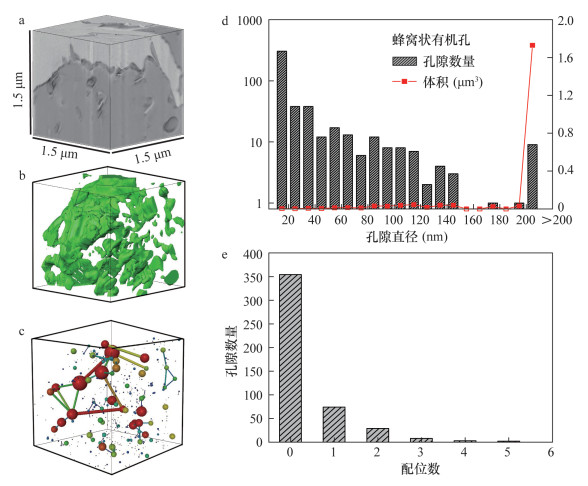
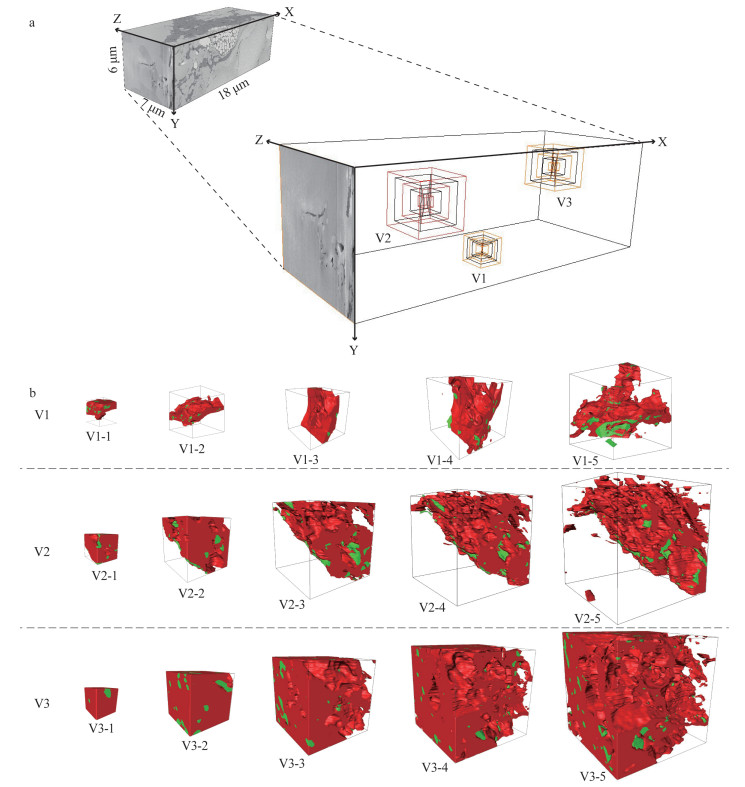
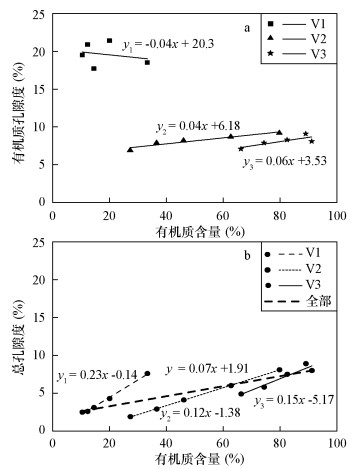
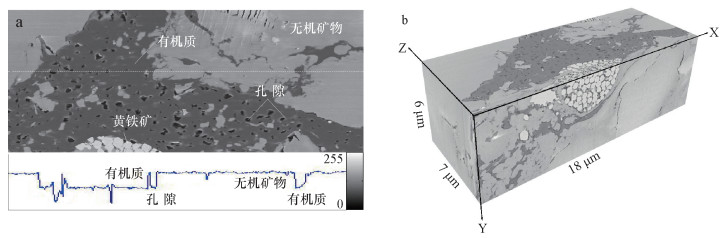
摘要: 页岩中纳米级有机孔的大小直接影响页岩气含气量,其连通性亦对气体运移和开采至关重要。本文选择漆辽地区龙马溪组富有机质页岩,利用聚焦离子束-扫描电镜(FIB-SEM)在纳米尺度上(10 nm)进行有机孔结构的三维重构。研究结果表明:① FIB-SEM方法适用于微米级页岩的纳米(>3 nm)孔隙结构特征研究。②蜂窝状有机孔发育均匀,孔径集中于10~200 nm,连通性较差;界面有机孔孔径集中于200~300 nm,局部连通性较好。③页岩总孔隙度与有机质含量成正比。研究认为,对于以有机孔为重要储集空间的页岩,有机质分布越集中,连续性越好,研究孔隙度的表征单元体尺度越小。
-
关键词:
- 聚焦离子束-扫描电镜 /
- 三维空间结构 /
- 有机孔 /
- 纳米孔隙结构 /
- 龙马溪组页岩
Abstract: The size of organic matter (OM) pore in shale directly affects shale gas content, and its connectivity is of great significance for gas migration and exploitation. Three-dimension reconstructions down to nanometer scale (about 10 nm) are performed on OM pores in samples from the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Qiliao area using Focused Ion Beam-Scanning Electron Microscope (FIB-SEM). The results indicate that FIB-SEM technique is an effective method for three-dimension characterization of nano-scale (>3 nm) pore structures of micro-scale shale samples. Honeycomb OM pores distribute uniformly with poor connectivity, and their diameters are dominated by 10-200 nm. Micro-crack like OM pores at the interface exhibit good connectivity on the local area, with diameters concentrated at 200-300 nm. Bulk porosity of shale is positively correlated to OM content. For shale with OM pores as host, the concentrated distribution of the organic matter and the good continuity will result in a small size of unit cell for characterization of porosity. -

-
[1] Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al.Spectrum of pore types for matrix-related mud pores[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1071-1098. doi: 10.1306/08171111061
[2] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 白斌, 等.中国油气储层中纳米孔首次发现及其科学价值[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(6):1857-1864. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201106024.htm
Zou C N, Zhu R K, Bai B, et al.First discovery of nano-pore throat in oil and gas reservoir in China and its scientific value[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(6):1857-1864. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201106024.htm
[3] 王羽, 金婵, 汪丽华, 等.应用氩离子抛光-扫描电镜方法研究四川九老洞组页岩微观孔隙特征[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(3):278-285. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.03.003
Wang Y, Jin C, Wang L H, et al.Characterization of pore structures of Jiulaodong Formation shale in the Sichuan Basin by SEM with Ar-ion milling[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(3):278-285. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.03.003
[4] 王羽, 金婵, 姜政, 等.渝东五峰组-龙马溪组页岩矿物成分与孔隙特征分析[J].矿物学报, 2016, 36(4):555-562. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TDKX201408020.htm
Wang Y, Jin C, Jiang Z, et al.Mineral composition and microscopic pore characteristics of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation shale in Eastern Chongqing City, China[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 36(4):555-562. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TDKX201408020.htm
[5] 马勇, 钟宁宁, 程礼军, 等.渝东南两套富有机质页岩的孔隙结构特征——来自FIB-SEM的新启示[J].石油实验地质, 2015, 37(1):109-116. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201501109
Ma Y, Zhong N N, Cheng L J, et al.Pore structure of two organic-rich shales in Southeastern Chongqing area:Insight from focused ion beam scanning electron microscope (FIB-SEM)[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2015, 37(1):109-116. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201501109
[6] Zhou S W, Yan G, Xue H Q, et al.2D and 3D nanopore characterization of gas shale in Longmaxi Formation based on FIB-SEM[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 73:174-180. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.02.033
[7] Klaver J, Desbois G, Littke R, et al.BIB-SEM pore characterization of mature and post mature Posidonia shale samples from the Hils area, Germany[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 158:78-89. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.03.003
[8] Wang Y, Wang L H, Wang J Q, et al.Investigating microstructure of Longmaxi shale in Shizhu area, Sichuan Basin, by optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and micro-computed tomography[J].Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2017, 28:163. doi: 10.1007/s41365-017-0317-5
[9] Ma L, Taylor K G, Lee P D, et al.Novel 3D centimetre-to nano-scale quantification of an organic-rich mudstone:The carboniferous Bowland shale, Northern England[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 72:193-205. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.02.008
[10] Wang Y, Pu J, Wang L, et al.Characterization of typical 3D pore networks of Jiulaodong Formation shale using nano-transmission X-ray microscopy[J].Fuel, 2016, 170:84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.11.086
[11] 吴松涛, 朱如凯, 崔京钢, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地长7湖相泥页岩孔隙演化特征[J].石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(2):167-176. doi: 10.11698/PED.2015.02.05
Wu S T, Zhu R K, Cui J G, et al.Characteristics of lacustrine shale porosity evolution, Triassic Chang 7 Member, Ordos Basin, NW China[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(2):167-176. doi: 10.11698/PED.2015.02.05
[12] 王羽, 汪丽华, 王建强, 等.利用纳米透射X射线显微成像技术研究页岩有机孔三维结构特征[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(6):563-573. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201703240038
Wang Y, Wang L H, Wang J Q, et al.Investigation of organic matter pore structures of shale in three dimensions using nano-X-ray microscopy[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(6):563-573. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201703240038
[13] Misch D, Mendez-Martin F, Hawranek G, et al.SEM and FIB-SEM investigations on potential gas shales in the Dniepr-Donets Basin (Ukraine):Pore space evolution in organic matter during thermal maturation[J].IOP Conference Series:Materials Science and Engineering, 2016, 109(012010). http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2016MS&E..109a2010M
[14] Jiang W B, Lin M, Yi Z X, et al.Parameter determination using 3D FIB-SEM images for development of effective model of shale gas flow in nanoscale pore clusters[J].Transport in Porous Media, 2017, 117(1):5-25. doi: 10.1007/s11242-016-0817-5
[15] Wang Y, Luo S, Wang L, et al.Synchrotron radiation-based/1-norm regularization on micro-CT imaging in shale structure analysis[J].Journal of Inverse and Ill-posed Problems, 2017, 25(4):483-498. http://www.degruyter.com/view/j/jiip.ahead-of-print/jiip-2015-0063/jiip-2015-0063.xml
[16] Loucks R G, Reed R M.Scanning-electron-microscope petrographic evidence for distinguishing organic matter pores associated with depositional organic matter versus migrated organic matter in mudrocks[J].Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies Journal, 2014, 3:51-60. http://www.mendeley.com/catalog/scanningelectronmicroscope-petrographic-evidence-distinguishing-organicmatter-pores-associated-depos/
[17] Zhu X J, Cai J G, Liu W X, et al.Occurrence of stable and mobile organic matter in the clay-sized fraction of shale:Significance for petroleum geology and carbon cycle[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 160-161:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.03.011
[18] Zhang H, Zhu Y M, Wang Y, et al.Comparison of organic matter occurrence and organic nanopore structure within marine and terrestrial shale[J].Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 32:356-363. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2016.04.040
[19] Ko L T, Loucks R G, Ruppel S C, et al.Origin and characterization of Eagle Ford pore networks in the South Texas Upper Cretaceous shelf[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2017, 101(3):387-418. doi: 10.1306/08051616035
[20] Jarvie D M, Hill R J, Ruble T E, et al.Unconventional shale-gas systems:The Mississippian Barnett shale of North-Central Texas as one model for thermogenic shale-gas assessment[J].American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 2007, 91(4):475-499. doi: 10.1306/12190606068
[21] Milliken K L, Rudnicki M, Awwiller D N, et al.Organic matter-hosted pore system, Marcellus Formation (Devonian), Pennsylvania[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(2):177-200. doi: 10.1306/07231212048
[22] Hu H, Hao F, Lin J, et al.Organic matter-hosted pore system in the Wufeng-Longmaxi (O3w-S11) shale, Jiaoshiba area, Eastern Sichuan Basin, China[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 2017, 173:40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2017.02.004
[23] 董大忠, 邹才能, 李建忠, 等.页岩气资源潜力与勘探开发前景[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(2/3):324-336. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95894A/201102/37549576.html
Dong D Z, Zou C N, Li J Z, et al.Resource potential, exploration and development prospect of shale gas in the whole world[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(2/3):324-336. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95894A/201102/37549576.html
[24] 杨珊, 廖泽文, 刘虎, 等.渝东漆辽剖面五峰组-龙马溪组页岩及残余干酪根中微量元素地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(6):1231-1237. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Magazine?magazineId=kwysdqhxtb&yearIssue=2015_6
Yang S, Liao Z W, Liu H, et al.Geochemical characteristics of trace elements of shales and their residual kerogens from Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in the Qiliao section, Eastern Chongqing, China[J].Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(6):1231-1237. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Magazine?magazineId=kwysdqhxtb&yearIssue=2015_6
[25] 王羽, 金婵, 汪丽华, 等.基于SEM图像灰度水平的页岩孔隙分割方法研究[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(6):35-41. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.06.005
Wang Y, Jin C, Wang L H, et al.Pore segmentation methods based on gray scale of SEM images[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(6):35-41. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.06.005
[26] Jiao K, Yao S P, Liu C, et al.The characterization and quantitative analysis of nanopores in unconventional gas reservoirs utilizing FESEM-FIB and image processing:An example from the Lower Silurian Longmaxi shale, upper Yangtze region, China[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 2014, 128-129:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2014.03.004
[27] Tang X L, Jiang Z X, Li Z, et al.The effect of the variation in material composition on the heterogeneous pore structure of high-maturity shale of the Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the Southeastern Sichuan Basin, China[J].Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 23:464-473. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2015.02.031
[28] Chen L, Lu Y C, Jiang S, et al.Heterogeneity of the lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in the Southeast Sichuan Basin of China[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 65:232-246. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.04.003
[29] Gitman I M, Askes H, Sluys L J.Representative volume:Existence and size determination[J].Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2007, 74(16):2518-2534. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2006.12.021
[30] 陈尚斌, 朱炎铭, 王红岩, 等.川南龙马溪组页岩气储层纳米孔隙结构特征及其成藏意义[J].煤炭学报, 2012, 37(3):438-444. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201203015.htm
Chen S B, Zhu Y M, Wang H Y, et al.Structure characteristics and accumulation significance of nanopores in Longmaxi shale gas reservoir in the Southern Sichuan Basin[J].Journal of China Coal Society, 2012, 37(3):438-444. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201203015.htm
[31] Mastalerz M, Schimmelmann A, Drobniak A, et al.Porosity of Devonian and Mississippian New Albany shale across a maturation gradient:Insights from organic petrology, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(10):1621-1643. doi: 10.1306/04011312194
[32] Wang P F, Jiang Z X, Tang X L, et al.Microscopic pore structure and heterogeneity quantitative characterization of shale reservoir-take in Chongqing Southeast Longmaxi shale case[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89:91-92. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2015.89.issue-s1
-



 下载:
下载: