Application of μ-XRF in Uranium Mineralogy of the Huanglongpu Carbonate-type Molybdenum Deposit, Shaanxi Province, China
-
摘要:
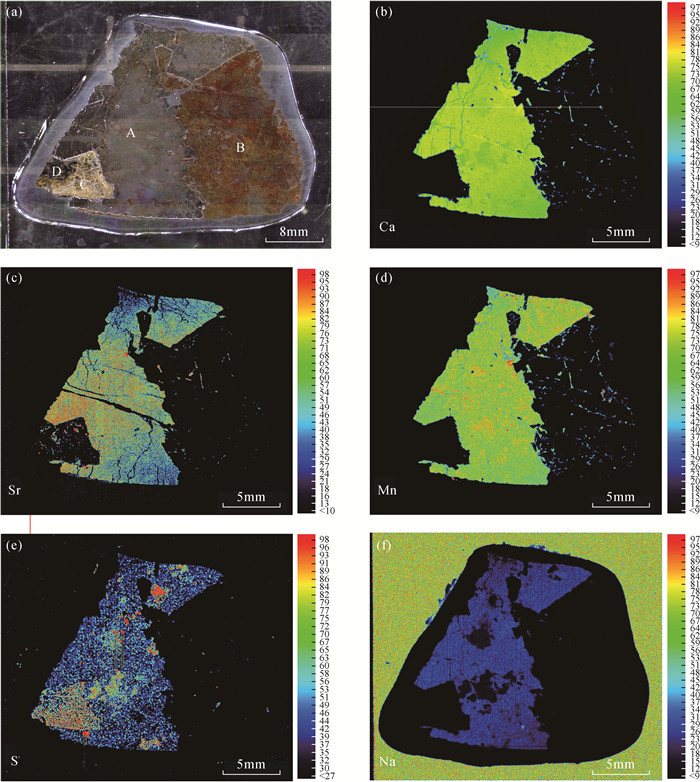
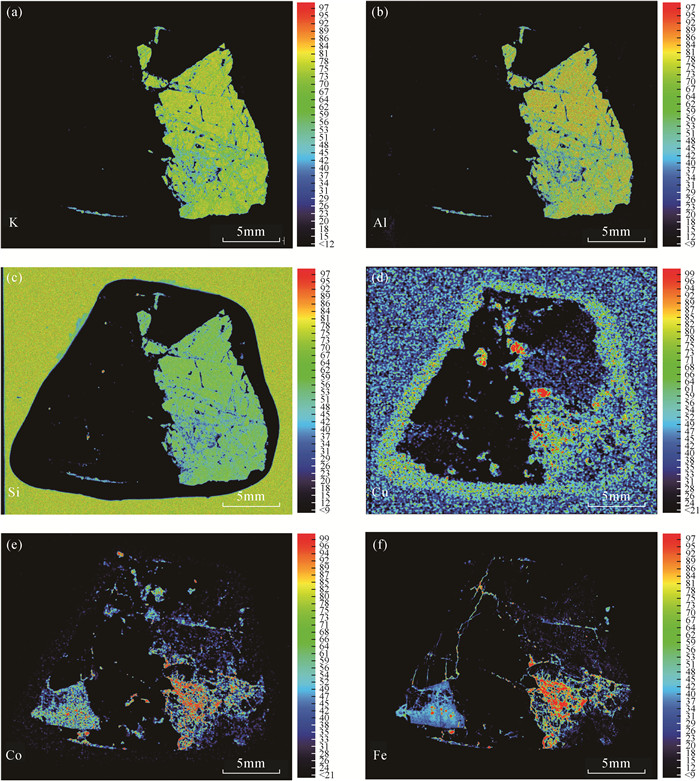
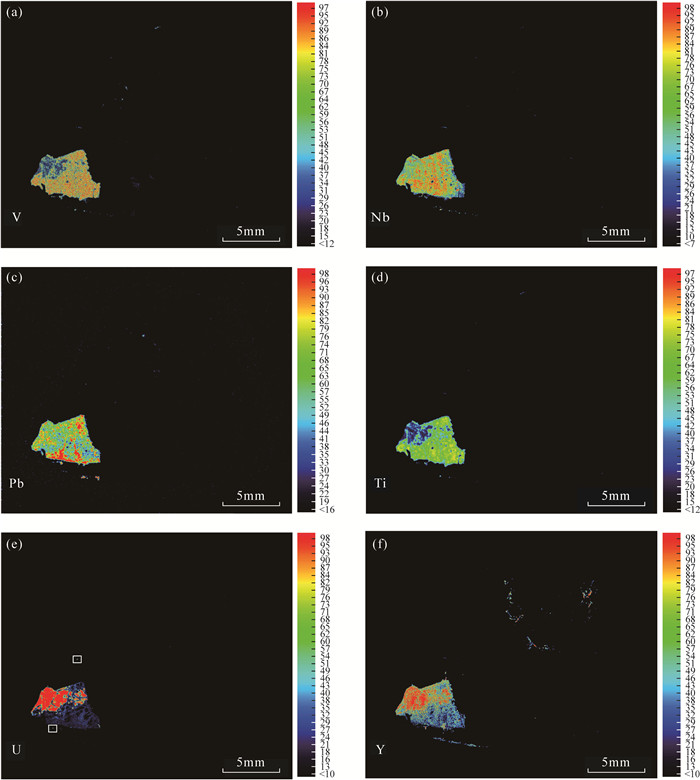
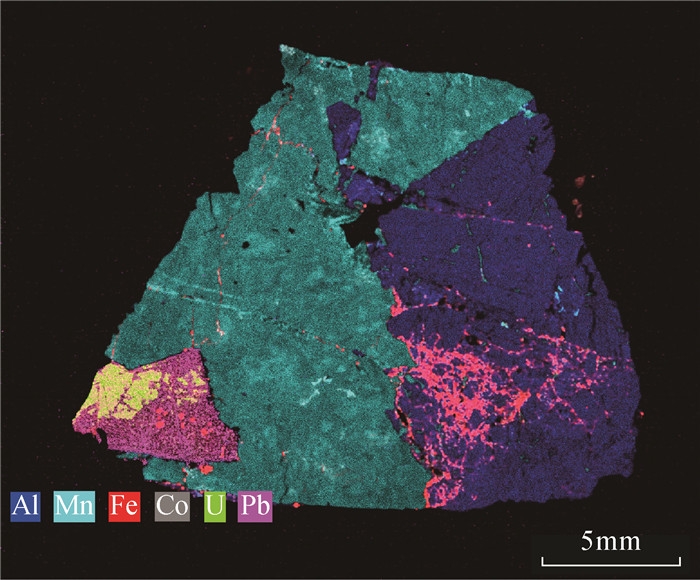
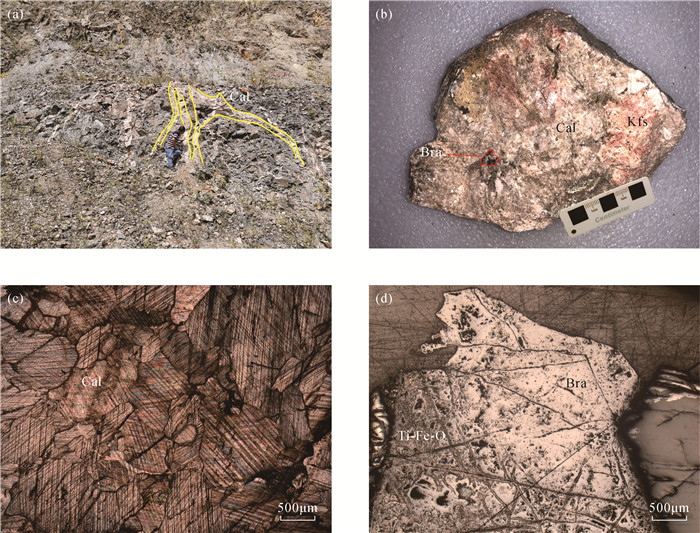
东秦岭碳酸岩型钼成矿带是全球最大的钼成矿带。该带内的黄龙铺矿床是中国最早发现的碳酸岩型钼矿床之一。最近的野外地质调查发现,部分钼矿石具有较高的放射性异常,但其放射性元素的赋存形式和矿物学特征尚不明确。本文借助聚毛细管微束X射线荧光光谱分析(μ-XRF)分析速度快、原位无损、高灵敏度的分析优势,快速查明铀矿物的空间位置,再结合扫描电镜分析(SEM)和X射线能谱分析(EDS),确定铀矿物的种类及其次生变化。研究表明:黄龙铺矿床高放射性矿石中主要的铀矿物为钛铀矿、铌钛铀矿和晶质铀矿,它们与方解石、长石、黄铁矿、辉钼矿和黄铜矿呈共生关系。矿石中铀矿物后期均遭受氧化性流体改造,发生了明显的蚀变,钛铀矿蚀变之后转变为含Nb的钛铁氧化物,铌钛铀矿和晶质铀矿蚀变后矿物内部形成大量空洞,流体来源可能为大气降水。背散射电子(BSE)图像上灰度差异明显,暗示着矿物中元素分布的不均一性。
Abstract:BACKGROUND The carbonatite-type molybdenum metallogenic belt in East Qinling is the largest molybdenum metallogenic belt in the world. The Huanglongpu deposit is one of the earliest discovered carbonatite-type molybdenum deposits in China. Our field survey found that the uranium grade of ores in this deposit was higher than the industrial uranium grade, being similar to the Huayangchuan U-Nb-Pb-REE deposit in the Qinling Orogenic Belt. However, the occurrences and mineralogical characteristics of radioactive elements are still unclear.
OBJECTIVES To explore the main mineral assemblages, U occurrences and other characteristics of uranium ores in the Huanglongpu deposit.
METHODS The detailed geological survey, μ-XRF, SEM and EDS analyses were carried out on the high-radioactivity ore from the Huanglongpu deposit.
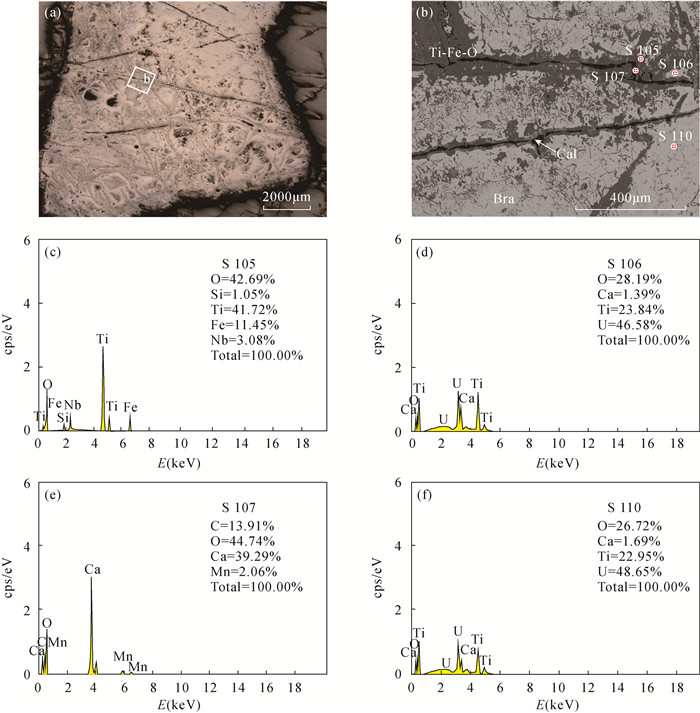
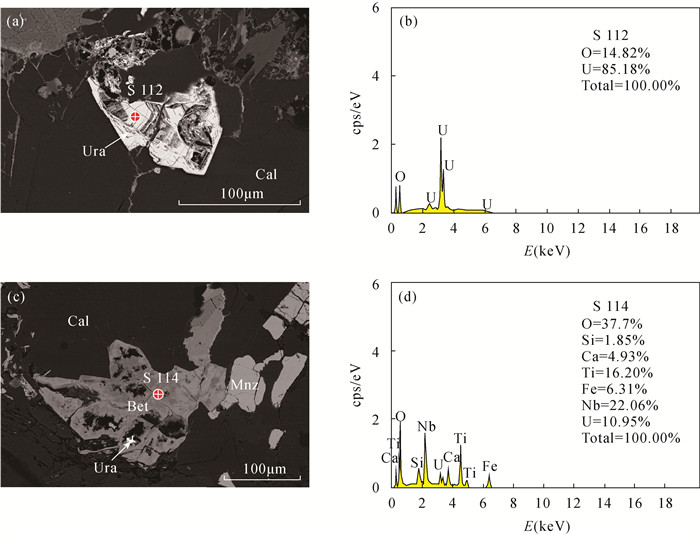
RESULTS The results showed that major uranium minerals in the Huanglongpu deposit were brannerite, betafite and uraninite, which were associated with calcite, feldspar, pyrite, molybdenite and chalcopyrite. Significant alteration and replacement of uranium minerals were observed in the studied ore sample. The betafite was transformed into Nb-rich Ti-Fe oxides after alteration. After alteration of brannerite and uraninite, a large number of cavities were formed within those minerals. The post-ore fluids were possible from meteoric water. The textural differences of altered brannerite and uraninite on BSE images suggested the variable chemical composition.
CONCLUSIONS μ-XRF technology has a great application prospect in the future research of uranium deposit genesis and prospecting prediction.
-
Key words:
- μ-XRF technology /
- SEM /
- EDS /
- uranium mineral /
- carbonatite /
- Huanglongpu deposit
-

-
[1] 黄典豪, 侯增谦, 杨志明, 等. 东秦岭钼矿带内碳酸岩脉型钼(铅)矿床地质-地球化学特征、成矿机制及成矿构造背景[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(12): 1968-1984. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.12.012
Huang D H, Hou Z Q, Yang Z M, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics, metallogenetic mechanism and tectonic setting of carbonatite vein-type Mo (Pb) deposits in the East Qinling molybdenum ore belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(12): 1968-1984. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.12.012
[2] Xu C, Kynicky J, Chakhmouradian A R, et al. A unique Mo deposit associated with carbonatites in the Qinling orogenic belt, central China[J]. Lithos, 2010, 118(1-2): 50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.03.013
[3] 王佳营, 李志丹, 张祺, 等. 东秦岭地区碳酸岩型钼-铀多金属矿床成矿时代: 来自LA-ICP-MS独居石U-Pb和辉钼矿Re-Os年龄的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(10): 2946-2964. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.011
Wang J Y, Li Z D, Zhang Q, et al. Metallogenic epoch of the carbonatite-type Mo-U polymetallic deposit in East Qinling: Evidence from the monazite LA-ICP-MS U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os isotopic dating[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(10): 2946-2964. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.011
[4] 黄典豪, 王义昌, 聂凤军, 等. 一种新的钼矿床类型——陕西黄龙铺碳酸岩脉型钼(铅)矿床地质特征及成矿机制[J]. 地质学报, 1985, 59(3): 241-257, 275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE198503006.htm
Huang D H, Wang Y C, Nie F J, et al. A new type of molybdenum deposit-Geological characteristics and metal-logenic mechanism of the Huanglongpu carbonatite vein-type of molybdenum (lead) deposit, Shanxi[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1985, 59(3): 241-257, 275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE198503006.htm
[5] 许成, 宋文磊, 漆亮, 等. 黄龙铺钼矿田含矿碳酸岩地球化学特征及其形成构造背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(2): 422-430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200902016.htm
Xu C, Song W L, Qi L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic setting of ore-bearing carbonatites in Hunglongpu Mo ore field[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(2): 422-430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200902016.htm
[6] Cangelosi D, Smith M, Banks D, et al. The role of sulfate-rich fluids in heavy rare earth enrichment at the Dashigou carbonatite deposit, Huanglongpu, China[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2020, 84(1): 65-80. doi: 10.1180/mgm.2019.78
[7] Song W L, Xu C, Smith M P, et al. Origin of unusual HREE-Mo-rich carbonatites in the Qinling Orogen, China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0001-8
[8] Smith M, Cangelosi D, Yardley B, et al. Mechanisms for the generation of HREE mineralization in carbonatites: Evidence from Huanglongpu, China[C]//Natural History Museum, SGA Conference Abstract, 2019: 1-5.
[9] Bai T, Chen W, Jiang S Y. Evolution of the carbonatite Mo-HREE deposits in the Lesser Qinling Orogen: Insights from in situ geochemical investigation of calcite and sulfate[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 113: 103069. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103069
[10] 惠小朝. 陕西省华阳川铀多金属成矿作用地球化学研究[D]. 北京: 核工业北京地质研究院, 2014.
Hui X Z. Study on mineralization and geochemistry of the Huayangchuan uranium ploymetallic deposit, Shaanxi Province[D]. Beijing: Research Institute of Uranium Geology, Beijing, 2014.
[11] 高成, 康清清, 江宏君, 等. 秦岭造山带发现新型铀多金属矿: 华阳川与伟晶岩脉和碳酸岩脉有关的超大型铀-铌-铅-稀土矿床[J]. 地球化学, 2017, 46(5): 446-455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.05.004
Gao C, Kang Q Q, Jiang H J, et al. Aunique uranium polymetallic deposit discovered in the Qinling orogenic belt: The Huayangchuan super-large U-Nb-Pb-REE deposit associated with pegmatites and carbonatites[J]. Geochimica, 2017, 46(5): 446-455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.05.004
[12] Zheng H, Chen H, Li D, et al. Timing of carbonatite-hosted U-polymetallic mineralization in the supergiant Huayangchuan deposit, Qinling Orogen: Constraints from titanite U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os dating[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2020, 11(5): 1581-1592. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.03.001
[13] 许涛, 罗立强. 原位微区X射线荧光光谱分析装置与技术研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2011, 30(3): 375-383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.03.028 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110327
Xu T, Luo L Q. Developments of micro-X-ray fluorescence spectrometer and applications[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(3): 375-383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.03.028 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110327
[14] Flude S, Haschke M, Storey M, et al. Application of benchtop micro-XRF to geological materials[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2017, 81(4): 923-948. doi: 10.1180/minmag.2016.080.150
[15] 罗立强, 沈亚婷, 马艳红, 等. 微区X射线荧光光谱仪研制及元素生物地球化学动态分布过程研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(4): 1003-1008. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201704003.htm
Luo L Q, Shen Y T, Ma Y H, et al. Development of laboratory microscopic X-Ray fluorescence spectrometer and the study on spatial distribution of elements in biofilms and maize seeds[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(4): 1003-1008. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201704003.htm
[16] Barker R D, Barker S L, Wilson S A, et al. Quantitative mineral mapping of drill core surfaces Ⅰ: A method for μ-XRF mineral calculation and mapping of hydrothermally altered, fine-grained sedimentary rocks from a carlin-type gold deposit[J]. Economic Geology, 2021, 116(4): 803-819. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4803
[17] Schmid S, Taylor W R, Jordan D P. The Bigrlyi tabular sandstone-hosted uranium-vanadium deposit, Ngalia Basin, central Australia[J]. Minerals, 2020, 20(10): 896. https://www.mdpi.com/2075-163X/10/10/896/htm
[18] Woldegabriel G, Boukhalfa H, Ware S, et al. Characterization of cores from an in-situ recovery mined uranium deposit in Wyoming: Implications for post-mining restoration[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 390: 32-45. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.10.009
[19] Herazo A, Reich M, Barra F, et al. Assessing the role of bitumen in the formation of strata bound Cu-(Ag) deposits: Insights from the Lorena deposit, Las Luces district, northern Chile[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 124: 103639. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103639
[20] 李六权, 崔江荣, 陈浩. 陕西木龙沟-黄龙铺地区钼、铼、稀土资源量概况及铼、稀土赋存特征[J]. 陕西地质, 2019, 37(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2019.01.001
Li L Q, Cui J R, Chen H. General situation of molybdenum, rhenium and rare earth resources and occurrence characteristics of rhenium and rare earth in Mulonggou-Huanglongpu area of Luonan County[J]. Geology of Shaanxi, 2019, 37(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2019.01.001
[21] 王运, 胡宝群, 孙占学, 等. 相山铀矿田邹家山矿床钛铀矿赋存特征及成因[J]. 铀矿地质, 2010, 26(6): 344-349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2010.06.004
Wang Y, Hu B Q, Sun Z X, et al. Occurring characteristics and genesis of brannerite at Zoujiashan uranium deposits, Xiangshan ore field[J]. Uranium Geology, 2010, 26(6): 344-349. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2010.06.004
[22] 李治兴, 漆富成, 张字龙, 等. 张家界下寒武统磷块岩中钛铀矿的晶出方式与成矿机理[J]. 矿物学报, 2017, 37(3): 305-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201703007.htm
Li Y X, Qi F C, Zhang Z L, et al. Crystallization and metallization of brannerite in marine phosphorite of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Zhangjiajie area, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2017, 37(3): 305-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201703007.htm
[23] 王贵, 王强, 苗爱生, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地纳岭沟铀矿床铀矿物特征与形成机理[J]. 矿物学报, 2017, 37(4): 461-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201704013.htm
Wang G, Wang Q, Miao A S, et al. Characteristics of uranium minerals in Nalinggou uranium deposit of Ordos Basin and their formation mechanism[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2017, 37(4): 461-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201704013.htm
[24] Cuney M. Geologic environment, mineralogy, and fluid inclusions of the Bois Noirs-Limouzat uranium vein, Forez, France[J]. Economic Geology, 1978, 73(8): 1567-1610. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.73.8.1567
[25] Hu R Z, Bi X W, Zhou M F, et al. Uranium metallogenesis in South China and its relationship to crustal extension during the Cretaceous to Tertiary[J]. Economic Geology, 2008, 103(3): 583-598. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.103.3.583
[26] 闵茂中, 张富生. 成因铀矿物学概论[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1992.
Min M Z, Zhang F S. Uranium minerageny[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 1992.
[27] Cuney M. Felsic magmatism and uranium deposits[J]. Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France, 2014, 185(2): 75-92. doi: 10.2113/gssgfbull.185.2.75
[28] Zhang L, Chen Z Y, Wang F Y, et al. Release of uranium from uraninite in granites through alteration: Implications for the source of granite-related uranium ores[J/OL]. Economic Geology, 2021, https://doi.org/10.5382/econgeo.4822.
[29] Rallakis D, Michels R, Brouand M, et al. The role of organic matter on uranium precipitation in Zoovch Ovoo[J]. Mongolia Minerals, 2019, 9(5): 310. https://www.mdpi.com/2075-163X/9/5/310/htm
[30] Scheinost A C, Hennig C, Somogyi A, et al. Uranium speciation in two Freital mine tailing samples: EXAFS, μ-XRD, and μ-XRF results[M]//Uranium in the Environment. Heidelberg: Springer, 2006.
-




 下载:
下载: