Determination of Trace Iodine in Soils, Sediments and Rocks by ICP-MS after Pressurized Acid Digestion-Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride Reduction
-
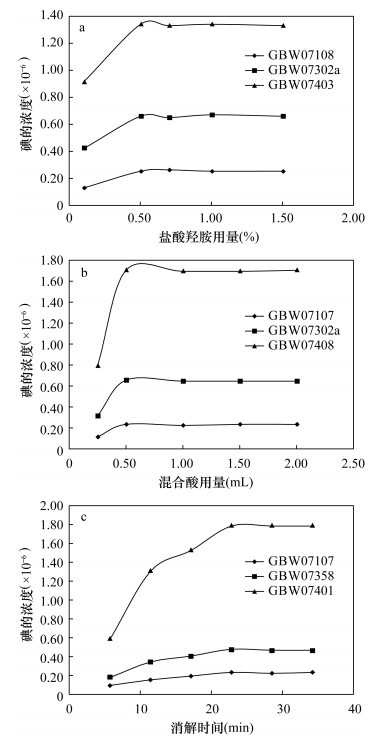
摘要: 碘是活跃元素,价态多,各价态间易相互转化,化学性质不稳定,使用ICP-MS测定土壤、沉积物和岩石样品中的痕量碘,样品前处理和测定结果的稳定性是主要问题。本文采用磷酸-高氯酸高压密闭消解处理样品,提高了样品分解效率,也避免了碘的挥发损失,通过加入0.5mL 20g/L盐酸羟胺溶液将碘还原为I-,提高了碘的稳定性,再于100℃烘箱中保温至少20min,以稀氨水作介质,降低了ICP-MS测定过程中的记忆效应。方法相对标准偏差(RSD)为4.88%~9.19%,相对误差为-6.90%~8.33%,回收率为92.5%~109.6%,检出限(3s)为0.012μg/g。本方法的测定数据与半熔法一致,解决了当前方法存在的分析流程长、空白高、岩石样品提取不完全、提取装置繁多等问题,可以作为土壤、沉积物、岩石中痕量碘测定方法的一种补充,适合批量样品分析。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDIodine is an active element with many valences. It is easy to transform each other between valence states and its chemical properties are unstable. In terms of determination of trace iodine in soil, sediment and rock samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), sample pretreatment and result stability are the main problems. OBJECTIVESTo obtain stable results, low blank, a short analysis period and complete extraction. METHODSThe sample was digested by phosphoric acid-perchloric acid under high-pressure sealed conditions. The decomposition efficiency of the sample was improved and the volatilization loss of iodine was avoided. The stability of iodine was improved by adding 0.5mL 20g/L hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution to reduce iodine to I-. The iodine was kept in an oven at 10℃ for at least 20 minutes, and the memory effect during ICP-MS analysis was reduced by using dilute ammonia water as the medium. RESULTSThe relative standard deviations of the method were 4.88%-9.19%, the relative errors were -6.90%-8.33%, the recoveries were 92.5%-109.6% and the detection limit (3s) was 0.012μg/g. CONCLUSIONSThe data obtained by this method are in good agreement with those obtained by the semi-melting method. It solves the problems of long analysis process, high blank, incomplete extraction of rock samples and various extraction devices. It can be used as a supplement to the determination of trace iodine in soil, sediment and rock, and is suitable for batch sample analysis. -

-
表 1 方法准确度和加标回收率
Table 1. Accuracy and spiked recovery tests of the method
标准物质
编号认定值
(mg/kg)加标前测定值
(mg/kg)加入量
(mg/kg)加标后测定值
(mg/kg)回收率
(%)相对误差
(%)GBW07107
(岩石)0.24±0.06 0.22 0.200 0.41 95.0 8.33 GBW07302a
(沉积物)0.64±0.12 0.65 0.500 1.17 104.4 -3.17 GBW07305a
(沉积物)2.4±0.4 2.4 2.500 5.14 109.6 -6.90 GBW07404
(土壤)9.4±1.1 9.1 5.000 13.8 94.0 1.06 GBW07407
(土壤)19±2 18.2 20.00 36.7 92.5 2.58 表 2 半熔法与本法碘测试结果比对
Table 2. Comparison of analytical results of iodine determined by semi-solution method and this study method
样品编号 样品
类型碘(μg/g) 半熔法 本法 HT-1 岩石 0.35 0.38 HT-2 岩石 0.44 0.43 HT-20 岩石 0.38 0.41 HT-21 岩石 0.69 0.68 HT-90 岩石 1.23 1.20 HT-92 岩石 0.54 0.57 HT-150 岩石 1.92 1.89 HT-152 沉积物 3.85 3.77 HT-203 沉积物 15.2 16.4 HT-235 沉积物 14.1 14.1 HT-272 沉积物 6.24 6.33 HT-352 沉积物 5.40 5.40 HT-367 沉积物 8.86 8.78 HT-462 土壤 0.82 0.89 HT-524 土壤 3.27 3.24 HT-685 土壤 7.77 7.65 HT-686 土壤 7.92 8.01 HT-728 土壤 0.88 0.86 HT-791 土壤 11.3 11.7 HT-899 土壤 0.45 0.48 HT-902 土壤 2.73 2.80 HT-1006 土壤 2.45 2.38 -
[1] 李冰, 何红蓼, 史世云, 等.电感耦合等离子体质谱同时测定地质样品中痕量碘溴砷硒的研究Ⅰ.不同阴离子形态及不同介质对分析信号的影响[J].岩矿测试, 2001, 20(3):161-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2001.03.001 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20010351
Li B, He H L, Shi S Y, et al.Determination of trace iodine, bromine, selenium and arsenic in geological samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry.Ⅰ.Signal response of different anion species in media[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2001, 20(3):161-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2001.03.001 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20010351
[2] 李冰, 史世云, 何红蓼, 等.电感耦合等离子体质谱同时测定地质样品中痕量碘溴砷硒的研究Ⅱ.土壤及沉积物标准物质分析[J].岩矿测试, 2001, 20(4):241-245. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2001.04.001 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20010471
Li B, Shi S Y, He H L, et al.Determination of trace iodine, bromine, selenium and arsenic in geological samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry.Ⅱ.Standard material analysis of soil and sediment[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2001, 20(4):241-245. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2001.04.001 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20010471
[3] Vanhoe H, Allemeersch F V, Versieck J, et al.Effect of solvent type on the determination of total iodine in milk powder and human serum by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Analyst, 1993, 118(8):1015-1019. doi: 10.1039/an9931801015
[4] Larsen E H, Ludwigsen M B.Determination of iodine in food-related certified reference materials using wet ashing and determination by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 1997, 12(6):435-439. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c01c01da0ead18e6e2bbc23e1737378e
[5] Pieoloto R S, Cruz S M, Mello P A, et al.Combining pyrohydrolysis and ICP-MS for bromine and iodine determination in airborne particulate matter[J].Microchemical Journal, 2014, 116:225-229. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2014.05.002
[6] Tagami K, Uchida S.Sample storage conditions and holding times for the determination of total iodine in natural water samples by ICP-MS[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2005, 26(6):209-214. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dbaba7eba761eea50c8f38ea7f4ff288
[7] Michel A, Villemant B.Determination of halogens (F, Cl, Br, I), sulfur and water in seventeen geological reference materials[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2003, 27(2):163-171. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2003.tb00643.x
[8] 赵庆令, 李清彩, 蒲军, 等.电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法同时测定土壤样品中砷硼铈碘铌硫钪锶钍锆等31种元素[J].岩矿测试, 2010, 29(4):455-457. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2010.04.026 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20100426
Zhao Q L, Li Q C, Pu J, et al.Simultaneous determination of 31 elements such as arsenic, boron, cerium, iodine, niobium, sulfur, scandium, strontium, thorium and zirconium in soil samples[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2010, 29(4):455-457. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2010.04.026 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20100426
[9] 程素敏, 王娟, 张岩, 等.分光光度法测定土壤中碘的方法改进[J].中国无机分析化学, 2015, 5(4):41-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2015.04.009
Cheng S M, Wang J, Zhang Y, et al.Improvement of spectrophotometric method for the determination of iodine in soil[J].China Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 5(4):41-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2015.04.009
[10] 阳国运, 唐裴颖, 张洁, 等.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定地球化学样品中的硼碘锡锗[J].岩矿测试, 2019, 38(2):154-159. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201805070055
Yang G Y, Tang P Y, Zhang J, et al.Determination of boron, iodine, tin and germanium in geochemical samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(2):154-159. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201805070055
[11] 李锦昕, 邵一立, 刘国均.流动注射G光度法测定地质样品中痕量碘[J].岩矿测试, 1993, 12(1):11-13. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_19930103
Li J X, Shao Y L, Liu G J.Flow injection G spectrophotometric determination of trace iodine in geological samples[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 1993, 12(1):11-13. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_19930103
[12] 张培新, 黄光明, 董丽, 等.电感耦合等离子体质谱法同时测定地质样品中锗碘[J].岩矿测试, 2005, 24(1):36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2005.01.008 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20050108
Zhang P X, Huang G M, Dong L, et al.Simultaneous determination of germanium and iodine in geological samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2005, 24(1):36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2005.01.008 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20050108
[13] 万兵, 孙立欣, 贾雨薇, 等.电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)法测定地球化学样品中的碘[J].中国无机分析化学, 2017, 7(4):57-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2017.04.012
Wan B, Sun L X, Jia Y W, et al.Determination of iodine in geochemical samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS)[J].China Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 7(4):57-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2017.04.012
[14] 董薇.催化动力学分光光度法测定区域地球化学样品中的碘[J].广州化工, 2018, 46(4):99-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2018.04.032
Dong W.Catalytic kinetic spectrophotometric determination of iodine in regional geochemical samples[J].Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2018, 46(4):99-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2018.04.032
[15] 张学华, 王君玉, 韩敏.氯胺T-四碱催化分光光度法测定河南省黄淮平原农业地质调查样品中痕量碘[J].岩矿测试, 2007, 26(5):391-394. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.05.011 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_200705134
Zhang X H, Wang J Y, Han M.Catalytic spectrophotometric determination of trace iodine in agricultural geological survey samples of Huanghuai Plain, Henan Province by chloramine T-tetraalkali[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2007, 26(5):391-394. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.05.011 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_200705134
[16] 安华娟, 张明杰, 戴雪峰, 等.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定地质样品中痕量碘[J].理化检验(化学分册), 2010, 46(6):692-693. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ykcs200103001
An H J, Zhang M J, Dai X F, et al.Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for the determination of trace iodine in geological samples[J].Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2010, 46(6):692-693. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ykcs200103001
[17] 马新荣, 李冰, 韩丽荣.稀氨水密封溶解-电感耦合等离子体质谱测定土壤沉积物及生物样品中的碘溴[J].岩矿测试, 2003, 22(3):174-178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2003.03.004 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20030345
Ma X R, Li B, Han L R.Determination of total iodine and bromine in soil, sediment and biological samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with dilute ammonia pressurizing decomposition[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2003, 22(3):174-178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2003.03.004 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20030345
[18] 宋萍, 温宏利.液氮冷凝吸收热解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定岩石土壤沉积物中的溴碘[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(4):384-388. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.04.008
Song P, Wen H L.Determination of bromine and iodine in rock and soil sediments by liquid nitrogen condensation absorption pyrolysis-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(4):384-388. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.04.008
[19] 吴磊, 刘义博, 王家松, 等.高压密闭消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定锰矿石中的稀土元素前处理方法研究[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(6):637-643. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712060189
Wu L, Liu Y B, Wang J S, et al.Study on the pretreatment method for determination of rare earth elements in manganese ores by high pressure sealed digestion-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(6):637-643. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712060189
[20] 贾双琳, 赵平, 杨刚, 等.混合酸敞开或高压密闭溶样-ICP-MS测定地质样品中稀土元素[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(2):186-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.02.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/b48c6aca-5c90-4b00-831e-1a788e3583c5
Jia S L, Zhao P, Yang G, et al.Determination of rare earth elements in geological samples by ICP-MS with mixed acid open or high pressure closed solution samples[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(2):186-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.02.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/b48c6aca-5c90-4b00-831e-1a788e3583c5
[21] 王祝, 苏思强, 邵蓓, 等.高压密闭消解-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱/质谱法测定鸡蛋中16种元素的含量[J].理化检验(化学分册), 2017, 52(4):108-112. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20172017051900161919
Wang Z, Su S Q, Shao B, et al.Determination of 16 elements in eggs by high pressure closed digestion-inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry/mass spectrometry[J].Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2017, 52(4):108-112. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20172017051900161919
[22] 张兴超, 刘超, 黄艺, 等.干法灰化处理对含有机质土壤样品铜同位素测量的影响[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(4):347-355. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201803290033
Zhang X C, Liu C, Huang Y, et al.The effect of dry-ashing method on copper isotopic analysis of soil samples with organic matter[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(4):347-355. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201803290033
[23] 任冬, 刘彤彤, 刘安安, 等.高压密闭消解处理草酸-草酸铵浸提剂方法的改进[J].中国土壤与肥料, 2019(3):198-201. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trfl201903030
Ren D, Liu T T, Liu A A, et al.Improvement of high pressure sealed digestion method for treating oxalic acid-ammonium oxalate extractant[J].Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2019(3):198-201. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trfl201903030
[24] 田娟娟, 杜慧娟, 潘秋红, 等.电热板消解与密闭罐消解对土壤中49种矿质元素ICP-MS法检测的影响[J].分析测试学报, 2009, 28(3):319-325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2009.03.014
Tian J J, Du H J, Pan Q H, et al.Effects of electrothermal plate digestion and closed tank digestion on the determination of 49 mineral elements in soil by ICP-MS[J].Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2009, 28(3):319-325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2009.03.014
[25] EN 13656: 2002.Characterization of Waste-microwave Assisted Digestion with Hydrofluoric (HF), Nitric (HNO3), and Hydrochloric (HCl) Acid Mixture for Subsequent Determination of Elements[S].
[26] Link D D, Kingston H M S, Harrilla G J, et al.Develop-ment of microwave-assisted drying methods for sample preparation for dried spot micro-X-ray fluorescence analysis[J].Analytical Chemistry, 2002, 74(5):1165-1170. doi: 10.1021/ac010726t
[27] 高孝礼, 黄光明, 张培新, 等.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定磷矿石中的碘[J].岩矿测试, 2009, 28(5):423-426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2009.05.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20090505
Gao X L, Huang G M, Zhang P X, et al.Determination of iodine in phosphate ore by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2009, 28(5):423-426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2009.05.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20090505
-



 下载:
下载: