Discrimination of HPHT-treated Type Ⅰa Cape Diamonds Using Optical and Photoluminescence Spectroscopic Techniques
-
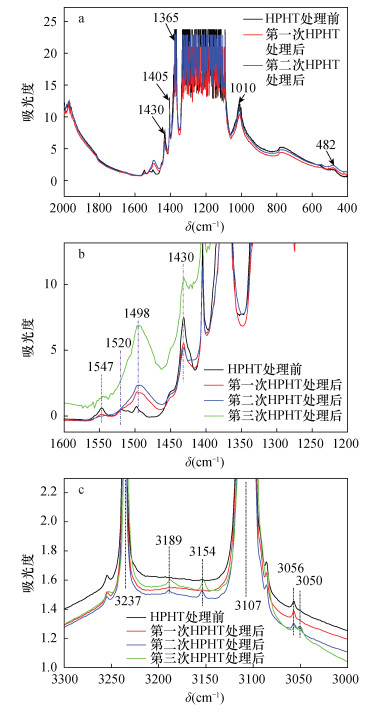
摘要: Ⅱa型钻石的高温高压改色及褪色研究已开展了大量工作,然而对Ⅰa型Cape系列褐色钻石在高温高压处理条件下的行为尚不明确。为解析实验室钻石鉴定工作中遇到的黄色钻石颜色成因问题,本文选取了Ⅰa型Cape系列褐色钻石作为研究对象,进行高温高压改色处理实验,并对处理前后的样品的紫外可见吸收光谱、红外吸收光谱以及光致发光光谱等谱学特征进行对比分析。结果表明:经高温高压改色处理后,钻石颜色由灰褐色变为褐黄色,钻石的紫外可见吸收光谱、红外吸收光谱和光致发光光谱也发生了很大改变。经处理的褐色钻石,其紫外可见吸收光谱中除原有的415nm和477nm吸收外,还产生503.2nm吸收,同时550nm至短波的吸收增强,钻石因此由原来的灰褐色变为褐黄色;红外吸收光谱中,1498、1520、1547cm-1三个峰变为一个以1498cm-1为中心的吸收宽峰;光致发光光谱中,产生了明显的H3(503.2nm)以及H2(986.2nm)缺陷。本研究获得的光谱变化特征为准确鉴定高温高压改色处理的Cape型钻石提供了依据,也为更好地理解晶格中氮、氢等相关的格子缺陷在高温高压条件下的变化机理提供了实验数据和分析。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDSpectroscopic characteristics for brown colored Type Ⅱa diamonds treated by high pressure high temperature (HPHT) processes have been investigated extensively. However, almost no reports are available on the variation of the spectroscopic features for the type Ⅰa Cape series brown colored diamonds treated by HPHT processes. OBJECTIVESTo help the laboratory to resolve the origin of yellow diamonds. METHODSThe ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) absorption spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and photoluminescence spectroscopy were used to analyze the spectral features for the samples before and after each treatment. RESULTSThe color of the diamonds changed from grayish brown to brownish yellow after the HPHT process. Meanwhile, the FTIR/UV-Vis absorption, as well as the photoluminescence was also greatly changed. Besides the 415nm and the 477nm absorption peaks, the treated diamonds also display H3 defect (503.2nm) and the gradually increasing absorption from 550nm to shortwave, resulted in the color changing from grayish brown to brownish yellow. In the mid-infrared region, the three peaks of 1498, 1520 and 1547cm-1 become a broad band centered at 1498cm-1 after treatment, and the photoluminescence spectrum displayed two distinct defects-H3 (503.2nm) and H2 (986.2nm). CONCLUSIONSThe spectroscopic features provide a basis for accurate identification of HPHT-treated type Ⅰa Cape series brown diamonds in gem laboratories, and increase understanding of the variation mechanism of the nitrogen and hydrogen related lattice defects in the diamonds during the HPHT processes. -

-
表 1 不同激光器激发下钻石的发光峰汇总
Table 1. PL lines of diamond under different lasers
峰位
(nm)相应的缺陷类型指派 使用激光器波长
(nm)处理前后各发光峰的存在状态 处理前 第一次处理后 第二次处理后 第三次处理后 415.2 N3 325 √ √ √ √ 489.8 与聚合氮有关 325,473 √ √ √ √ 490.7 与塑性变形有关 473 × × × × 503.2 H3 473 × √ √ √ 557.5 未知缺陷 473,532 √ √ √ √ 575.0 NV0 473,532 × × √ √ 603.8 未知缺陷 325,473,532 √ √ √ √ 633.0 未知缺陷 473,532 √ √ √ √ 637.0 NV- 473,532 × × × × 640.7 未知 325,473,532 √ √ √ √ 644.0 未知 325,473,532 √ √ √ √ 673.5 未知 473,532 × √ √ √ 700.7 与聚合氮有关 325,473,532 √ √ √ √ 986.0 H2 785 × × × √ 注:“√”表示可以检测到该峰,“×”表示未检测到该峰。 -
[1] Hainschwang T.HPHT treatment of different classes of typeⅠ brown diamond[J].Journal of Gemmology, 2005, 29(5/6):261-273. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925963508000733
[2] King J M, Shigley J E, Gelb T H, et al.Characterization and grading of natural-color yellow diamonds[J].Gems & Gemology, 2005, 41(2):88-115. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bb3f257100428885233b25513b960402
[3] 宋中华, 魏华, 田晶.钻石辨假[M].北京:文化出版社, 2017.
Song Z H, Wei H, Tian J.Identification of Diamonds[M].Beijing:Cultural Development Press, 2017.
[4] Collins A T.The colour of diamond and how it may be changed[J].Journal of Gemmology, 2001, 27(6):341-359. doi: 10.15506/JoG.2001.27.6.341
[5] Schmetzer K.Clues to the process used by general electric to enthance the GE Pol diamonds[J].Gems & Gemology, 1999, 35(4):186-190.
[6] Fisher D, Spits R A.Spectroscopic evidence of GE pol HPHT-treated natural type Ⅱa diamonds[J].Gems & Gemology, 2000, 36(1):42-49.
[7] Reinitz I M, Buerki P R, Shigley J E, et al.Identification of HPHT-treated yellow to green diamonds[J].Gems & Gemology, 2000, 36(2):128-137. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5460303c17fc86be278a0ca3377df970
[8] Collins A T, KandaH, Kitawaki H.Colour changes pro-duced in natural brown diamonds by high-pressure, high-temperature treatment[J].Diamond and Related Materials, 2000(9):113-122. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2000DRM.....9..113C
[9] 宋中华, 陆太进, 苏隽, 等.无色-近无色高温高压合成钻石的谱图特征及其鉴别方法[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(5):496-504. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.05.008
Song Z H, Lu T J, Su J, et al.The spectral characteristics and identification techniques for colorless and near-colorless HPHT synthetic diamonds[J].Rock and mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(5):496-504. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.05.008
[10] Schmetzer K.High pressure and high temperature treatment of diamonds-A review of the patent literature from five decades[J].The Journal of Gemmology, 2010, 32(1-4):52-65. doi: 10.15506/JoG.2010.32.1-4.52
[11] Fisher D.Brown diamonds and high pressure high tem-perature treatment[J].Lithos, 2009, 112S:619-624. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493709000723
[12] 宋中华, 陆太进, 苏隽, 等.利用吸收和发光光谱技术分析高温高压处理天然富氢钻石的鉴定特征[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(1):64-69.
Song Z H, Lu T J, Su J, et al.Identification of HPHT-treated hydrogen-rich diamonds optical absorption and photo luminescence spectroscopic techniques[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(1):64-69.
[13] 宋中华, 陆太进, 苏隽, 等.不同类型褐色钻石的高温高压处理结果初析[C]//中国国际珠宝首饰学术交流会论文集, 2017: 15-17.
http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201705040072 Song Z H, Lu T J, Su J, et al.HPHT-treated Experiment for Different Types of Brown Diamonds[C]//Proceedings of China International Gems & Jewelry Academic Conference, 2017: 15-17.
[14] DeWeerdt F, Collions A T.The influence of pressure on high-pressure, high-temperature annealing of type Ⅰa diamond[J].Diamond and Related Materials, 2003, 12:507-510. doi: 10.1016/S0925-9635(02)00319-9
[15] Collions A T.The detection of colour-enhanced and synthetic gem diamonds by optical spectroscopy[J].Diamond and Related Materials, 2003, 12:1976-1983. doi: 10.1016/S0925-9635(03)00262-0
[16] Fritsch E, Hainschwang T, Massi L, et al.Hydrogen-related optical centers in natural diamond-An update[J].New Diamond and Frontier Carbon Technology, 2007, 17(2):63-89. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=922f195c430668e39837a286344441bd
[17] Breeding C M, Eaton-Magaña S, Shigley J E.Natural-color green diamonds:A beautiful conundrum[J].Gems & Gemology, 2018, 54(1):2-27. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3f35c4e99ca1bc160a0b30512fc8c7c0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[18] Fritsch E, Scarratt K V G.Optical properties of some natural diamonds with high hydrogen content[J].Diamond Optic Ⅱ, 1989, 1146:201-206. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1b9d411deb07183df5f26baed7b9eef1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[19] Massi L, Fritsch E, Collins A T, et al.The "amber centres" and their relation to the brown colour in diamond[J].Diamond and Related Materials, 2005, 14:1623-1629. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2005.05.003
[20] Dobrinets I A, Vins VG, Zaitsev A M.HPHT-treated diamonds[EB/OL].2013.
[21] Baker J M.A new proposal for the structure of platelets in diamond[J].Diamond and Related Materials, 1998, 7:1282-1290. doi: 10.1016/S0925-9635(98)00188-5
[22] Goss J P, Briddon P R, Hill V, et al.Identification of the structure of the 3107cm-1 H-related defect in diamond[J].Journal of Physics:Condensed Matter, 2014, 26:1-6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c3f541f58d44196f076d2fe36d8c8486
[23] Woods G S.Platelets and the Infrared Absorption of Type Ⅰa Diamonds[C]//Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 1986: 219-238.
[24] Hainschwang T, Fritsch E, Massi L, et al.The C center isolated nitrogen-related infrared absorption at 2688cm-1:Perfect harmony in diamond[J].Journal of Applied Spectroscopy, 2012, 79(5):737-743. doi: 10.1007/s10812-012-9664-5
[25] Tretiakova L.Spectroscopic methods for the identification of natural yellow gem-quality diamonds[J].European Journal of Mineralogy, 2009, 21:43-50. doi: 10.1127/0935-1221/2009/0021-1885
[26] Buerki P R, Reinitz I M, Muhlmeister S, et al. Observation of the H2 defect in gem-quality type Ⅰa diamond[J].Diamond and Related Materials, 1999, 8:1061-1066. doi: 10.1016/S0925-9635(99)00094-1
[27] Hainschwang T, Notari F, Fritsch E, et al.Natural, un-treated diamonds showing the A, B and C infrared absorptions ("ABC diamonds"), and the H2 absorption[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2006, 15:1555-1564. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2005.12.029
[28] Goss J P, Jones R.Properties, Growth and Applications of Diamond[M].London:INSPEC, IEEE, 2001.
[29] Collions A T.Vacancy enhanced aggregation of nitrogen in diamond[J].Journal of Physics C:Solid State Physics, 1980, 13:2641-2650. doi: 10.1088/0022-3719/13/14/006
[30] Wang W Y, Mose T M.Gem quality CVD synthetic dia-monds from gemesis[J].Gems & Gemology, 2011, 71(3):227-228. https://www.gia.edu/gems-gemology/summer-2012-cvd-synthetic-diamonds-gemesis-corp-wang
-




 下载:
下载: