Determination of Trace Selenium in High-Carbon and High-Sulfur Geological Samples by Thiol Cotton Fiber Separation-Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry
-
摘要:
氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS)应用于测定地质样品中的痕量硒具有较高的灵敏度,但复杂的基质仍会增加分析难度,尤其是富含有机质样品与硫化物样品中的有机碳、复杂配合物和共存离子等带来的干扰,故样品前处理十分重要。采用常规的巯基棉(thiol cotton fibre,TCF)富集分离方法处理富含有机质样品与硫化物样品时,常会出现回收率不稳定、TCF过早饱和的现象。因此,本文针对富含有机质样品,使用双TCF柱法,通过两次吸附可以有效减少有机质的干扰;针对硫化物样品,可通过增加TCF的用量或者减少称样量来提高硒的回收率。标准物质和实际样品的测定结果表明优化的方法可满足分析要求,对富有机质样品,硒的回收率大于95.1%±0.37%;对硫化物样品,硒的回收率大于95.5%±1.92%。同时,研究也表明,采用微波消解处理样品,能够有效地避免硒在消解过程中的损失。改进后的方法提升了富集分离效果,适用于有机质和硫化物地质样品中的痕量硒(ng/g~μg/g级)分析要求。
-
关键词:
- 高碳高硫地质样品 /
- 硒 /
- 微波消解 /
- 巯基棉 /
- 氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法
Abstract:BACKGROUND Hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (HG-AFS) is highly sensitive for the determination of trace selenium in geological samples. However, the complex matrix increases the analysis difficulty, especially owing to interference caused by organic carbon, complicated complexes, and coexisting ions in samples rich in organic matter and sulfides. Therefore, sample pretreatment is important. The use of conventional thiol cotton fiber (TCF) to enrich and separate selenium often leads to unstable recovery and premature saturation of the TCF when dealing with samples rich in organic matter and sulfides.
OBJECTIVES To establish a method suitable for the determination of trace selenium in geological samples rich in organic matter and sulfides.
METHODS For samples rich in organic matter, a double TCF column (mTCF=0.15g) was used to carry out adsorption twice. The recovery for high-sulfur geological samples could be increased either by increasing the amount of TCF (mTCF ≤ 0.2g) or reducing the sample amount.
RESULTS The measurement results for the reference materials and actual samples showed that the optimized method satisfied the analysis requirements as selenium recoveries of >95.1% and >95.5% were achieved for the organic-rich and sulfide samples, respectively. Microwave digestion can effectively avoid the loss of selenium during digestion; the measured selenium content was consistent with that reported in the literature.
CONCLUSIONS The improved method is suitable for geological samples rich in organic matter and sulfides, which can be used to determine trace selenium (ng/g to μg/g levels) in geological samples.
-

-
表 1 优化后的实验条件和流程
Table 1. Optimized experimental conditions and processes in this study
样品处理和分析步骤 具体操作流程和实验条件 样品消解 浓硝酸(6mL),氢氟酸(2mL),200℃微波消解90min 硒的还原 ①样品蒸干后赶酸,加入15mL 5mol/L盐酸定容,静置过夜
②沸水浴30min,冷却至室温TCF富集分离硒 ①5mol/L的盐酸介质,15mL样品+15mL超纯水,调节至2.5mol/L的盐酸介质
②TCF柱准备:0.15~0.2g,放入微柱中压实
③洗涤:2.5mL+2.5mL超纯水洗涤TCF柱
④平衡:2.5mL+2.5mL 2.5mol/L盐酸平衡TCF柱
吸附Se(Ⅳ):30mL样品以0.05mL/s通过TCF柱硒的解吸 ①取下TCF后转移比色管中,加入2mL 12mol/L浓盐酸、2滴浓硝酸
②沸水浴,3min,冷却至室温
③离心:将絮状溶液离心后,转移上层清液
④多次回收TCF上的硒:3mL+5mL超纯水,清洗比色管,充分振荡
⑤多次离心,将上层清液混合,稀释至上机浓度准备测试HG-AFS测试 载流:5%盐酸溶液还原剂:2%硼氢化钾溶液 表 2 不同处理体系测定富有机质地质样品中的硒含量结果
Table 2. Analytical results of selenium content in organic-rich geological samples pretreated by different processing systems
处理体系分组 样品编号 岩性 硒推荐值(μg/g) 硒测定值(n=2)(μg/g) 硒回收率(%) 硒平均回收率(%) T-1 SGR-1b 油气页岩 3.5 2.87±0.01 82.0 77.6±4.43 SGR-1b 油气页岩 3.5 2.56±0.04 73.1 GBW07303 水系沉积物 1±0.2 0.87±0.05 87.0 85.5±1.50 GBW07303 水系沉积物 1±0.2 0.84±0.06 84.0 GBW07407 土壤 1.34±0.17 1.07±0.07 79.9 80.6±0.75 GBW07407 土壤 1.34±0.17 1.09±0.01 81.3 MA-4 黑色页岩 7.1 5.56±0.08 78.3 76.5±1.83 MA-4 黑色页岩 7.1 5.30±0.11 74.6 MA-5 黑色页岩 33.2 27.14±0.16 81.7 83.1±1.37 MA-5 黑色页岩 33.2 28.05±0.14 84.5 T-2 SGR-1b 油气页岩 3.5 3.47±0.14 99.1 101.1±2.00 SGR-1b 油气页岩 3.5 3.61±0.05 103.1 GBW07303 水系沉积物 1±0.2 0.90±0.03 90.0 91.5±1.50 GBW07303 水系沉积物 1±0.2 0.93±0.02 93.0 GBW07407 土壤 1.34±0.17 1.37±0.09 102.2 100.0±2.24 GBW07407 土壤 1.34±0.17 1.31±0.04 97.8 MA-4 黑色页岩 7.1 6.73±0.19 94.8 96.4±1.62 MA-4 黑色页岩 7.1 6.96±0.07 98.0 MA-5 黑色页岩 33.2 34.1±0.15 102.7 99.4±3.31 MA-5 黑色页岩 33.2 31.9±0.11 96.1 T-3 SGR-1b 油气页岩 3.5 3.44±0.06 98.3 103.6±5.29 SGR-1b 油气页岩 3.5 3.81±0.01 108.9 GBW07303 水系沉积物 1±0.2 1.02±0.01 102.0 101.5±0.50 GBW07303 水系沉积物 1±0.2 1.01±0.05 101.0 GBW07407 土壤 1.34±0.17 1.28±0.02 95.5 95.1±0.37 GBW07407 土壤 1.34±0.17 1.27±0.03 94.8 MA-4 黑色页岩 7.1 6.82±0.12 96.1 99.2±3.10 MA-4 黑色页岩 7.1 7.26±0.09 102.3 MA-5 黑色页岩 33.2 35.67±0.24 107.4 106.2±1.23 MA-5 黑色页岩 33.2 34.85±0.17 105.0 注:n为测定次数,"硒测定值(n=2)"为两次测定平均值。T-1组为单柱法不加H2O2体系;T-2为单柱法加H2O2体系;T-3为双柱法不加H2O2体系。 表 3 不同处理体系测定硫化物样品中硒含量结果
Table 3. Analytical results of selenium content in sulfide samples pretreated by different processing systems
处理体系分组 样品编号 样品性质 TCF用量(g) 硒推荐值(μg/g) 硒测定值(n=2)(μg/g) 硒回收率(%) 硒平均回收率(%) S-1 GBW07237 锌矿石 0.15 2.3±0.6 2.05±0.04 89.1 89.6±0.43 GBW07237 锌矿石 2.3±0.6 2.07±0.04 90.0 GBW07270 闪锌矿 0.15 3 2.73±0.03 91.0 89.2±1.83 GBW07270 闪锌矿 3 2.62±0.03 87.3 MA-1 全岩硫化物 0.15 39.3 29.23±0.05 74.4 73.9±0. 47 MA-1 全岩硫化物 39.3 28.86±0.04 73.4 MA-2 全岩硫化物 0.15 27.6 23.94±0.07 86.7 86.2±0.58 MA-2 全岩硫化物 27.6 23.62±0.07 85.6 MA-3 辉钼矿 0.15 0.78 0.65±0.01 83.3 80.8±2.56 MA-3 辉钼矿 0.78 0.61±0.02 78.2 S-2 GBW07237 锌矿石 0.20 2.3±0.6 2.37±0.05 103.0 103.3±0.22 GBW07237 锌矿石 2.3±0.6 2.38±0.01 103.5 GBW07270 闪锌矿 0.20 3 3.11±0.01 103.7 99.2±4.50 GBW07270 闪锌矿 3 2.84±0.03 94.7 MA-1 全岩硫化物 0.20 39.3 38.35±0.02 97.6 97.4±0.18 MA-1 全岩硫化物 39.3 38.21±0.04 97.2 MA-2 全岩硫化物 0.20 27.6 28.89±0.09 104.7 103.4±1.23 MA-2 全岩硫化物 27.6 28.21±0.08 102.2 MA-3 辉钼矿 0.20 0.78 0.73±0.01 93.6 95.5±1.92 MA-3 辉钼矿 0.78 0.76±0.03 97.4 注:n为测定次数,"硒测定值(n=2)"为两次测定平均值。 表 4 不同处理步骤硒标准溶液的回收率
Table 4. Recovery of selenium standard solution treated by different processing steps
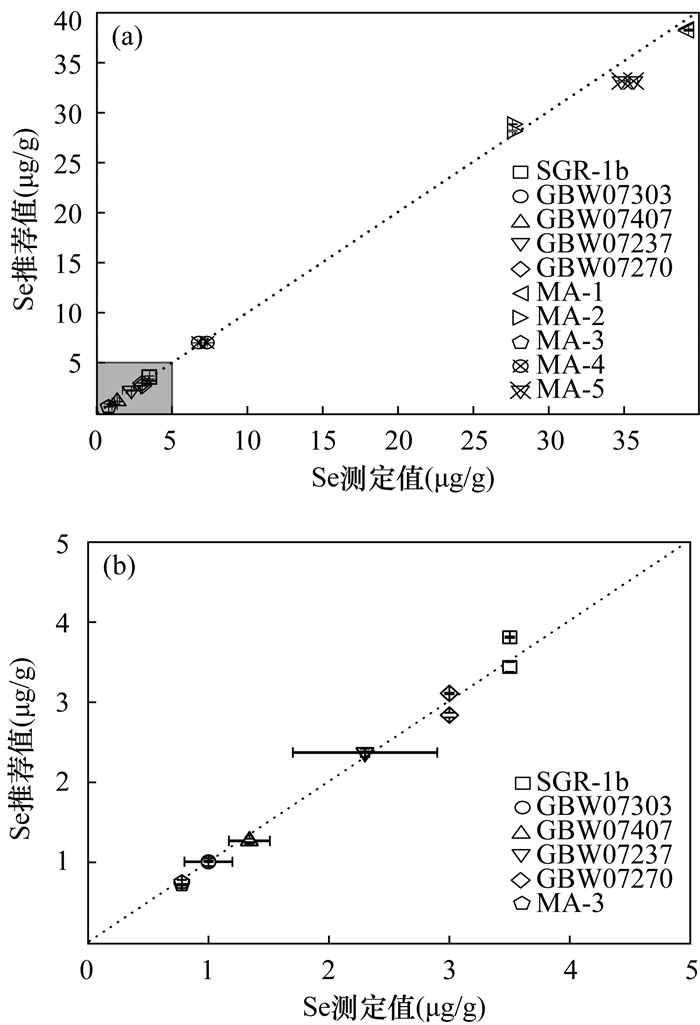
分组 编号 硒含量(ng) 消解前添加无硒玄武岩 消解后添加无硒玄武岩 还原处理 TCF纯化后硒含量(ng) 硒回收率(%) 硒平均回收率(%) B-1 β-1 0 √ × √ 0 - - β-2 0 √ × √ 0 - B-2 β-3 150 × × × 107.01 71.3 72.3±0.92 β-4 150 × × × 109.77 73.2 B-3 β-5 150 × × √ 112.89 75.3 78.3±3.08 β-6 150 × × √ 122.12 81.4 B-4 β-7 150 √ × √ 151.97 101.3 100.5±0.80 β-8 150 √ × √ 149.57 99.7 B-5 β-9 150 × √ √ 153.56 102.4 101.9±0.44 β-10 150 × √ √ 152.24 101.5 表 5 改进后的方法与不同研究中硒的测定值比较
Table 5. Comparison of the measured values of selenium with improved method (this work) and other studies
-
[1] U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral commodity summaries 2020[R]. U.S. Geological Survey, 2020, https://doi.org/10.3133/mcs2020.
[2] 陈炳翰, 丁建华, 叶会寿, 等. 中国硒矿成矿规律概要[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(6): 1063-1077. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202006007.htm
Chen B H, Ding J H, Ye H S, et al. Metallogenic regularity of selenium ore in China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2020, 39(6): 1063-1077. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202006007.htm
[3] 李静贤, 刘家军. 硒矿资源研究现状[J]. 资源与产业, 2014, 16(2): 90-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZIYU201402020.htm
Li J X, Liu J J. Advances in selenium resource study[J]. Resources and Industries, 2014, 16(2): 90-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZIYU201402020.htm
[4] Wen H J, Carignan J. Selenium isotopes trace the source and redox processes in the black shale-hosted Se-rich deposits in China[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2011, 75(6): 1411-1427. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.12.021
[5] 涂光炽, 高振敏, 胡瑞忠, 等. 分散元素地球化学及成矿机制[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004: 1-153.
Tu G C, Gao Z M, Hu R Z, et al. The geochemistry and ore-forming mechanism of the dispersed elements[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing Housee, 2004: 1-153.
[6] König S, Luguet A, Lorand J P, et al. Selenium and tellurium systematics of the Earth's mantle from high precision analyses of ultra-depleted orogenic peridotites[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 86: 354-366. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.03.014
[7] Yierpan A, Knig S, Labidi J, et al. Recycled selenium in hot spot-influenced lavas records ocean-atmosphere oxygenation[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(39): EABB6179. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb6179
[8] Tian H, Ma Z Z, Chen X L, et al. Geochemical chara-cteristics of selenium and its correlation to other elements and minerals in selenium-enriched rocks in Ziyang County, Shaanxi Province, China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2016, 27(5): 763-776. doi: 10.1007/s12583-016-0700-x
[9] Quang T D, Cui Z W, Huang J, et al. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: A review[J]. Environment International, 2018, 112(3): 294-309. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/29438838
[10] 李刚, 胡斯宪, 陈琳玲. 原子荧光光谱分析技术的创新与发展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2013, 32(3): 358-376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.03.003 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/0c8cca2d-b0a6-46c7-be65-25f1c32a1e6b
Li G, Hu S X, Chen L L. Innovation and development for atomic fluorescence spectrometry analysis[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(3): 358-376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.03.003 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/0c8cca2d-b0a6-46c7-be65-25f1c32a1e6b
[11] 陈海杰, 马娜, 白金峰, 等. 基于外供氢气-氢化物-原子荧光光谱法测定地球化学样品中硒的研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2020, 40(9): 2896-2900. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN202009046.htm
Chen H J, Ma N, Bai J F, et al. Study on determination of Se in geochemical samples by external supply H2-hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(9): 2896-2900. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN202009046.htm
[12] 张欣, 许俊玉, 范凡, 等. 断续流动氢化物发生-原子吸收光谱法测定地质样品中的硒[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2016, 36(1): 191-194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2016.01.026
Zhang X, Xu J Y, Fan F, et al. Determination of selenium in geological samples by intermittent-flow hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2016, 36(1): 191-194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2016.01.026
[13] Marin L, Lhomme J, Carignan J. GFAAS determination of selenium after separation with thiol cotton in lichens and plants: The importance of adding a mineral matrix before decomposition[J]. Talanta, 2003, 61(2): 119-125. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(03)00272-8
[14] Marin L, Lhomme J, Carignan J. Determination of selen-ium concentration in sixty five reference materials for geochemical analysis by GFAAS after separation with thiol cotton[J]. Geostandards Newsletter, 2001, 25: 317-324. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2001.tb00608.x
[15] Rouxel O, Ludden J, Carignan J, et al. Natural variations of Se isotopic composition determined by hydride generation multiple collector coupled mass spectrometer[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002, 66(18): 3191-3199. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00918-3
[16] Fan H F, Wen H J, Hu R Z, et al. Determination of total selenium in geological samples by HG-AFS after concentration with thiol cotton fiber[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2008(1): 90-96. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/ssam/10009426/2008/00000027/00000001/art00012
[17] Yu M Q, Liu G Q, Jin Q. Determination of trace arsenic, antimony, selenium and tellurium in various oxidation states in water by hydride generation and atomic-absorption spectrophotometry after enrichment and separation with thiol cotton[J]. Talanta, 1983, 30(4): 265-270. doi: 10.1016/0039-9140(83)80060-5
[18] Yu M, Sun D, Tian W, et al. Systematic studies on adsorption of trace elements Pt, Pd, Au, Se, Te, As, Hg, Sb on thiol cotton fiber[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2002, 456(1): 147-155. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(02)00004-1
[19] Yu M, Tian W, Sun D, et al. Systematic studies on adsorption of 11 trace heavy metals on thiol cotton fiber[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2001, 428(2): 209-218. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(00)01238-1
[20] Shan X Q, Hu K J. Matrix modification for determination of selenium in geological samples by graphite-furnace atomic-absorption spectrometry after preseparation with thiol cotton fibre[J]. Talanta, 1985, 32(1): 23-26. doi: 10.1016/0039-9140(85)80008-4
[21] 樊海峰, 温汉捷, 凌宏文, 等. 氢化物-原子荧光光谱法测定地质样中的痕量硒——不同溶样方式的比较[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2005, 24(3): 200-203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2005.03.004
Fan H F, Wen H J, Ling H W, et al. Determination of total selenium in geological samples by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry-A comparative experiment of two different dissolution methods[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2005, 24(3): 200-203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2005.03.004
[22] 刘芸, 曹国松, 程佩, 等. 微波消解-ICP-MS法测定土壤中的硒含量[J]. 化学与生物工程, 2017, 34(11): 67-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2017.11.017
Liu Y, Cao G S, Chen P, et al. Determination of selenium content in soil by microwave digestion-ICP-MS[J]. Chemistry and Bioengineering, 2017, 34(11): 67-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2017.11.017
[23] 杨萍, 李惠. 微波消解-氢化物发生-原子荧光法测定土壤中的砷[J]. 环境研究与监测, 2019, 32(3): 17-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX201806002.htm
Yang P, Li H. Determination of arsenic in soil by microwave digestion-hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Environmental Research and Monitoring, 2019, 32(3): 17-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX201806002.htm
[24] 李媛媛, 纪轶. 微波消解技术在环境化学分析中的应用研究[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2020, 38(10): 74-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2020.10.020
Li Y Y, Ji Y. Research on application of microwave digestion technology in environmental chemistry analysis[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2020, 38(10): 74-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2020.10.020
[25] 赵学沛. 微波消解-石墨炉原子吸收光谱法测定痕量银的研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2019, 38(2): 112-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201902009.htm
Zhao X P. Determination of trace amounts of silver by microwave digestion graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry[J]. Acta Petrologica Et Mineralogica, 2019, 38(2): 112-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201902009.htm
[26] Kurzawa T, König S, Labidi J, et al. A method for Se isotope analysis of low ng-level geological samples via double spike and hydride generation MC-ICP-MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2017, 466: 219-228. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.06.012
[27] Elwaer N, Hintelmann H. Selective separation of selen-ium(Ⅳ) by thiol cellulose powder and subsequent selenium isotope ratio determination using multicollector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2008, 23(5): 733-743. doi: 10.1039/b801673a
[28] 贺欣宇, 王军, 张丽娟. 巯基棉分离富集-多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱测量矿石中硒的同位素丰度[J]. 环境化学, 2010, 29(5): 982-983. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201005040.htm
He X Y, Wang J, Zhang L J. Determination of selenium isotope abundance in ores by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after sulfhydryl cotton separation and enrichment[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2010, 29(5): 982-983. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201005040.htm
[29] Stueeken E E, Foriel J, Nelson B K, et al. Selenium isotope analysis of organic-rich shales: Advances in sample preparation and isobaric interference correction[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2013, 28(11): 1734-1749. doi: 10.1039/c3ja50186h
[30] García J B, Krachler M, Chen B, et al. Improved deter-mination of selenium in plant and peat samples using hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry (HG-AFS)[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2005, 534(2): 255-261. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2004.11.043
[31] von Strandmann P, Coath C D, Catling D C, et al. Analysis of mass dependent and mass independent selenium isotope variability in black shales[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2014, 29(9): 1648-1659. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00124A
[32] 张文河, 穆桂金. 烧失法测定有机质和碳酸盐的精度控制[J]. 干旱区地理, 2007(3): 455-459. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6060.2007.03.021
Zhang W H, Mu G J. Precision control on measuring organic and carbonate content with loss on ignition method[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2007(3): 455-459. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6060.2007.03.021
[33] 成勇. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定油品中铁, 铜, 铅, 锡, 砷, 银, 铬, 镍, 钒[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2011, 1(4): 64-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2011.04.0016
Cheng Y. Determination of iron, copper, lead, tin, arsenic, silver, chromium, nickel and vanadium in oil by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 1(4): 64-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2011.04.0016
[34] 张羽旭, 温汉捷, 樊海峰. 地质样品中Mo同位素测定的前处理方法研究[J]. 分析化学, 2009, 37(2): 216-220. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2009.02.010
Zhang Y X, Wen H J, Fan H F. Chemical pretreatment methods for measurement of Mo isotope ratio on geological samples[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 37(2): 216-220. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2009.02.010
[35] 刘向磊, 孙文军, 文田耀, 等. 三酸分步消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定土壤详查样品中23种金属元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(5): 164-171. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201902270026
Liu X L, Sun W J, Wen T Y, et al. Determination of 23 metal elements in detailed soil survey samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry with three acid stepwise digestion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(5): 164-171. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201902270026
[36] 邬景荣, 许廷波, 符峙宗, 等. 微波消解-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定膨润土中6种元素[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2020, 56(2): 185-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH202002013.htm
Wu J R, Xu T B, Fu S Z, et al. ICP-AES determination of 6 elements in bentonite with microwave digestion[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2020, 56(2): 185-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH202002013.htm
[37] Savard D, Bédard L P, Barnes S J. TCF selenium precon-centration in geological materials for determination at sub-μg·g-1 with INAA (Se/TCF-INAA)[J]. Talanta, 2006, 70(3): 566-571. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2006.01.010
[38] 董亚妮, 田萍, 熊英, 等. 焙烧分离-氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法测定铜铅锌矿石中的硒[J]. 岩矿测试, 2011, 30(2): 164-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.02.008
Dong Y N, Tian P, Xiong Y, et al. Determination of trace selenium in copper ore, lead ore and zinc ore by hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry with baking separation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(2): 164-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.02.008
[39] 管希云, 李玉珍. 表面活性剂的应用研究——动力学光度法测定痕量硒碲[J]. 岩矿测试, 2000, 29(1): 14-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2000.01.004
Guan X Y, Li Y Z. Application research on surfactant-kinetic spectrophotometric determination of trace selenium and tellurium[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2000, 29(1): 14-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2000.01.004
-



 下载:
下载: