Infrared Spectroscopy, Portable XRF and Magnetic Susceptibility Analysis of Drill Core for Exploration of the Taihe Vanadium Titano-Magnetite Deposit in the Panxi Area, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
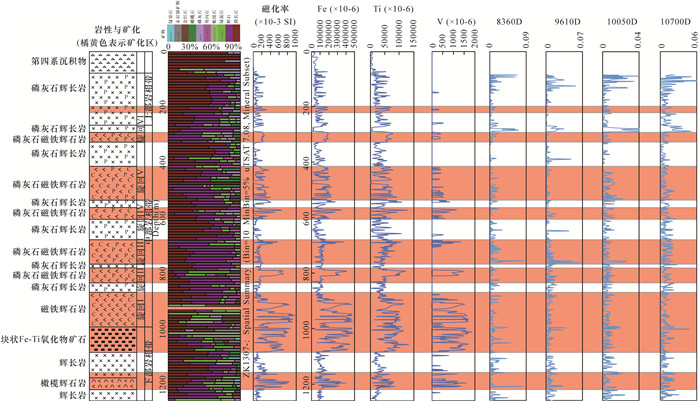
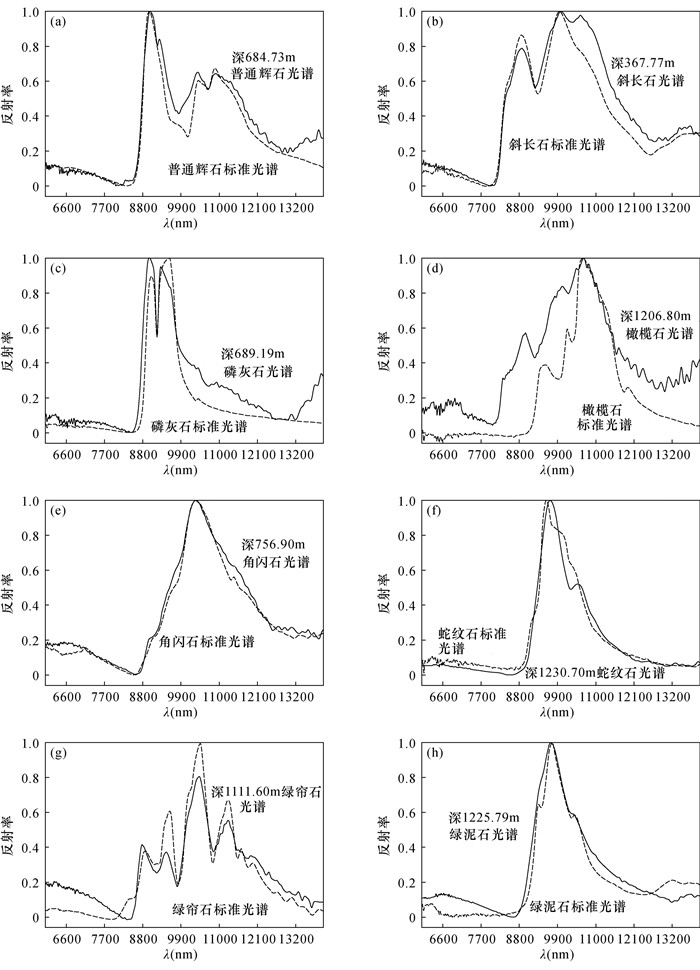
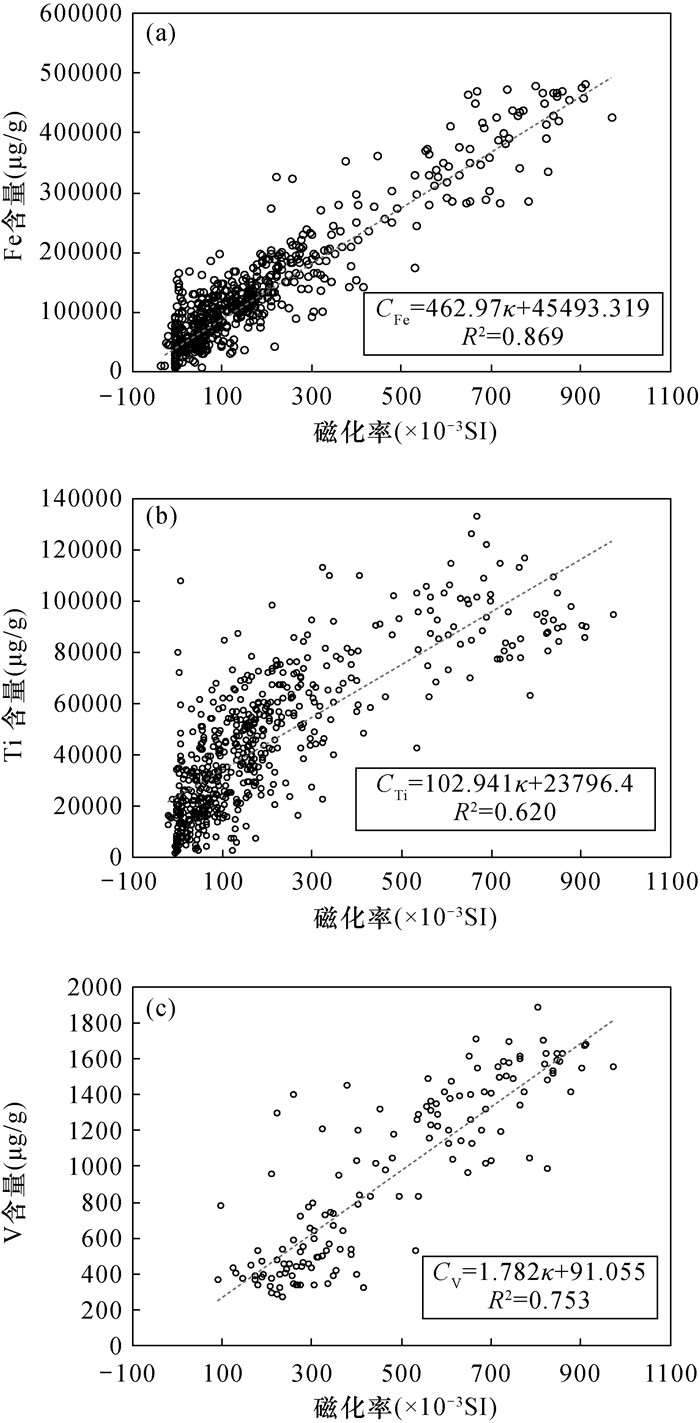
近年来,红外光谱技术因其可以绿色、快速、无损、精确探测矿物和提高勘查效率而备受关注。攀西超大型太和钒钛磁铁矿床位于镁铁质-超镁铁质层状岩体中,该矿床的典型矿物的红外光谱特征研究相对缺乏,制约了勘查效率的提高。本文应用便携式傅里叶变换红外光谱仪对四川太和钒钛磁铁矿床钻孔ZK1307岩心开展热红外光谱测试工作,并辅以便携式X射线荧光光谱(XRF)元素含量分析和磁化率值的综合分析,参考岩心编录情况,分析研究了钻孔岩性-矿物组合-元素含量-磁化率之间的对应关系。研究表明:热红外光谱可以实现快速、无损对辉石特征吸收峰的信息提取,识别含磁铁辉石岩体分布范围,快速界定含矿岩体;太合矿床Fe、Ti、V元素含量可以用磁化率值进行线性拟合,较高的Fe、Ti、V金属元素含量和磁化率值可作为判断地质体矿化的指示信息。
Abstract:BACKGROUND The Panxi super large-scale Taihe vanadium-titanium magnetite deposit is located in the mafic-ultramafic layered intrusions. Research on the characteristics of infrared spectroscopy of the typical minerals of this deposit is relatively lacking, restricting exploration efficiency. The Panxi area would benefit from the use of infrared spectroscopy technology, which in recent years has attracted much attention because of its green, fast, non-destructive and accurate detection of minerals, and improvement of exploration efficiency.
OBJECTIVES To analyze the characteristics of different minerals and to efficiently identify ore-bearing intrusions and mineralized regions in the Taihe vanadium titano-magnetite deposit in the Panxi area, Sichuan Province.
METHODS Minerals were identified using Handheld FTIR through thermal infrared (TIR). The contents of Fe, Ti, and V were analyzed by Vanta VMW portable XRF. The magnetic susceptibility was analyzed by KM-7 portable magnetic susceptibility tester. Based on the core catalog, the relationship between borehole lithology, mineral assemblage, element content, and magnetic susceptibility value was studied.
RESULTS TIR can be used to achieve rapid and non-destructive extraction of the characteristic absorption peaks of pyroxene, identify the distribution of magnetite-bearing pyroxenite, and quickly define ore-bearing rock masses. The contents of Fe, Ti, and V in the Taihe deposit can be linearly fitted by magnetic susceptibility values. Different kinds of rocks and ores have different contents of Fe, Ti, V and magnetic susceptibility value.
CONCLUSIONS TIR technology is useful for prospecting magnetite-bearing rocks or deposits in unknown areas. The higher contents of Fe, Ti, and V and magnetic susceptibility values can be used as indicative information for judging the mineralization of geological bodies.
-

-
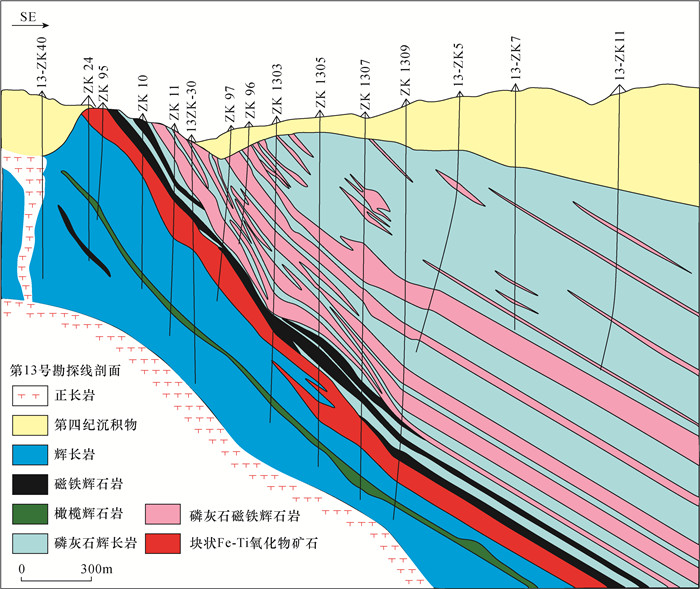
图 1 太和钒钛磁铁矿床第13号勘探线剖面图[5]
Figure 1.
-
[1] 胡受奚, 叶瑛, 方长泉. 交代蚀变岩岩石学及其找矿意义[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004: 1-109.
Hu S X, Ye Y, Fang C Q. Petrology of metasomatic alteration rocks and its prospecting significance[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004: 1-109.
[2] 张世涛, 陈华勇, 韩金生, 等. 鄂东南铜绿山大型铜铁金矿床成矿岩体年代学、地球化学特征及成矿意义[J]. 地球化学, 2018, 47(3): 240-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201803002.htm
Zhang S T, Chen H Y, Han J S, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry, and mineralization of quartz monzodiorite and quartz monzodiorite porphyry in Tonglüshan Cu-Fe-Au deposit, Edongnan ore district, China[J]. Geochimica, 2018, 47(3): 240-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201803002.htm
[3] 陈华勇, 张世涛, 初高彬, 等. 鄂东南矿集区典型矽卡岩-斑岩矿床蚀变矿物短波红外(SWIR)光谱研究与勘查应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(12): 3629-3643. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.12.04
Chen H Y, Zhang S T, Chu G B, et al. The short wave infrared (SWIR) spectral characteristics of alteration minerals and applications for ore exploration in the typical skarn-porphyry deposits, Edong ore district, eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(12): 3629-3643. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.12.04
[4] Zhang Z C, Hou T, Santosh M, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution and tectonic settings of the major iron deposits in China: An overview[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 57: 247-263. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.08.021
[5] 佘宇伟. 四川太和层状岩体及其富磷灰石钒钛磁铁矿床成因[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2015.
She Y W. Petrogenesis and apatite-rich Fe-Ti-V oxide mineralization of the Taihe mafic-ultramafic layered intrusion in the Sichuan Province, SW China[D]. Beijing: The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015.
[6] 魏宇, 郭耀文, 柳维, 等. 西昌太和钒钛磁铁矿矿体特征及成因[J]. 四川地质学报, 2014, 34(3): 368-372. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2014.03.012
Wei Y, Guo Y W, Liu W, et al. Geological features and genesis for the Taihe vanadic titanomagnetite deposit[J]. Geological Journal of Sichuan, 2014, 34(3): 368-372. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2014.03.012
[7] 李松键, 攀西太和钒钛磁铁矿含矿岩体及矿床地质特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2015.
Li S J. Characteristics of ore-bearing rocks and deposit geology of Taihe vanadium titano-magnetite deposit in Panzhihua-Xichang District[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2015.
[8] 童鹏, 刘鹏飞, 赵英俊, 等. 磁化率在太和钒钛磁铁矿钻孔岩芯分析中的应用[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(增刊1): 301-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2018S1067.htm
Tong P, Liu P F, Zhao Y J, et al. Application of the magnetic susceptibility in the core analysis of Taihe vanadium titano-magnetite[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(Supplement 1): 301-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2018S1067.htm
[9] Hou T, Zhang Z C, Encarnacion J, et al. Petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Taihe gabbroic intrusion associated with Fe-Ti-oxide ores in the Panxi District, Emeishan Large Igneous Province, southwest China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 49: 109-127. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.09.004
[10] She Y W, Yu S Y, Song X Y, et al. The formation of P-rich Fe-Ti oxide ore layers in the Taihe layered intrusion, SW China: Implications for magma-plumbing system process[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 57: 539-559. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.07.007
[11] She Y W, Song X Y, Yu S Y, et al. Variations of trace element concentration of magnetite and ilmenite from the Taihe layered intrusion, Emeishan Large Igneous Province, SW China: Implications for magmatic fractionation and origin of Fe-Ti-V oxide ore deposits[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 1117-1131. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.029
[12] She Y W, Song X Y, Yu S Y, et al. Apatite geochemistry of the Taihe layered intrusion, SW China: Implications for the magmatic differentiation and the origin of apatite-rich Fe-Ti oxide ores[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 78: 151-165. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.04.004
[13] 钟宏, 徐桂文, 朱维光, 等. 峨眉山大火成岩省太和花岗岩的成因及构造意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2009, 28(2): 99-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2009.02.001
Zhong H, Xu G W, Zhu W G, et al. Petrogenesis of the Taihe granites in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province and its tectonic implications[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2009, 28(2): 99-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2009.02.001
[14] 佘宇伟, 宋谢炎, 于宋月, 等. 磁铁矿和钛铁矿成分对四川太和富磷灰石钒钛磁铁矿床成因的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(5): 1443-1456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201405018.htm
She Y W, Song X Y, Yu S Y, et al. The compositions of magnetite and ilmenite of the Taihe layered intrusion, Sichuan Province: Constraints on the formation of the P-rich Fe-Ti oxide ores[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(5): 1443-1456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201405018.htm
[15] 代晶晶, 赵龙贤, 姜琪, 等. 热红外高光谱技术在地质找矿中的应用综述[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(8): 2520-2533. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.08.026
Dai J J, Zhao L X, Jiang Q, et al. Review of thermal-infrared spectroscopy applied in geological ore exploration[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(8): 2520-2533. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.08.026
[16] Van der Meer F D, Van der Werff H M A, Van Ruitenbeek F J A, et al. Multi- and hyperspectral geologic remote sensing: A review[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2012, 14: 112-128. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2011.08.002
[17] 张莹彤, 肖青, 闻建光, 等. 地物波谱数据库建设进展及应用现状[J]. 遥感学报, 2017, 21(1): 12-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB201701002.htm
Zhang Y T, Xiao Q, Wen J G, et al. Progress and application status of ground object spectrum database[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 21(1): 12-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB201701002.htm
[18] 吴泽群, 田淑芳. 利用热红外遥感提取层状硅酸盐蚀变矿物信息研究——以甘肃北山地区为例[J]. 西北地质, 2016, 49(1): 241-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2016.01.025
Wu Z Q, Tian S F. Study on the extraction of layered silicate altered mineral information by thermal infrared remote sensing-A case study of Beishan Region, Gansu Province[J]. Geology of Northwest China, 2016, 49(1): 241-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2016.01.025
[19] Baldridge A M, Hook S J, Grove C I, et al. The ASTER spectral library Version 2.0[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2009, 113(4): 711-715. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2008.11.007
[20] Lampinen H M, Laukamp C, Occhipinti S A, et al. Mineral footprints of the paleoproterozoic sediment-hosted abra Pb-Zn-Cu-Au deposit Capricorn Orogen, western Australia[J]. Ore Geology Review, 2019, 104: 436-461. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.11.004
[21] Thomas C. Mineral mapping for exploration: An Australian journey of evolving spectral sensing technologies and industry collaboration[J]. Geosciences, 2016, 6(4): 52-100. doi: 10.3390/geosciences6040052
[22] 刘德长, 邱骏挺, 田丰, 等. 区域控矿断裂带的航空高光谱遥感技术研究——以黑石山-花牛山深大断裂带为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015, 51(2): 366-375. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201502018.htm
Liu D C, Qiu J F, Tian F, et al. Application of airborne hyper-spectrum remote sensing to mapping of ore-control faults: A case study of the Heishishan-Huaniushan Fault[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2015, 51(2): 366-375. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201502018.htm
[23] 刘德长, 叶发旺, 赵英俊, 等. 航空高光谱遥感金矿床定位模型及找矿应用——以甘肃北山柳园-方山口地区为例[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2015, 17(12): 1545-1553. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXX201512019.htm
Liu D C, Ye F W, Zhao Y J, et al. Airborne hyperspectral remote sensing for gold prospecting around Liuyuan-Fangshankou area, Gansu Province, China[J]. Journal of Geo-Informatics Science, 2015, 17(12): 1545-1553. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXX201512019.htm
[24] 刘德长, 闫柏琨, 邱骏挺. 航空高光谱遥感固体矿产预测方法与示范应用[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37(3): 349-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201603016.htm
Liu D C, Yan B K, Qiu J T. The application of airborne hyper-spectral remote sensing technology to mineral resources exploration[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2016, 37(3): 349-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201603016.htm
[25] 史维鑫, 易锦俊, 王浩, 等. 马坑铁矿钻孔岩心红外光谱特征及蚀变分带特征研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(6): 934-943. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060004
Shi W X, Yi J J, Wang H, et al. Study on the characteristics of infrared spectrum and the alteration zoning law of drill core in Makeng iron deposit[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(6): 934-943. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060004
[26] 回广骥, 高卿楠, 宋利强, 等. 新疆可可托海稀有金属矿床矿物和岩石热红外光谱特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(1): 134-144. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060001
Hui G J, Gao Q N, Song L Q, et al. Thermal infrared spectra characteristics of rare metal minerals and rock in the Keketuohai deposit, Xinjiang[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(1): 134-144. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060001
[27] 黄宇飞, 李智慧, 宁慧, 等. 应用ASTER遥感图像的岩矿信息提取研究[J]. 航天器工程, 2019, 28(6): 130-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HTGC201906021.htm
Huang Y F, Li Z H, Ning H, et al. Research on rock and mineral information extraction based on ASTER remote sensing image[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2019, 28(6): 130-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HTGC201906021.htm
[28] 宋亮, 刘善军, 虞茉莉, 等. 基于可见-近红外和热红外光谱联合分析的煤和矸石分类方法研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(2): 416-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201702020.htm
Song L, Liu S J, Yu M L, et al. A classification method based on the combination of visible, near-infrared and thermal infrared spectrum for coal and gangue distinguishment[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(2): 416-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201702020.htm
[29] 王东, 刘善军, 毛亚纯, 等. 鞍山式铁矿SiO2含量的热红外光谱分析方法[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(7): 2101-2106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201807025.htm
Wang D, Liu S J, Mao Y C, et al. A method based on thermal infrared spectrum for analysis of SiO2 content in Anshan-type iron[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(7): 2101-2106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201807025.htm
[30] 夏军, 张飞. 热红外光谱的干旱区土壤含盐量遥感反演[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2019, 39(4): 1063-1069. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201904015.htm
Xia J, Zhang F. A study on remote sensing inversion of soil salt content in arid area based on thermal infrared spectrum[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(4): 1063-1069. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201904015.htm
[31] 侯艳军, 塔西甫拉提·特依拜, 张飞, 等. 荒漠土壤全磷含量热红外发射率光谱估算研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(2): 350-354. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)02-0350-05
Hou Y J, Tashpolat T, Zhang F, et al. Study on estimation of deserts soil total phosphorus content from thermal-infrared emissivity[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(2): 350-354. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)02-0350-05
[32] 郭娜, 刘栋, 唐菊兴, 等. 基于短波红外技术的蚀变矿物特征及勘查模型——以斯弄多银铅锌矿床为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2018, 37(3): 556-570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201803007.htm
Guo N, Liu D, Tang J X, et al. Characteristics of alteration minerals and prospecting model revealed by shortwave infrared technique: Taking Sinongduo Ag-Pb-Zn deposit as an example[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2018, 37(3): 556-570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201803007.htm
-



 下载:
下载: