Study on REE Distribution and Mineralogical Characteristics of Different Garnets by Electron Probe and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry
-
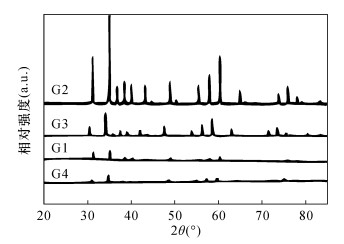
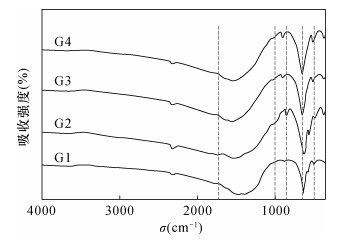
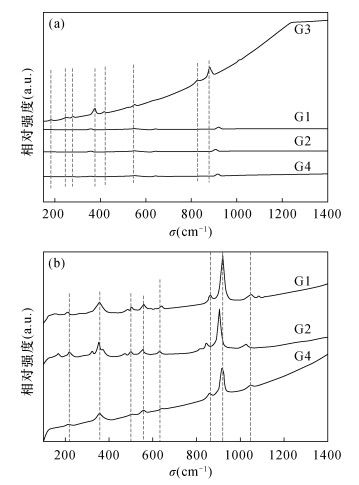
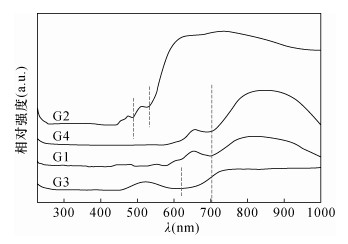
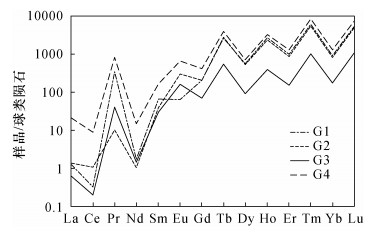
摘要: 石榴子石是变质岩和岩浆岩中一种常见的硅酸盐矿物,其类质同象非常普遍。已有资料表明,不同成分的石榴子石的颜色颇为不同,但石榴子石的成分和颜色之间相互关系尚未进行系统研究和总结。本文应用电子探针、电感耦合等离子体质谱、X射线粉晶衍射、拉曼光谱、红外光谱和紫外可见吸收光谱等手段对常见的红色(G1)、橙色(G2)、绿色(G3)和褐红色(G4)石榴石进行了系统测试,旨在揭示石榴子石成分、结构和颜色的内在关系和变异规律,以期为不同地质体中产出的石榴子石矿物学特征的总结及地质应用提供依据。研究结果表明,G1、G4样品含有较多Fe元素(Fe3+:0.24%、0.24%;Fe2+:1.01%、0.89%);G2样品含有较高的Mn元素(2.76%);G3样品含有很高的Cr、V元素(3453×10-6、1458×10-6)。类质同象对石榴石的晶体结构产生影响,晶胞参数有较大差别,分别是a=11.530nm(G1)、11.563nm(G2)、11.849nm(G3)和11.470nm(G4)。石榴石中的微量元素和稀土元素对于示踪物源及形成过程具有很强的指示意义。石榴石中的稀土元素总量分布不均匀,LREE/HREE比值小于1,表现为重稀土元素富集,Eu/Eu*比值小于1,为Eu负异常。所有样品的Ce异常均不明显。石榴石样品的拉曼光谱呈现出峰强和峰位的明显差异也反映了类质同象的存在:G1、G4在570nm处出现Fe3+电子跃迁吸收峰;G2在460nm和520nm附近出现Mn2+电子跃迁吸收峰;G3在690nm处出现Cr3+电子跃迁吸收峰。紫外可见吸收光谱特征显示,红色和褐红色样品出现在570nm处的Fe3+电子跃迁吸收峰,与其成分中含有大量Fe有关;橙色样品于460nm和520nm附近的特征吸收峰归属于Mn2+,对应其主要成分中大量的Mn;绿色样品690nm处出现强的吸收峰,由Cr3+跃迁产生,是微量元素Cr的存在所致。研究结果表明,石榴石的颜色与其成分和结构具有良好的对应关系。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDGarnet is a common silicate mineral in metamorphic and magmatic rocks, and its isomorphism is very common. The existing data show that the color of garnet with different composition is quite different, but the relationship between the composition and color of garnet has not been systematically studied. OBJECTIVESTo reveal the internal relationship and variation law of garnet composition, structure and color, and provide a basis for the summary and geological application of the mineralogical characteristics of garnet in different geological environments. METHODSCommon red (G1), orange (G2), green (G3) and maroon (G4) garnet have been tested systematically by electron microprobe, inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry, X-ray powder crystal diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy and ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy. RESULTSThe results showed that the samples of G1 and G4 contained more Fe (Fe3+:0.24%, 0.24%, Fe2+:1.01%, 0.89%). The samples of G2 contained higher Mn (2.76%), whereas the samples of G3 have higher Cr and V contents of 3453×10-6 and 1458×10-6, respectively. Isomorphic substitution greatly affected the crystal structure of garnet. The cell parameters were a=11.530nm(G1), 11.563nm(G2), 11.849nm(G3) and 11.470nm(G4). Trace and rare earth elements in garnet can be used to indicate the source and formation process. The rare earth element analysis showed that the total rare earth elements of garnet were distributed unevenly, and the ratio of LREE/HREE was less than 1, with enriched heavy rare earth elements. The Eu/Eu* ratio was less than 1, which was a negative Eu anomaly. Ce abnormalities of all samples were not obvious. G1 and G4 have Fe3+ electronic transition absorption peak at 570nm. G2 has Mn2+ electronic transition absorption peak near 460nm and 520nm, whereas G3 has Cr3+ electronic transition absorption peaks at 690nm. The Raman spectra of garnet samples showed obvious differences in peak intensity and position, which also reflected the ubiquitous existence of isomorphism in these garnets. The ultraviolet-visible absorption spectra of these garnets showed high consistency with its color and characteristic elements. The absorption peaks of Fe3+ in red and maroon samples at 570nm were related to the high content of Fe, while the characteristic absorption peaks of orange sample near 460 and 520nm belong to Mn2+, corresponding to the large amount of Mn (2.76%). A strong absorption peak was observed at 690nm in the green sample, which was caused by the transition of Cr3+ and the presence of trace element Cr (3453×10-6). The results showed that the color of garnet had a good correspondence with its composition and structure. CONCLUSIONSThe color characteristics of garnet can be used as a typomorphic feature of minerals to indicate the existence of different characteristic elements. These methods can be used to study the isomorphism and color origin of garnet effectively. -

-
表 1 石榴子石样品中的主量元素电子探针分析结果
Table 1. EMPA results of major elements in garnet samples
样品编号 含量(%) SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Cr2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO 8种氧化物之和 Si Ti Al Cr Fe3+ Fe2+ Mn Mg Ca Uvt And Py Sps Grs Alm G1 37.65 0 21.34 0 19.87 4.12 16.13 1.33 100.44 2.82 0 1.88 0 0.24 1.01 0.26 1.8 0.11 0 11.1 56.66 8.22 0 31.76 G2 35.67 0.06 19.99 0 0.84 39.39 2.23 0.75 98.93 2.95 0 1.95 0 0.06 0 2.76 0.28 0.07 0 2.81 8.87 88.99 0 0 G3 36.60 0.40 20.74 0.17 0.06 5.98 0.55 34.81 99.31 2.85 0.02 1.91 0.01 0 0 0.40 0.06 2.91 0.47 0.17 1.9 11.37 85.73 0 G4 37.61 0.06 21.34 0 18.03 4.52 15.87 3.04 100.47 2.81 0 1.88 0 0.24 0.89 0.29 1.77 0.24 0 11.41 55.56 8.99 0 27.8 注:以12个氧原子和8个阳离子为计算基础。Uvt—钙铬榴石; And—红柱石; Py—黄铁矿; Sps—锰铝榴石; Grs—钙铝榴石。 表 2 石榴石样品中的微量元素和稀土元素组成
Table 2. Trace elements and rare earth elements composition of garnet samples
微量元素 含量(×10-6) G1 G2 G3 G4 Cr 233 60.9 3453 126 V 132 1.42 1358 30.3 Zn 3447 1851 2188 3116 Ni 1.21 2.09 < 0.05 3.3 Rb 0.18 0.38 0.25 0.21 Sr 3.60 1.93 3.83 1.59 Ba 4.31 6.39 3.55 1.66 Pb 2.92 0.85 1.68 0.84 Nb 12.6 19.8 13.8 1.43 Ta 0.31 0.35 0.15 0.32 Zr 18.7 10.3 43.9 88.9 Hf 1.21 1.01 2.1 2.55 Be < 0.05 0.59 1.03 0.07 Sc 282 5.67 11.8 118 Cu 2.49 4.25 2.22 2.18 Ga 7.93 51.7 77.8 5.51 Mo 0.42 0.13 0.52 0.29 Cd 0.90 0.56 0.18 0.24 Cs 0.05 0.16 0.2 0.06 W 1.02 0.45 0.39 0.85 La 0.39 0.42 0.2 6.58 Ce 0.26 0.85 0.2 7.07 Pr 41.5 1.23 4.9 101 Nd 1.03 0.63 0.9 8.93 Sm 12.7 7.59 5.9 32.6 Eu 4.76 21.9 12 47.8 Gd 52.9 52.5 18 108 Tb 123 130 26 187 Dy 181 171 30 232 Ho 191 169 28 235 Er 205 181 32 269 Tm 196 175 33 271 Yb 189 169 36 269 Lu 174 161 36 243 Y 202 190 33 276 REE 1574 1433 296 2293 LREE/ HREE 0.04 0.02 0.1 0.1 Eu/Eu* 0.15 0.73 1 0.68 Ce/Ce* 0.01 1.04 0.1 0.13 注:Eu/Eu*=2EuN/(SmN+GdN),无单位;Ce/Ce*=2CeN/(LaN+PrN),无单位;LREE/HREE无单位。 -
[1] 冯晓燕, 沈美冬, 张勇, 等.软玉中的一种绿色斑点——钙铝榴石[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(4):608-612. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201907310115
Feng X Y, Shen M D, Zhang Y, et al.The green spots in nephrite-Grossularite[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(4):608-612. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201907310115
[2] 梁祥济.钙铝榴石-钙铁系列石榴子石的特征及其交代机理[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 1994, 13(4):342-352.
Liang X J.Garnets of grossular-andradite series:Their characteristics and metasomatic mechanism[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 1994, 13(4):342-352.
[3] Stockton C M, Manson D V.A proposed new classification for gem-quality garnets[J].Gems and Gemology, 1985, 21(4):205-218. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/271301180_A_Proposed_New_Classification_for_Gem-Quality_Garnets
[4] 应立娟, 唐菊兴, 王登红, 等.西藏甲玛超大型铜矿石榴子石特征及成因意义[J].地质学报, 2012, 86(11):1735-1747. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201211003
Ying L J, Tang J X, Wang D H, et al.Features of garnet in the Jiama super-large Cu polymetallic deposit and its genetic significance[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(11):1735-1747. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201211003
[5] 郑伟, 陈懋弘, 赵海杰, 等.广东省天堂铜铅锌多金属矿床夕卡岩矿物学特征及其地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(1):23-40. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94932X/20131/44587211.html
Zheng W, Chen M H, Zhao H J, et al.Skarn mineral characteristics of the Tiantang Cu-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit in Guangdong Province and their geological significance[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2013, 32(1):23-40. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94932X/20131/44587211.html
[6] 姚远, 陈俊, 陆建军, 等.华南三类含钨锡夕卡岩中石榴子石的成分、微量元素及红外光谱[J].矿物学报, 2013, 33(3):315-328.
Yao Y, Chen J, Lu J J, et al.Composition, trace element and infrared spectrum of garnet from three types of W-Sn bearing skarns in the South of China[J].Acta Mieralogica Sinica, 2013, 33(3):315-328.
[7] 刘春蕊, 陈美华, 潘少逵.一种钙铁质锰铝榴石的宝石矿物学特征[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2018, 20(4):10-15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-BSHB201804002.htm
Liu C R, Chen M H, Pan S K.Gemmological and mineralogical characteristics of calcareous and iron spessartine[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2018, 20(4):10-15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-BSHB201804002.htm
[8] 陈涛, 刘云贵, 尹作为, 等.黑龙江穆棱地区宝石级石榴石的宝石学及谱学特征[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2013, 33(11):2964-2967. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90993X/201311/47535752.html
Chen T, Liu Y G, Yin Z W, et al.Gemology and spectra characterization of gem garnet from Muling City, Heilongjiang Province[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2013, 33(11):2964-2967. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90993X/201311/47535752.html
[9] 罗跃平, 郑秋菊, 王春生.石榴石的品种及鉴定[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2015, 17(3):36-42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-BSHB201503006.htm
Luo Y P, Zheng Q J, Wang C S.Variety and identification of garnet[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2015, 17(3):36-42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-BSHB201503006.htm
[10] 陈丁滢.运用X射线荧光光谱法对石榴石分类鉴定[J].上海计量测试, 2007, 34(6):11-13. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/shjlcs200706002
Chen D Y.Make use of X-ray fluorescence spectrum to classify and identify the garnet[J].Shanghai Measurement and Testing, 2007, 34(6):11-13. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/shjlcs200706002
[11] 聂飞, 董国臣, 王霞, 等.太行山北段浮图峪矿田石榴子石环带特征研究[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(3):439-449. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201907310115
Nie F, Dong G C, Wang X, et al.The zoning characteristics of garnets in the Futuyu orefield of the northern Taihang Mountain[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(3):439-449. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201907310115
[12] 刘琰, 邓军, 王丽华.大型光谱仪器在翡翠检测中的应用[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2006, 26(3):577-582. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=21497735
Liu Y, Deng J, Wang L H.Application of large-scale spectrometers in the detection of jadeite[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2006, 26(3):577-582. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=21497735
[13] 刘琰, 邓军, 邢延炎, 等.白钨矿的振动光谱与颜色成因初探[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2008, 28(1):121-124. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTEMP-GUAN200801028.htm
Liu Y, Deng J, Xing Y Y, et al.Vibrational spectra of scheelite and its solor genesis[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2008, 28(1):121-124. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTEMP-GUAN200801028.htm
[14] 刘琰, 沈战武, 邓军, 等.锡石振动光谱特征与矿物成因类型[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2008, 28(7):1506-1509. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx200807015
Liu Y, Shen Z W, Deng J, et al.Vibration spectra and genetic type of gassiterites[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2008, 28(7):1506-1509. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx200807015
[15] 杨晓丹, 施光海, 刘琰.新疆和田黑色透闪石质软玉振动光谱特征及颜色成因[J].光谱与光谱学分析, 2012, 54(14):681-685. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201203025
Yang X D, Shi G H, Liu Y.Vibrational spectra of black species of Hetian nephrite (Tremolite jade) and its color genesis[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 54(14):681-685. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201203025
[16] 范建良, 刘学良, 郭守国.石榴石族宝石的拉曼光谱研究及鉴别[J].应用激光, 2007, 27(4):310-313. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YYJG200704010.htm
Fan J L, Liu X L, Guo S G.Study on Raman spectra of garnets and relative identification[J].Applied Laser, 2007, 27(4):310-313. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YYJG200704010.htm
[17] Bersani D, Andò S, Vignola P, et al.Micro-Raman determination of the composition of ugrandite garnets[C]//AIP Conference Proceedings, 2009, doi: 10.1063/1.3222891.
[18] 吴菲, 张晓超, 朱仲良.石榴石金属离子含量与拉曼位移的定量关系研究[J].光散射学报, 2015, 27(4):350-354. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GSSX201504009.htm
Wu F, Zhang X C, Zhu Z L.Quantitative relation between Raman shift and metal ion content in garnet[J].The Journal of Light Scattering, 2015, 27(4):350-354. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GSSX201504009.htm
[19] 王锦荣, 王一铭, 张大骞, 等.红外吸收光谱特征对石榴石种属及颜色成因的指示——以一颗黄色石榴石为例[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2020, 22(1):20-25. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90026A/202001/7101586650.html
Wang J R, Wang Y M, Zhang D Q, et al.FTIR investigation of Garnet:Indification for specific species and coloration:A case study of a yellow garnet[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2020, 22(1):20-25. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90026A/202001/7101586650.html
[20] 刘翠红, 陈超洋, 邵天, 等.变色石榴石的紫外-可见吸收光谱与3D荧光光谱研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2020, 40(7):2148-2152.
Liu C H, Chen C Y, Shao T, et al.UV-Vis absorption spectra and 3D fluorescence spectra study of color-change garnet with red fluorescence[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(7):2148-2152.
[21] 刘春花, 杨林, 尹京武, 等.新疆库鲁克塔格兴地塔格群中石榴石的矿物学特征研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2011, 30(2):234-242. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yskwxzz201102008
Liu C H, Yang L, Yin J W, et al.Mineralogical characteristics of garnets from Xingditage Group of Kuruk Tag, Xinjiang Acta[J].Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2011, 30(2):234-242. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yskwxzz201102008
[22] 陈武, 钱汉东.石榴石族宝石矿物的产状和成因[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2000, 2(4):33-37. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=4970855
Chen W, Qian H D.Genesis and occurrence of group of garnet gem mineral[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2000, 2(4):33-37. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=4970855
[23] Irving A.A review of experimental studies of crystal/liquid trace element partitionin[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1978, 42(6):743-770. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0016703778900911
[24] Pride C, Muecke G K.Rare earth element distributions among coexisting granulite facies minerals, Scourian Complex, NW Scotland[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1981, 76:463-471. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00371488
[25] Gaspar M, Knaack C, Meinert L D, et al.REE in skarn systems:A LA-ICP-MS study of garnets from the Crown Jewel gold deposit[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72:185-205. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016703707005546
[26] 刘晓菲, 袁顺达, 双燕, 等.湖南金船塘锡铋矿床石榴子石原位LA-ICP-MS稀土元素分析及其意义[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(1):163-177. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94579X/201401/48736550.html
Liu X F, Yuan S D, Shuang Y, et al.In situ LA-ICP-MS REE analyses of the skarn garnets from the Jinchuantang tin-bismuth deposit in Hunan Province, and their significance[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(1):163-177. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94579X/201401/48736550.html
[27] Boyd F R, Pearson D G, Hoal K O, et al.Garnet lherzolites from Louwrensia, Namibia:Bulk composition and P/T relations[J].Lithos, 2004, 77(1-4):573-592. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/resolve/reference/ADS?id=2004Litho..77..573B
[28] Alessandra S, Simona Q, Federico B, et al.Fe2+-O and Mn2+-O bonding and Fe2+-and Mn2+-vibrational properties in synthetic almandine-spessartine solid solutions[J].European Journal of Mineralogy, 2004, 16(5):801-808.
[29] Hofmeister A M, Fagan T J, Campbell K M, et al.Single-crystal IR spectroscopy of pyrope-almandine garnets with minor amounts of Mn and Ca[J].American Mineralogist, 1996, 81(3-4):418-428. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1996AmMin..81..418H
[30] Moore R K, White W B, Long T V.Vibrational spectra of the common silicates:Ⅰ.The garnets[J].American Mineralogist, 1971, 56:54-71. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284046328_Vibrational_spectra_of_the_common_silicates_I_The
[31] 王奎仁, 彭捷, 杨学明, 等.我国某些矽卡岩型矿床中石榴石的波谱学研究[J].安徽地质, 1992(4):1-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-AHDZ199204000.htm
Wang K R, Peng J, Yang X M, et al.Spectroscopic study of garnet in some skarn deposits in China[J].Geology of Anhui Province, 1992(4):1-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-AHDZ199204000.htm
[32] 何谋春, 洪斌, 吕新彪.钙铝榴石-钙铁榴石的拉曼光谱特征光[J].散射学报, 2002, 14(2):121. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GSSX200202013.htm
He M C, Hong B, Lü X B.The feature of Raman spectra of grossular-andradite[J].Chinese Journal of Light Scattering, 2002, 14(2):121. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GSSX200202013.htm
[33] 向亭译.浅析铬钒钙铝榴石的颜色成因[J].科学技术与工程, 2012, 12(30):7995-7998.
Xiang T Y.Analysis of chrome vanadium grossular color genesis[J].Science Technology and Engineering, 2012, 12(30):7995-7998.
-



 下载:
下载: